Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Linear Algebra Column Vector Guide
Загружено:
harshit0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров1 страницаA column vector is a matrix with a single column of m elements, while a row vector is a matrix with a single row of m elements. The transpose of a row vector is a column vector and vice versa. Column and row vectors each form their own vector space, with the dimensions equaling the number of entries in the vector. The column space can be viewed as the dual space to the row space.
Исходное описание:
ROW MATRIX
Оригинальное название
Row Matrix
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документA column vector is a matrix with a single column of m elements, while a row vector is a matrix with a single row of m elements. The transpose of a row vector is a column vector and vice versa. Column and row vectors each form their own vector space, with the dimensions equaling the number of entries in the vector. The column space can be viewed as the dual space to the row space.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров1 страницаLinear Algebra Column Vector Guide
Загружено:
harshitA column vector is a matrix with a single column of m elements, while a row vector is a matrix with a single row of m elements. The transpose of a row vector is a column vector and vice versa. Column and row vectors each form their own vector space, with the dimensions equaling the number of entries in the vector. The column space can be viewed as the dual space to the row space.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
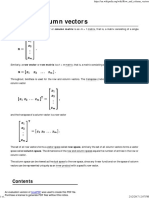
In linear algebra, a column vector or column matrix is an m 1 matrix, that is, a matrix
consisting of a single column of m elements,
Similarly, a row vector or row matrix is a 1 m matrix, that is, a matrix consisting of a
single row of m elements[1]
Throughout, boldface is used for the row and column vectors. The transpose (indicated
by T) of a row vector is a column vector
and the transpose of a column vector is a row vector
The set of all row vectors forms a vector space called row space, similarly the
set of all column vectors forms a vector space called column space. The
dimensions of the row and column spaces equals the number of entries in the
row or column vector.
The column space can be viewed as the dual space to the row space, since any
linear functional on the space of column vectors can be represented uniquely as
an inner product with a specific row vector.
Contents
[hide]
1Notation
2Operations
3Preferred input vectors for matrix transformations
4See also
5Notes
6References
Notation[edit]
To simplify writing column vectors in-line with other text, sometimes they are
written as row vectors with the transpose operation applied to them.
or
Вам также может понравиться
- Change of Basis: Preliminary NotionsДокумент6 страницChange of Basis: Preliminary NotionsAtiksha100% (1)
- Row and Column Vectors - WikipediaДокумент5 страницRow and Column Vectors - WikipediaSaad MehmoodОценок пока нет
- Vectors & Matrices: Same TypeДокумент20 страницVectors & Matrices: Same TypeAli Abalfazl MohsinОценок пока нет
- Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsДокумент19 страницEigenvalues and EigenvectorsSung Woo Jang100% (1)
- Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsДокумент29 страницEigenvalues and EigenvectorsRakesh S K100% (1)
- Lab Session 02: Defining Scalar VariablesДокумент14 страницLab Session 02: Defining Scalar VariablesShahansha HumayunОценок пока нет
- ThfkiДокумент59 страницThfkiRohit RajОценок пока нет
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент24 страницыEigenvalues and Eigenvectors - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediabmxengineeringОценок пока нет
- TensorДокумент20 страницTensoremma698Оценок пока нет
- Numerical Analysis Module 2 Fundamentals of Vector SpacesДокумент26 страницNumerical Analysis Module 2 Fundamentals of Vector SpacesDevenderОценок пока нет
- Bra-ket notation explainedДокумент12 страницBra-ket notation explainedfaisalphyОценок пока нет
- S. C. Johnson Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, New Jersey: Case ConstantДокумент1 страницаS. C. Johnson Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, New Jersey: Case ConstantPusheen VIIIОценок пока нет
