Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Oxidative Addition - PDF Coordination
Загружено:
Sandeep YadavОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oxidative Addition - PDF Coordination
Загружено:
Sandeep YadavАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
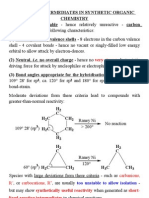
MECHANISMS FOR OXIDATIVE ADDITION AN OVERVIEW
Ox. Addn. Type of LxM Type of X-Y Features
Mechanism
Concerted (1) coord. Unsat., (2) sterically uncongested, (3) Fairly non-polar substrates: (1) cis-addition
(3-centre 3rd > 2nd >> 1st row TM, (4) filled orbital capable of H-H, R3C-H, R3Si-H (2) retention of config. at RRRC-Y
addition) interacting with the * orbital of incoming X-Y strained R3C-CR3, (3) 2nd order, S ~ -30 e.u., rate not
Often d8 complexes [e.g. IrCl(CO)(PR3)2]. Ar-X not very common greatly affected by solvent polarity.
Nucleophilic Nucleophilic metals Polarized substrates: (1) cis- or trans-addition
(SN2) e.g. IrCl(CO)(PR3)2, Ni(PR3)4, Pd(PR3)n R3C-X (1o > 2o > 3o) (2) inversion of config. at RRRC-Y
(MeI > EtI > iPrI), (3) 2nd order, S ~ -40 to -50 e.u.,
Also Cl2, Br2, I2 rate accelerated in polar solvents.
Radical Non-chain = Ni(PPh3)3, Pt(PPh3)3 R3C-X, R3Sn-X (1) cis- or trans-addition
(chain or Chain = IrCl(CO)(PMe3)2 (3o > 2o > 1o) (2) racemization of RRRC-Y
non-chain Binuclear = Mn2(CO)5, Co(CN)53- (3) only the radical chain mechanism
mechanisms) is accelerated by radical initiators
and retarded by radical inhibitors
Ionic (H+ or X- (a) 18 e- Pt(PPh3)4 + H=Cl- (H+ attacks first) H-X -
attacks first) (a) 16 e- Ir(COD)(PR3)2+ + H+Cl- (Cl- attacks first) (largely dissociated in solution)
In general : Non polar substrates (e.g. H-H, C-H, Si-H) Concerted Alkyl halides Nucleophilic (SN2) or Radical
Halogens (Cl2, Br2, I2) Nucleophilic Acids (HCl, HBr, HI) Ionic
For Alkyl Halides, distinguish a SN2 or radical mechanism by determining whether 3 o, 2 o or 1o R-X react faster, whether the reaction leads to
racemization or inversion at RRRC-X, and whether the reaction is accelerated by radical initiators and retarded by radical inhibitors.
For a radical mechanism, distinguish between a chain or non-chain process by whether the reaction is affected by radical initiators or inhibitors.
If it is necessary to distinguish between a concerted or SN2 mechanism, determine whether X and Y are cis- or trans-disposed in the product,
whether the reaction leads to retention or inversion of stereochemistry in RRRC-X, and whether the reaction is accelerated in polar solvents.
