Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lipids
Загружено:
John Fritz Gerald BascoАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lipids
Загружено:
John Fritz Gerald BascoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lipids
Organic substances that are insoluble in water but
soluble in organic solvents
Composed of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen with
no definite ratio
Number of Oxygen atoms is very much less
compared to hydrogen atoms
Storage of energy and important component of the
cell membrane
Spingomyelin
Only phospholipid membrane
not derive from glycerol but
amino alcohol sphingosine
Niemann-Pick disease:
accumulation of spingomyelin in
the liver and spleen
Cephalin
DONT FORGET
Building blocks are fatty acids and glycerol
Transported in the blood by four major plasma
lipoprotein classes and several quantitatively
minor lipoproteins
Presence of LIPID-BOUND phosphate the only
unique feature common to all phospholipids
Mature Lung Function correlates strongly with
L/S ratio > 2
Method for L/S ratio: TLC followed by
densitometric quantitation
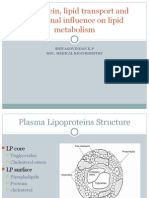
Main Lipids
(human plasma)
Phospholipids
Cholesterol
Unsaturated steroid alcohol
Triglycerides
Amphipathic
Fatty acids
Synthesize in the liver
Fat soluble vitamins (ADEK)
Found on the surface of lipid layers
Almost exclusively synthesize by animals; not
catabolized by most cells; does not serve as a
source of fuel
Transport and excretion is promoted by
ESTROGEN
Important constituent in the assembly of cell
membrane and bile acids
Precursor of 5 major classes of steroids:
Phospholipids
Conjugated
Most abundant lipid from phosphatidic acid
Originates in the liver
They are AMPHIPATHIC
Hydrophilic (water loving)
Hydrophobic (water fearing)
Saturated fatty acid content is reported to be an
independent risk factor for atherosclerosis
CHOLESTEROL
Progestins, glucocorticoids,
mineralocoticoids, androgens, estrogens
Forms:
Contains 2 fatty acid
Cholesterol Ester = 70%
Alter the surface tension (surfactant)
Free Cholesterol = 30%
Spingomyelin: reference material during
3rd trimester of pregnancy
Important substrates for lipoprotein metabolizing
enzyme
Forms:
Lecithin/Phosphatidyl choline
Cholesterol Ester
Present in plasma and serum
Bound to fatty acid
Neutral lipid, not charge, not found in the
surface of lipid layer, located in the center
of lipid drops
Undergoes esterification by LCAT
Excess is re-esterified by ACAT
LCAT (Lecithin-Cholesterol Acyl Transferase)
Catalyze the esterification of cholesterol
by promoting the transfer of fatty acids
from lecithin to cholesterol which results
in the formation of lysolecithin and
cholesterol ester
Synthesize in the liver and activated by
ApoA-1
ACAT (Acyl:Cholesterol Acyl Transferase)
Free Cholesterol
Present in plasma, serum, RBC
Produced via lysosomal hydrolysis and
becomes available for membrane,
hormone and bile acid synthesis
TRIGLYCERIDE
Triacylglycerol or Neutral Fat
Very hydrophobic and water insoluble
Main storage lipid in man
Allows the body to compactly store fatty acids
Breakdown of TAG by lipoprotein lipase
(LPL),epinephrine, cortisol fatty acids are
released converted into energy
Fasting requirement: 12-14 hours
FATTY ACIDS
Mostly found as constituents of phospholipids and
TAG
Mainly derived from hydrolysis of TAG in adipose
tissues
LCAT
Hydrolyzes TAG and phospholipids from
HDL, Hydrolyzes lipids on VLDL and
IDL
Catalyze esterification of cholesterol from
HDL; enables HDL to accumulate
cholesterol as cholesterol ester
Endothelial Lipase
Hydrolyzes phospholipids and TAG in
HDL
LIPOPROTEIN
Main purpose is to transport TAG and cholesterol
to sites of energy storage and utilization
TAG and Cholesterol travel in plasma not as free
