Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Syllabus
Загружено:
Amit KumarАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Syllabus
Загружено:
Amit KumarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Civil Engineering
13 of 27
http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~acad/intranet/CourseStructure/ceUG2010onwards.htm
2. M.L. Gambhir, Fundamentals of Reinforced Concrete Design, Prentice Hall India, 2006.
3. A. K. Jain, Reinforced concrete: Limit state design, Nem Chand and Bros. 1999.
th
4. J. Macgregor and J. K. Wight, Reinforced Concrete: Mechanics and Design, Prentice Hall, 5 edition, 2008.
5. R. Park and T. Paulay, Reinforced Concrete Structures, John Wiley and Sons, 1975.
CE 312 HYDRAULICS AND HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES LAB (0 0 2 2)
Determination of resistance coefficient in open channels, Experimental study on variation of specific energy with depth of flow in open channels,
Measurement of flow using weirs and notches, Measurement of flow using a Parshall flume, Experiments on gradually varied flow (GVF) in open
channels, Experimental study on hydraulic jumps, Experimental studies on centrifugal and reciprocating pumps, Experimental studies on impulse
and reaction turbines.
Texts/References:
1. P.N. Modi and S.M. Seth, Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics, Standard Book House, 1998.
2. K. L Kumar, Engineering Fluid Mechanics, Eurasia Publishing Company (P) Ltd., New Delhi, 1999.
CE 313 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING - II LAB (0 0 2 2)
Direct shear test, Vane shear test, Unconfined compression test; Triaxial compression tests: Unconsolidated undrained, Consolidated undrained,
Consolidated drained; Consolidation test, Standard penetration test.
Texts:
1. Fratta, D. Aguettant, J. and Roussel- Smith, L., Soil mechanics laboratory testing, Boca Raton, CRC Press, USA, 2007.
2. J. Bardet, Experimental soil mechanics, Upper Saddle River, Prentice Hall, USA,1992.
References:
1. Liu, C. and Evett, J. B. , Soil properties: testing, measurement and evaluation, Upper Saddle River, Prentice Hall, USA, 1997.
2. Biarez, J. and Hicher, P-Y., Elementary mechanics of soil behaviour: saturated remoulded soils, Rotterdam A.A., Balkema, USA, 1994.
3. Jack, R., Understanding soil mechanics, Albany Delmar Pub., 1995
CE 304 TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING - I (3 0 0 6)
Introduction to Transportation Engineering; Vehicle and driver characteristics; Pavement materials and characterization; Pavement analysis and
design: Flexible pavements, Rigid pavements; Geometric design of Highways: Cross sectional elements, Horizontal alignment, Vertical alignment;
Evaluation of Transportation Improvement; Terminology used in railways; Track design; Points and crossings; Capacity of Railway transit
systems.
3/9/2012 4:02 PM
Civil Engineering
14 of 27
http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~acad/intranet/CourseStructure/ceUG2010onwards.htm
Texts:
1. P. Chakroborty and A. Das, Principles of Transportation Engineering, Prentice Hall India, 2003.
2. S.C. Saxena and S.P. Arora, A text book of Railway engineering, Dhanpat Rai, 2001.
References:
1. C.J. Khisty and B.K. Lall, Transportation Engineering: an introduction, Prentice Hall India, 2003.
2.F.L. Mannering, W.P. Kilareski, and S.S. Washburn, Principles of Highway engineering and traffic analysis, John Wiley and Sons, 2005.
3. C.S. Papacostas and P.D. Prevedouros, Transportation Engineering and Planning, Prentice Hall India, 2001.
4. J.H. Banks, Introduction to Transportation Engineering, McGraw-Hill, 2002.
5. N.A. Harold, Highway materials, Soil and Concrete, Prentice Hall, 2004.
6. S.K. Khanna and C.E.G. Justo, Highway Engineering, Nem Chand Bros., 2002.
7. Y. H. Huang, Pavement Analysis and Design, Pearson Education, India 2008.
CE 307 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING - I (3 0 0 6)
Introduction, Population Forecasting and Water Demand, Physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of Water and Wastewater,
Wastewater Flow, Sewerage system and sewer design, Basic Microbiology: cells, classification and characteristics of living organisms.
Metabolic Processes, Microorganisms in Natural Water Systems, Biological Oxidation of Organic Matter. Introduction to Environmental
Chemistry, Stoichiometry and Kinetics of Chemical Reactions, Equilibrium Constant and Solubility Products, pH and Alkalinity. Development of
Oxygen Sag Model. Flow sheets for Water and Wastewater Treatment, Introduction to Solid Waste, Air Pollution and Noise Pollution.
