Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Creating A Thread
Загружено:
Shanmuka SreenivasОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Creating A Thread
Загружено:
Shanmuka SreenivasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
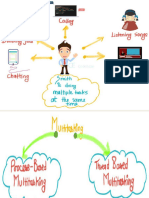
Creating a thread
Java defines two ways by which a thread can be created.
By implementing the Runnable interface.
By extending the Thread class.
Implementing the Runnable Interface
The easiest way to create a thread is to create a class that implements the runnable
interface. After implementing runnable interface , the class needs to implement
the run() method, which is of form,
public void run()
run() method introduces a concurrent thread into your program. This thread will
end when run() returns.
You must specify the code for your thread inside run() method.
run() method can call other methods, can use other classes and declare variables
just like any other normal method.
class MyThread implements Runnable
public void run()
System.out.println("concurrent thread started running..");
class MyThreadDemo
public static void main( String args[] )
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
Thread t = new Thread(mt);
t.start();
Output : concurrent thread started running..
To call the run() method, start() method is used. On calling start(), a new stack is
provided to the thread and run() method is called to introduce the new thread into the
program.
Extending Thread class
This is another way to create a thread by a new class that extends Thread class and
create an instance of that class. The extending class must override run() method which
is the entry point of new thread.
class MyThread extends Thread
public void run()
System.out.println("Concurrent thread started running..");
classMyThreadDemo
public static void main( String args[] )
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
mt.start();
Output : concurrent thread started running..
In this case also, as we must override the run() and then use the start() method to start
and run the thread. Also, when you create MyThread class object, Thread class
constructor will also be invoked, as it is the super class, hence MyThread class object
acts as Thread class object.
What if we call run() method directly without using start() method ?
In above program if we directly call run() method, without using start() method,
public static void main( String args[] )
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
mt.run();
Doing so, the thread won't be allocated a new call stack, and it will start running in the
current call stack, that is the call stack of the main thread. Hence Multithreading won't be
there.
Can we Start a thread twice ?
No, a thread cannot be started twice. If you try to do
so, IllegalThreadStateException will be thrown.
public static void main( String args[] )
{
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
mt.start();
mt.start(); //Exception thrown
When a thread is in running state, and you try to start it again, or any method try to
invoke that thread again using start() method, exception is thrown.
Вам также может понравиться
- Java ThreadsДокумент85 страницJava ThreadsabhishekkumarjhafbgОценок пока нет
- Muti Threaded Programming NotesДокумент10 страницMuti Threaded Programming NotesSharon Stefi GHОценок пока нет
- Thread and Design Pattern Lab in JavaДокумент17 страницThread and Design Pattern Lab in JavatinsaeОценок пока нет
- Multi Threading in Java by Durga SirДокумент75 страницMulti Threading in Java by Durga SirLalitОценок пока нет
- Multi Threading in Java by Durga SirДокумент68 страницMulti Threading in Java by Durga SirLalitОценок пока нет
- Rohan Pahwa Roll No-A17 Reg No-10809673 Mca (Hons) .: Modern Programming Tools & Techniques I For Honors Homework 3Документ15 страницRohan Pahwa Roll No-A17 Reg No-10809673 Mca (Hons) .: Modern Programming Tools & Techniques I For Honors Homework 3vivek19354Оценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Concurrent ProgrammingДокумент31 страницаUnit 5 Concurrent ProgrammingMathesh ParamasivamОценок пока нет
- Unit4 Java FullДокумент21 страницаUnit4 Java Fullmadani hussainОценок пока нет
- Multi ThreadingДокумент17 страницMulti ThreadingMadhu SudhanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 - Multi-Threading in JavaДокумент29 страницChapter 10 - Multi-Threading in JavaTanveer Ahmed HakroОценок пока нет
