Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Thin Spherical Mirrors
Загружено:
Rizza Mae AcasioАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Thin Spherical Mirrors
Загружено:
Rizza Mae AcasioАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
THIN SPHERICAL MIRRORS
INTRODUCTION
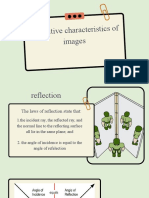
The laws of reflection hold for spherical mirrors. When a ray of light strikes
the spherical mirror, it is reflected such that the angle of incidence is equal to the
angle of reflection. However, due to the curvature of the surface, parallel incident
rays on the mirror may converge or diverge after reflection. Concave mirrors are
called converging mirrors because the incident parallel rays are converged at the
focus after reflection. On the other hand, convex mirrors are called diverging mirrors
because they diverge the incident parallel rays after reflection. In this experiment,
you will study the different types of images formed by spherical mirrors.
Spherical mirrors are said to be one of the easiest to analyze. The spherical
mirror has the shape of a piece that has been cut out of a spherical surface. The
reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is a portion of a spherical surface. In plane
mirrors, the images that is formed are only virtual and erect images which are of the
same size as the object but spherical mirrors can also form real images which are
inverted and these real images may be smaller or larger than the object. Concave
and concave are the two types of spherical mirrors. Concave mirrors are the type of
mirror that are silvered on the inside of the sphere and most likely to magnify
objects placed close to them. The law of reflection occurs in concave mirror but the
angle at which the light hits the surface which is the incident angle is different
depending on which part of the mirror the light hits thus causing it to focus light
similar to the way that a lens in a camera focuses light and forms an image where
the image formed is a real image that are being projected out in front of the mirror
at where the light focuses. Concave mirrors not only form real images but also
produce a virtual image and is the only type of mirror that is capable of doing so. To
determine whether the image formed by a concave mirror is real or virtual is by
determining the object distance and the object size and the image distance and the
image size. Real images tend to be inverted with respect to the object and also
magnified while the virtual images tend to be upright with respect to the object and
is also magnified. The characteristic difference between the real and virtual is that
after the reflection that occurs in the mirror where the light rays emitted by that
object converge on a real image but diverge from a virtual image. Another type of
mirror which is the convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curves outward and
has a point that is where the light that strikes it appears to focus that are called
focal point. Convex mirrors always produce the same kind of image whether where
the original object is located. A convex mirror will always formed an image that are
virtual, upright and smaller than the object.
Вам также может понравиться
- What Is Visible Light Science Presentation in Light Blue Black Hand Drawn StyleДокумент21 страницаWhat Is Visible Light Science Presentation in Light Blue Black Hand Drawn StyleJuliusОценок пока нет
- 7th LightДокумент30 страниц7th Lightsmi_santhoshОценок пока нет
- Convex and Concave MirrorДокумент2 страницыConvex and Concave MirrorManivannanMudhaliarОценок пока нет
- Physics Spherical MirrorsДокумент12 страницPhysics Spherical MirrorsHardik AdnaniОценок пока нет
- Images: Does Light Travel in Straight Line?Документ3 страницыImages: Does Light Travel in Straight Line?Narasimha MurthyОценок пока нет
- Reflection of Light by Different SurfacesДокумент6 страницReflection of Light by Different SurfacesShaik HidayathullaОценок пока нет
- 7th LightДокумент29 страниц7th Lightsmi_santhoshОценок пока нет
- Differences: Concave Mirror Convex MirrorДокумент3 страницыDifferences: Concave Mirror Convex MirrorGelaОценок пока нет
- XJHNZDMZ NHD Ahw AYag 3 RДокумент38 страницXJHNZDMZ NHD Ahw AYag 3 RVenu GopalОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionДокумент12 страницChapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionSuhani GosainОценок пока нет
