Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Practical Exam
Загружено:
Irfan AliАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Practical Exam
Загружено:
Irfan AliАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TECHNO NJR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
PRACTICAL EXAM
Subject Code: 7EE8
POWER SYSTEM MODELING & SIMULATION LAB
(IV B. Tech VII Semester EE)
Practical Questions
1. (a). Simulate Swing Equation in Simulink (MATLAB)
(b). A 50 Hz synchronous generator is connected to an infinite bus through
a line. The p.u. reactances of generator and the line are j0.3 p.u. and j0.2 p.u. respectively. The
generator no load voltage is 1.1 p.u. and that of infinite bus is 1.0 p.u. The inertia constant of
the generator is 3 MW-sec/MVA. Determine the frequency of natural oscillations if the generator
is loaded to (i) 60% and (ii) 75% of its maximum power transfer capacity and small perturbation
in power is given
(c ). A motor is receiving 25% of the power that it is capable of receiving from an infinite bus. If the load
on the motor is doubled, calculate the maximum value of during the swinging of the rotor around its new
equilibrium position.
2. (a) Simulate Multimachine Stability Modeling using Synchronous Machine. (MATLAB)
(b). A 50 Hz generator is delivering 50% of the power that it is capable of delivering through a transmission line
to an infinite bus. A fault occurs that increases the reactance between the generator and the infinite bus to 500%
of the value before the fault. When the fault is isolated, the maximum power that can be delivered is 75% of the
original maximum value. Determine the critical clearing angle for the condition described.
(c ). Fig. shows a generator connected to a metropolitan system (infinite bus) through high voltage lines.
The numbers on the figure indicate the reactances in p.u. Breakers adjacent to a fault on both sides are arranged
to clear simultaneously. Determine the critical clearing angle for the generator for a 3-phase fault at the point P
when the generator is delivering 1.0 p.u. power. Assume that the voltage behind transient reactance is 1.2 p.u.
for the generator and that the voltage at the infinite bus is 1.0 p.u.
3. (a). Simulate Modeling of Induction Machine. (MATLAB)
(b). Two power stations A and B are located close together. Station A has four identical generator sets each rated
100 MVA and each having an inertia constant of 9 MJ/MVA whereas station B has three sets each rated 200
MVA, 4MJ/MVA. Calculate the inertia constant of the equivalent machines of both the stations on 150 MVA
base.
(c ). A turboalternator with 4-pole, 50 Hz, 80 MW, p.f. 0.8 lag and moment of inertia 40,000 kgm2 is
interconnected via a short transmission line to another alternator with 2-pole, 50 Hz, 100 MW, p.f. 0.8 lag and
moment of inertia 10,000 kgm2. Determine the inertia constant of the single equivalent machine on a base of
100 MVA.
4. (a) Simulate PWM Control of Induction Machine. (MATLAB)
(b). Station A transmits 50 MW of power to station B through a tie line. The maximum steady state capacity of
the line is 100 MW. Determine the allowable sudden load that can be switched on without loss of stability.
(c ). A 4-pole, 50 Hz, 22 kV turboalternator has a rating of 100 MVA p.f. 0.8 lag. The moment of inertia of rotor
is 8000 kgm2. Determine M and H.
5. (a). Simulate a Single Phase Non Linear Load Model. (MATLAB)
(b). Determine the kinetic energy stored by a 50 MVA, 50 Hz two pole alternator with an inertia constant (H) of
5 kW sec. per KVA. If the machine is running steadily at synchronous speed with a shaft input (minus rotational
losses) of 65000 HP when the electrical power developed suddenly changes from its normal value to a value of
40 MW, determine the acceleration or deceleration of the rotor. If the acceleration computed for the generator is
constant for a period of 10 cycles, determine the change in torque angle in that period and the r.p.m. at the end
of the 10 cycles.
(c ). Derive an expression for the maximum power transfer between two nodes. Show that this power is
maximum when X = 3R , where X is the reactance and R the resistance of the system.