- MultiThreading and SynchronizationДокумент43 страницыMultiThreading and SynchronizationricketbusОценок пока нет
- MultithreadingДокумент33 страницыMultithreadingKarthik KeyanОценок пока нет
- Multi Threading ShrikantДокумент106 страницMulti Threading ShrikantKomal RansingОценок пока нет
- ADVANCED JAVA PROGRAMMING Java Unit5Документ43 страницыADVANCED JAVA PROGRAMMING Java Unit5ShangaviОценок пока нет
- MultithreadingДокумент2 страницыMultithreadingprasadgr931Оценок пока нет
- CH 1Документ26 страницCH 1Oz GОценок пока нет
- Java KMДокумент8 страницJava KMKetan BhadekarОценок пока нет
- Process Based - Executing Several Tasks Simultaneously - Each Task Is A Separate Independent Process. ThisДокумент13 страницProcess Based - Executing Several Tasks Simultaneously - Each Task Is A Separate Independent Process. ThisWeecky HunterОценок пока нет
- Java - Multithreading: Life Cycle of A ThreadДокумент7 страницJava - Multithreading: Life Cycle of A ThreadRahul GuptaОценок пока нет
- Threads, Processes and Multitasking: Java® TutorialДокумент5 страницThreads, Processes and Multitasking: Java® Tutorialajay_anavОценок пока нет
- MultithreadingДокумент4 страницыMultithreadingR RОценок пока нет
- ConcurrencyДокумент42 страницыConcurrencySebastian RomaniucОценок пока нет
- Multi Threaded Programming: Megha Aggarwal IGIT, GGSIP University, Delhi EmailДокумент30 страницMulti Threaded Programming: Megha Aggarwal IGIT, GGSIP University, Delhi EmailJamuna Prasad GuptaОценок пока нет
- Multithreading Class Notes JavaДокумент65 страницMultithreading Class Notes Javadaniel007workОценок пока нет
- OOPJ MultiThreading NJB PDFДокумент27 страницOOPJ MultiThreading NJB PDFRaj ShahОценок пока нет
- Lect01: Multithreaded Programming: Writing Concurrently Running ThreadsДокумент20 страницLect01: Multithreaded Programming: Writing Concurrently Running ThreadsGeay PeterОценок пока нет
- Thread - Java WorldДокумент54 страницыThread - Java WorldkumarharshОценок пока нет
- Java - MultithreadingДокумент8 страницJava - MultithreadingKoushik Sinha100% (1)
- Java Programming UNIT-4: ThreadДокумент22 страницыJava Programming UNIT-4: Threaduddagiri sirishaОценок пока нет
- Java Programming UNIT-4: ThreadДокумент22 страницыJava Programming UNIT-4: Threaduddagiri sirishaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 15 - Java MultiThreadingДокумент44 страницыLecture 15 - Java MultiThreadingMuhammad TayyabОценок пока нет
- Multithreading and Generic ProgrammingДокумент58 страницMultithreading and Generic ProgrammingmahalakshmiОценок пока нет
- (AJP) Chapter 3Документ32 страницы(AJP) Chapter 3abdi geremewОценок пока нет
- Multithreading:-: Smallest Unit of ProcessingДокумент3 страницыMultithreading:-: Smallest Unit of ProcessingAmit JainОценок пока нет
- Thread: Thread. Even If You Don't Create Any New Threads in Your Program, Threads Are BackДокумент28 страницThread: Thread. Even If You Don't Create Any New Threads in Your Program, Threads Are BackKuldeep KumarОценок пока нет
- MultithreadingДокумент33 страницыMultithreadingVarun BonkinpallewarОценок пока нет
- PROGRAMMING PARADIGMS - Unit VДокумент33 страницыPROGRAMMING PARADIGMS - Unit VKanthimathi SureshОценок пока нет
- ThreadsДокумент12 страницThreadsabhishek_pОценок пока нет
- Core JavaДокумент9 страницCore Javachaubeyabhi7070Оценок пока нет
- Week 02Документ12 страницWeek 02Sadia ZarОценок пока нет
- Chapter One MotiДокумент32 страницыChapter One MotiBeka BekoОценок пока нет
- A Quick Tutorial On How To Implement Threads in JavaДокумент9 страницA Quick Tutorial On How To Implement Threads in JavaPraveen100% (5)
- Java p12Документ5 страницJava p12Khan.aliОценок пока нет
- Multithreaded Programming Using Java ThreadsДокумент55 страницMultithreaded Programming Using Java ThreadscupidcallinОценок пока нет
- Java MultithreadingДокумент21 страницаJava MultithreadingKuldeep SinghОценок пока нет
- Multithreading in JavaДокумент9 страницMultithreading in JavaxrtesportsofficialОценок пока нет
- Multi ThreadingДокумент65 страницMulti Threadingcontact.me90Оценок пока нет
- Multithreading in JavaДокумент30 страницMultithreading in JavaSwaragyam PalakuraОценок пока нет
- Lecture9 JavaДокумент9 страницLecture9 Javaمعتز العجيليОценок пока нет
- JAVA PresentationДокумент24 страницыJAVA PresentationfmfaustinaОценок пока нет
