Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Building Background Knowledge in As Lit
Загружено:
api-345242472Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Building Background Knowledge in As Lit
Загружено:
api-345242472Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
June 18, 2015
Strategies designed to develop students' background knowledge
By: Cal Hastings, Senior Director, Adolescent Literacy
Run of Play
Introductions and Learning Targets
Presentation and discussion
Planning and designing
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 2
Learning Targets
1. Deepen our understanding of the role background knowledge plays in
supporting comprehension
2. Assess our current practice through the lens of building background
knowledge
3. Explore several strategies to build student background knowledge
4. Raise questions and issues specific increasing our success
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 3
Why does background knowledge matter?
According to Fisher and Frey (2009), a student's prior knowledge about a
subject is probably the best predictor of reading comprehension. Research
indicates that children "continue to spin their wheels" when they don't have
the background knowledge required to understand much of what they are
reading (Fisher, Frey, and Lapp 2009; Langer 1984).
As the National Reading Panel (2000) noted, readers "access their background
knowledge to construct meaning from the text...Children read and comprehend
text by utilizing their linguistic and background knowledge combined with
their word reading skill." For students whose word reading skills are weak,
they depend primarily on their background knowledge of the topic and
memory of what they've read to comprehend the text.
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 4
Assessing Our Practice
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 5
Three Practices Linked to Background Knowledge
Assess what students already know
Plan lessons and activities that build background knowledge
Design ways to activate students knowledge by having them interact with
content
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 6
Assessing What Students Know
Using interest surveys
Opnionairre
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 7
Activating What Students Know
Role of establishing a purpose for work/activities
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 8
The Role of Establishing Purpose
Establishing purpose is key to activating background knowledge
Include:
Content: We will be preparing for a debate on the topic of whether it
is right to keep whales in aquariums?
Language: What words might we encounter as we explore this topic
Social: Youll be working in small groups to analyze different types
of information on whales in captivity.
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 9
Quick Conversations and Quick Writes
Brief conversation and written response to a question
Should be a thought-provoking question: Are zoos an appropriate place
for all wild animals?
Gives students a psychologically safe environment to speculate
Avoid questions that are too simplistic
Extend these quick conversation and write questions by inviting students to
engage in structured partner or whole group discussions
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 10
Strategies to Build Background Knowledge
Modeling
Teacher modeling of comprehension skills is effective with adolescents
(Alfassi, 2004)
Provides students with insights into the ways that an expert makes
cognitive decisions
An opportunity to profile discipline-specific expertise
Wide reading
Graphic organizers to strengthen schema
Guest speakers
Field trips and experiential learning
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 11
Wrap Up
Big ideas
1. Background knowledge matters
2. Assess, activate and build!
3. If we want it to happen we must plan for it.
June 18, 2015 Presentation title here 12
Вам также может понравиться
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Writingsupportsample2 Constructedresponsequestion RaceДокумент2 страницыWritingsupportsample2 Constructedresponsequestion Raceapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Old Highland Park Baptist Church E01Документ74 страницыOld Highland Park Baptist Church E01Lawrence Garner100% (2)
- Case Study Analysis - WeWorkДокумент8 страницCase Study Analysis - WeWorkHervé Kubwimana50% (2)
- Basler Electric TCCДокумент7 страницBasler Electric TCCGalih Trisna NugrahaОценок пока нет
- Woop OverviewДокумент1 страницаWoop Overviewapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Speakingsample1 GroupdiscussionguideДокумент1 страницаSpeakingsample1 Groupdiscussionguideapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Girls Club Community Agreements FlyerДокумент1 страницаGirls Club Community Agreements Flyerapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Expl Protocols ResourcesДокумент66 страницExpl Protocols Resourcesapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Wordlistsample1 WordsotherthanДокумент1 страницаWordlistsample1 Wordsotherthanapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Writingsupportsample1 CounterclaimsgoДокумент2 страницыWritingsupportsample1 Counterclaimsgoapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Speakingwritingsupportsample1 Toulminargumentgraphicorganizer Docx 1Документ2 страницыSpeakingwritingsupportsample1 Toulminargumentgraphicorganizer Docx 1api-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Vocabularytechnology 1Документ1 страницаVocabularytechnology 1api-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Evidence BasedvocabularyinstructionДокумент2 страницыEvidence Basedvocabularyinstructionapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Evidence BasedvocabularyinstructionДокумент2 страницыEvidence Basedvocabularyinstructionapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- ScaffoldingДокумент6 страницScaffoldingapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- College and Career Readiness