floating molecules, but as part of water-soluble
complexes called LIPOPROTEIN
LIPOPROTEIN METABOLISM
Major function
Transport of triglycerides and cholesterol from
sites of exogenous origin (intestine) and
endogenous origin (liver) to sites of energy storage
and utilization
Apolipoprotein
Specific proteins that comprise the protein portion
of a lipoprotein
They interact with specific cell-surface receptors
and direct the lipids to the correct target organs
and tissues
Contain a structural motif called AMPHIPATIC
HELIX - ability of protein to bind to lipids
Lipoproteins are differentiated based on:
Particle size (expressed in Amstrong)
Small amount is present in plasma (free
unesterified form)
Chemical composition (expressed in percentage by
weight)
Most bound to albumin
Physicochemical and flotation characteristics
Very important source of energy
Electrophoretic mobility
LIPOLYTIC ENZYMES
LPL
Hydrolyzes TAG in lipoproteins, &
release of FA and glycerol
Hepatic Lipase
Four Major
Lipoprotein Classes:
Chylomicrons
Largest but the least dense lipoproteins
Density: < 0.95 kg/L
Produced by intestine
PRODUCTION: INTESTINES
Transports exogenous/dietary TAG
Major composition: 90% TAG (non-fasting plasma),
1-2% protein
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION : TAG and
Transports exogenousTAG
VLDL
Very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL)
TURBID
Secreted by the liver
PRODUCTION: LIVER
Density: 0.95-1.006 kg/L
Transports endogenous TAG
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION : TAG and
Transports endogenous TAG
Major composition: 65% TAG (fasting plasma), 16%
Chol, 6-10% protein
LDL
No Change in Appearance
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
Bad Cholesterol
Synthesize by the liver
PRODUCTION: LIVER
Density: 1.019-1.063
produced through the metabolism of VLDL in
circulation
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION:
Cholesterol Transports cholesterol to
tissue
constitutes about 50% of the total lipoprotein mass in
human plasma
HDL
Good Cholesterol
Transports cholesterol to the peripheral tissues
PRODUCTION: LIVER, INTESTINES
Primary target of cholesterol lowering therapy
Better marker for CHD risk
Chemical composition : Protein and
Transports cholesterol away from tissue
Important in assessing patient with or without CHD
Major composition: 50% chol, 18-20% protein
Minor lipoproteins
Intermediate-density lipoprotein or IDL
Product of VLDL catabolism
Migrates pre-beta or beta region
Lipoprotein (a) or Lp(a)
Sinking pre-beta Lipoprotein
Variable migration:n pre-beta, sometimes between
LDL and albumin
Increased level may indicate premature CHD and
stroke
Independent risk factor for atherosclerosis
Density: 1.045 1.080 kg/L
High-density lipoproteins (HDL)
Smallest but the most dense lipoprotein
Density: 1.063 1.21 kg/L
Produced by the liver and intestine
Transports excess cholesterol from the tissues and
returns to the liver
HDL2 transport effectively the lipids and is more
cardioprotective
Major composition: 30% phospholipids, 20% chol,
45-50% protein
LIPOPROTEIONS
ABNORMAL LIPOPROTEINS
Chylomicrons:
LpX
MILKY
Floating Creamy Layer
Abnormal lipoprotein found in patients with obstructive
biliary disease and LCT deficiency
Specific and sensitive indicator or cholestasis
apoB-48
Composed of 90% phospholipids, unesterified cholesterol and
very little esterified cholesterol
Remaining 10% is composed of apoC and some albumin
BETA VLDL
Floating beta lipoprotein
Abnormal lipoprotein accumulates in people with
type III hyperproteinemia or
dysbetalipoproteinemia
Richer in cholesterol than VLDL
Appears to result from the faulty catabolism of
VLDL
Found in the VLDL density range but migrates
with or near LDL
ApoC
Major constituent of VLDL and minor constituent
of HDL and LDL
