Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
The Reverse Learning Technique Guide
Загружено:
kalbertog0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
140 просмотров9 страницaprender con reverse learning
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документaprender con reverse learning
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
140 просмотров9 страницThe Reverse Learning Technique Guide
Загружено:
kalbertogaprender con reverse learning
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
The Reverse Learning
Technique
GUIDE
The Reverse Learning Technique
Checklist
Step 1: Choose the right problem
! Identify a set of concepts youve been struggling with. Good places to
look are homework problems youre totally lost on, or procedure steps
you have to constantly keep referring back to your notes or textbook. In
our example: centripetal acceleration, energy, force-balance.
! Find an example problem(s), with the full solution available, that
encompasses these concepts well. In our example: a roller-coaster
problem that requires the ability to calculate velocity based on energy
balance, understand centripetal acceleration and its relationship to
gravity.
Step 2: Start asking why and how
! Start at the solution to the problem, and work your way back towards the
question. Slowly and methodically work your way backwards, making
sure you understand each detail and logical step required to get to the
answer.
! Ask things like Why is this the answer?, How did they solve for that?,
Why was this assumption made?, etc. Write down these questions on
the printout of the solution.
! Answer your own questions as you go. Try to figure it out on your own
from the clues give from the problem itself, or what you remember from
class. If youre still at a loss, then its time to venture over to Google.
Write down your answers on the printout as you come across them.
Step 3: Finish strong and review your work
! Keep pushing with the Q&A process until you get back to the problem
statement, making sure you dont leave any gaps in your understanding.
Then take an overall look at the ground youve covered. Which concepts
or what logic didnt you understand before that now makes sense? What
surprised you? What insights can you pull out of your work?
2
The Reverse Learning Technique
Example: Roller-Coaster Problem
Suppose you are having trouble with the concept of Centripetal Acceleration.
Youre going through practice problems and plugging in the a=V^2/r equation,
but you dont fully understand whats going on.
You keep flipping back to the textbook and lecture description, but thats not
helping too much.
(Photo: Knights Physics for Scientists and Engineers)
The Reverse Learning Technique
Step 1: Choose the right problem
So following our process above, you select an example problem in which you
need to find the acceleration vector of the roller coaster cart when it has
completed the first quarter of the loop shown below.
Here you have the solution you copied down during class to work off of.
The Reverse Learning Technique
Step 2: Start asking why and how
Now you start working your way up the page from the final answer for the
acceleration vector
Question 1: Why is there an acceleration downwards of 9.81 m/s2?
Answer 1: Well thats gravity. As long as the Earth is down, which in this case
we are assuming it is, there will always be a downwards acceleration acting
on the cart of 9.81 m/s2.
Question 2: Why is there an acceleration to the left of 43.20 m/s2?
This is a bit trickier, so well need to look for some other clues in the solution
and ask ourselves some additional questions before we can get our answer
here.
Whats happening to the cart at that point in time?
The Reverse Learning Technique
And where will it go after that? Up and to the left.
So to keep the cart from flying straight up in the air (like it was shooting off a
ramp), there must be something turning that cart to the left as it rises. Well,
the only thing there is the track.
Ahh the track thats whats moving the cart to the left.
Okay, so how does the track accelerate something even though it doesnt
itself move?
Oh yeaahh, thats the Normal Force (reaction force provided by a solid
object). Thats why he has that marked as FN on the force diagram.
Answer 2: The Normal Force supplied by the track is generating the
acceleration to the left of 43.20 m/s2.
Question 3: So then whats this equation he wrote using FN?
Answer 3: The Oh wait, thats showing ac and v2/r. I remember seeing that in
lecture. Right thats Centripetal Acceleration, from our diagram before.
6
The Reverse Learning Technique
And taking that a step further, the answer they get for the x-direction
acceleration (at the end) is the same thing he gets when he calculates
Centripetal Acceleration, which as we just saw, is related to the Normal
Force. So the Normal Force must be causing the Centripetal Acceleration,
which is moving the cart up and to the left!
The Reverse Learning Technique
Step 3: Finish strong and review your work
Look at the ground weve covered with just a few of the most obvious
questions we can ask ourselves about this problem. And theres still 75% of
the work involved in the problem that we havent tried to explain yet.
Now youve related concept #3 (Centripetal Acceleration) the one we care
about in this context to a concept you already have familiarity with, concept
#2 Normal Force.
