Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dengue
Загружено:
KASHYAPАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dengue
Загружено:
KASHYAPАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
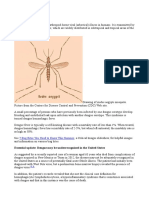
ARBOVIRUS
These are group of virus transmitted to humans indecently and spread among humans by
arthropods
E,g dengue virus , Yellow fever virus, Kyasanur Forest disease,
DENGUE
Dengue fever used to be called "break-bone fever" because it can entail excruciating
joint and muscle pain.
Etiopathogenesis
Dengue has been found mainly in Asia and Africa
Dengue fever is caused by any of four closely related dengue viruses (dengue 1
4).
Dengue viruses are transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected mosquito,
most commonly daytime-biting Aedes aegypti(also vector of yellow fever and
chikungunya viruses)
Breeds in relatively fresh water from sources
The incubation period is from 5 to 6 days and immunity after the illness is
serospecific.
A subsequent infection with a different serotype of dengue virus leads causes
Dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) and Dengue shock syndrome (DSS)
Clinical features
Two forms of the disease are recognized
a) Uncomplicated (classic) dengue
Characterised by abrupt onset of fever, malaise, headache, retrobulbar pain,
conjunctival suffusion and severe backache, which is a prominent symptom.
The rash is morbiliform and is first seen on the limbs and then spreads to involve
the trunk.
The fever subsides after 3-4 days, the patient remains afebrile for a couple of days,
and then the fever returns, together with the features mentioned above, but milder.
This biphasic or saddleback pattern is considered characteristic.
b) Dengue hemorrhagic fever
It is a severe form of dengue fever and is believed to be the result of sequential
infection with two different dengue serotypes
Fever is high grade
Distinguished from uncomplicated dengue fever by
Hemorrhagic manifestations (e.g., spontaneous GI bleeding without
preexisting lesions)
Increased vascular permeability -Ascites, pleural effusions,
hemoconcentration
Usually occurs 37 days after onset of illness
Dengue shock syndrome-
It is due to vascular leakage of fluid.
Dengue shock syndrome has all features of DHF with additional hypotension.
Differential diagnosis
Leptospirosis
Malaria
Laboratory Tests
The diagnosis usually is made on clinical grounds.
Nonspecific laboratory findings
Complete blood count -Leukopenia ,Thrombocytopenia ,Hemoconcentration.
Platelets can be <10,000 in dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Liver biochemical panel -Modest (25 times upper limit of normal) to marked
(515 times) elevations in aminotransferase levels.
Elvated CK and abnormal renal functions are occationaly features
Specific diagnostic studies
IgM ELISA for dengue-usually positive after 1 week
Virus isolation
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for classic dengue fever.
It is important to exclude other treatable diagnoses
Treatment is symptomatic.
Immediate replacement of plasma loss with isotonic salt solution, plasma or
plasma expanders is required in cases of profound shock.
Electrolyte and acid-base balance must be maintained.
Blood loss must be replaced.
* Read yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis
Вам также может понравиться
- Alternative NamesДокумент4 страницыAlternative NamesregineОценок пока нет
- Dengue ReviewerДокумент3 страницыDengue ReviewerSidney Bon LuceroОценок пока нет
- DengueДокумент30 страницDengueMimi Saringan89% (9)
- Dengue Syndrome: Presented By: A.Sahaya Mary M.SC Nursing I Yr Scon, SimatsДокумент57 страницDengue Syndrome: Presented By: A.Sahaya Mary M.SC Nursing I Yr Scon, Simatssagi muОценок пока нет
- Dengue FeverДокумент52 страницыDengue FeverNadia FarahОценок пока нет
- Dengue Fever: Thrombocytopenic Purpura"Документ8 страницDengue Fever: Thrombocytopenic Purpura"christian quiaoitОценок пока нет
- Blood: Symptoms of Dengue FeverДокумент7 страницBlood: Symptoms of Dengue FeverPrincess Viluan PazОценок пока нет