Different groups:
ApoC-I
ApoC-II
APOLIPOPROTEIN
Activator of the enzyme
lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
Result to reduced clearance of
triglyceride-rich lipoproteins
ApoC-III
ApoE
ApoA
Major protein components of HDL
Major component:
ApoA-I
constitutes 75% of apoA in HDL
Synthesize in the liver and
intestine
Arginine-rich lipoprotein found in VLDL, IDL,
remnant lipoproteins, chylomicrons and HDL
Minor apolipoprotein
ApoD
ApoA-IV
Activator of enzyme
Lecithin:Cholesterol
Acyltransferase (LCAT)
esterifies cholesterol in plasma
Constitute 20% of apoA in HDL
Density >1.21 fraction of plasma in HDL
and also in very small amount as a
constituent of chylomicrons
Cherubs Everywhere in
Heavens Above
ApoB
Chylomicrons = All
While
HDL = ApoA
Lucifer Below
LDL = ApoB
Major protein constituent of LDL
Constitute 40% of CHON moiety of VLDL and
Chylomicrons
for he is
Several forms:
Very Bad
Minor component that makes up around
5% of HDL proteins
ApoA-II
Synthesized by the intestine and
it is found in chylomicrons
VLDL = ApoB
apoB-100
Most common form
Synthesized by the liver and
found in endogenous origin in
VLDL and LDL
Electrophoresis
Pattern: HDL, VLDL, LDL, Chylomicrons
Supporting Medium: agarose-gel
Lipid-staining dyes: Oil Red O, Fat Red 7B, Sudan
Black B
Calculations
Autosomal recessive caused by defective
apoB synthesis
VLDL,LDL & chylomicrons = absent in the
plasma
Cholesterol and TAG = low
LDL = Total Cholesterol HDL VLDL
Friedwald Formula:
VLDL = TAG/2.175 (mmol/L)
VLDL = TAG/5 (mg/dL)
Disorders
Fredrickson Classification
TYPE 1: Hyperchylomicronemia
apoB deficiency resulting from point
mutation in apo-B
LDL and Tchol = low
VLDL and TAG = low or normal
Niemann-Pick disease (Lipid Storage Disease)
Inherited disorder of lipid metabolism
TYPE 2
Accumulation of spingomyelin in the bone
marrow, spleen, lymph nodes
Type 2A: Familial
Hypercholesterolemia
Type 2B: Mixed Defect
(Familial Combined Hyperlipidemia)
TYPE 3: Familial Dysbetalipoproteinemia
TYPE 4: Familial Hypertriglycedemia
TYPE 5
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
(Type 2a)
Autosomal dominant caused by defective or
deficient LDL receptors
Tangier's Disease
Rare autosomal recessive
Complete absence of HDL due to mutation
in ABCA1 gene on chromosome 9
Results to build up of cholesterol in the cell
Increase HDL catabolism
Yellow or orange discoloration of tonsils
and pharynx
LPL deficiency
Rare autosomal recessive
Increased Tchol and LDL
Inability to clear chylomicron particles
Familial Dysbetalipoproteinemia (Type 3)
Deficiency of ApoC-II
Accumulation of plasma VLDL rich in
cholesterol and chylomicrons remnants
VLDL fraction migrates abnormally in the
beta region (B-VLDL) creating broad
Beta band (pre B) electrophoretic pattern
Equal elevation of cholesterol and TAG and
presence of B-VLDL
(Familial LPL deficiency)
Hypobetalipoproteinemia
Pathognomonic Feature: a broad abnormal
band between VLDL and LDL (B-VLDL)
Abetalipoproteinemia (Bassen-Kornzweig
Syndrome)
LCAT deficiency
Due to mutation in LCAT gene
Fish-eye disease: milder form of LCAT
deficiency
Tay-Sachs Disease
An inherited neurodegenerative disorder of
lipid metabolism
Deficiency in enzyme hexosminidase A
Results to accumulation of spingolipids in
the brain
Chylomicron Retention Disease (Anderson's
Disease)
Only ApoB-48 is affected
Characterized by hypocholesterolemia,
chronic diarrhea, deficiency of fat soluble
vitamins
Вам также может понравиться
- Planned Parenthood Response To DHHДокумент5 страницPlanned Parenthood Response To DHHKevin LittenОценок пока нет
- Jameswaslaski Pelvicstabilization Uploadable VersionДокумент12 страницJameswaslaski Pelvicstabilization Uploadable VersionMarco PMTОценок пока нет
- Grass Cutting Risk AssessmentДокумент4 страницыGrass Cutting Risk AssessmentKaiser Carlo100% (1)