And you also know that both (1) acceleration due to Gravity and (2)
Centripetal Acceleration can interact at the same time on one object,
independent of one another.
These are the big insights you need to be able to solve tough exam problems.
The Reverse Learning Technique
What now?
Have questions? Feedback?
Want more answers?
Want to tell your prof. to shove-it because you never knew how simple it
could be??
Send me a note at tom@wtfprofessor.com.
Or check out tons more learning strategies, problem-solving tactics, and
practice problem solutions at http://wtfprofessor.com.
And if youve found this guide useful please, share it far and wide, and help
fight back against the needless agony experienced by college students
everywhere.
Вам также может понравиться
- Practice Momentum TestДокумент5 страницPractice Momentum TestKinalPatelОценок пока нет
- Before the Application: How to Become the Ideal College Candidate (A Step-by-Step Guide to Making Each Year of High School Count)От EverandBefore the Application: How to Become the Ideal College Candidate (A Step-by-Step Guide to Making Each Year of High School Count)Оценок пока нет
- AP Physics 1 Summer PacketДокумент14 страницAP Physics 1 Summer PacketAkhil DonapatiОценок пока нет
- The Portrait Of A Super Student: Sure ways to improve memory, concentration and personalityОт EverandThe Portrait Of A Super Student: Sure ways to improve memory, concentration and personalityОценок пока нет
- AP Academy HandbookДокумент12 страницAP Academy HandbookNatashaОценок пока нет
- Etkina TeacherContentKnowledgeДокумент28 страницEtkina TeacherContentKnowledgeMrsriyansyahОценок пока нет
- Physics Grade 11 Physics Ch17 ElectrostaticsДокумент50 страницPhysics Grade 11 Physics Ch17 Electrostaticsapi-19999615Оценок пока нет
- Phys 121 f15 AllДокумент5 страницPhys 121 f15 AllAnonymous bZTdTpLОценок пока нет
- Ap18 FRQ Physics 1 PDFДокумент12 страницAp18 FRQ Physics 1 PDFshalini kumariОценок пока нет
- Welcome To Calculus PDFДокумент329 страницWelcome To Calculus PDFPhilippe DubostОценок пока нет
- AP Physics C SyllabusДокумент2 страницыAP Physics C Syllabusskrewy20Оценок пока нет
- Ap Physics 1 - Summer AssignmentsДокумент93 страницыAp Physics 1 - Summer AssignmentsNicole Saint-AubinОценок пока нет
- AP Physics NotesДокумент18 страницAP Physics Notesfhsphysics100% (1)
- SSH 105 Course Outline Fall 2015Документ4 страницыSSH 105 Course Outline Fall 2015Alex JonesОценок пока нет
- Pacing Guide - Ap Computer Science PrinciplesДокумент3 страницыPacing Guide - Ap Computer Science Principlesapi-632735520Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Linear MotionДокумент42 страницыChapter 4 Linear MotionChidube MekkamОценок пока нет
- Course Syllabus - Mcv4uДокумент6 страницCourse Syllabus - Mcv4uapi-285245808Оценок пока нет
- AP Physics B SyllabusДокумент2 страницыAP Physics B Syllabusskrewy20Оценок пока нет
- Transforming FunctionsДокумент8 страницTransforming FunctionsSelva RajОценок пока нет
- How Does Color Affect Heating by Absorption of Light - Science ProjectДокумент6 страницHow Does Color Affect Heating by Absorption of Light - Science Projectjimena100% (1)
- AP Physics: Describing Motion: Kinematics in One DimensionДокумент54 страницыAP Physics: Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimensionmgoogol0Оценок пока нет
- JAM Study Plan and TipsДокумент8 страницJAM Study Plan and TipsRajdeep Sarmah50% (2)
- Cen3031 80558 Fa13Документ3 страницыCen3031 80558 Fa13aperture321Оценок пока нет
- Social and Political PhilosophySOPPHILSyllabusДокумент9 страницSocial and Political PhilosophySOPPHILSyllabusDennis ApolegaОценок пока нет
- University of Waterloo Physics 115 Final ExamДокумент13 страницUniversity of Waterloo Physics 115 Final ExamAashish GauravОценок пока нет
