Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Geometry Study Guide
Загружено:
api-241117521Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Geometry Study Guide
Загружено:
api-241117521Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Geometry/Area/Perimeter Study Guide
3.9 The student will estimate and use U.S. Customary and metric units to
measure area and perimeter.
Estimate and use U.S. Customary and metric units to measure area and
perimeter.
Determine the actual measure of area or perimeter using U.S. Customary and
metric
3.10 The student will measure the distance around a polygon in order to
determine perimeter; and count the number of square units needed to cover a
given surface in order to determine area.
Measure each side of a variety of polygons and add the measures of the sides to
determine the perimeter of each polygon.
Determine the area of a given surface by estimating and then counting the
number of square units needed to cover the surface.
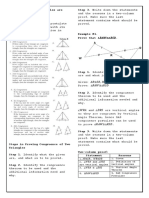
3.14 The student will identify, describe, compare, and contrast
characteristics of plane and solid geometric figures (circle, square, rectangle,
triangle, cube, rectangular prism, square pyramid, sphere, cone, and cylinder) by
identifying relevant characteristics, including the number of angles, vertices, and
edges, and the number and shape of faces, using concrete models.
Identify models and pictures of plane geometric figures (circle, square,
rectangle, and triangle) and solid geometric figures (cube, rectangular prism,
square pyramid, sphere, cone, and cylinder) by name.
Identify and describe plane geometric figures by counting the number of sides
and angles.
Identify and describe solid geometric figures by counting the number of angles,
vertices, edges, and by the number and shape of faces.
Compare and contrast characteristics of plane and solid geometric figures (e.g.,
circle/sphere, square/cube, triangle/square pyramid, and rectangle/rectangular
prism), by counting the number of sides, angles, vertices, edges, and the number
and shape of faces.
Compare and contrast characteristics of solid geometric figures (i.e., cube,
rectangular prism, square pyramid, sphere, cylinder, and cone) to similar objects
in everyday life (e.g., a party hat is like a cone).
Identify characteristics of solid geometric figures (cylinder, cone, cube, cube,
square pyramid, and rectangular prism).
3.15 The student will identify and draw representations of points, line
segments, rays, angles, and lines.
Identify examples of points, line segments, rays, angles, and lines.
Draw representations of points, line segments, rays, angles, and lines, using a ruler or
straightedge.
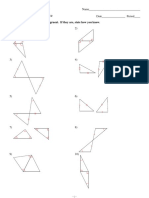
3.16 The student will identify and describe congruent and non-congruent plane
figures.
Identify examples of congruent and non-congruent figures. Verify their
congruence by laying one on top of the other using drawings or models.
Determine and explain why plane figures are congruent or non-congruent, using
tracing procedures.
Study Resources:
Textbook:
~Topic 16: Lessons 16-1; 16-2; 16-3; 16-5; 16-6; VA-12
~Topic 10: Lessons 10-1 through 10-7; VA-7
~Topic 11: Lesson 11-1; VA-8
IXL Math: Optional On-Line Student Resource
Website: www. ixl.com
Username: first initial, last name, last 4 digits of lunch number
Password: rcs2016
Tab: Third Grade Math
Count and compare sides and vertices CC.2
Is it a polygon? CC. 4
Lines, line segments, and rays CC.5
Parallel, perpendicular, and intersecting lines CC.7
Identify congruent shapes CC.9
Symmetry CC.10
Identify 3 Dimensional Shapes EE.1
Count vertices, edges, and faces EE.2
Identify faces of three-dimensional shapes EE.3
Shapes of Everyday Objects EE.4
Shapes of Everyday Objects EE.5
Perimeter FF.1
Perimeter: word problems FF.3
Find the area of figures made of unit squares FF.4
Create figures with a given area FF.5
Find the area of rectangles and squares FF.6
Find the area of rectangles: word problems FF.8
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Day 1 Intro To Transformations Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницDay 1 Intro To Transformations Lesson Planapi-301240874Оценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Math LAA 3rd QuarterДокумент74 страницыGrade 9 Math LAA 3rd QuarterSJ HarОценок пока нет