- Lipoproteins, Lipoprotein Metabolism and Disease (LDL, HDL, LP (A) ) PDFДокумент17 страницLipoproteins, Lipoprotein Metabolism and Disease (LDL, HDL, LP (A) ) PDFAdreiTheTripleAОценок пока нет
- Safety Legislation, Regulation and PolicyДокумент110 страницSafety Legislation, Regulation and PolicyNichoОценок пока нет
- Lipid Metabolism - 3rd LectureДокумент38 страницLipid Metabolism - 3rd LectureLe Uyen Nguyen100% (1)
- Blood Cells MorphologyДокумент20 страницBlood Cells MorphologyKevin MikeОценок пока нет
- Ra 10918 PDFДокумент19 страницRa 10918 PDFJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein Types and TransportДокумент33 страницыLipoprotein Types and TransportSissiОценок пока нет
- Plasma Lipids, Lipoprotein & Apolipoprotein ProteinsДокумент45 страницPlasma Lipids, Lipoprotein & Apolipoprotein Proteinskiedd_04100% (5)
- 3 Lipid MetabolismДокумент54 страницы3 Lipid MetabolismRahadatul Aisy100% (1)
- Seminar On Committee ReportsДокумент11 страницSeminar On Committee ReportsUdaya Sree100% (2)
- Lipoprotein Metabolism: PSC 3110 Fall 2004Документ99 страницLipoprotein Metabolism: PSC 3110 Fall 2004Irma MarianyОценок пока нет
- Movie Review: Temple Grandin by Tabatha O.Документ6 страницMovie Review: Temple Grandin by Tabatha O.Tabatha100% (1)
- LG - Lipid MetabolismДокумент116 страницLG - Lipid MetabolismRawa AyubОценок пока нет
- 07 Lipids and LipoproteinsДокумент63 страницы07 Lipids and LipoproteinsBebreilynne LepartoОценок пока нет
- Lipid Transport & Storage (Lipoproteins) : Abdul Salam M. Sofro Faculty of Medicine YARSI UniversityДокумент43 страницыLipid Transport & Storage (Lipoproteins) : Abdul Salam M. Sofro Faculty of Medicine YARSI UniversitydmsОценок пока нет
- Lipids and Dyslipoproteinemia - 2020Документ116 страницLipids and Dyslipoproteinemia - 2020Aria Jean MostajoОценок пока нет
- Lipioprotein Lec11 PDFДокумент44 страницыLipioprotein Lec11 PDFحسن محمد سعيد جاسمОценок пока нет
- Lipid Transport & StorageДокумент33 страницыLipid Transport & StorageWahidinSchleiden100% (1)
- Lipids StudentДокумент38 страницLipids StudentJoshua BalcitaОценок пока нет
- Lipid Transport & StorageДокумент33 страницыLipid Transport & StorageRaja Friska YulandaОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein Group 5Документ46 страницLipoprotein Group 5SharОценок пока нет
- Komponen Lipid, Katabolisme Asam Lemak, Biosintesis Asam LemakДокумент69 страницKomponen Lipid, Katabolisme Asam Lemak, Biosintesis Asam Lemakalvaedison00Оценок пока нет
- 5 Lipid MetabolismДокумент148 страниц5 Lipid MetabolismAzrin SyahidaОценок пока нет
- Lec. 12 Biochemistry IIДокумент22 страницыLec. 12 Biochemistry IIGames beautifulОценок пока нет
- Metabolism of Lipids And: LipoproteinsДокумент50 страницMetabolism of Lipids And: LipoproteinsRichoco SapoetraОценок пока нет
- Module 11 Lipids 1Документ10 страницModule 11 Lipids 1cassseeeyyyОценок пока нет
- Lipid Profile Disease and DiagnosisДокумент31 страницаLipid Profile Disease and DiagnosisGeetanjali JhaОценок пока нет
- Lipid Profile Disease and DiagnosisДокумент31 страницаLipid Profile Disease and DiagnosisGeetanjali Jha100% (1)
- (WWW - Indowebster.com) Lipid Transport Amp StorageДокумент33 страницы(WWW - Indowebster.com) Lipid Transport Amp StorageRs93Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry, Synthesis and Functions of Lipoproteins (LDL, VLDL, Chylomicrons) Learning ObjectivesДокумент8 страницChemistry, Synthesis and Functions of Lipoproteins (LDL, VLDL, Chylomicrons) Learning ObjectivesPatar HutagalungОценок пока нет
- Cclec Lipids and LipoproteinsДокумент59 страницCclec Lipids and LipoproteinsBles Cy LagrimasОценок пока нет
- DM Lipid ProfileДокумент54 страницыDM Lipid ProfileDM MagtotoОценок пока нет