- Active Calculus CH 1-8 (v.8.19.13) PDFДокумент523 страницыActive Calculus CH 1-8 (v.8.19.13) PDFDr Milan Glendza Petrovic NjegosОценок пока нет
- Angular MotionДокумент21 страницаAngular Motionsuperman618Оценок пока нет
- Ap Chemistry Review SheetДокумент9 страницAp Chemistry Review Sheetapi-595413521Оценок пока нет
- 99 SAT Reading Erica SummaryДокумент6 страниц99 SAT Reading Erica SummaryShafi UBОценок пока нет
- Ap CSP Student Task Directions PDFДокумент28 страницAp CSP Student Task Directions PDFDylanОценок пока нет
- BC10 Examstudy U2Документ91 страницаBC10 Examstudy U2Bryant Villarin BaldivicioОценок пока нет
- Physical World: What Is Physics?Документ72 страницыPhysical World: What Is Physics?Bright MoonОценок пока нет
- Usaco 2010-2011Документ4 страницыUsaco 2010-2011nimzaanaОценок пока нет
- Whs Act Workkeys Outline To Parents 2Документ2 страницыWhs Act Workkeys Outline To Parents 2api-292707326Оценок пока нет
- Issb Complete ProcedureДокумент14 страницIssb Complete Procedurewaqar_co_mardanОценок пока нет
- Workbook PhysicsДокумент29 страницWorkbook PhysicsKemuel De CastroОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion ProblemДокумент32 страницыCircular Motion ProblemAnjani SinghОценок пока нет
- Stuyvesant High School: Jie ZhangДокумент2 страницыStuyvesant High School: Jie ZhangRebecca RamsammyОценок пока нет
- 7 Fluids Weekend Review KeyДокумент3 страницы7 Fluids Weekend Review KeyDarin Manalo100% (1)
- Calculating Uniformly Accelerated MotionДокумент13 страницCalculating Uniformly Accelerated MotionBrianne Ventoso100% (1)
- Math 103 Quiz EsДокумент17 страницMath 103 Quiz Esalfredomedardo100% (1)
- Blyth Academy Sph4u Evaluation SchemeДокумент1 страницаBlyth Academy Sph4u Evaluation Schemeapi-253252566Оценок пока нет
- AP Biology GuidelinesДокумент2 страницыAP Biology Guidelinesbiologyfreak132Оценок пока нет
- How To Nurture, Rebuild RelationshipsДокумент18 страницHow To Nurture, Rebuild RelationshipsAli KhwajaОценок пока нет
- Nyela Dorsey - Day1-Wksh1-OneAndTwoStepProblemsSTUDENTHWДокумент2 страницыNyela Dorsey - Day1-Wksh1-OneAndTwoStepProblemsSTUDENTHWNyela Dorsey100% (1)
- MCV4U Exam Review PDFДокумент2 страницыMCV4U Exam Review PDFAnita Gloria0% (1)
- AP CalculusДокумент13 страницAP CalculusJoanna WangОценок пока нет
- Tech Mahindra Interview DetailsДокумент62 страницыTech Mahindra Interview Detailssarita panigrahiОценок пока нет
- Physics Time TableДокумент1 страницаPhysics Time TableNeil ShahОценок пока нет
- Function Transformations: Just Like Transformations in Geometry, We Can Move and Resize The Graphs of FunctionsДокумент8 страницFunction Transformations: Just Like Transformations in Geometry, We Can Move and Resize The Graphs of FunctionsKez MaxОценок пока нет
- Physics Ap SyllabusДокумент3 страницыPhysics Ap Syllabusapi-468586701Оценок пока нет
- Pedagogy Professional KnowledgeДокумент6 страницPedagogy Professional Knowledgemamumeed100% (3)
- 80 Rules To Solve Sentence Correction PDFДокумент19 страниц80 Rules To Solve Sentence Correction PDFMariam IkramОценок пока нет
- DP Math: G12 SL Function Transformation Review: 1a. (2 Marks) The Diagram Below Shows The GraphДокумент1 страницаDP Math: G12 SL Function Transformation Review: 1a. (2 Marks) The Diagram Below Shows The GraphAlex SteinkampОценок пока нет
- Tutorials in Introductory Physics (Physics Education Research User S Guide)Документ9 страницTutorials in Introductory Physics (Physics Education Research User S Guide)Ana PaulaОценок пока нет
- Permutations and Combinations Basics - Gr8AmbitionZДокумент6 страницPermutations and Combinations Basics - Gr8AmbitionZsushantsavantОценок пока нет
- Ap Chemistry SummerДокумент12 страницAp Chemistry SummerAnonymous h03yEw6Оценок пока нет
