Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Series Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
sharmanator99Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Series Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
sharmanator99Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
1.
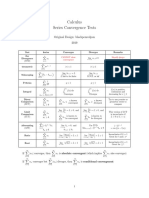
Convergence and Divergence Tests for Series
Test
When to Use
Divergence Test
Integral Test
for any series
X
1
Conclusions
X
1
Diverges if lim |an | =
6 0.
an
n!1
n=0
an with an
0 and an decreasing
Comparison Test
an and
1
X
n=0
n=0
1
an , (an > 0). Choose
n=0
n!1
if lim
n!1
if lim
n!1
for alternating Series
Absolute Convergence
1
X
1
X
an
=L
bn
an diverges =)
1
X
with 0 < L < 1
n=0
1
an
=0
bn
n=0
1
an
=1
bn
( 1)n an (an > 0)
bn diverges.
an and
1
X
bn both converge/diverge
n=0
bn converges =)
bn diverges =)
1
X
an converges.
n=0
1
an diverges.
n=0
converges if
n=0
lim an = 0 and an is decreasing
for any series
X
1
for any series
1
X
For any series
n!1
1
an
If
|an | converges, then
1
X
|an | diverges but
n=0
an
if
n=0
1
n!1
Calculate lim
n!1
an converges,
n=0
1
X
an converges.
n=0
an conditionally converges
n=0
1
X
Calculate lim
1
X
(definition of absolutely convergent series.)
an ,
there are 3 cases:
n=0
Root Test:
an converges.
n=0
1
n=0
n=0
n=0
Ratio Test:
1
X
bn , (bn > 0)
n=0
Conditional Convergence
bn converges =)
n=0
n=0
if lim
Convergent test
an both converge/diverge
n=0
1
X
bn
if 0 an bn
1
X
1
X
where f (n) = an .
n=0
Limiting Comparison Test
f (x)dx and
n=0
1
X
an+1
=L
an
if L < 1, then
p
n
if L > 1, then
|an | = L
1
X
n=0
1
X
n=0
|an | converges ;
|an | diverges;
if L = 1, no conclusion can be made.
2. Important Series to Remember
Series
How do they look
Conclusions
Geometric Series
Converges to
p-series
arn
n=0
1
X 1
n=1
np
a
1
if |r| < 1 and diverges if |r|
Converges if p > 1 and diverges if p 1
Вам также может понравиться
- Microsoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыMicrosoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetHunterKing199375% (4)
- Paul's Online Math Notes - Linear AlgebraДокумент342 страницыPaul's Online Math Notes - Linear Algebrabackswimmer89% (18)
- Real Analysis Cheat SheetДокумент6 страницReal Analysis Cheat SheetMattia Janigro100% (1)
- Formulas For Calculus-Based Physics 2Документ1 страницаFormulas For Calculus-Based Physics 2Steven J. BiarsОценок пока нет
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsДокумент5 страницCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralshyd arnes100% (5)
- ODE Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыODE Cheat SheetMuhammad Rizwan88% (8)
- Series Convergence Tests BlackpenredpenДокумент1 страницаSeries Convergence Tests BlackpenredpenKarolina Padilla ValdezОценок пока нет
- Real Analysis Cheat SheetДокумент8 страницReal Analysis Cheat SheetJoannaWilliamsОценок пока нет
- Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves 2nd Edition PDFДокумент638 страницEngineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves 2nd Edition PDFxieapi88% (42)
- Multiple Choice Questions: Linear Algebra (Mts4 B04) Core Course - BSC Mathematics Iv SemesterДокумент27 страницMultiple Choice Questions: Linear Algebra (Mts4 B04) Core Course - BSC Mathematics Iv Semesterkirki pОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыLinear Algebra Cheat SheetBrian WilliamsonОценок пока нет
- Linear Dependence and Independence of VectorsДокумент17 страницLinear Dependence and Independence of VectorsR NishanОценок пока нет
- Calculus of Residue and Contour IntegrationДокумент78 страницCalculus of Residue and Contour IntegrationPrateekKumarJaysinghaniОценок пока нет
- Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesДокумент11 страницTaylor and Maclaurin Seriesapi-243574449Оценок пока нет
- Calculus Cheat SheetДокумент6 страницCalculus Cheat SheetDino99% (75)
- Vectors Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыVectors Cheat SheetganeshykrОценок пока нет
- WS 1 3solsДокумент2 страницыWS 1 3solssharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- Adaptive Filter Theory 5th Edition Haykin 013267145X Solution ManualДокумент36 страницAdaptive Filter Theory 5th Edition Haykin 013267145X Solution Manualjames100% (23)
