Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kulliyyah of Engineering Semester Exam for Communication Engineering
Загружено:
adibОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kulliyyah of Engineering Semester Exam for Communication Engineering
Загружено:
adibАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY MALAYSIA
END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION
SEMESTER I, 2012/2013 SESSION
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING
Programme
: COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Level of Study: UG 1
Time
: 2:30 pm - 5:30 pm
Date
: 08/01/2013
Duration
: 3 Hrs
Section(s)
: 1
Course Code : ECE 4339
Course Title
: Selected Topic in Communications (Introduction to Radar Systems)
This Question Paper Consists of Three (3) Printed Pages (Including Cover Page) With
Six (6) Questions.
INSTRUCTION(S) TO CANDIDATES
DO NOT OPEN UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO
Total marks of this examination is 100.
This examination is worth 50% of the total assessment.
Answer any 5 (Five) questions.
Any form of cheating or attempt to cheat is a serious
offence which may lead to dismissal.
Introduction to Radar Systems
ECE 4339
[Answer any Five (5) questions]
Q.1 [20 marks]
A continuous wave (CW) Ka-band Doppler radar is used to control traffic lights at a road
construction site whenever vehicles approach the obstruction. The radar is mounted
above the traffic lights facing the direction from which vehicles approach. The radar can
detect approaching bicycle and rider at distance of 30 m. The transmitter and the receiver
experience total loss of 3 dB. The threshold in the receiver is set to S/N = 25 dB. Listed
below are parameters of the radar.
Frequency
24.0 GHz
Receiver noise figure
20 dB
Antenna beamwidth
30
Azimuth plane
30
Elevation plane
2
Bicycle + rider
Typical radar cross section
0.5 m
Determine:
(i) the gain of the antenna.
(2 marks)
(ii) the dimension of the antenna.
(2 marks)
(iii) the system noise temperature of the receiver.
(6 marks)
(iv) the transmitter power when detecting the bicycle and its rider.
(10 marks)
Q.2 [20 marks]
The maximum legal speed at which vehicles should approach the automated enforcement
system (AES) camera recently installed is 90 km/hr. The camera incorporates a 24.0 GHz
Doppler radar in its configuration. The radar does not respond to a motorcyclist travelling
at the speed of 6 km/hr, but capable of detecting any approaching motorcycle at 15
km/hr. The radar somehow is programmed to respond only to law-breaking vehicles
travelling up to 160 km/hr. The detection circuit at threshold uses an rms value of 1 V
into an impedance of 50 ohms to trigger the camera. Determine:
(i) the upper and lower cut-off frequencies of the radar filter.
(4 marks)
(ii) the receiver noise power for the radar.
(8 marks)
(iii) the receiver gain
(8 marks)
Q.3 [20 marks]
The to-be-built KLIA2 would require a surface movement radar (SMR) to detect aircrafts
and vehicles on the tarmac of the airport. It is expected that the SMR is required to
provide high accuracy of about 7.5 m, high update rate of 1 per second; and high
resolution that is less than 20 m detection of airfield targets. The area of coverage should
be 20 km about 50% reduction of its theoretical value. Propose the detailed configuration
of such system including its infrastructure i.e. tower for the evaluation and consideration
by Malaysian Department of Civil Aviation (DCA).
(20 marks)
Introduction to Radar Systems
ECE 4339
Q.4 [20 marks]
(a)
(b)
The Thales Star 2000, an L-band air traffic control radar with 23 cm
operates a 6 m diameter dish antenna with antenna efficiency of 60%.
Determine:
(i) the antenna gain.
(ii) the number of beam positions for the coverage of whole sky.
(iii) the width of the radar beam.
wavelength
(2 marks)
(2 marks)
(2 marks)
The KLIA air traffic control (ATC) radar, Selex ATCR-33 S-band comes equipped
with a phased array antenna transmitting a 1 x 1 pencil beam. The radar
designated range is 150 km with 45 elevation coverage. Determine turning rate
of the radar (revolution per minute).
(14 marks)
Q.5 [20 marks]
(a)
A radar designed for detecting targets of 2 m2 cross section at range of 200 nmi is
likely to have following characteristics; operating frequency at L-band (1230
MHz), antenna efficiency of 60% and receiver minimum detectable signal 3 x 1013
W. The unit cost of transmitter is $2.20 per watt of peak power, the unit cost of
antenna is $1,400 per square meter of physical area and the cost of the receiver
and other items is $1,000,000. Calculate:
(i) the lowest peak power.
(3 marks)
(ii) the smallest antenna physical area.
(3 marks)
(iii) the cost of the transmitter.
(3 marks)
(iv) the cost of the antenna.
(3 marks)
(b)
A Royal Malaysian Air Force (RMAF) ground based air defence radar; the
Martello 743D is located at Bukit Puteri, Jertih, Terengganu. The radar was
designed to provide coverage of 225 nmi range. It is expected to be able to detect
all targets with radar cross section of 2 m2. The peak power of such radar is 15
MW with pulse width of 10 s. The operating frequency of this radar is 1510
MHz. Its antenna is 10 m wide by 5 m high and the antenna aperture efficiency is
0.6. Determine the radar receiver minimum detectable signal.
(8 marks)
Q.6 [20 marks]
(a)
Sketch and label a typical Air Defence radar configuration during deployment
consisting of 8 components.
