Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lecture 09 - Mapping Genes Bacterial Genetics
Загружено:
RamiroCruzoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lecture 09 - Mapping Genes Bacterial Genetics
Загружено:
RamiroCruzoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lecture 09 - Mapping Genes; Bacterial Genetics
What is the distance between two linked genes?
o Failure to observe independent assortment suggests linkage
o Frequency of recombination indicates distance
o Use the frequency of observing different types of gametes to map genes
Recombination Frequency correlates with distance
Recombination serves as the basis for mapping genes to a chromosome
o Why should distance between loci influence the amount of recombination that
happens between them?
o Recombination occurs randomly throughout the chromosome
o Genes that are farther apart have more chance that recombination event occurs
between them
Genes very far apart on chromosome appear unlinked
o Looks like independent assortment if >50 map units apart
o As though genes are on separate chromosomes
Can have multiple crossovers on same chromosome
o Determining Probabilities:
Remember the product rule of probabilities
Probability of 2 independent events is the product of their
individual probabilities
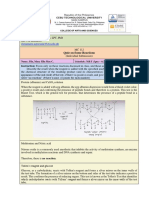
E.g. A----0.2----B----0.3----C
o Probability of double crossover between A-B and B-C:
P = 0.2 x 0.3 = 0.06 = 6% of gametes
Mapping Genes to Chromosomes
o Single crossover events (SCO) determine distance between two genes
o To determine sequence (order) of genes in chromosome is more difficult
Either do multiple pairwise crosses
Or (better) do a 3-point cross and look at enough progeny to see doublecrossover events (DCOs) on same chromosome
3-Point Mapping of Genes to Chromosomes
o 3 Criteria must be met:
1) Genotype of organism producing the crossover gametes must be
heterozygous at all loci under consideration
2) The cross must be constructed so that genotypes of all gametes can be
determined accurately by observing phenotypes of resulting progeny
recover representative sample of all crossover classes
Figuring Out Gene Order from 3-Point Mapping Experiments
o Perform cross and count the F2s
What are the most rare gene classes?
These classes represent DCOs
The one that flips is the one in the middle!!!
Figuring out map distances with results of crosses:
o Use this equation:
o (SCO + DCO) / # of progeny examined
This is fraction of recombination
o Multiply by 100 to give you map units
How to do similar genetic analysis in humans?
o Large #s of crosses, not easy or ethical
o Hard to do test crosses
o How to map genes and traits to chromosomes?
Human genetics revolutionized by DNA markers
o Use DNA changes instead of phenotypes (like wrinkled/round) to track genes
In humans, often look at linkage of disease trait (1st locus) with DNA
3) Sufficient # of offspring must be produced in mapping experiment to
markers (2nd locus)
Very useful for other organisms too
Bacteria
o Single-celled organisms that lack nucleus
o Haploid genome
o Very small (0.5 to 5 micrometers long)
o Can live in wide variety of environments
o Studying them made it possible to study eukaryotic genetics
o Facilitate use of recombinant DNA in lab
o Shape our immune system, aid our digestion, affect our wait, etc.
Advantages of Genetic Analysis in Bacteria
o Bacteria reproduce rapidly
Many progeny produced
Growth in lab easy and requires little space
o Bacteria are haploid
Allows all mutant phenotypes to be evident
o Bacteria have small genomes
Can also carry additional small pieces of DNA as plasmids
Wild-Type Bacteria need a few things to grow
o Need carbon source (e.g. lactose) and variety of ions (e.g. Na+, K+, Mg++, Ca++,
NH4+)
o Can synthesize own amino acids, vitamins, etc.