- Vector AssignmentДокумент7 страницVector AssignmentDJ AFRO MOVIESОценок пока нет
- Intergal CalculusДокумент20 страницIntergal CalculusElizabeth ErwanОценок пока нет
- Functional AnalysisДокумент37 страницFunctional AnalysisCarlos RogerОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыLinear Algebra Cheat SheetNooraniManshadОценок пока нет
- Strauss Calculus AnswersДокумент47 страницStrauss Calculus AnswersDeepak SrivasОценок пока нет
- Fourier Series and Fourier IntegralsДокумент20 страницFourier Series and Fourier IntegralsManoj KumarОценок пока нет
- The Fundamental Theorem of CalculusДокумент48 страницThe Fundamental Theorem of CalculusManjunath MaigurОценок пока нет
- Limit FormulasДокумент6 страницLimit FormulasRahul DubeyОценок пока нет
- Special Function MCQ Questions:: DefiniteДокумент1 страницаSpecial Function MCQ Questions:: DefiniteAli SaiviОценок пока нет
- Convergence of Taylor Series (Sect. 10.9) PDFДокумент7 страницConvergence of Taylor Series (Sect. 10.9) PDFTu ShirotaОценок пока нет
- Numerical IntegrationДокумент67 страницNumerical IntegrationMisgun SamuelОценок пока нет
- Rodrigues Formula and Lengendary's PolynomialДокумент26 страницRodrigues Formula and Lengendary's Polynomialarun kumarОценок пока нет
- 3D Analytical GeometryДокумент3 страницы3D Analytical GeometryMaths Home Work 123100% (1)
- Complex Analysis 1Документ8 страницComplex Analysis 1xeemac100% (1)
- Partial FractionsДокумент12 страницPartial FractionsMathathlete100% (1)
- Complex Numbers: Topic M-11-2Документ15 страницComplex Numbers: Topic M-11-2Anant Kumar100% (1)
- Infinite SeriesДокумент11 страницInfinite SeriesH100% (1)
- Vector AnalysisДокумент72 страницыVector AnalysisAileenMTОценок пока нет
- Real Analysis NotesДокумент141 страницаReal Analysis NotesSam Higginbotham100% (4)
- Linear Algebra Nut ShellДокумент6 страницLinear Algebra Nut ShellSoumen Bose100% (1)
- Multiple IntegralsДокумент133 страницыMultiple Integralsmanasa raajheshОценок пока нет
- 2 Analytic FunctionДокумент5 страниц2 Analytic FunctionAshutosh Singh100% (2)
- Calculus Cheat SheetsДокумент5 страницCalculus Cheat Sheetsanon-524795100% (72)
- Definite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandDefinite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОценок пока нет
- Limits and Continuity (Calculus) Engineering Entrance Exams Question BankОт EverandLimits and Continuity (Calculus) Engineering Entrance Exams Question BankОценок пока нет
- Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations in EngineeringОт EverandNonlinear Partial Differential Equations in EngineeringРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankОценок пока нет
- Practical Conic Sections: The Geometric Properties of Ellipses, Parabolas and HyperbolasОт EverandPractical Conic Sections: The Geometric Properties of Ellipses, Parabolas and HyperbolasОценок пока нет
- 0.1 Practical Guide - Series of Real NumbersДокумент3 страницы0.1 Practical Guide - Series of Real NumbersEmilОценок пока нет
- Series Tests 2Документ3 страницыSeries Tests 2Kyle KoofersОценок пока нет
- Tests For Convergence TableДокумент2 страницыTests For Convergence TableCamden KrupalaОценок пока нет
- Convergence TestsДокумент3 страницыConvergence TestsVincent WongОценок пока нет
- 2J - Summary of SeriesДокумент4 страницы2J - Summary of Seriespissed1109Оценок пока нет
- Infinite Series Covergance-Divergance TestsДокумент3 страницыInfinite Series Covergance-Divergance TestsSergey KojoianОценок пока нет
- 12b) Power Series in XДокумент6 страниц12b) Power Series in XAtikah JОценок пока нет
- Tests For Series For NooooooooooobbbbbbbbbДокумент2 страницыTests For Series For NooooooooooobbbbbbbbbHT KangОценок пока нет
- Summary of Convergence and Divergence Tests For SeriesДокумент1 страницаSummary of Convergence and Divergence Tests For SeriesaleybaniОценок пока нет
- CSU MTH182 Summer16 1.2585948.HW04Документ9 страницCSU MTH182 Summer16 1.2585948.HW04HaardikGargОценок пока нет
- Calculus Unit 5Документ4 страницыCalculus Unit 5OmegaUserОценок пока нет
- Convergence TestsДокумент3 страницыConvergence TestsAren LorensonОценок пока нет
- Important Series in CalculusДокумент2 страницыImportant Series in CalculusBob leОценок пока нет