- Case Discussion On Dengue Fever Dengue VirusДокумент5 страницCase Discussion On Dengue Fever Dengue VirusMichelle Vera GabunОценок пока нет
- Dengue Milanie F. Valenton Medical ResidentДокумент31 страницаDengue Milanie F. Valenton Medical ResidentFrangelle Claudine ALvaradoОценок пока нет
- Dengue Health TalkДокумент20 страницDengue Health TalkAnnamalai MОценок пока нет
- Dengue FeverДокумент10 страницDengue Feversajeeb sarker100% (2)
- Dr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinДокумент68 страницDr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinSourav NathОценок пока нет
- Transmission of Dengue FeverДокумент11 страницTransmission of Dengue FeverPatricia E. Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverДокумент74 страницыDengue Hemorrhagic FeverGERSON RYANTOОценок пока нет
- Dengue Is Transmitted by The Bite of An Aedesmosquito Infected With Any One of The Four DengueДокумент6 страницDengue Is Transmitted by The Bite of An Aedesmosquito Infected With Any One of The Four DengueKatrina PonceОценок пока нет
- Tropical Infection DiseasesДокумент60 страницTropical Infection DiseasesVerarisna100% (1)
- DengueДокумент9 страницDengueWinna Gonato100% (2)
- Case Presentation on Dengue Fever (17 charactersДокумент37 страницCase Presentation on Dengue Fever (17 charactersSafoora RafeeqОценок пока нет
- Presentation On DengueДокумент39 страницPresentation On DenguearmanОценок пока нет
- The Deadly Mosquito-Borne Dengue Fever VirusДокумент52 страницыThe Deadly Mosquito-Borne Dengue Fever VirusnotchОценок пока нет
- Dengue MedscapeДокумент58 страницDengue MedscapearuhulaminiОценок пока нет
- Flavivirus: Febrile Diseases Tropics Virus Serotypes FlaviviridaeДокумент3 страницыFlavivirus: Febrile Diseases Tropics Virus Serotypes FlaviviridaeshezarОценок пока нет
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverДокумент47 страницDengue Hemorrhagic FeveriamELHIZAОценок пока нет
- DengueДокумент5 страницDenguematin550% (2)
- Etiologic Agent: Fatality As High As 40-50%Документ7 страницEtiologic Agent: Fatality As High As 40-50%Jolancr MarianoОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTION - Dengue Hemorragic FeverДокумент2 страницыINTRODUCTION - Dengue Hemorragic FeverTintin CosicoОценок пока нет
- Dengue Fever Facts: Headache Fever Joint Pain Swollen Glands Lymphadenopathy Rash Rash Headache Bleeding GumsДокумент5 страницDengue Fever Facts: Headache Fever Joint Pain Swollen Glands Lymphadenopathy Rash Rash Headache Bleeding GumsKeith Gulmatico FantinalgoОценок пока нет
- Home Examination English in Nursung Science: BY: A Class Neneng Aisyah 1219010Документ14 страницHome Examination English in Nursung Science: BY: A Class Neneng Aisyah 1219010neneng aisyahОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Case DiscussionДокумент8 страницDiagnosis and Case DiscussionMichelle Vera GabunОценок пока нет
- Casestudy DengueДокумент57 страницCasestudy DengueMJ Amarillo93% (14)
- DengueДокумент3 страницыDenguemommydaddyОценок пока нет
- DENGUEДокумент9 страницDENGUERahul KhulbeyОценок пока нет
- Dengue Fever - 1Документ55 страницDengue Fever - 1Anam AbidОценок пока нет
- Background: What Are Dengue Fever Symptoms and Signs?Документ12 страницBackground: What Are Dengue Fever Symptoms and Signs?Hussain SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Arboviral Diseases and Dengue FinalДокумент73 страницыArboviral Diseases and Dengue FinalBinayaОценок пока нет
- Dengue: Cadawas, Daphne Gail S. BSN2-D5Документ6 страницDengue: Cadawas, Daphne Gail S. BSN2-D5Daphne Gail CadawasОценок пока нет
- DHF SympДокумент1 страницаDHF SympArmenesОценок пока нет
- A. Definition of Dengue Fever (DB) or Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)Документ16 страницA. Definition of Dengue Fever (DB) or Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)roullionОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverДокумент12 страницPathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Feverdadah_09Оценок пока нет
- PBL Blok 12 Infeksi Dan ImunitasdocxДокумент15 страницPBL Blok 12 Infeksi Dan ImunitasdocxChip BentoОценок пока нет