- Transformation From: Linear Algebra MA2033Документ6 страницTransformation From: Linear Algebra MA2033akilОценок пока нет
- Coordinate Vector: The Standard Representation ExamplesДокумент4 страницыCoordinate Vector: The Standard Representation ExamplesAtikshaОценок пока нет
- Eigen Vectors, Eigen Values and MatricesДокумент2 страницыEigen Vectors, Eigen Values and MatricesShashank KumarОценок пока нет
- Praktikum Matlab: Chapter 2-Creating ArraysДокумент19 страницPraktikum Matlab: Chapter 2-Creating ArraysGannissyah RamadhanОценок пока нет
- Math - Course NotesДокумент9 страницMath - Course NotesminanabilОценок пока нет
- Eigen Vectors: TopicДокумент7 страницEigen Vectors: TopicUmar HaroonОценок пока нет
- 1.9.rank of A MatrixДокумент7 страниц1.9.rank of A MatrixqwertyuiopОценок пока нет
- LinearalgebraДокумент3 страницыLinearalgebramohdamaankhan.workОценок пока нет
- Formal Definition History Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of MatricesДокумент18 страницFormal Definition History Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of Matricesanwer fadelОценок пока нет
- Matrix (Mathematics)Документ19 страницMatrix (Mathematics)Teka KamОценок пока нет
- Array Data Type: Not To Be Confused WithДокумент7 страницArray Data Type: Not To Be Confused WithYacob HartawanОценок пока нет
- Wikipedia: MatrixДокумент19 страницWikipedia: MatrixMaiara e maraiara100% (1)
- Intro Octave MatlabДокумент26 страницIntro Octave MatlabJosue AparicioОценок пока нет
- Block 3 Linear Algebra: Second Order Differential EquationsДокумент50 страницBlock 3 Linear Algebra: Second Order Differential EquationsKrishanОценок пока нет
- 06 Unit_4_Part AДокумент30 страниц06 Unit_4_Part ARajnandini NagaraleОценок пока нет
- CL2014 - MATLAB Programming - Lec03Документ16 страницCL2014 - MATLAB Programming - Lec03UmarОценок пока нет
- Matrix Algebra For Beginners, Part II Linear Transformations, Eigenvectors and EigenvaluesДокумент16 страницMatrix Algebra For Beginners, Part II Linear Transformations, Eigenvectors and EigenvaluesPhine-hasОценок пока нет
- On The Topic: Submitted byДокумент10 страницOn The Topic: Submitted byAkshay KumarОценок пока нет
- Matlab Lecture 3Документ15 страницMatlab Lecture 3waqasОценок пока нет
- Asa 8x Regex ConfigДокумент30 страницAsa 8x Regex ConfigDanarОценок пока нет
- In Linear AlgebraДокумент2 страницыIn Linear AlgebraTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印Оценок пока нет
- MAT 203 - Lecture 2 SlidesДокумент29 страницMAT 203 - Lecture 2 Slides14mervekaya01Оценок пока нет
- Complete Lorentz GroupДокумент28 страницComplete Lorentz GroupTomás CampoОценок пока нет
- MATLABДокумент18 страницMATLABOkelola EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- Quantum Mechanics Vector RepresentationsДокумент19 страницQuantum Mechanics Vector RepresentationsC.R.Оценок пока нет
- T&S BookДокумент8 страницT&S BookFun TimeОценок пока нет
- Vector Field: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент11 страницVector Field: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediarachitОценок пока нет
- GGHFДокумент31 страницаGGHFRohit RajОценок пока нет
- Vector Space - Linear Algebra With ApplicationsДокумент86 страницVector Space - Linear Algebra With Applicationsradhikaseelam1Оценок пока нет
- Matrix calculusДокумент56 страницMatrix calculusvineetguleriaОценок пока нет
- Vectors and Scalars (Repaired)Документ27 страницVectors and Scalars (Repaired)maysara mohammadОценок пока нет
- Affine Transformation - WikipediaДокумент8 страницAffine Transformation - WikipediasukhoiОценок пока нет
- Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsДокумент153 страницыEigenvalues and EigenvectorsBalayya BОценок пока нет
- LITERATURE SURVEY LAДокумент5 страницLITERATURE SURVEY LAabinashreddy792Оценок пока нет
- Functional: Definition of TermsДокумент2 страницыFunctional: Definition of TermsChristelle AfricaОценок пока нет
- Data Structures: 3.1 Dynamic Range Minimum QueriesДокумент10 страницData Structures: 3.1 Dynamic Range Minimum QueriesThejas SatheeshОценок пока нет
- Normed Vector SpaceДокумент5 страницNormed Vector Spacesreekantha2013Оценок пока нет
- Programming Language - Common Lisp 15. ArraysДокумент21 страницаProgramming Language - Common Lisp 15. ArraysBenjamin CulkinОценок пока нет
- Vector Field: Vector Fields On Subsets of Euclidean SpaceДокумент8 страницVector Field: Vector Fields On Subsets of Euclidean SpaceDiego VillalobosОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ34 страницыLecture 2Sita HammondОценок пока нет