- GordanДокумент5 страницGordanSania ZafarОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: Faculty of English Linguistics and LiteratureДокумент9 страницLesson Plan: Faculty of English Linguistics and LiteratureTrúc Nguyễn Thị ThanhОценок пока нет
- (Mirjana Radovic Markovic Dhe Aidin Salamzadeh) THEIMPORTANCEOFCOMMUNICATIONINBUSINESSMANAGEMENT PDFДокумент19 страниц(Mirjana Radovic Markovic Dhe Aidin Salamzadeh) THEIMPORTANCEOFCOMMUNICATIONINBUSINESSMANAGEMENT PDFBesnik KryeziuОценок пока нет
- Flower Identification Using Machine Learning This Report Conferred To The Department of CSE of Daffodil InternationalДокумент42 страницыFlower Identification Using Machine Learning This Report Conferred To The Department of CSE of Daffodil InternationalSaddam JanjuaОценок пока нет
- Levin and NolanДокумент6 страницLevin and Nolanapi-247309530Оценок пока нет
- Past TenseДокумент11 страницPast TenseMuhammad Ilham SyaputraОценок пока нет
- Focus Group Discussion Assessment RubricДокумент2 страницыFocus Group Discussion Assessment RubricIyam Akuba100% (1)
- Managing Students BehaviorДокумент47 страницManaging Students Behaviorbevelyn caramoanОценок пока нет
- Towson University Instructional Lesson Plan: I. Value of The LessonДокумент5 страницTowson University Instructional Lesson Plan: I. Value of The Lessonapi-242539690Оценок пока нет
- Understanding THE: F.L. Vargas College SY 2019-2020Документ26 страницUnderstanding THE: F.L. Vargas College SY 2019-2020Ikaw Lang Onalac100% (1)
- Destroy Negative Thoughts!Документ107 страницDestroy Negative Thoughts!yeabsira semuОценок пока нет
- The Epistemological Nature..., Balboni 2006Документ52 страницыThe Epistemological Nature..., Balboni 2006TabusoAnalyОценок пока нет
- Soal Latihan Soal Kelas XДокумент2 страницыSoal Latihan Soal Kelas XYeni YuliantiОценок пока нет
- Physical Education PDFДокумент10 страницPhysical Education PDFdimfaОценок пока нет
- Salience PaperДокумент9 страницSalience PaperSarah Mae EsparesОценок пока нет
- Mobile Phone PDFДокумент358 страницMobile Phone PDFShakeel AhmadОценок пока нет
- Fuzzy Jerry M. MendelДокумент2 страницыFuzzy Jerry M. MendelJuan Pablo Rodriguez HerreraОценок пока нет
- Šeškauskienė - LeksikologijaДокумент14 страницŠeškauskienė - LeksikologijaIngrida VerbickaiteОценок пока нет
- Tema - 7 Oposiciones Maestros InglésДокумент11 страницTema - 7 Oposiciones Maestros InglésEsther Ibañez Ruiz100% (1)
- Effective Integration of Music in The ClassroomДокумент18 страницEffective Integration of Music in The ClassroomValentina100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceДокумент5 страницDaily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceHannae pascuaОценок пока нет
- Unit 7: Cultures: by William BarnesДокумент3 страницыUnit 7: Cultures: by William BarnesOanh TrầnОценок пока нет
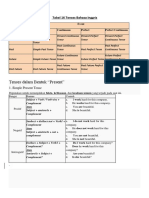
- Tabel 16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisДокумент8 страницTabel 16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisAnonymous xYC2wfV100% (1)
- Human Resource Management - MGT501 Fall 2008 Final Term Paper Session 2Документ13 страницHuman Resource Management - MGT501 Fall 2008 Final Term Paper Session 2The Legendary (H.A)Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Report FormatДокумент4 страницыLaboratory Report FormatthienmakbОценок пока нет
- LET Review - Part1Документ63 страницыLET Review - Part1NathanJil HelardezОценок пока нет
- M.Phil. and Ph.D. Research at ThecentreДокумент7 страницM.Phil. and Ph.D. Research at ThecentreJones AОценок пока нет
- Action Plan in English - 2023Документ2 страницыAction Plan in English - 2023Wendy MagnayeОценок пока нет
- Activity CRAAP Test WorksheetДокумент1 страницаActivity CRAAP Test Worksheetazrin adilaОценок пока нет
- Sub-Conscious MindДокумент5 страницSub-Conscious Mindburhanuddin bhavnagarwalaОценок пока нет