Texts:
1. H. S Peavy, D. R. Rowe and George Tchobanoglous, Environmental Engineering, McGraw-Hill International Ed., 1985.
2. T. J McGhee, Water Supply and Sewerage, McGraw-Hill Inc., 1991.
References:
1. M. L Davis and D. A Cornwell, Introduction to Environmental Engineering, McGraw-Hill, Inc.,1991.
2. Metcalf & Eddy, Wastewater Engineering- Treatment and Reuse (Revised by G. Tchobanoglous, F. L. Burton and H. D. Stensel), Tata
McGraw Hill, 4th Edn., 2004.
3. C. N Sawyer, P. L McCarty and G. F. Parkin, Chemistry for Environmental Engineers, McGraw- Hill, 1994.
4. APHA, Standard Methods Examination of Water and Wastewater, American Public Health Association, Washington DC, 1995.
5. Manual for Sewer and Sewerage, Central Public Health & Environmental Engineering Organisation, Ministry of Housing and Urban
Development, Govt. of India, 1993.
6. Manual for water supply and treatment, Central Public Health & Environmental Engineering Organisation, Ministry of Housing and Urban
Development, Govt. of India, 1999.
CE 308 CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT (3 0 0 6)
3/9/2012 4:02 PM
Civil Engineering
15 of 27
http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~acad/intranet/CourseStructure/ceUG2010onwards.htm
Construction as industry and its challenges, Role of construction management, Methods of construction managements, Basic requirements of
construction management: Learning structures, Life cycle of construction projects: Examples of real projects and its learning requirements,
Stages of awarding contract, types of contract, contract documents, arbitration and settlement of disputes, contract laws and handling of
contracts, commissioning of project,
Principles of estimation, Principles of general and detailed specifications, Introduction to network based project management techniques:
Defining activities and their interdependence, drawing of network, time and resource estimations, use of network as scheduling techniques, use
of network as control techniques i.e. project monitoring, Construction Technology: construction of superstructure and substructures, Various
construction methods: Excavation, Earth-moving, Drilling, Blasting, Dewatering, foundation, Finishing items, painting, flooring, brick works.
Examples of construction of structures such as buildings, bridges, roads, tunnels, industrial structures, Quality Management and Construction
safety, Use of information technology in
construction industries, Automation in construction industry: a general discussion.
Texts:
1. F. Harris, R. McCaffer and F. Edum-Fotwe, Modern Construction Management, Blackwell Publishing, 2006.
2. C. J. Schexnayder and R. E. Mayo, Construction Management Fundamentals, McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2003.
References:
1. J. Singh, Heavy Constructon-Planning, equipment and methods, Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt 1993.
2. R.L. Peurifoy and C.J. Schexnayder, Construction planning and equipment, and methods, Sixth edition, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2006.
3. D.S. Berrie and B.c. Paulson, Professional construction management including C.M., Design construct and general contracting, Third
edition, McGraw Hill International edition, 1992.
4. L.S. Srinath, PERT and CPM principles and Applications, Third edition, Affiliated east-west press Pvt Ltd, 2001.
5. D.G. Carmichael, Construction engineering Networks: Techniques, planning and management, Ellis Horwood Publishers Chichester 1989.
6. K.K. Chitkara, Construction project management: planning, scheduling and controlling, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2008.
CE 309 DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES (3 1 0 8)
Steel structures - advantages, design loads, structural steel sections, material properties, Codes and Specifications: IS 800, 2007, Design
Concepts: Working stress design, limit state design, plastic design, LRFD. Classification of sections, Forms of constructions, Design of
connections, types of connections, Bolt connections: ordinary black bolts, HSFG bolts and their design in shear, bearing, bending, tension; prying
force, slip resistance, block shear failure. Welded connections: different types of weld connections and design, detailing of connections. Design
of eccentric connections, Design of tension members: design criteria, net and gross area, examples, Design of compression members: concept
of stability and buckling, failure modes, effective lengths, local and global buckling, design of compression members of various types. Design of
flexural members: moment curvature relations, stability and lateral-torsional buckling, design against shear, serviceability requirements,
beamcolumn design. Design of base plates, load transfer mechanism, design of slab base, gusseted base and anchorage. Steel structural
systems.