6. (A) Simulate Model of Synchronous Machine with FACTS device. (MATLAB)
(B) Simulate Synchronous Machine with FACTS devices. (MATLAB)
(C ). What is equal area criterion ? Discuss its application and limitation in the study of power system stability.
7. (a). Simulate a SMIB system with FACT Controller. (MATLAB)
(b). Discuss the application of equal area criterion for the system stability study when (i) a sudden increase in
load takes place, and (ii) a short circuit on one of the parallel feeders takes place which is cleared after certain
time.
( c) Differentiate between steady state stability and transient stability of a power system. Discuss the factors that
affect (i) steady state stability, and (ii) transient state stability of the system.
Вам также может понравиться
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsОт EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsОценок пока нет
- Assignment PSEДокумент5 страницAssignment PSEdipakk beraОценок пока нет
- Asynchronous Machines Tutorial Sheets (EL-208Документ10 страницAsynchronous Machines Tutorial Sheets (EL-208Kushagra BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Electrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsДокумент4 страницыElectrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsPranav MenonОценок пока нет
- What Is Ferranti EffectДокумент3 страницыWhat Is Ferranti Effectboopelectra50% (2)
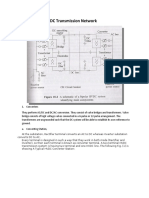
- Component of HVDC Transmission NetworkДокумент5 страницComponent of HVDC Transmission NetworkIqbalilah RamdaniОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6 Synchronous Machine ModelingДокумент57 страницLecture 6 Synchronous Machine ModelingManuelОценок пока нет
- SSSC PPT (Autosaved)Документ14 страницSSSC PPT (Autosaved)shubham bansalОценок пока нет
- IARE AC Machines Lab ManualДокумент52 страницыIARE AC Machines Lab ManualNaveen KumarОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip TestДокумент3 страницыExperiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip Test61EEPrabhat PalОценок пока нет
- Switchgear and Protection 2Документ4 страницыSwitchgear and Protection 2vimal067Оценок пока нет
- Thyristor ReportДокумент9 страницThyristor ReportDhaval GamiОценок пока нет
- PQ Unit 1Документ21 страницаPQ Unit 1Ezhiln 0328sОценок пока нет
- Tutorial on single phase induction motor parameters and performanceДокумент1 страницаTutorial on single phase induction motor parameters and performanceHimanshu Saini0% (1)
- MCQs Question Bank Basic Electrical Engineering AKTUДокумент13 страницMCQs Question Bank Basic Electrical Engineering AKTURaj ChauhanОценок пока нет
- A Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IДокумент34 страницыA Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IDhruv PatelОценок пока нет
- Publication 1 19208 6043Документ13 страницPublication 1 19208 6043Stephen Velasco Villaruz0% (1)
- HVDC SlidesДокумент25 страницHVDC SlidesAreeb ZulkifleОценок пока нет
- MTDC System PDFДокумент17 страницMTDC System PDFAshok Kumar67% (3)
- Basic Structure of A Power SystemДокумент9 страницBasic Structure of A Power Systembiruke6Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Power Systems (Eceg-3176) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)Документ38 страницIntroduction To Power Systems (Eceg-3176) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)DANIEL ABERAОценок пока нет
- Cmps Paper Objective PaperДокумент27 страницCmps Paper Objective PaperJeetu Bhardwaj0% (2)
- Assignment Induction MotorsДокумент3 страницыAssignment Induction MotorsMallikarjunBhiradeОценок пока нет
- Power Quality Improvement in Transmission Line Using DPFCДокумент7 страницPower Quality Improvement in Transmission Line Using DPFCVIVA-TECH IJRIОценок пока нет