- Lipid DisordersДокумент65 страницLipid DisordersNguyễn Minh Phương UyênОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент26 страницLipidsparneetkaurbediОценок пока нет
- Hormonal Influence On Lipid MetabolismДокумент43 страницыHormonal Influence On Lipid MetabolismKuzhandai VeluОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Cholesterol Metabolism BC100Документ27 страницCholesterol Metabolism BC100Anthony KabadiОценок пока нет
- Sirera, DyslipidemiaДокумент68 страницSirera, Dyslipidemiarsirera6409Оценок пока нет
- Metabolismoflipoproteins 171020040454Документ66 страницMetabolismoflipoproteins 171020040454Afeeda RazikОценок пока нет
- Digestion of Lipids. Transport Forms of LipidsДокумент91 страницаDigestion of Lipids. Transport Forms of LipidsAhmed FtsОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент13 страницLipidsalianaОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein Lipase (Lipemia Clearing Factor) Hepatic Lipase Endothelial Lipase Apolipoprotein ChylomicronsДокумент7 страницLipoprotein Lipase (Lipemia Clearing Factor) Hepatic Lipase Endothelial Lipase Apolipoprotein ChylomicronsJass LintaoОценок пока нет
- Metabolisme Kolesterol, Lipoprotein Dan ApolipoproteinДокумент32 страницыMetabolisme Kolesterol, Lipoprotein Dan ApolipoproteinAlmira Ulfa Utari NasutionОценок пока нет
- Lipoproteins All Lipoproteins Are Soluble, Spherical Lipid Traffickers Which Consist of A HydrophobicДокумент4 страницыLipoproteins All Lipoproteins Are Soluble, Spherical Lipid Traffickers Which Consist of A HydrophobicrajeshmangalОценок пока нет
- Abetalipoproteinemia Powerpoint ReportДокумент43 страницыAbetalipoproteinemia Powerpoint Reportpurpleflurp23Оценок пока нет
- Lipid Metabolism: Preparedby: Ma - Angelica T. Cepeda Rodencio Jr. E. Marzan Noralyn NgislawanДокумент31 страницаLipid Metabolism: Preparedby: Ma - Angelica T. Cepeda Rodencio Jr. E. Marzan Noralyn NgislawanTnylfОценок пока нет
- Review: - ACC RegulationДокумент41 страницаReview: - ACC RegulationNico AturdidoОценок пока нет
- Biochem1 Practical6Документ8 страницBiochem1 Practical6puhranee nathanОценок пока нет
- Review: - ACC RegulationДокумент41 страницаReview: - ACC RegulationAlecs LunganОценок пока нет
- LipoproteinДокумент99 страницLipoproteinriosilalahi17Оценок пока нет
- Lipid TransportДокумент31 страницаLipid TransportSantino MajokОценок пока нет
- Lipid Metabolisam2Документ9 страницLipid Metabolisam2dhruviksuthar1407Оценок пока нет
- Instructor's Presentation-Lipids and LipoproteinsДокумент43 страницыInstructor's Presentation-Lipids and Lipoproteinsjomel rondinaОценок пока нет
- Lipoproteins: SummaryДокумент3 страницыLipoproteins: SummaryEzekiel Morena RiveraОценок пока нет
- Student Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentДокумент5 страницStudent Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody PardilloОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein - WikipediaДокумент38 страницLipoprotein - WikipediaTejaswiОценок пока нет
- Agricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyДокумент74 страницыAgricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyZainab Jamal SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Lipid Digestion and MetabolismДокумент65 страницLipid Digestion and MetabolismEricaОценок пока нет
- Plasma Lipoproteins: FunctionsДокумент2 страницыPlasma Lipoproteins: FunctionsAnitha KaurОценок пока нет
- Guc 2705 59 28561 2023-05-18T10 45 27Документ47 страницGuc 2705 59 28561 2023-05-18T10 45 27malak00mohamed229Оценок пока нет
- Lipids Part 3Документ32 страницыLipids Part 3lmoiefrОценок пока нет
- VLDLДокумент15 страницVLDLMoses WijayaОценок пока нет
- Dr. Shyam Babu Prasad: Course Code: ZOOL 4008 (Biochemistry and Metabolism)Документ17 страницDr. Shyam Babu Prasad: Course Code: ZOOL 4008 (Biochemistry and Metabolism)Brama AtmajaОценок пока нет