Вам также может понравиться
- Cocaine SynthesisДокумент4 страницыCocaine Synthesisb69260030% (1)
- CHM 213 - Final Exam - 2Q2017-18Документ4 страницыCHM 213 - Final Exam - 2Q2017-18cfmonarquia100% (1)
- CH 6 - Organic ReactionsДокумент18 страницCH 6 - Organic Reactionskevincai96Оценок пока нет
- Module 6 (Chemistry)Документ152 страницыModule 6 (Chemistry)Adabala Durgarao NaiduОценок пока нет
- II PUC Chemistry Short Notes-2024 (Other)Документ63 страницыII PUC Chemistry Short Notes-2024 (Other)preitaphilena75% (4)
- Energy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Документ8 страницEnergy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Venice Gwyn ChavezОценок пока нет
- Disha Publication Reaction-Mechanism PDFДокумент101 страницаDisha Publication Reaction-Mechanism PDFSridhar Marella50% (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Metal Carbonyls May Be Mononuclear or PolynuclearДокумент48 страницMetal Carbonyls May Be Mononuclear or PolynuclearcoolrulzОценок пока нет
- Lecture 25-28 - CH410 - Akshai KumarДокумент19 страницLecture 25-28 - CH410 - Akshai KumarManadip SutradharОценок пока нет
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X Reaction of Alkanes With CL & BR (F Is Too Reactive, I Is Unreactive)Документ20 страницPreparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X Reaction of Alkanes With CL & BR (F Is Too Reactive, I Is Unreactive)davidtomyОценок пока нет
- Hydro Carbons TheoryДокумент54 страницыHydro Carbons TheoryRonak GurJarОценок пока нет
- Alkyl Halides: R-X (X F, CL, BR, I)Документ40 страницAlkyl Halides: R-X (X F, CL, BR, I)ranjit singh randhawaОценок пока нет
- Alkane: General Methods of Preparation: (1) by Catalytic Reduction of Alkenes and AlkynesДокумент11 страницAlkane: General Methods of Preparation: (1) by Catalytic Reduction of Alkenes and AlkynesaashishОценок пока нет
- HydrocarbonДокумент94 страницыHydrocarbonArshОценок пока нет
- Halogen Derivatives: B.SC Part - 1 (Honour's and Subsidiary)Документ18 страницHalogen Derivatives: B.SC Part - 1 (Honour's and Subsidiary)Lokesh BorseОценок пока нет
- Intraligand Lowest Excited States in Tricarbon Ylhalobis (Styrylpyridine) Rhenium (ComplexesДокумент7 страницIntraligand Lowest Excited States in Tricarbon Ylhalobis (Styrylpyridine) Rhenium (ComplexesluizdrОценок пока нет
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Chemistry: Regd. Office:Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Ph.011-47623456Документ4 страницыConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Chemistry: Regd. Office:Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Ph.011-47623456Ananya SamantaОценок пока нет
- Elias Inorg Lec 5 PDFДокумент14 страницElias Inorg Lec 5 PDFNidhi SisodiaОценок пока нет
- 18 Electron Rule: How To Count ElectronsДокумент14 страниц18 Electron Rule: How To Count ElectronsGA GAОценок пока нет
- OrangometaicДокумент9 страницOrangometaicscimohammedkamalfathyabudeifОценок пока нет
- 2º Taller de Química Inorgánica IIДокумент2 страницы2º Taller de Química Inorgánica IIEMMANUEL ALEJANDRO FERNANDEZ GAVIRIAОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент10 страницUntitledAnant M NОценок пока нет
- Hydro Carbons Theory-Jeemain - Guru PDFДокумент54 страницыHydro Carbons Theory-Jeemain - Guru PDFPjj CghОценок пока нет
- G.O.C: Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Документ1 страницаG.O.C: Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024rajaniyug1982Оценок пока нет
- 719 Oxidative-AdditionДокумент13 страниц719 Oxidative-AdditionAhmed Atef100% (1)
- Revision Notes On Organic Compounds Containing HalogensДокумент3 страницыRevision Notes On Organic Compounds Containing HalogensSUSHMAОценок пока нет
- Organometallics and Catalysis - IVДокумент36 страницOrganometallics and Catalysis - IVankit guptaОценок пока нет
- Jee Main 27 Jan 2024 Shift 2 Chemistry Memory Based Paper Solution - PHPДокумент9 страницJee Main 27 Jan 2024 Shift 2 Chemistry Memory Based Paper Solution - PHPdhanu20119381Оценок пока нет
- Barta2001Bis (Acetylacetonato) Zinc (II)Документ2 страницыBarta2001Bis (Acetylacetonato) Zinc (II)Horatiu MoldovanОценок пока нет