Texts:
1. N. Subramanian, Design of Steel Structures, Oxford University Press, 2008.
2. L. S. Negi, Design of Steel Structures, Tata McGraw Hill, 1997.
3/9/2012 4:02 PM
Civil Engineering
16 of 27
http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~acad/intranet/CourseStructure/ceUG2010onwards.htm
References:
1.
2.
3.
4.
S. A. Raz, Structural Design in Steel, New Age International Publisher, 2002.
M. Edwin, J. Gaylord and J. E. Stallmeyer, Design of Steel Structures, McGraw-Hill, 1991.
P. Dayaratnam, Design of Steel Structures, S. Chand & Co., 2003.
S. M. A. Kazimi and R. S. Jindal, Design of Steel Structures, Prentice Hall of India Pvt Ltd, 1988.
CE 311 HYDROLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING (3 0 0 6)
Surface water hydrology - hydrologic cycle, rainfall and its measurement, mean rainfall, runoff; Flow measurements; Infiltration losses; Storm
hydrology; Unit Hydrograph; Storm hydrograph; Reservoir planning - Investigations, life of reservoir; Flood estimation and routing, flood
forecasting; Surface and sub-surface drainage, water logging, remedial measures, drainage of land; Ground water hydrology - Introduction,
types of aquifers, wells, well yield; Soil-Water-Plant relationships, crop water requirement; Layout of canal system; Types and methods of
irrigation.
Texts:
1. V.T. Chow, D.R. Maidment, and L.W. Mays, Applied Hydrology, McGraw Hill, 1998.
2. V.P. Singh, Elementary Hydrology, Prentice Hall, 1993.
References:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
H.M. Raghunath, Hydrology Principles, Analysis and Design, Wiley Eastern Ltd., 1986.
A.M. Michael, Irrigation Theory and Practice, Vikas Publishing House, 1987.
D.K. Todd, Groundwater Hydrology, John Wiley & Sons, 1993.
K. Linsley, Water Resources Engineering, McGraw Hill, 1995.
S.K. Garg, Irrigation Engineering and Hydraulic Structures, Khanna Publishers, 1992.
H.P. Ritzema (Editor-in-Chief), Drainage Principles and Applications, ILRI Publication 16, 1994.
CE 314 TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING - I LAB (0 0 2 2)
Laboratory: Evaluation of road aggregates for various properties: Sieve Analysis, Los Angeles Test, Flakiness and Elongation Test, Impact Test,
Angularity Number Test, Evaluation of Bitumen for various properties: Softening Point Test, Penetration Test, Viscosity Test, Ductility Test,
Stripping Test, Bituminous mix design Marshal Mix Design Method.
Texts:
1. S.K. Khanna and C.E.G. Justo, Highway Engineering, Nem Chand Bros., 2002.
2. N.A. Harold, Highway materials, Soil and Concrete, Prentice Hall, 2004.
3/9/2012 4:02 PM
Civil Engineering
17 of 27
http://shilloi.iitg.ernet.in/~acad/intranet/CourseStructure/ceUG2010onwards.htm
References:
1. IS Codes and IRC Codes.
CE 315 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING - I LAB (0 0 3 3)
Solid analysis; pH, Alkalinity, Turbidity and Conductivity measurements; Estimation of Hardness, Dissolved Oxygen, BOD and COD; Plate Counts
and MPN test; Estimation of Fluoride and metals using colorimetric methods, Introduction to advance instruments i.e. Atomic Adsorption
Spectroscopy (AAS).
Texts/References:
1. C. N Sawyer, P. L McCarty and G. F. Parkin, Chemistry for Environmental Engineers, McGraw-Hill,1994.
2. APHA, Standard Methods Examination of Water and Wastewater, American Public Health Association, Washington DC, 1995.
3. Manual for Sewer and Sewerage, Central Public Health & Environmental Engineering Organisation, Ministry of Housing and Urban
Development, Govt. of India, 1993.
4. Manual for water supply and treatment , Central Public Health & Environmental Engineering Organisation, Ministry of Housing and Urban
Development, Govt. of India, 1999.
CE 400 INTRODUCTION TO PROJECT (0 0 3 3)
This course is designed to teach the students about different aspects of carrying out the research project in different areas of Civil Engineering.