- Unit4 JavaДокумент17 страницUnit4 JavapoomanimОценок пока нет
- Java Multithreading PDFДокумент9 страницJava Multithreading PDFPhanidhar S GadiyaramОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - MultiThreadingДокумент36 страницChapter 5 - MultiThreadingnoahmullerОценок пока нет
- Threads in JavaДокумент6 страницThreads in JavaNandana BobanОценок пока нет
- MultithreadingДокумент24 страницыMultithreadingJosé Damián López DíazОценок пока нет
- Cs8392-Oops - Unit IvДокумент91 страницаCs8392-Oops - Unit IvMangaiyarkarasi DuraisamyОценок пока нет
- Java Chap2Документ18 страницJava Chap2Lady BugОценок пока нет
- Introduction To ThreadsДокумент40 страницIntroduction To ThreadsriyaОценок пока нет
- Multithreaded Programming Using Java ThreadsДокумент33 страницыMultithreaded Programming Using Java ThreadsMITMCAОценок пока нет
- Online Fashion Designer Registration Form: A Project Report OnДокумент4 страницыOnline Fashion Designer Registration Form: A Project Report OnShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Data Analysis Penna Cement 1 NEWДокумент22 страницыData Analysis Penna Cement 1 NEWShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Embossing Machine Catalouge PDFДокумент2 страницыEmbossing Machine Catalouge PDFShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- HTML AddДокумент13 страницHTML AddShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- DocumentationДокумент37 страницDocumentationShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- A Study On Loans and Advances by Rohit RДокумент91 страницаA Study On Loans and Advances by Rohit RChandrashekhar GurnuleОценок пока нет
- Abhudaya SchoolДокумент1 страницаAbhudaya SchoolShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Unit 5:structures in C' Structure-Defination: Defination1:A Group of One or More Variables of Different Data Types OrganizedДокумент18 страницUnit 5:structures in C' Structure-Defination: Defination1:A Group of One or More Variables of Different Data Types OrganizedShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Recruitment & SelectionДокумент70 страницRecruitment & SelectionShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Internet Based Discussion FormДокумент5 страницInternet Based Discussion FormShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Lanco ProfileДокумент16 страницLanco ProfileShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Library Management System: A Project Report Submitted in Practical Fulfillment of The Requirements ForДокумент5 страницLibrary Management System: A Project Report Submitted in Practical Fulfillment of The Requirements ForShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Customer Satisfaction SUJALA PIPESДокумент74 страницыCustomer Satisfaction SUJALA PIPESShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Usha Additional PagesДокумент2 страницыUsha Additional PagesShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Sub:-Academic Project of Final Year Master of Business AdministrationДокумент1 страницаSub:-Academic Project of Final Year Master of Business AdministrationShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Resume BaluДокумент1 страницаResume BaluShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Std11 CommEng PDFДокумент360 страницStd11 CommEng PDFSparkdstudios VenkyОценок пока нет
- Event Registration Form: Sri Rama Krishna Degree (Autonomous) CollegeДокумент45 страницEvent Registration Form: Sri Rama Krishna Degree (Autonomous) CollegeShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- 10 Reasons To Leaarn EnglishДокумент3 страницы10 Reasons To Leaarn EnglishShanmuka Sreenivas100% (1)
- Audio EditingДокумент1 страницаAudio EditingShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Saturday Fest 01-09-2018Документ1 страницаSaturday Fest 01-09-2018Shanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Internet Based Discussion Forum: Modules and Their DescriptionДокумент4 страницыInternet Based Discussion Forum: Modules and Their DescriptionSapna MathapathiОценок пока нет
- AutoCAD 3D Course ManualДокумент166 страницAutoCAD 3D Course ManualJed Tedor98% (47)
- Talent ScoutДокумент5 страницTalent ScoutShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Mba ProjectДокумент57 страницMba Projectkavitha n100% (1)