(4 marks)
(b)
Describe the properties of the two (2) types of over-the-horizon (OTH) radar and
cite their examples.
(6 marks)
(c)
Justify the requirement of a complex for passive radar.
(d)
Highlights the superiority of passive radar Kolchuga over Vera-E. (4 marks)
(6 marks)
Вам также может понравиться
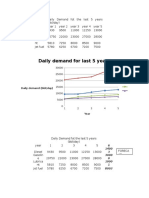
- Shelter Side SelectionДокумент9 страницShelter Side SelectionadibОценок пока нет
- Exam 2016 RadarДокумент13 страницExam 2016 Radaradib50% (2)
- Frank and Lillian Gilbreth Were A HusbandДокумент3 страницыFrank and Lillian Gilbreth Were A HusbandadibОценок пока нет
- ECE4346 FinalSample1Документ4 страницыECE4346 FinalSample1adibОценок пока нет
- Communications Engineering Lab 1: Experiment: 2Документ11 страницCommunications Engineering Lab 1: Experiment: 2adibОценок пока нет
- Case StdyДокумент5 страницCase StdyadibОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Lesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeДокумент5 страницLesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeRey Bello MalicayОценок пока нет
- Raptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12Документ68 страницRaptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12JaimeОценок пока нет
- Study Quran Online - The Online Quran Teaching Academy UK - QutorДокумент9 страницStudy Quran Online - The Online Quran Teaching Academy UK - QutorQutor co ukОценок пока нет
- Minimum Fees To Be Taken by CAДокумент8 страницMinimum Fees To Be Taken by CACA Sanjay BhatiaОценок пока нет
- C++ Programmierung (Benjamin Buch, Wikibooks - Org)Документ257 страницC++ Programmierung (Benjamin Buch, Wikibooks - Org)stefano rossiОценок пока нет
- Checklist For Mold RemediationДокумент2 страницыChecklist For Mold Remediation631052Оценок пока нет
- Ohta, Honey Ren R. - Activity 7.2 (Reflection Agriculture and Religion)Документ5 страницOhta, Honey Ren R. - Activity 7.2 (Reflection Agriculture and Religion)honey ohtaОценок пока нет
- Expose Anglais TelephoneДокумент6 страницExpose Anglais TelephoneAlexis SoméОценок пока нет
- 4 DiscussionДокумент2 страницы4 DiscussiondreiОценок пока нет
- Yamaha RX-A3000 - V3067Документ197 страницYamaha RX-A3000 - V3067jaysonОценок пока нет
- NRSPДокумент27 страницNRSPMuhammad Farhan67% (3)
- Digestive System Song by MR ParrДокумент2 страницыDigestive System Song by MR ParrRanulfo MayolОценок пока нет
- 37 Operational Emergency and Abnormal ProceduresДокумент40 страниц37 Operational Emergency and Abnormal ProceduresLucian Florin ZamfirОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Paired and Two Sample T TestДокумент18 страницModule 3 Paired and Two Sample T TestLastica, Geralyn Mae F.Оценок пока нет
- John PFTДокумент231 страницаJohn PFTAlexander Santiago ParelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1Nor-man KusainОценок пока нет
- Eating and HealingДокумент19 страницEating and HealingMariana CoriaОценок пока нет
- Lay Out New PL Press QltyДокумент68 страницLay Out New PL Press QltyDadan Hendra KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Programming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduДокумент34 страницыProgramming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduNaruto DragneelОценок пока нет
- Hercules SegersДокумент15 страницHercules SegerssuneelaamjadОценок пока нет
- IBM Systems Journal PerspectivesДокумент24 страницыIBM Systems Journal PerspectivesSmitha MathewОценок пока нет
- Conservation of Kuttichira SettlementДокумент145 страницConservation of Kuttichira SettlementSumayya Kareem100% (1)
- Reaction CalorimetryДокумент7 страницReaction CalorimetrySankar Adhikari100% (1)
- Product Data: T T 13 SEER Single - Packaged Heat Pump R (R - 410A) RefrigerantДокумент36 страницProduct Data: T T 13 SEER Single - Packaged Heat Pump R (R - 410A) RefrigerantJesus CantuОценок пока нет
- BE 510 Business Economics 1 Problem Set 5 SolutionsДокумент5 страницBE 510 Business Economics 1 Problem Set 5 SolutionsCreative Work21stОценок пока нет
- tsb16 0008 PDFДокумент1 страницаtsb16 0008 PDFCandy QuailОценок пока нет
- 1 20《经济学家》读译参考Документ62 страницы1 20《经济学家》读译参考xinying94Оценок пока нет
- Types of Sensor and Their ApplicationДокумент6 страницTypes of Sensor and Their Applicationpogisimpatiko0% (1)
- Gas Chromatography - COLIN F. POOLE 2012 PDFДокумент743 страницыGas Chromatography - COLIN F. POOLE 2012 PDFVo Manh Tien100% (1)
- Optimum Work Methods in The Nursery Potting ProcessДокумент107 страницOptimum Work Methods in The Nursery Potting ProcessFöldi Béla100% (1)