- Electrical Drives: An Introduction to Power Electronics and Variable Speed AC and DC Motor DrivesДокумент37 страницElectrical Drives: An Introduction to Power Electronics and Variable Speed AC and DC Motor DrivesDawit Shimeles TesfayeОценок пока нет
- Control System Lab ManualДокумент62 страницыControl System Lab ManualVenkata Subramanian0% (1)
- UNIT-1 of HVEДокумент8 страницUNIT-1 of HVEAayush Patidar100% (2)
- Optimization Techniques For Power System ProblemsДокумент12 страницOptimization Techniques For Power System ProblemsAhsan SaleemОценок пока нет
- 17ee82 - Ida - Mod 3 NotesДокумент38 страниц17ee82 - Ida - Mod 3 NotesManish Kumar SahaniОценок пока нет
- Switchgear and Protection 3Документ4 страницыSwitchgear and Protection 3vimal067Оценок пока нет
- Represent Power System ComponentsДокумент14 страницRepresent Power System ComponentsRume EmujekarohwoОценок пока нет
- Module Information Module Title Electric Drives and Control Module Code MMD2511Документ4 страницыModule Information Module Title Electric Drives and Control Module Code MMD2511Ashley KaОценок пока нет
- Speeed ControlДокумент3 страницыSpeeed ControlChristine GomezОценок пока нет
- Voltage and Frequency ControlДокумент12 страницVoltage and Frequency ControlKhawarAminОценок пока нет
- Power System OperationДокумент11 страницPower System OperationMATHANKUMAR.SОценок пока нет
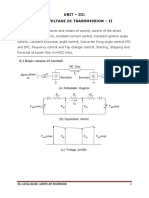
- HVDC Unit IIIДокумент22 страницыHVDC Unit IIISreenivas Reddy BodimallaОценок пока нет
- Part BДокумент10 страницPart BVenkat ManiОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Ac MachinesДокумент4 страницыQuestion Bank Ac Machinesashwin paulОценок пока нет
- IDA - QuesbankДокумент10 страницIDA - QuesbankKavitha KaviОценок пока нет
- Solid State Drives Short BookДокумент48 страницSolid State Drives Short BookGomathi Raja MОценок пока нет
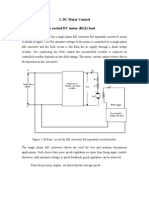
- Experiment 4 - Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifierДокумент13 страницExperiment 4 - Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifierAaaa DdddОценок пока нет
- Glover 10 ExДокумент13 страницGlover 10 ExAseel Bait MaditОценок пока нет
- Power System Operation and Control NotesДокумент61 страницаPower System Operation and Control Notesanon_613151744100% (1)
- Synchronous Machine ProblemsДокумент5 страницSynchronous Machine Problemsbhuvana71Оценок пока нет
- M.Tech II Semester Exam Questions Surge Phenomena Insulation CoordinationДокумент2 страницыM.Tech II Semester Exam Questions Surge Phenomena Insulation Coordinationprakash_yeee100% (1)
- DC Link CurrentДокумент8 страницDC Link CurrentsubbannaОценок пока нет
- Sheet 3Документ3 страницыSheet 3geo_bi100% (1)
- Eee-Vi-power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - NotesДокумент119 страницEee-Vi-power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - NotesNurul Islam Faruk0% (1)
- Power System Control and OperationДокумент3 страницыPower System Control and OperationSantosh ThapaОценок пока нет
- 4-Economics MCQ Part PDFДокумент13 страниц4-Economics MCQ Part PDFAhmadОценок пока нет
- 2015 Distance Relay ExampleДокумент2 страницы2015 Distance Relay ExampleAmanОценок пока нет
- 17ee82 - Ida - Mod 4 NotesДокумент18 страниц17ee82 - Ida - Mod 4 NotesManish Kumar SahaniОценок пока нет
- Psa MCQДокумент26 страницPsa MCQrohanОценок пока нет
- RACTIFIERДокумент19 страницRACTIFIERDhananjay Aghara100% (1)
- NDW Series Computer Controlled Torsion Testing MachineДокумент5 страницNDW Series Computer Controlled Torsion Testing Machinegosaye desalegnОценок пока нет
- Frog Leg WindingДокумент9 страницFrog Leg WindingAbhijeet RedekarОценок пока нет
- FulltextThesis 2Документ209 страницFulltextThesis 2Kean PagnaОценок пока нет
- EEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20Документ11 страницEEE 805 Assignment Questions For Chapter 20ayeniОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Theology B.A. (Hons.) Theology: 1. English LanguageДокумент1 страницаFaculty of Theology B.A. (Hons.) Theology: 1. English LanguageIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Modular Multilevel Converter Control Strategy Based on Arm Current ControlДокумент10 страницModular Multilevel Converter Control Strategy Based on Arm Current ControlIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Mechatronics LabДокумент1 страницаMechatronics LabIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Trends in Active Power Line Conditioners: Electrical Engineering FieldsДокумент7 страницTrends in Active Power Line Conditioners: Electrical Engineering FieldsIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- 3 - D Printer LabДокумент1 страница3 - D Printer LabIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Theology: B. A. (Hons.)Документ3 страницыFaculty of Theology: B. A. (Hons.)Irfan AliОценок пока нет
- Certificate in Recitation of Quran - QiratДокумент2 страницыCertificate in Recitation of Quran - QiratIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Belec 12islamicperspective 150202141131 Conversion Gate02Документ98 страницBelec 12islamicperspective 150202141131 Conversion Gate02Irfan AliОценок пока нет
- AMU Guide Adm 2017 18Документ144 страницыAMU Guide Adm 2017 18munibfazalОценок пока нет
- I Sem Faculty Time Table 2017-18Документ6 страницI Sem Faculty Time Table 2017-18Irfan AliОценок пока нет
- 6ec1 6ec2 6ec3 6ec4 6ec5 6ec6.2Документ1 страница6ec1 6ec2 6ec3 6ec4 6ec5 6ec6.2Irfan AliОценок пока нет
- V Sem EE & EEEДокумент2 страницыV Sem EE & EEEIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Physics LabДокумент1 страницаPhysics LabIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- My Personal Time Table (23.08.2017)Документ1 страницаMy Personal Time Table (23.08.2017)Irfan AliОценок пока нет
- III Sem ECE Time Table 19-8-2017 (T)Документ1 страницаIII Sem ECE Time Table 19-8-2017 (T)Irfan AliОценок пока нет
- NJR Tech Udaipur BTech II Sem EE EEE Time Table Aug-Dec 2017Документ1 страницаNJR Tech Udaipur BTech II Sem EE EEE Time Table Aug-Dec 2017Irfan AliОценок пока нет
- B.Tech TimetableДокумент3 страницыB.Tech TimetableIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam Schedule For 2nd Year & 3rd Year ECEДокумент1 страницаMidterm Exam Schedule For 2nd Year & 3rd Year ECEIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Techno India NJR Institute of Technology, Udaipur: DAY MON Tues WED Thurs FRI SaturДокумент1 страницаTechno India NJR Institute of Technology, Udaipur: DAY MON Tues WED Thurs FRI SaturIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Absent Students PDFДокумент1 страницаAbsent Students PDFIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- List of Students (Ee/Eee) Who Were Absent Today in Matlab TrainingДокумент1 страницаList of Students (Ee/Eee) Who Were Absent Today in Matlab TrainingIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Bosch Selected-Facebook UpdateДокумент4 страницыBosch Selected-Facebook UpdateIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- IoT Course OutlineДокумент8 страницIoT Course OutlineIrfan Ali100% (1)
- NJR Tech ECE Dept Circuit Analysis Lecture ScheduleДокумент1 страницаNJR Tech ECE Dept Circuit Analysis Lecture ScheduleIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- VirtualДокумент1 страницаVirtualIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Intel HacksДокумент1 страницаIntel HacksIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- IoT Course OutlineДокумент8 страницIoT Course OutlineIrfan Ali100% (1)