- Lab 1Документ4 страницыLab 1sharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- Math 52, Fall 2007 - Solutions To Homework 6Документ4 страницыMath 52, Fall 2007 - Solutions To Homework 6sharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- Dis 1H - Week 4Документ21 страницаDis 1H - Week 4sharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- 11 U3 Ws 4Документ2 страницы11 U3 Ws 4sharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- Final Exam Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыFinal Exam Cheat Sheetsharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- Series Strategies and Tests For Convergence: Test Name When To Use DetailsДокумент3 страницыSeries Strategies and Tests For Convergence: Test Name When To Use Detailssharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- Statistics Chapter 4 Notes Section 4.1 Designing Studies: Definition: Population and SampleДокумент6 страницStatistics Chapter 4 Notes Section 4.1 Designing Studies: Definition: Population and Samplesharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- Philanthropy Project - Indian Army Veteran InitiativeДокумент4 страницыPhilanthropy Project - Indian Army Veteran Initiativesharmanator99Оценок пока нет
- 2012 Maths Practice Paper (M1 & M2) Marking SchemeДокумент23 страницы2012 Maths Practice Paper (M1 & M2) Marking SchemeKc LeungОценок пока нет
- St. Peter's College Sabayle ST., Poblacion, Iligan City: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыSt. Peter's College Sabayle ST., Poblacion, Iligan City: ObjectiveDonnald YambaОценок пока нет
- Book NumericalДокумент388 страницBook Numericalgeorgez111Оценок пока нет
- MB0048 Operations ResearchДокумент320 страницMB0048 Operations ResearchSiddhant AgrawalОценок пока нет
- PPT-Math 10 - Q1 - Week 4 and 5Документ19 страницPPT-Math 10 - Q1 - Week 4 and 5Jackie John LlanoraОценок пока нет
- Special Types of MatricesДокумент2 страницыSpecial Types of MatricesIannah MalvarОценок пока нет
- Sadaf Saeed NM Assignment EE-20309: Question No 01: DataДокумент3 страницыSadaf Saeed NM Assignment EE-20309: Question No 01: DataHafiza SadafОценок пока нет
- Error Function - SfeДокумент12 страницError Function - Sfesgshekar30Оценок пока нет
- Nyquist Plot PDFДокумент24 страницыNyquist Plot PDFvidyagbargeОценок пока нет
- NimraДокумент9 страницNimraFarzana RiazОценок пока нет
- Topology and Geometry PDFДокумент86 страницTopology and Geometry PDFProg VkОценок пока нет
- 3D Stress Analysis PDFДокумент20 страниц3D Stress Analysis PDFLogan PatrickОценок пока нет
- Time Dep SCH EqnДокумент33 страницыTime Dep SCH Eqnutkarsh khandelwalОценок пока нет
- 19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20Документ22 страницы19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20sai tejaОценок пока нет
- NJC Probability Lecture Notes Student EditionДокумент14 страницNJC Probability Lecture Notes Student EditionbhimabiОценок пока нет
- Trig IdentitiesДокумент4 страницыTrig IdentitiesShreya SudarshanОценок пока нет
- Inverse of A Matrix To The NTH Power Is The NTH Power of The Inverse of The Matrix: ProofДокумент3 страницыInverse of A Matrix To The NTH Power Is The NTH Power of The Inverse of The Matrix: Proofsankofakanian0% (1)
- Logarithm of Product: - Log (B) CДокумент3 страницыLogarithm of Product: - Log (B) CRodrigoОценок пока нет
- Intelligent Routines II - Solving Linear Algebra and Differential Geometry With SageДокумент319 страницIntelligent Routines II - Solving Linear Algebra and Differential Geometry With SageNuno Neves100% (2)
- Multi FractalДокумент11 страницMulti FractalmishrajibiteshОценок пока нет
- CH 3 Probability TheoryДокумент14 страницCH 3 Probability TheoryPoint BlankОценок пока нет
- A. Steps in Queuing Analysis Queuing Process Refers To The NumberДокумент7 страницA. Steps in Queuing Analysis Queuing Process Refers To The NumberstudentoneОценок пока нет
- On The Interval Differential Equation: Novel Solution MethodologyДокумент23 страницыOn The Interval Differential Equation: Novel Solution MethodologyDaniel Reyes SierraОценок пока нет
- Anisotropic Materials Ansys PDFДокумент22 страницыAnisotropic Materials Ansys PDFCalgaryPureОценок пока нет
- MATA29 Assignment 1 - Functions (BLANK)Документ7 страницMATA29 Assignment 1 - Functions (BLANK)annaОценок пока нет
- Gerstman PP07Документ35 страницGerstman PP07narayanОценок пока нет