o Wild-type are prototrophs
Auxotrophs require nutritional supplements
Need certain amino acids or vitamins
Bacteria and Exogenous DNA
o Easy to get DNA from environment
o Can be like communities that share a genome
o Different species of bacteria can share info
Ways to get Exogenous DNA
o Conjugation
Receive DNA by mating w/ other bacteria
o Transformation
Take up DNA from media
o Transduction
Receive DNA from bacteriophage, which are viruses of bacteria
Nutritional Requirements
o If bacteria is for some nutritional thing, the media needs to have it added in for
the bacteria to grow
Cell Contact Required for Genetic Info Transfer
o F+ strain donates F to F- strain
o F Factor = Fertility Factor, needed for mating
o F+ cells: random stuff giving
o Hfr: faster, and not random; stuff that is given is in specific order
Вам также может понравиться
- Lecture 02 - More On Mendelian GeneticsДокумент2 страницыLecture 02 - More On Mendelian GeneticsRamiroCruzoОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Lecture 05 - More On Modifications of Mendelian RatiosДокумент2 страницыLecture 05 - More On Modifications of Mendelian RatiosRamiroCruzoОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Lecture 03 - Pedigrees and ProbabilityДокумент2 страницыLecture 03 - Pedigrees and ProbabilityRamiroCruzoОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Lecture 12 - Regulation of Gene ExpressionДокумент2 страницыLecture 12 - Regulation of Gene ExpressionRamiroCruzoОценок пока нет
- Statement of PurposeДокумент1 страницаStatement of PurposeShilpi GodiyalОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Business and Society Ethics Sustainability and Stakeholder Management 9th Edition Carroll Solutions ManualДокумент9 страницBusiness and Society Ethics Sustainability and Stakeholder Management 9th Edition Carroll Solutions Manualkaylintocwc100% (32)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- HoltAPRG 08 C10 FinalДокумент10 страницHoltAPRG 08 C10 Finaledward_wang_1Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Theory Papers Odd Semester 2008-2009 Civil Engineering Theory Papers Odd-SemesterДокумент47 страницTheory Papers Odd Semester 2008-2009 Civil Engineering Theory Papers Odd-SemesterVijay KumarОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- General Biology Quarter 1 Week 7 8Документ28 страницGeneral Biology Quarter 1 Week 7 8Edreyan Adong Cortez LimbagaОценок пока нет
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFДокумент8 страницSummary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFmohammedОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Bio May Exam 2014 - Paper 2Документ8 страницBio May Exam 2014 - Paper 2Eva MayseОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Bilogia Laboratorios Compressed 81 609-1-40Документ40 страницBilogia Laboratorios Compressed 81 609-1-40kevin oliverosОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- DNA and Snorks PDFДокумент3 страницыDNA and Snorks PDFTeam kalogxz CompilationОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- PILA 1B MC 112 Quiz On Rxns May 24, 2021Документ2 страницыPILA 1B MC 112 Quiz On Rxns May 24, 2021Mary Ella Mae PilaОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- DNA Replication and RepairДокумент7 страницDNA Replication and RepairJhun Lerry TayanОценок пока нет
- UNIT-II ChloramphenicolAntibioticsДокумент4 страницыUNIT-II ChloramphenicolAntibioticsAminn Alhassan ContehОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Dna Transcription NotesДокумент3 страницыDna Transcription NotesviennaОценок пока нет
- Bi 341 Chapter 7 Bacterial GeneticsДокумент39 страницBi 341 Chapter 7 Bacterial GeneticsMATHIXОценок пока нет
- Si RNAДокумент29 страницSi RNALuis MonteroОценок пока нет
- Phosphomannose Isomerase and Phosphomannomutase Gene Disruptions inДокумент8 страницPhosphomannose Isomerase and Phosphomannomutase Gene Disruptions inLuisa Fernanda Zapata OchoaОценок пока нет
- ART Action and Resistance Mechanisms of Antibiotics A Guide For CliniciansДокумент16 страницART Action and Resistance Mechanisms of Antibiotics A Guide For CliniciansHECTORIBZAN ACERO SANDOVALОценок пока нет
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol2311.501 05f Taught by John Burr (Burr)Документ2 страницыUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol2311.501 05f Taught by John Burr (Burr)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry For Medical Laboratory Science Course Outline 2018Документ4 страницыBiochemistry For Medical Laboratory Science Course Outline 2018Vincent Cuyuca100% (1)
- Chromosome AberrationДокумент37 страницChromosome AberrationAli Abbas AslamОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Lesson 4 Materials and Energy Cycle in The EcosystemДокумент28 страницLesson 4 Materials and Energy Cycle in The EcosystemBelle JariolneОценок пока нет
- 1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureДокумент32 страницы1 Lec.1 (w1) Overview and Plant StructureRabiatul AdawiyyahОценок пока нет
- Agpath-Id One Step RT PCR Reagents: User GuideДокумент16 страницAgpath-Id One Step RT PCR Reagents: User GuidechiralicОценок пока нет
- PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 4 - MD3N3Документ4 страницыPhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 4 - MD3N3Dorlisca Montes GarcesОценок пока нет
- 1SC0 1BF Que 20201107Документ20 страниц1SC0 1BF Que 20201107Thasanya AlgamaОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Covid19 Diagnosticproducts List enДокумент74 страницыCovid19 Diagnosticproducts List enRakesh ShahОценок пока нет
- Teaching - Education - 83Документ12 страницTeaching - Education - 83EconaurОценок пока нет
- Pub - Microbiology A Human Perspective PDFДокумент884 страницыPub - Microbiology A Human Perspective PDFsamon sumulongОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 Cellular Respiration FS2014 VO Part 2Документ29 страницTopic 1 Cellular Respiration FS2014 VO Part 2宛仪Оценок пока нет
- New York Sars-Cov-2 Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase (RT) - PCR Diagnostic PanelДокумент27 страницNew York Sars-Cov-2 Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase (RT) - PCR Diagnostic PanelcassОценок пока нет