- Organogold CompoundsДокумент10 страницOrganogold Compoundsamit tiwariОценок пока нет
- PWK-CHEM-01 - Chemistry - Final KCET Revision With Mock Test - Sreeja Mam - UdaysinghДокумент7 страницPWK-CHEM-01 - Chemistry - Final KCET Revision With Mock Test - Sreeja Mam - Udaysinghcalmerr.05Оценок пока нет
- Very Strong: Carbanions, R Carbocations, RДокумент11 страницVery Strong: Carbanions, R Carbocations, RSandeep ThakurОценок пока нет
- Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms-Part IIДокумент44 страницыInorganic Reaction Mechanisms-Part IIUsama El-AyaanОценок пока нет
- Komplexone XLVII. The Stability Yalladium (I1) Complexes With Aminopolycarboxylate AnionsДокумент14 страницKomplexone XLVII. The Stability Yalladium (I1) Complexes With Aminopolycarboxylate AnionsPaolo BrosioОценок пока нет
- 634 Notes Combined PDFДокумент184 страницы634 Notes Combined PDFJennifer Carolina Rosales NoriegaОценок пока нет
- Chm152 OutlinesДокумент24 страницыChm152 OutlinesWiseserpantОценок пока нет
- Clusters: Coordination ChemistryДокумент4 страницыClusters: Coordination ChemistryBadalОценок пока нет
- Methal-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling ReactionsДокумент40 страницMethal-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling ReactionsLuisОценок пока нет
- Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides: S 1, S 2, E1 & E2 ReactionsДокумент38 страницSubstitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides: S 1, S 2, E1 & E2 ReactionsarikahoyaОценок пока нет
- Test-4 SolutionsДокумент11 страницTest-4 SolutionspreethiОценок пока нет
- Reaction Mechanism IДокумент15 страницReaction Mechanism IFilmodeОценок пока нет
- OrganometallicsДокумент53 страницыOrganometallicsSaman KadambОценок пока нет
- 4-Nonelementary Reaction KineticsДокумент23 страницы4-Nonelementary Reaction KineticsHerman FaturohmanОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry: Section A: Straight Objective TypeДокумент26 страницOrganic Chemistry: Section A: Straight Objective TypeAmarОценок пока нет
- Hall 1980Документ9 страницHall 1980Elvis RenzoОценок пока нет
- 27th Shift 1 CheДокумент8 страниц27th Shift 1 Chesudhanshu12958Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry Shift-1 27-01-2024Документ8 страницChemistry Shift-1 27-01-2024manasreddynaguru590Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry Shift-1 27-01-2024Документ7 страницChemistry Shift-1 27-01-2024jayanth ragavendraОценок пока нет
- Bag. 6 StreokimiaДокумент24 страницыBag. 6 StreokimiaAesyah FadhilahОценок пока нет
- Jee Main 27 Jan 2024 Shift 1 Chemistry Memory Based Paper SolutionДокумент7 страницJee Main 27 Jan 2024 Shift 1 Chemistry Memory Based Paper Solutionnaveennaveennkj66Оценок пока нет
- Cis - (MN (En) : 2NO (G) 2N O (G) O (G) +Документ1 страницаCis - (MN (En) : 2NO (G) 2N O (G) O (G) +Tomislav CarОценок пока нет
- Sn2 MechanismДокумент18 страницSn2 MechanismDian MustikasariОценок пока нет
- A Novel Rearrangement Around The (P N) Double Bond1')Документ2 страницыA Novel Rearrangement Around The (P N) Double Bond1')Ihsan Nur AripinОценок пока нет
- Theme 2.3 Part 2 Substitution and Elimination RxnsДокумент33 страницыTheme 2.3 Part 2 Substitution and Elimination RxnsOrlando Wilson Da Sousa MelimОценок пока нет
- General Organic Chemistry Theory 1Документ28 страницGeneral Organic Chemistry Theory 1OasisEducation OesОценок пока нет
- Isomerism in Rhodium Ancillary Ligand Effects : N, S-Donor Heteroscorpionates: Ring Substituent andДокумент12 страницIsomerism in Rhodium Ancillary Ligand Effects : N, S-Donor Heteroscorpionates: Ring Substituent andBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouОценок пока нет
- Lecture Guide 3 Conduction-through-a-Homogenous-Cylinder-WallДокумент8 страницLecture Guide 3 Conduction-through-a-Homogenous-Cylinder-WallCllyan ReyesОценок пока нет
- 2016 Lect6a Substitution Elimination (Alkilhalides)Документ144 страницы2016 Lect6a Substitution Elimination (Alkilhalides)Bryan SuryapranataОценок пока нет