- Reporting in Science About Curved MirrorsДокумент26 страницReporting in Science About Curved Mirrorsadrian pabyОценок пока нет
- Plane and Spherical MirrorsДокумент9 страницPlane and Spherical Mirrorschinkayaby16Оценок пока нет
- Optics 1Документ8 страницOptics 1Stephson Micayee Da LastbornОценок пока нет
- Concave and Convex MirrorДокумент6 страницConcave and Convex MirrorVijayalakshmi MuraliОценок пока нет
- Reflection and MirrorsДокумент30 страницReflection and MirrorsDavidis DotaroОценок пока нет
- Class 10 Light Till PG No 163Документ2 страницыClass 10 Light Till PG No 163Darshana BariaОценок пока нет
- Reflection of LightДокумент11 страницReflection of Lightlohitha charyОценок пока нет
- Class 7 Light NotesДокумент5 страницClass 7 Light Noteschotu bhanuОценок пока нет
- Spherical MirrorsДокумент8 страницSpherical MirrorsJunaid HussainОценок пока нет
- Light: 1.what Are The Types of Mirrors? Lenses?Документ1 страницаLight: 1.what Are The Types of Mirrors? Lenses?Arniel ToraynoОценок пока нет
- Reflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionДокумент11 страницReflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionmathclubОценок пока нет
- Mirror NotesДокумент6 страницMirror Notesmarife gupaal100% (1)
- E111 - AgustinДокумент20 страницE111 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS - Reflection and MirrorsДокумент20 страницPHYSICS - Reflection and MirrorsJaycob Sedrick TaboОценок пока нет
- Light - NotesДокумент6 страницLight - NotesToshit Kumar NaikОценок пока нет
- Physics Class X For 2017 18 5 42Документ38 страницPhysics Class X For 2017 18 5 42jatinder kohliОценок пока нет
- Quarter2 Module3Документ23 страницыQuarter2 Module3Ma. Jenica CatacutanОценок пока нет
- PHYS101L LabReport11Документ9 страницPHYS101L LabReport11Leidee Charmellie SerranoОценок пока нет
- MIRRORДокумент11 страницMIRRORAlbenJames TabuldanОценок пока нет
- Geometric OpticsДокумент3 страницыGeometric OpticsYeizmin KimОценок пока нет
- Science 10 Quarter 2 - Module 3: Qualitative Characteristics of Images (REVIEWER)Документ4 страницыScience 10 Quarter 2 - Module 3: Qualitative Characteristics of Images (REVIEWER)Ella AuriaОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Questions-AnsweredДокумент7 страницModule 3 Questions-AnsweredVincee SamsonОценок пока нет
- 2 Navneeta Kunwar Public School Varanasi-1Документ12 страниц2 Navneeta Kunwar Public School Varanasi-1shashwatraipro1Оценок пока нет
- LightДокумент6 страницLightRenuОценок пока нет
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesДокумент78 страницThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaОценок пока нет
- LightДокумент38 страницLightcassandrapalmadoОценок пока нет
- Class 10 LightДокумент23 страницыClass 10 LightMathew AbrahamОценок пока нет
- Light ReflectionДокумент13 страницLight ReflectionDivya PriolkarОценок пока нет
- Formation of Images by A Plane MirrorsДокумент4 страницыFormation of Images by A Plane MirrorsAmir FaheemОценок пока нет
- Light Mirrors and Lenses - Ray DiagrammingДокумент52 страницыLight Mirrors and Lenses - Ray DiagrammingJelia fei MadarangОценок пока нет
- Concave and Convex Part of SpoonДокумент12 страницConcave and Convex Part of SpoonRamona Esteves67% (3)
- Q2 Module 2 Mirrors and LensesДокумент15 страницQ2 Module 2 Mirrors and LensesIrene DulayОценок пока нет
- Revision Notes On LIGHTДокумент8 страницRevision Notes On LIGHTTapas Banerjee100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet 4 q4 and ST 2Документ14 страницLearning Activity Sheet 4 q4 and ST 2Daniel Angelo Esquejo ArangoОценок пока нет
- Assign #1 (Optics)Документ3 страницыAssign #1 (Optics)janmariefernandez0Оценок пока нет
- Reflection Mirrors 2022 2023Документ92 страницыReflection Mirrors 2022 2023Jeon ManobanОценок пока нет
- Physics ProjectДокумент9 страницPhysics ProjectHussain AhmedОценок пока нет
- Spherical MirrorsДокумент5 страницSpherical MirrorsAshir GillОценок пока нет
- Plane MirrorsДокумент18 страницPlane MirrorsBianca Gabrielle D. CodillaОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorДокумент23 страницыChapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorKay LagunaОценок пока нет
- Revision Note LightДокумент13 страницRevision Note LightRaman -Оценок пока нет
- GRADE 10 - SCIENCE Notes 3 (2nd Quarter)Документ3 страницыGRADE 10 - SCIENCE Notes 3 (2nd Quarter)gwenn enaje100% (1)
- Differences Between Specular and Diffused ReflectionДокумент4 страницыDifferences Between Specular and Diffused ReflectionTHANMAYA GARIMELLA 9 TH JEE SECTIONОценок пока нет
- Chapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktДокумент17 страницChapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktSarveshyaОценок пока нет
- Science 3 4 ReviewerДокумент3 страницыScience 3 4 ReviewerAngelica VersolaОценок пока нет
- Answer Key OpticsДокумент14 страницAnswer Key OpticsLeah ClovisОценок пока нет
- 10 Reflection of LightДокумент8 страниц10 Reflection of LightMugdhaОценок пока нет
- Science 11.9Документ2 страницыScience 11.9준준챤Оценок пока нет
- Light Physics Class 10 Part 1Документ12 страницLight Physics Class 10 Part 1Kishwar SachanОценок пока нет
- I Can See Planets and Stars from My Room! How The Telescope Works - Physics Book 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksОт EverandI Can See Planets and Stars from My Room! How The Telescope Works - Physics Book 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksОценок пока нет
- Kaup 2015Документ128 страницKaup 2015crash2804Оценок пока нет
- The Philippine Stock Exchange, Inc Daily Quotations Report March 16, 2012Документ8 страницThe Philippine Stock Exchange, Inc Daily Quotations Report March 16, 2012srichardequipОценок пока нет
- 12 Romances Op.21 No. 5 Lilacs Sergei RachmaninoffДокумент4 страницы12 Romances Op.21 No. 5 Lilacs Sergei RachmaninoffNatalie Christensen100% (1)
- Book Review Kapt ZumazliДокумент3 страницыBook Review Kapt Zumazliafiq_ismail_2Оценок пока нет
- A Semiotic Analysis of Five Horror Movie PostersДокумент15 страницA Semiotic Analysis of Five Horror Movie Postersapi-375702257100% (1)
- DeviantartДокумент10 страницDeviantartanon-679883Оценок пока нет
- Mario VIC.m3uДокумент10 страницMario VIC.m3uPabloDelgadilloОценок пока нет
- Wellness Activity PlanДокумент6 страницWellness Activity PlanjizzaОценок пока нет
- 2020 COE Manual - A - 75 - 121 (Individual Police Kit Required For Deployment)Документ2 страницы2020 COE Manual - A - 75 - 121 (Individual Police Kit Required For Deployment)Buzz 845Оценок пока нет
- 11 Sewing Patterns For Womens Dresses Other Pretty Projects PDFДокумент46 страниц11 Sewing Patterns For Womens Dresses Other Pretty Projects PDFmynameisgook67% (3)
- Rab Interior Hotel FixДокумент4 страницыRab Interior Hotel FixDhimas Surya NegaraОценок пока нет
- City of DijishyДокумент59 страницCity of DijishyPeter Bearden100% (8)
- CA-BA-BS-120 Product IntroductionДокумент36 страницCA-BA-BS-120 Product IntroductionsilentОценок пока нет
- Samsung LN52A550P3FXZA TroubleshootingДокумент38 страницSamsung LN52A550P3FXZA TroubleshootingPterocarpousОценок пока нет
- Recipes From People's Pops by Nathalie Jordi, David Carrell, and Joel HorowitzДокумент14 страницRecipes From People's Pops by Nathalie Jordi, David Carrell, and Joel HorowitzThe Recipe Club0% (1)
- MSX Computing - Nov 1984Документ52 страницыMSX Computing - Nov 1984Buleste100% (1)
- Imc Cronos PL ManualДокумент242 страницыImc Cronos PL ManualJulián MinatelОценок пока нет
- Daddy Yankee On Apple MusicДокумент3 страницыDaddy Yankee On Apple MusicJosé GarcíaОценок пока нет
- GM Bluetooth Starter Guide PDFДокумент5 страницGM Bluetooth Starter Guide PDFTin_AmoОценок пока нет
- TTO4Документ12 страницTTO4Jona MagudsОценок пока нет
- (AC-S13) Week 13 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz - INGLES IV (12926)Документ4 страницы(AC-S13) Week 13 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz - INGLES IV (12926)Ariana Ivonne PalominoОценок пока нет
- Data SheetДокумент2 страницыData SheetdatasheetysОценок пока нет
- Marzetti 80066 Best Honey Mustard EverДокумент8 страницMarzetti 80066 Best Honey Mustard EverMark MihalkoОценок пока нет
- Choose The Present Perfect or Past SimpleДокумент2 страницыChoose The Present Perfect or Past Simplememolkan100% (1)
- Xii Maths Book-1 Based (Solutions) Self-Assessment Tests 2022-23 (Amit Bajaj)Документ26 страницXii Maths Book-1 Based (Solutions) Self-Assessment Tests 2022-23 (Amit Bajaj)Dheeraj SinhaОценок пока нет
- Young September-October 2011Документ4 страницыYoung September-October 2011Straight Talk FoundationОценок пока нет
- Sighisoara, A Beautiful TownДокумент1 страницаSighisoara, A Beautiful TownRazvan VisoiuОценок пока нет
- Year 4 Optional Maths SAT Paper AДокумент18 страницYear 4 Optional Maths SAT Paper Apace_saОценок пока нет
- Transformers Lecture 2Документ10 страницTransformers Lecture 2Ritesh JindalОценок пока нет
- Escape From NY RulebookДокумент6 страницEscape From NY RulebookDizetSma100% (1)