- SRKDC Front 222Документ5 страницSRKDC Front 222Shanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- INDEXДокумент1 страницаINDEXShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- FORMAT OF BANKER AndhraДокумент1 страницаFORMAT OF BANKER AndhraShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- FORMAT OF BANKER AndhraДокумент1 страницаFORMAT OF BANKER AndhraShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- Narendra RESUMEДокумент2 страницыNarendra RESUMEShanmuka SreenivasОценок пока нет
- First Page PDFДокумент1 страницаFirst Page PDFVenkata DeekshitОценок пока нет
- StatisticsДокумент2 страницыStatisticsmarydahyllamarinduqueОценок пока нет
- SubtractorДокумент11 страницSubtractorRocky SamratОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Manpower LevelingДокумент24 страницыModule 2 Manpower LevelingrandomstalkingwomenОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Answer Key Final 1 Grade 6Документ9 страницWorksheet Answer Key Final 1 Grade 6EslamAhmedElsharkawyОценок пока нет
- Data Mining and Warehouse MCQS With Answer GoodДокумент30 страницData Mining and Warehouse MCQS With Answer GoodKanwal Preet74% (70)
- Vedic MathsДокумент8 страницVedic Mathsnithin s gowda100% (1)
- Length Power Dynamic Viscosity Heat FluxДокумент19 страницLength Power Dynamic Viscosity Heat FluxWilson UmaliОценок пока нет
- Mikroniek 2010 2 1Документ7 страницMikroniek 2010 2 1Vipin YadavОценок пока нет
- Yaron Herman - ThesisДокумент115 страницYaron Herman - ThesisBojan MarjanovicОценок пока нет
- 300+ TOP Neural Networks Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersДокумент29 страниц300+ TOP Neural Networks Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersJAVARIA NAZIRОценок пока нет
- 1 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Eigenspaces: Eigenvalue Characteristic ValueДокумент17 страниц1 Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors, Eigenspaces: Eigenvalue Characteristic ValueSarit BurmanОценок пока нет
- Triangulation: StatementДокумент3 страницыTriangulation: StatementИлија Хаџи-Пурић V-4Оценок пока нет
- Encyclopedia of Greek and Roman Mythology (Facts On File Library of Religion and Mythology)Документ241 страницаEncyclopedia of Greek and Roman Mythology (Facts On File Library of Religion and Mythology)Саша ПаповићОценок пока нет
- 8 Math Eng PP 2023 24 1Документ7 страниц8 Math Eng PP 2023 24 1aamirneyazi12Оценок пока нет
- Geomitric DistributionДокумент18 страницGeomitric DistributionTaanzОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 1Документ2 страницыLab Report 1api-249188694Оценок пока нет
- Merryland High School - Entebbe S5 Term 2020 Holiday Break Mathematics P1 Pure Maths Instructions: Answer ALL QuestionsДокумент4 страницыMerryland High School - Entebbe S5 Term 2020 Holiday Break Mathematics P1 Pure Maths Instructions: Answer ALL QuestionsVictor Lusiba100% (1)
- Generalized FunctionsДокумент56 страницGeneralized Functionsm-rasheedОценок пока нет
- ENME 599 Final Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыENME 599 Final Formula SheetNormanОценок пока нет
- Etap - Key Points For Load Summary, Part 4: Lumped Load ApplicationsДокумент2 страницыEtap - Key Points For Load Summary, Part 4: Lumped Load ApplicationsMarcelОценок пока нет
- Definitions: Figure 1. The Normal Distribution GraphДокумент8 страницDefinitions: Figure 1. The Normal Distribution GraphAndres BrutasОценок пока нет
- Memorandum of in Crafting The School Improvement Plan: Rodelio T. Laxamana Edna M. DabuДокумент3 страницыMemorandum of in Crafting The School Improvement Plan: Rodelio T. Laxamana Edna M. DabuMarife MagsinoОценок пока нет
- Solutionsfor Uniformly Accelerated Motion Problems Worksheets CH 6Документ3 страницыSolutionsfor Uniformly Accelerated Motion Problems Worksheets CH 6Abreham GirmaОценок пока нет
- Compiler Construction NotesДокумент16 страницCompiler Construction NotesApoorva BhattОценок пока нет
- Bernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragДокумент4 страницыBernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragABHIJEETОценок пока нет
- Curious Numerical Coincidence To The Pioneer AnomalyДокумент3 страницыCurious Numerical Coincidence To The Pioneer AnomalylivanelОценок пока нет
- TestДокумент4 страницыTestSreekumar K SОценок пока нет
- Fractions, Decimals, Percents: Learners Module in Business MathematicsДокумент29 страницFractions, Decimals, Percents: Learners Module in Business MathematicsJamaica C. AquinoОценок пока нет