- Wikipedia - Covariance and Contravariance of VectorsДокумент11 страницWikipedia - Covariance and Contravariance of VectorscarlosgmОценок пока нет
- Lecture - I Vector SpaceДокумент5 страницLecture - I Vector SpaceAbhijit Kar GuptaОценок пока нет
- Matlab Lecture 3Документ15 страницMatlab Lecture 3waqasОценок пока нет
- The Concept of Linear Combination of VectorsДокумент8 страницThe Concept of Linear Combination of VectorsAmit TripathiОценок пока нет
- LAB 2Документ10 страницLAB 2Enas QtaifanОценок пока нет
- Nonnegative Matrices and Applicable Topics in Linear AlgebraОт EverandNonnegative Matrices and Applicable Topics in Linear AlgebraОценок пока нет
- The Name of Festive Days As Well As The Rituals of Diwali Vary Significantly Among HindusДокумент1 страницаThe Name of Festive Days As Well As The Rituals of Diwali Vary Significantly Among HindusharshitОценок пока нет
- Limit state design method for singly reinforced rectangular sectionsДокумент3 страницыLimit state design method for singly reinforced rectangular sectionsnirmal sutharОценок пока нет
- ChallengeДокумент1 страницаChallengeharshitОценок пока нет
- Constant LSMДокумент1 страницаConstant LSMharshitОценок пока нет
- 50 ChallengeДокумент1 страница50 ChallengeharshitОценок пока нет
- Functionals Groups PropertiesДокумент12 страницFunctionals Groups PropertiesharshitОценок пока нет
- Jee Main 2016 Detailed Analysis by Resonance EduventuresДокумент7 страницJee Main 2016 Detailed Analysis by Resonance EduventuresharshitОценок пока нет
- Lecture 50 ChallengeДокумент1 страницаLecture 50 ChallengeharshitОценок пока нет
- Hindu Fiji Guyana India Malaysia Mauritius Myanmar Nepal Singapore Sri Lanka Suriname Trinidad and Tobago SindhДокумент1 страницаHindu Fiji Guyana India Malaysia Mauritius Myanmar Nepal Singapore Sri Lanka Suriname Trinidad and Tobago SindhharshitОценок пока нет
- After ApplewhiteДокумент1 страницаAfter ApplewhiteharshitОценок пока нет
- While The Modern Game of Golf Originated in 15thДокумент1 страницаWhile The Modern Game of Golf Originated in 15thharshitОценок пока нет
- Sport Clubs Balls Course Ball Games Tee Box Putting Green: Golf Is A Club and BallДокумент1 страницаSport Clubs Balls Course Ball Games Tee Box Putting Green: Golf Is A Club and BallharshitОценок пока нет
- A Golf Course Consists of Either 9 or 18 HolesДокумент1 страницаA Golf Course Consists of Either 9 or 18 HolesharshitОценок пока нет
- Matrix Multiplication Dot ProductДокумент1 страницаMatrix Multiplication Dot ProductharshitОценок пока нет
- Haloalkanes Are Alkanes That Contain One or More Members of The Halogen Family. The HalogensДокумент1 страницаHaloalkanes Are Alkanes That Contain One or More Members of The Halogen Family. The HalogensharshitОценок пока нет
- Frequently A Row Vector Presents Itself For An Operation WithinДокумент1 страницаFrequently A Row Vector Presents Itself For An Operation WithinharshitОценок пока нет
- Marshall Herff Applewhite Was Born inДокумент1 страницаMarshall Herff Applewhite Was Born inharshitОценок пока нет
- One Year All India Test Series: For Jee (Main) & Jee (Advanced)Документ2 страницыOne Year All India Test Series: For Jee (Main) & Jee (Advanced)siddhartha2862Оценок пока нет
- Marshall Herff ApplewhiteДокумент1 страницаMarshall Herff ApplewhiteharshitОценок пока нет
- Warsaw Capital City of Poland History FactsДокумент1 страницаWarsaw Capital City of Poland History FactsharshitОценок пока нет
- In 2012 TheДокумент1 страницаIn 2012 TheharshitОценок пока нет
- The City Is The Seat of A Roman Catholic ArchdioceseДокумент1 страницаThe City Is The Seat of A Roman Catholic ArchdioceseharshitОценок пока нет
- ET Life SearchДокумент1 страницаET Life SearchharshitОценок пока нет
- For All Organic Matter To Be Completely OxidizedДокумент1 страницаFor All Organic Matter To Be Completely OxidizedharshitОценок пока нет
- Motto Phrase Clan Political Commercial Religious: Oxford Dictionary of EnglishДокумент1 страницаMotto Phrase Clan Political Commercial Religious: Oxford Dictionary of EnglishharshitОценок пока нет
- Potassium Dichromate Sulfuric Acid NДокумент1 страницаPotassium Dichromate Sulfuric Acid NharshitОценок пока нет
- Exam18 English II Sample Prelim PaperДокумент4 страницыExam18 English II Sample Prelim PaperharshitОценок пока нет