- Lake MonitoringДокумент1 страницаLake MonitoringIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Lake MonitoringДокумент1 страницаLake MonitoringIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Intel HacksДокумент1 страницаIntel HacksIrfan AliОценок пока нет
- Curl and DivergenceДокумент5 страницCurl and DivergenceChernet TugeОценок пока нет
- Understanding the Mole ConceptДокумент23 страницыUnderstanding the Mole ConceptMuyatwa LiksОценок пока нет
- Cbiescsu 06Документ4 страницыCbiescsu 06neomatrix70Оценок пока нет
- Vortex-Induced Oscillation-A Selective ReviewДокумент18 страницVortex-Induced Oscillation-A Selective ReviewWade ZhouОценок пока нет
- EE207 Problem Set 1Документ2 страницыEE207 Problem Set 1Rishabh AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Sae Technical Paper Series: Tankut Acarman and Umit OzgunerДокумент9 страницSae Technical Paper Series: Tankut Acarman and Umit OzgunerLeonel Bejar VelardeОценок пока нет
- Wiles1994 - in Situ Stress Determination Using The Under-Excavation Technique - I. TheoryДокумент8 страницWiles1994 - in Situ Stress Determination Using The Under-Excavation Technique - I. TheoryRisantoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Lecture 2Документ30 страницChapter 5 Lecture 2burhanuddinОценок пока нет
- Compiled FluMach Problems - GROUP6 - BSME31Документ58 страницCompiled FluMach Problems - GROUP6 - BSME31Jhun Briones100% (1)
- G1 Group 1CДокумент72 страницыG1 Group 1CNH SyzlnОценок пока нет
- Lang SethДокумент52 страницыLang Sethrrmerlin_2Оценок пока нет
- Energy Interactions With The Earth SurfaceДокумент3 страницыEnergy Interactions With The Earth SurfaceAmirulTarliОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsДокумент90 страницLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsLharie Mae BecinaОценок пока нет
- Dimensional Analysis Worksheet 2Документ4 страницыDimensional Analysis Worksheet 2German ToledoОценок пока нет
- Slope stability analysis for access tunnel portalДокумент3 страницыSlope stability analysis for access tunnel portal2685866Оценок пока нет
- ASTM D287 - 12bДокумент5 страницASTM D287 - 12bmancjaОценок пока нет
- EMI and ACДокумент14 страницEMI and ACbharathОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3 MOMДокумент6 страницExperiment 3 MOMHafiz HamzaОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Parameter Identification of The Universal Robots UR5 PDFДокумент7 страницDynamic Parameter Identification of The Universal Robots UR5 PDFAyman DamounОценок пока нет
- 2016 Ibh2 Waves Interference RevisionДокумент28 страниц2016 Ibh2 Waves Interference RevisionAreeb AlamОценок пока нет
- Energy Balance CalculationДокумент2 страницыEnergy Balance CalculationSzelee KuekОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Raycap Baja TensionДокумент250 страницCatalogo Raycap Baja TensionDomingo RuizОценок пока нет
- Calculable Cross CapacitorДокумент43 страницыCalculable Cross Capacitornova1234Оценок пока нет
- DC CircuitДокумент142 страницыDC CircuitBela FirmantoyoОценок пока нет
- Voltage Drop and Short CircuitДокумент39 страницVoltage Drop and Short CircuitMinerva Abanto100% (1)
- 2018 Experimental and CFD Analysis of Solar Air Heater With Rectangular ShapedДокумент5 страниц2018 Experimental and CFD Analysis of Solar Air Heater With Rectangular ShapedaliОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding MCQДокумент15 страницChemical Bonding MCQVinay Krishna Kodali50% (4)
- De La Salle University Dasmarinas: Experiment No. 4 DC Shunt MotorДокумент6 страницDe La Salle University Dasmarinas: Experiment No. 4 DC Shunt MotorMizhar GerardoОценок пока нет
- Lab Act 1 - Energy G8-1Документ3 страницыLab Act 1 - Energy G8-1LevitogamingОценок пока нет
- Voltage and Frequency Control of Inverters Connected in Parallel Forming A Micro-GridДокумент6 страницVoltage and Frequency Control of Inverters Connected in Parallel Forming A Micro-GridShad Rahman100% (1)