Standards For Vocabulary InstructionДокумент1 страницаCollege and Career Readiness Standards For Vocabulary Instructionapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Vocabularyshiftsforstandards AlignedinstructionДокумент1 страницаVocabularyshiftsforstandards Alignedinstructionapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Background Interest BlankДокумент1 страницаBackground Interest Blankapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Self-Assessing Background KnowledgeДокумент1 страницаSelf-Assessing Background Knowledgeapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Opinionnaire FutureДокумент1 страницаOpinionnaire Futureapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- India Vs Pakistan Cricket MatchДокумент3 страницыIndia Vs Pakistan Cricket Matchapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Planning For Building Student Background KnowledgeДокумент1 страницаPlanning For Building Student Background Knowledgeapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Assessing InterestДокумент1 страницаAssessing Interestapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Forging Strong Connections FNLДокумент8 страницForging Strong Connections FNLapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Getting Meta About How We Use Background KnowledgeДокумент1 страницаGetting Meta About How We Use Background Knowledgeapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Msbrief 2011-1Документ8 страницMsbrief 2011-1api-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Srsdself RegulationДокумент1 страницаSrsdself Regulationapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Stages of SRSD Writing Instruction: Stages Suggestions For Each StageДокумент1 страницаStages of SRSD Writing Instruction: Stages Suggestions For Each Stageapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- TeachthewritingprocessДокумент1 страницаTeachthewritingprocessapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Srsdmnemonicdevices 1Документ2 страницыSrsdmnemonicdevices 1api-345242472Оценок пока нет
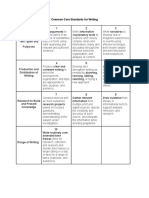
- Write Arguments To Write Narratives To: Common Core Standards For WritingДокумент1 страницаWrite Arguments To Write Narratives To: Common Core Standards For Writingapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- StageofreadingДокумент1 страницаStageofreadingapi-345242472Оценок пока нет
- Mehdi Semati - Media, Culture and Society in Iran - Living With Globalization and The Islamic State (Iranian Studies)Документ294 страницыMehdi Semati - Media, Culture and Society in Iran - Living With Globalization and The Islamic State (Iranian Studies)Alexandra KoehlerОценок пока нет
- Adhesive Film & TapeДокумент6 страницAdhesive Film & TapeJothi Vel MuruganОценок пока нет
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 3 Parent Tip Sheet 1Документ2 страницыEureka Math Grade 2 Module 3 Parent Tip Sheet 1api-324573119Оценок пока нет
- API IND DS2 en Excel v2 10081834Документ462 страницыAPI IND DS2 en Excel v2 10081834Suvam PatelОценок пока нет
- Andromeda: Druid 3 Warborn06Документ5 страницAndromeda: Druid 3 Warborn06AlanОценок пока нет
- TSC M34PV - TSC M48PV - User Manual - CryoMed - General Purpose - Rev A - EnglishДокумент93 страницыTSC M34PV - TSC M48PV - User Manual - CryoMed - General Purpose - Rev A - EnglishMurielle HeuchonОценок пока нет
- Pell (2017) - Trends in Real-Time Traffic SimulationДокумент8 страницPell (2017) - Trends in Real-Time Traffic SimulationJorge OchoaОценок пока нет
- Internal Gear Pump: Replaces: 03.08 Material No. R901216585 Type PGH.-3XДокумент36 страницInternal Gear Pump: Replaces: 03.08 Material No. R901216585 Type PGH.-3XbiabamanbemanОценок пока нет
- DescriptiveДокумент1 страницаDescriptiveRizqa Anisa FadhilahОценок пока нет
- Ezpdf Reader 1 9 8 1Документ1 страницаEzpdf Reader 1 9 8 1AnthonyОценок пока нет
- Onco Case StudyДокумент2 страницыOnco Case StudyAllenОценок пока нет
- ERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingДокумент3 страницыERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingtpeppermanОценок пока нет
- Errata V0.1 For IT8212F V0.4.2Документ2 страницыErrata V0.1 For IT8212F V0.4.2tryujiОценок пока нет
- Teaching Plan - Math 8 Week 1-8 PDFДокумент8 страницTeaching Plan - Math 8 Week 1-8 PDFRYAN C. ENRIQUEZОценок пока нет
- Airworthiness Directive: FAA Aviation SafetyДокумент2 страницыAirworthiness Directive: FAA Aviation SafetyCarlos VarrentiОценок пока нет
- DISTRICT CENSUS HANDBOOK North GoaДокумент190 страницDISTRICT CENSUS HANDBOOK North Goants1020Оценок пока нет
- Ladies Code I'm Fine Thank YouДокумент2 страницыLadies Code I'm Fine Thank YoubobbybiswaggerОценок пока нет
- Fish Culture in Ponds: Extension Bulletin No. 103Документ32 страницыFish Culture in Ponds: Extension Bulletin No. 103Bagas IndiantoОценок пока нет
- Forensic My Cology Mcgraw HillДокумент8 страницForensic My Cology Mcgraw HillJayanti RaufОценок пока нет
- Bofa Turkish Banks-Back On The RadarДокумент15 страницBofa Turkish Banks-Back On The RadarexperhtmОценок пока нет
- Prediction of Mechanical Properties of Steel Using Artificial Neural NetworkДокумент7 страницPrediction of Mechanical Properties of Steel Using Artificial Neural NetworkInternational Association of Scientific Innovations and Research (IASIR)Оценок пока нет
- Ccu 3900alДокумент3 страницыCcu 3900alTourchianОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet: - AdsealДокумент12 страницMaterial Safety Data Sheet: - Adsealwuhan lalalaОценок пока нет
- Corregidor Title DefenseДокумент16 страницCorregidor Title DefenseJaydee ColadillaОценок пока нет
- MFD16I003 FinalДокумент16 страницMFD16I003 FinalAditya KumarОценок пока нет
- Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis Provides Update As Hurricane Ian Prompts EvДокумент1 страницаFlorida Gov. Ron DeSantis Provides Update As Hurricane Ian Prompts Evedwinbramosmac.comОценок пока нет
- TOR AND SCOPING Presentation SlidesДокумент23 страницыTOR AND SCOPING Presentation SlidesSRESTAA BHATTARAIОценок пока нет