- Lipoprotein Metabolism: PSC 3110 Fall 2004Документ99 страницLipoprotein Metabolism: PSC 3110 Fall 2004Jhost Clinton PurbaОценок пока нет
- Lipids and LipoproteinsДокумент47 страницLipids and LipoproteinsUzair MansoorОценок пока нет
- Capillary Fragility (Resistance) Test:: Assays For Primary HaemostasisДокумент18 страницCapillary Fragility (Resistance) Test:: Assays For Primary HaemostasisJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Capillary Fragility (Resistance) Test:: Assays For Primary HaemostasisДокумент18 страницCapillary Fragility (Resistance) Test:: Assays For Primary HaemostasisJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Rizal Midterm ReviewerДокумент3 страницыRizal Midterm ReviewerJohn Fritz Gerald Basco50% (2)
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Virtual Reality - EricaДокумент7 страницIntroduction To Virtual Reality - EricaJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Code of EthicsДокумент2 страницыCode of EthicsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент6 страницLipidsJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- (ThichTiengAnh - Com) de Theo Cau Truc Moi Nam 2017 de 1 Khong Dap AnДокумент101 страница(ThichTiengAnh - Com) de Theo Cau Truc Moi Nam 2017 de 1 Khong Dap AnRoland VietnamОценок пока нет
- Mapping Bellvitge 2023Документ8 страницMapping Bellvitge 2023Lluís Cavallé MorenoОценок пока нет
- P9 Lecture Child Abuse PDFДокумент53 страницыP9 Lecture Child Abuse PDFVira PebrianaОценок пока нет
- Stress MGMT in Call CentersДокумент70 страницStress MGMT in Call CentersJayesh Kambli100% (1)
- The Bromley Trust: 1. Organisation DetailsДокумент6 страницThe Bromley Trust: 1. Organisation DetailsFranziska TeşcanОценок пока нет
- Ethics Module 3Документ10 страницEthics Module 3Shean BucayОценок пока нет
- Accredited BAI Laboratory Animal Shelters 2018Документ8 страницAccredited BAI Laboratory Animal Shelters 2018ShanaiaОценок пока нет
- Sodium Metabisulfite SDSДокумент8 страницSodium Metabisulfite SDSChaib AhmedОценок пока нет
- Kings UK Uni Pathways Alumni 2015 16Документ18 страницKings UK Uni Pathways Alumni 2015 16Joins 세계유학Оценок пока нет
- Block Learning Guide (BLG) : Block II Hematoimmunology System (HIS)Документ6 страницBlock Learning Guide (BLG) : Block II Hematoimmunology System (HIS)ASTAGINA NAURAHОценок пока нет
- Accomplishment ReportДокумент5 страницAccomplishment ReportTuTit100% (1)
- ADHD and The Endocannabinoid SystemДокумент11 страницADHD and The Endocannabinoid Systempn100% (1)
- Edmond Locard: Written By: Haley FischerДокумент2 страницыEdmond Locard: Written By: Haley FischerHaley MichelleОценок пока нет
- How The Red Cross Raised Half A Billion Dollars For Haiti - and Built Six Homes - ProPublicaДокумент15 страницHow The Red Cross Raised Half A Billion Dollars For Haiti - and Built Six Homes - ProPublicaGina PistolОценок пока нет
- Jain College, Bangalore Mock Paper - 1, March - 2021 II PUC - EnglishДокумент6 страницJain College, Bangalore Mock Paper - 1, March - 2021 II PUC - EnglishSuchit KarnamОценок пока нет
- Bài tập tiếng anhДокумент8 страницBài tập tiếng anhLinh KhánhОценок пока нет
- Grade 5 ScienceДокумент6 страницGrade 5 ScienceGephelyn GordonОценок пока нет
- Practical Research 2Документ6 страницPractical Research 2meioОценок пока нет
- MSDS-Irganox 1010Документ10 страницMSDS-Irganox 1010Seshagiri KalyanasundaramОценок пока нет
- Industrial Counseling HWДокумент3 страницыIndustrial Counseling HWJoyce SisonОценок пока нет
- Garrison, NancyДокумент139 страницGarrison, NancyBrunoОценок пока нет
- GHGK SДокумент48 страницGHGK SAnonymous Syr2mlОценок пока нет
- New Patient Medical Form: in One SentenceДокумент1 страницаNew Patient Medical Form: in One SentenceAzra BarliОценок пока нет