- Pythagorean Theorem On SpheresДокумент6 страницPythagorean Theorem On SpheresMvdSchalkОценок пока нет
- Q4 PPT W2 Applying Theorems On Triangle InequalitiesДокумент24 страницыQ4 PPT W2 Applying Theorems On Triangle InequalitiesMarione Angeli D. CanonizadoОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics SA1 2011 Question PaperДокумент11 страницCBSE Class 9 Mathematics SA1 2011 Question PaperravilullaОценок пока нет
- The Nine-Point CircleДокумент9 страницThe Nine-Point CircleMr. Bran100% (1)
- 4 Mark Type (Triangles)Документ12 страниц4 Mark Type (Triangles)sreejaps45Оценок пока нет
- Class Vii Assignment New October 2022Документ9 страницClass Vii Assignment New October 2022Sidra QueenОценок пока нет
- LAS Math5 Q3 Wk3 PolygonsДокумент10 страницLAS Math5 Q3 Wk3 PolygonsVanessa Mae ModeloОценок пока нет
- MATH 7 Q3 Week 2 RBI:EditedДокумент7 страницMATH 7 Q3 Week 2 RBI:Editednylxyxzy0411 albОценок пока нет
- Amado M. Quirit Sr. National High SchoolДокумент4 страницыAmado M. Quirit Sr. National High SchoolKrizell Jane Ojarliza AchaОценок пока нет
- Quarter 3 - Week 1Документ5 страницQuarter 3 - Week 1Valein PrincenaОценок пока нет
- Teach Yourself Trigonometry-AbbottДокумент198 страницTeach Yourself Trigonometry-Abbottbookreader1968Оценок пока нет
- Patran 2010 Reference Manual Part 2: Geometry ModelingДокумент828 страницPatran 2010 Reference Manual Part 2: Geometry ModelingDonОценок пока нет
- Subject: English Communicative Text Books:: Delhi Public School Bokaro Steel CityДокумент30 страницSubject: English Communicative Text Books:: Delhi Public School Bokaro Steel CityLakshya KumarОценок пока нет
- 4-ASA and AAS Congruence PDFДокумент4 страницы4-ASA and AAS Congruence PDFMaam PreiОценок пока нет
- 1.𝐴𝑅≅𝑆𝑅, 𝑊𝑅≅𝐷𝑅 1. Given 2. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 and ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 are vertical angles 2. Definition of vertical angles 3. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 3. Vertical Angle Theorem 4. Δ𝑅𝐴𝑊≅Δ𝑅𝑆𝐷 4. SAS Congruence PostulateДокумент9 страниц1.𝐴𝑅≅𝑆𝑅, 𝑊𝑅≅𝐷𝑅 1. Given 2. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 and ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 are vertical angles 2. Definition of vertical angles 3. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 3. Vertical Angle Theorem 4. Δ𝑅𝐴𝑊≅Δ𝑅𝑆𝐷 4. SAS Congruence PostulatenowilОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 (Illustrate Triangle Congruent)Документ13 страницGrade 8 (Illustrate Triangle Congruent)MA Remoroza, Gillian FОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ39 страницChapter 6dallaramОценок пока нет
- Congruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct AnswersДокумент87 страницCongruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct Answersmsmmpb100% (2)
- Q3 Week 2Документ22 страницыQ3 Week 2Randel Roy Gazo Raluto67% (6)
- Name: LRN: Score: Grade & Section: Date: Parent'S SignatureДокумент7 страницName: LRN: Score: Grade & Section: Date: Parent'S SignatureAries C. FigueroaОценок пока нет
- Postulates and TheoremsДокумент6 страницPostulates and TheoremsAngelique E. RanocoОценок пока нет
- Jmapge Regents Book by TypeДокумент200 страницJmapge Regents Book by TypeSaurabh SinghОценок пока нет
- Summative Test 2 - TunayДокумент2 страницыSummative Test 2 - TunayCharina Ortiz100% (1)
- D.A.V. Public School, Sector 14, Gurugram ACADEMIC PLAN 2022-2023 Class Ix Mathematics IndexДокумент37 страницD.A.V. Public School, Sector 14, Gurugram ACADEMIC PLAN 2022-2023 Class Ix Mathematics IndexAbhishek VashistОценок пока нет
- Congruent TriangleДокумент17 страницCongruent TriangleDahlia SwaffordОценок пока нет
- Geometry Packet Answer 5Документ24 страницыGeometry Packet Answer 5Mariah PrudencioОценок пока нет
- Checked-Math-10 LP Q2 WK-5Документ10 страницChecked-Math-10 LP Q2 WK-5Christine IdurrОценок пока нет
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3 Triangle CongruenceДокумент26 страницMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3 Triangle CongruenceJane rizee BatesОценок пока нет