- Exam18 English II Sample Prelim PaperДокумент4 страницыExam18 English II Sample Prelim PaperharshitОценок пока нет
- Exam18 Biology Sample Prelim PaperДокумент6 страницExam18 Biology Sample Prelim PaperQims QuestОценок пока нет
- Matrices Study GuideДокумент42 страницыMatrices Study GuideKgaogelo Mawasha (Washa de deejay)Оценок пока нет
- Numerics Chapter 2Документ90 страницNumerics Chapter 2Matusal GizawОценок пока нет
- Week 6 (PCA, SVD, LDA)Документ14 страницWeek 6 (PCA, SVD, LDA)nirmalaОценок пока нет
- 11-12 Lecture NotesДокумент10 страниц11-12 Lecture NotesMasoud OweisiОценок пока нет
- ECE 602 Kalman Decomposition ExamplesДокумент3 страницыECE 602 Kalman Decomposition Examplesbecool12345Оценок пока нет
- Solutions of Homework Set #1 For Math 301Документ2 страницыSolutions of Homework Set #1 For Math 301Jacky PoОценок пока нет
- IIST MA211 - Linear Algebra Tutorial-I SolutionsДокумент3 страницыIIST MA211 - Linear Algebra Tutorial-I SolutionsShiva YadavОценок пока нет
- Mini-Introduction To Matrix AlgebraДокумент10 страницMini-Introduction To Matrix AlgebraYHTRTRОценок пока нет
- MH3511Документ8 страницMH3511Alex0% (1)
- Tutorial 2Документ1 страницаTutorial 2gunjan ranabhattОценок пока нет
- MATH-1201 Note Jan 12, 2022Документ7 страницMATH-1201 Note Jan 12, 2022Kunal KОценок пока нет
- Proof Trace (Ab) Trace (Ba)Документ1 страницаProof Trace (Ab) Trace (Ba)Cri Sam Ouili DisОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Matrix Algebra and Its ApplicationДокумент41 страницаUnit 2 Matrix Algebra and Its ApplicationAbrha63675% (4)
- Lecture-72 Bus Admittance MatrixДокумент33 страницыLecture-72 Bus Admittance MatrixAbhishekОценок пока нет
- Module 3: Linear EquationsДокумент5 страницModule 3: Linear EquationsAbedaОценок пока нет
- 1 Write The Size of Each Matrix in The FormДокумент3 страницы1 Write The Size of Each Matrix in The FormboobooОценок пока нет
- Inverse of A Matrix Using Elementary Row Operations (Gauss-Jordan)Документ3 страницыInverse of A Matrix Using Elementary Row Operations (Gauss-Jordan)ronald5123Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 NotesДокумент3 страницыChapter 14 NotesklerinetОценок пока нет
- Linear Algebra and Its Applications - D. C. LayДокумент71 страницаLinear Algebra and Its Applications - D. C. LayKaryl VizcondeОценок пока нет
- Gyanendra Mishra: Class XII (Matrix)Документ1 страницаGyanendra Mishra: Class XII (Matrix)Aditya ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- BMS PROJECTqqqqqqqqДокумент13 страницBMS PROJECTqqqqqqqqAdityaОценок пока нет
- A4P-Matrices & DeterminantsДокумент2 страницыA4P-Matrices & DeterminantsABCDОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Methods in Physics (Part I)Документ72 страницыMathematical Methods in Physics (Part I)Correos WebОценок пока нет
- La m1 HandoutsДокумент17 страницLa m1 HandoutsKen Nuguid100% (1)
- Craig-Bampton Method For A Two Component System: This Is A Work in ProgressДокумент15 страницCraig-Bampton Method For A Two Component System: This Is A Work in ProgressnemaderakeshОценок пока нет
- Antilinear OperatorsДокумент12 страницAntilinear OperatorsjofoltssonОценок пока нет
- 09 Power MethodДокумент72 страницы09 Power Methodnayeem4444Оценок пока нет
- [Algebra Practice Workbook With Answers Improve Your Math Fluency Series] Chris McMullen - Systems of Equations Substitution Simultaneous Cramer s Rule Algebra Practice Workbook With Answers Improve Your Math Fluency Series 20 ChrДокумент374 страницы[Algebra Practice Workbook With Answers Improve Your Math Fluency Series] Chris McMullen - Systems of Equations Substitution Simultaneous Cramer s Rule Algebra Practice Workbook With Answers Improve Your Math Fluency Series 20 ChrLuis Rodríguez100% (7)
- What case does not exist in complexity theoryДокумент3 страницыWhat case does not exist in complexity theoryDhandeep KuhshvahaОценок пока нет
- Two Examples On Eigenvector and EigenvalueДокумент11 страницTwo Examples On Eigenvector and EigenvalueNo Al PrianОценок пока нет















































































































![[Algebra Practice Workbook With Answers Improve Your Math Fluency Series] Chris McMullen - Systems of Equations Substitution Simultaneous Cramer s Rule Algebra Practice Workbook With Answers Improve Your Math Fluency Series 20 Chr](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/414981997/149x198/127d032d27/1713386973?v=1)