CE 401 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING - II (3 0 0 6)
Particle Fluid Mechanics as applied to the settling of Type I and II suspensions. Design and operation of Sedimentation Tanks. Coagulation and
Flocculation. Hydraulics of Filtration, Design and Operation of Filter Units. Disinfection Methods. Ion exchange and Adsorption. Water Softening,
Manganese and Iron Removal. Wastewater Treatment Preliminary, Primary and Secondary Treatment Units. Aerobic and Anaerobic
Processes. Purpose,
theory and design of aeration units. Sludge treatment and disposal, Wastewater stabilization ponds, Aerated ponds and Oxidation ditches.
Site-visits to Water and Wastewater Treatment Works.
Texts:
1. H. S Peavy, D. R Rowe and G. Tchobanoglous, Environmental Engineering, McGraw-Hill International Ed.,1985.
2. Metcalf & Eddy, Wastewater Engineering- Treatment and Reuse (Revised by G. Tchobanoglous, F. L. Burton and H. D. Stensel), Tata
McGraw Hill, 4th
Edn., 2004.
References:
1. T. J McGhee, Water Supply and Sewerage, McGraw-Hill, Inc,1991.
3/9/2012 4:02 PM
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Way of The Samurai, Shadowrun BookДокумент19 страницThe Way of The Samurai, Shadowrun BookBraedon Montgomery100% (8)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Game Audio - Tales of A Technical Sound Designer Volume 02Документ154 страницыGame Audio - Tales of A Technical Sound Designer Volume 02Joshua HuОценок пока нет
- Hung201 PDFДокумент14 страницHung201 PDFMua Dong Tuyet RoiОценок пока нет
- 033 - Flight Planning Monitoring - QuestionsДокумент126 страниц033 - Flight Planning Monitoring - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (4)
- Dihing Feb 17Документ1 страницаDihing Feb 17Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- JE CivilДокумент8 страницJE CivilAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Official Proced. For Laboratory Jar Test 4-15 PDFДокумент2 страницыOfficial Proced. For Laboratory Jar Test 4-15 PDFAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- JE CivilДокумент8 страницJE CivilAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Monday: 10-10.55 Am 2-2.55 PM 3-3.55 PM 4-4.55 PM 5-5.55 PMДокумент1 страницаMonday: 10-10.55 Am 2-2.55 PM 3-3.55 PM 4-4.55 PM 5-5.55 PMAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Well HydraulicsДокумент41 страницаModule 3 Well HydraulicsAmit Kumar100% (1)
- Coagulation - FlocculationДокумент2 страницыCoagulation - FlocculationAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Jar TestingДокумент24 страницыJar TestingAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- IrrigationДокумент28 страницIrrigationArmando BasocОценок пока нет
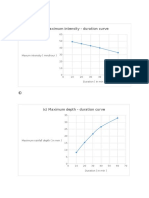
- (B) Maximum Intensity - Duration Curve: Maxum Intensity (Mm/hour)Документ2 страницы(B) Maximum Intensity - Duration Curve: Maxum Intensity (Mm/hour)Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Jar TestingДокумент24 страницыJar TestingAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- 19Документ53 страницы19Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Dihing Feb 17Документ1 страницаDihing Feb 17Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Subsurface Water: A Presentation OnДокумент29 страницSubsurface Water: A Presentation OnAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationДокумент1 страницаNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Nptel ceTEI L25Документ4 страницыNptel ceTEI L25kamalwaxОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент1 страницаSyllabusAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- On 6 Jan There Will Be No Class For CE 311 (Only)Документ1 страницаOn 6 Jan There Will Be No Class For CE 311 (Only)Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Parson'S - Social System TheoryДокумент16 страницParson'S - Social System TheoryAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- On 6 Jan There Will Be No Class For CE 311 (Only) UpdatedДокумент1 страницаOn 6 Jan There Will Be No Class For CE 311 (Only) UpdatedAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- 7939 NMMSДокумент14 страниц7939 NMMSAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Notice Steno C&D 2016 - Updated - 06052016Документ4 страницыNotice Steno C&D 2016 - Updated - 06052016Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- MTS 2016 Final NoticeДокумент38 страницMTS 2016 Final NoticeManprita BasumataryОценок пока нет