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverДокумент3 страницыDengue Hemorrhagic FeverhelimpОценок пока нет
- Patient History Dengue FeverДокумент5 страницPatient History Dengue FeverJen Faye Orpilla100% (1)
- DENGUE Hemorrhagic FeverДокумент4 страницыDENGUE Hemorrhagic FeverTonee Marie GabrielОценок пока нет
- Dengue FeverДокумент9 страницDengue FeverMade HarryОценок пока нет
- Dengue PampletДокумент2 страницыDengue Pampletemme77Оценок пока нет
- Dengue Clinical Presentation - History, Physical ExaminationДокумент3 страницыDengue Clinical Presentation - History, Physical ExaminationKeren Singam100% (1)
- Dengue Fever 03Документ11 страницDengue Fever 03Dr. GhauriОценок пока нет
- Journal Reading: Ade Cahyo Islami Dewinta Putri UtamiДокумент17 страницJournal Reading: Ade Cahyo Islami Dewinta Putri UtamiAde Cahyo IslamiОценок пока нет
- DengueДокумент7 страницDengueHafsah MangarunОценок пока нет
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (KULIAH)Документ90 страницDengue Hemorrhagic Fever (KULIAH)pitapitulОценок пока нет
- Dengue FeverДокумент53 страницыDengue FeverAnnsha VeiОценок пока нет
- DENGUEДокумент31 страницаDENGUEVanlal RemruatiОценок пока нет
- Decee Marie T. Miranda Saint Mary'S University BSN Group6: Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverДокумент5 страницDecee Marie T. Miranda Saint Mary'S University BSN Group6: Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverJeff Mac Rae RamosОценок пока нет
- Penegakan Diagnosis dan Pengelolaan pada Penderita Dengue Syok SyndromeДокумент16 страницPenegakan Diagnosis dan Pengelolaan pada Penderita Dengue Syok SyndromeArdityaОценок пока нет
- Denguedhf Information For Health Care Practitioners 2009Документ4 страницыDenguedhf Information For Health Care Practitioners 2009Nateen MyanmarОценок пока нет
- Dengue fever causes, symptoms, treatment and preventionДокумент5 страницDengue fever causes, symptoms, treatment and preventiontristanpaulОценок пока нет
- The Flu: A Guide for Prevention and TreatmentОт EverandThe Flu: A Guide for Prevention and TreatmentРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Encephalitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandEncephalitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (16)
- Legionnaire's Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandLegionnaire's Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea EsДокумент27 страницFunctional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea EsKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Algoritma EmergensiДокумент24 страницыAlgoritma EmergensitikamoesthafaОценок пока нет
- 2014 Guidelines Management of GoiterДокумент9 страниц2014 Guidelines Management of GoiterRika MeliauwatiОценок пока нет
- HyperaldosteronismДокумент28 страницHyperaldosteronismKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- OralprecancerouslesionsДокумент78 страницOralprecancerouslesionsKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Central Neck DissectionДокумент6 страницCentral Neck DissectionKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Radiodine TherapyДокумент12 страницRadiodine TherapyKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Hormonal Replacement in Hypopituitarism in Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice GuidelineДокумент34 страницыHormonal Replacement in Hypopituitarism in Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice GuidelineMark Vertiz Cerna100% (1)
- Androge Therapy in Women EsДокумент22 страницыAndroge Therapy in Women EsAdinarayana KashyapОценок пока нет
- FilariasisДокумент4 страницыFilariasisKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Pneumonics CДокумент3 страницыAnatomy Pneumonics CKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- AMOEBIASISДокумент4 страницыAMOEBIASISKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Thou Pls Let Us Download For Free Please. GagagagagagaggagagagagДокумент1 страницаThou Pls Let Us Download For Free Please. GagagagagagaggagagagagKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- MiccccДокумент1 страницаMiccccKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- All The Best For Your InternshipДокумент1 страницаAll The Best For Your InternshipKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Thou Pls Let Us Download For Free Please. PlasДокумент1 страницаThou Pls Let Us Download For Free Please. PlasKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Thou Pls Let Us Download For Free Please. Gagagagagagaggagagagagaaa AAДокумент1 страницаThou Pls Let Us Download For Free Please. Gagagagagagaggagagagagaaa AAKASHYAPОценок пока нет