- Screenshot 2024-01-28 at 5.55.12 AMДокумент7 страницScreenshot 2024-01-28 at 5.55.12 AMNarendra YadavОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - Shift 2 - 27 01 2024Документ9 страницChemistry - Shift 2 - 27 01 2024hemacsv2009Оценок пока нет
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsОт EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsОценок пока нет
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972От EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverОценок пока нет
- Kinetics III Exercises - With SolutionsДокумент20 страницKinetics III Exercises - With SolutionsPratham JhaОценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet For Grade Vi Quarter 4 Week 2 Name: - ELAISHA MAE M. ARIAS School: - MCCNHS - Teacher: MS. I. ObjectivesДокумент5 страницActivity Sheet For Grade Vi Quarter 4 Week 2 Name: - ELAISHA MAE M. ARIAS School: - MCCNHS - Teacher: MS. I. Objectivesanjero hortelanoОценок пока нет
- FutureChemistry AppNote3.4 FlowStart Paal-KnorrДокумент4 страницыFutureChemistry AppNote3.4 FlowStart Paal-KnorrHarsh KoshtiОценок пока нет
- CHE 140A Problem Set No. 4: Fogler, 3-10 (A, B), P. 134Документ3 страницыCHE 140A Problem Set No. 4: Fogler, 3-10 (A, B), P. 134Biniyam haileОценок пока нет
- Answer: A: General Chemistry Exam Practice Questions - CH 14Документ10 страницAnswer: A: General Chemistry Exam Practice Questions - CH 14فاطمة كليبОценок пока нет
- Kinetic-Quantum Chemical Model For Catalytic Cycles The Haber-Bosch Process and TheДокумент10 страницKinetic-Quantum Chemical Model For Catalytic Cycles The Haber-Bosch Process and TheD CHОценок пока нет
- SCES3329 2 Approximation Student 01Документ18 страницSCES3329 2 Approximation Student 01hairul_tajuddinОценок пока нет
- CRE 2-Final ExamДокумент3 страницыCRE 2-Final ExamNabil RadianОценок пока нет
- Grignard Reagents - Flash Cards - FinalДокумент1 страницаGrignard Reagents - Flash Cards - FinalAyush guptaОценок пока нет
- LAS General Chemistry 2 Reinforcement ActivitiesДокумент16 страницLAS General Chemistry 2 Reinforcement ActivitiesMarlon C. CambayОценок пока нет
- SBV Project ProposalДокумент2 страницыSBV Project ProposalKeyang SunОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Methods of Analysis: Chapter 15 - 1Документ9 страницKinetic Methods of Analysis: Chapter 15 - 1natsdorfОценок пока нет
- How FastДокумент54 страницыHow FastKaushal Silva RanpatabendigeОценок пока нет
- hwk5 KeysДокумент5 страницhwk5 KeysElizabeth WardenОценок пока нет
- Reaction Engineering and Kinetics IntroductionДокумент3 страницыReaction Engineering and Kinetics IntroductionMuzzy VoraОценок пока нет
- Reviewer On ThermochemistryДокумент5 страницReviewer On ThermochemistryJhomar EncisoОценок пока нет
- Li 2014Документ10 страницLi 2014ArunОценок пока нет
- Chemical KineticsДокумент34 страницыChemical KineticsThamaraiselvi CSEОценок пока нет
- Palladium Precatalyst Design and Its Applications in Cross-CouplingДокумент27 страницPalladium Precatalyst Design and Its Applications in Cross-CouplingiammouliОценок пока нет
- Deriving The Michaelis MENTEN EQUTIONДокумент5 страницDeriving The Michaelis MENTEN EQUTIONManish GaurОценок пока нет
- G. Cravotto, A. Procopio, M. Oliverio, L. Orio, D. Carnaroglio, Green Chemistry, 2011, 13, 2806-2809.Документ4 страницыG. Cravotto, A. Procopio, M. Oliverio, L. Orio, D. Carnaroglio, Green Chemistry, 2011, 13, 2806-2809.Mentu SiasmaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1bДокумент2 страницыTutorial 1bKamilia AfiqahОценок пока нет
- Week 7 CYJ Steady-State Nonisothermal Reactor Design 1-FullДокумент23 страницыWeek 7 CYJ Steady-State Nonisothermal Reactor Design 1-FullElyse Kymberly TeohОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics Question BankДокумент5 страницChemical Kinetics Question BankShivam kumarОценок пока нет
- Chem 4Документ4 страницыChem 4Cao Thị Vân GiangОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Brown Test Bank DownloadДокумент40 страницOrganic Chemistry 8th Edition Brown Test Bank DownloadChelsea Mathur100% (23)
- Enzymes PPT by Utkarsh SatishДокумент7 страницEnzymes PPT by Utkarsh SatishUtkarsh SatishОценок пока нет