- 7 - Social Systems - ParsonsДокумент38 страниц7 - Social Systems - ParsonsAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент1 страницаSyllabusAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Vesic (1973) Analysis of Ultimate Loads of Shallow FoundationsДокумент14 страницVesic (1973) Analysis of Ultimate Loads of Shallow FoundationsJuan Felipe Zambrano Bustillo100% (7)
- Laboratory Experiments For Geotechnical Lab-IIДокумент1 страницаLaboratory Experiments For Geotechnical Lab-IIAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Settlement 1Документ16 страницSettlement 1Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Herbert SpencerДокумент4 страницыHerbert SpencerAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- What Is A Timer?Документ12 страницWhat Is A Timer?Hemraj Singh Rautela100% (1)
- ASM NetworkingДокумент36 страницASM NetworkingQuan TranОценок пока нет
- LS3954A LS3954 LS3955 LS3956 LS3958: Linear Integrated SystemsДокумент3 страницыLS3954A LS3954 LS3955 LS3956 LS3958: Linear Integrated SystemsJCMОценок пока нет
- Meyer and Zack KM CycleДокумент16 страницMeyer and Zack KM Cyclemohdasriomar84Оценок пока нет
- CFA L1 Ethics Questions and AnswersДокумент94 страницыCFA L1 Ethics Questions and AnswersMaulik PatelОценок пока нет
- English 7 q3 Week2 Daily Lesson LogДокумент5 страницEnglish 7 q3 Week2 Daily Lesson LogKILVEN MASIONОценок пока нет
- Travel OrderДокумент2 страницыTravel OrderStephen EstalОценок пока нет
- E34-1 Battery Charging and Dishcharging BoardДокумент23 страницыE34-1 Battery Charging and Dishcharging BoardGanesa MurthyОценок пока нет
- Series R: 3 Piece Ball Valves With Integrated Handle DN8 - DN50 Butt Weld, Threaded, Socket Weld and Flanged VersionДокумент2 страницыSeries R: 3 Piece Ball Valves With Integrated Handle DN8 - DN50 Butt Weld, Threaded, Socket Weld and Flanged VersionАртем КосовОценок пока нет
- RRC & RabДокумент14 страницRRC & RabSyed Waqas AhmedОценок пока нет
- Calculating Measures of Position Quartiles Deciles and Percentiles of Ungrouped DataДокумент43 страницыCalculating Measures of Position Quartiles Deciles and Percentiles of Ungrouped DataRea Ann ManaloОценок пока нет
- 04 10 ALINT DatasheetДокумент2 страницы04 10 ALINT DatasheetJoakim LangletОценок пока нет
- Industrial Training ReportДокумент19 страницIndustrial Training ReportKapil Prajapati33% (3)
- I. Matching Type. Write Letters Only. (10pts) : Adamson University Computer Literacy 2 Prelim ExamДокумент2 страницыI. Matching Type. Write Letters Only. (10pts) : Adamson University Computer Literacy 2 Prelim ExamFerrolinoLouieОценок пока нет
- Course Specifications: Fire Investigation and Failure Analysis (E901313)Документ2 страницыCourse Specifications: Fire Investigation and Failure Analysis (E901313)danateoОценок пока нет
- Computerised Project Management PDFДокумент11 страницComputerised Project Management PDFsrishti deoli50% (2)
- Val Ed SyllabusДокумент25 страницVal Ed Syllabusroy piamonteОценок пока нет
- Preparation of Kevlar-49 Fabric/E-Glass Fabric/Epoxy Composite Materials and Characterization of Their Mechanical PropertiesДокумент10 страницPreparation of Kevlar-49 Fabric/E-Glass Fabric/Epoxy Composite Materials and Characterization of Their Mechanical PropertiesIndhu ElangoОценок пока нет
- VISCOLAM202 D20 Acrylic 20 Thickeners 202017Документ33 страницыVISCOLAM202 D20 Acrylic 20 Thickeners 202017Oswaldo Manuel Ramirez MarinОценок пока нет
- Revised Study Material - Economics ChandigarhДокумент159 страницRevised Study Material - Economics ChandigarhvishaljalanОценок пока нет
- Grade 10 LP Thin LensДокумент6 страницGrade 10 LP Thin LensBrena PearlОценок пока нет
- DLP in EmpowermentДокумент13 страницDLP in EmpowermentTek Casonete100% (1)
- Atmosphere Study Guide 2013Документ4 страницыAtmosphere Study Guide 2013api-205313794Оценок пока нет
- Skin Care Creams, Lotions and Gels For Cosmetic Use - SpecificationДокумент33 страницыSkin Care Creams, Lotions and Gels For Cosmetic Use - SpecificationJona Phie Montero NdtcnursingОценок пока нет
- Flyweis Services Pvt. LTDДокумент11 страницFlyweis Services Pvt. LTDFlyweis TechnologyОценок пока нет