- Association of Serum Uric Acid Level with Coronary Artery DiseaseДокумент25 страницAssociation of Serum Uric Acid Level with Coronary Artery Diseasedr.jkОценок пока нет
- A Community-Based Mothers and Infants CenterДокумент10 страницA Community-Based Mothers and Infants CenterRazonable Morales RommelОценок пока нет
- Reference DataДокумент7 страницReference DataDicky D HutapeaОценок пока нет
- 8 Abnormal BehaviorДокумент34 страницы8 Abnormal BehaviorRyanito MarquezОценок пока нет
- 847 - Protein Energy MalnutritionДокумент20 страниц847 - Protein Energy MalnutritionSandip DuttaОценок пока нет
- Prioritization LectureДокумент6 страницPrioritization LecturesamОценок пока нет
- Classification of Periodontal DiseasesДокумент20 страницClassification of Periodontal DiseasesDhinda AuliaОценок пока нет
- Facts and Figures: Sleep ApneaДокумент2 страницыFacts and Figures: Sleep ApneaNazir AhmadОценок пока нет
- Patient Details Patient ID: Temp: BP: Weight: Height: Consultation ID: Date: Mode of Consult: Follow UpДокумент1 страницаPatient Details Patient ID: Temp: BP: Weight: Height: Consultation ID: Date: Mode of Consult: Follow UpSabari PramanikОценок пока нет
- Batu Saluran Kemih GuideДокумент33 страницыBatu Saluran Kemih GuideernamahyuniОценок пока нет
- Adjustment DisorderДокумент7 страницAdjustment DisorderRif'aОценок пока нет
- Final NCP PediaДокумент2 страницыFinal NCP PediaKuro HanabusaОценок пока нет
- The Candida Die Off Handbook 1.51 PDFДокумент4 страницыThe Candida Die Off Handbook 1.51 PDFRajОценок пока нет
- PeriodontitisДокумент32 страницыPeriodontitisDimitrios PapadopoulosОценок пока нет
- QR Dengue Infection PDF Final PDFДокумент8 страницQR Dengue Infection PDF Final PDFina2407jrОценок пока нет
- Notes On Care of The Mother During The Postpartum PeriodДокумент29 страницNotes On Care of The Mother During The Postpartum PeriodGwyneth EstradaОценок пока нет
- Morning Case Report: 34yo Female with Amphetamine IntoxicationДокумент15 страницMorning Case Report: 34yo Female with Amphetamine IntoxicationPradnya ParamithaОценок пока нет
- Abg Tic Tac Toe Part 1 and 2Документ6 страницAbg Tic Tac Toe Part 1 and 2Elizabeth McKeeОценок пока нет
- PE and HealthДокумент3 страницыPE and HealthRia Ellaine Cornelio LachicaОценок пока нет
- Kayexalate Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыKayexalate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- How Physiotherapy Helps - Patient StoriesДокумент2 страницыHow Physiotherapy Helps - Patient StoriesDobreanu Bianca100% (1)
- .Au Files Dysbiosis ScoreДокумент2 страницы.Au Files Dysbiosis ScorekenetmartinОценок пока нет
- Occupational HealthДокумент10 страницOccupational HealthMr AqmahlОценок пока нет
- Anaesthesia and CopdДокумент7 страницAnaesthesia and CopdAshish PandeyОценок пока нет
- DMSF College of Nursing Anatomy and Physiology MDTERMS QUIZ 1Документ2 страницыDMSF College of Nursing Anatomy and Physiology MDTERMS QUIZ 1Trisha TamsiОценок пока нет
- Bilingual Medical Certificate Certificado Médico BilingüeДокумент2 страницыBilingual Medical Certificate Certificado Médico Bilingüejemal0% (1)
- Successful Resuscitation of VF Cardiac Arrest with Early CPR and DefibrillationДокумент1 страницаSuccessful Resuscitation of VF Cardiac Arrest with Early CPR and DefibrillationAfdhalia Khairunnisa SyammarhanОценок пока нет
- Tog 12685Документ3 страницыTog 12685saeed hasan saeedОценок пока нет
- Diseases Caused by MicroorganismsДокумент9 страницDiseases Caused by MicroorganismsKhushbuGuptaОценок пока нет
- 8-Hemodynamic Monitoring: Central Venous Pressure (CVP)Документ6 страниц8-Hemodynamic Monitoring: Central Venous Pressure (CVP)AsmaaYL100% (1)