Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
(IM Ward) History Taking Tool PDF
Загружено:
leapacisОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
(IM Ward) History Taking Tool PDF
Загружено:
leapacisАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Date: Informant:
History Taken By: Reliability:
IDENTIFYING DATA:
Name (First Name, Middle Name, Last Name):
Age: Gender: Civil Status:
Birthdate: (Month, Day, Year): Birth Place:
Present Address:
Nationality: Occupation: Religion:
Number of Times Admitted to this Hospital: Name of Hospital: Date of Current Admission:
CHIEF COMPLAINT:
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS:
8 Critical Characteristics:
1. Timing (Onset, Duration, Frequency)
2. Location
3. Setting
4. Character or Quality
5. Quantity or Severity
6. Associated Factors
7. Aggravating or Relieving Factors
8. Patients Perception
If consultation was made: Indicate diagnosis of
the physician (if any), laboratory examinations
requested and results, and medications given.
Medications:
Generic name
Brand name (in parenthesis)
Preparation
Dosage
Response to treatment
PQRSTU of Pain:
P: Precipitating (Provocative)/ Aggravating/
Palliative (Alleviating or Relieving Factors)
Precipitating Factors: What brings out the
symptoms?
Aggravating Factors: What makes the
symptoms worse?
Palliative Factors: What relieves the
symptom?
Q: Quality (Character)/ Type of Symptom/ Quantity
What is the symptom like?
R: Region (Location) and Radiation of Symptoms
Ask if pain is localized, if not, to where does it
radiate
S: Severity/Intensity and its Progression
Mild little or no effect to daily
Moderate there is limitation to daily
activities
Severe unable to perform daily activities
T: Timing
Duration: How long does the symptom last?
Frequency: Continuous or intermittent (recur
at intervals)?
U: Understanding Patients Perception of Pain
Describe how the patient understands the
significance of pain
PAST HEALTH HISTORY:
Childhood Diseases [ ] Mumps, [ ] Measles, [ ] Chicken Pox, [ ] German Measles
Immunizations Received:
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 1
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Adult Past Illnesses:
A. Medical (Past Illnesses, Hospitalizations and Ambulatory Care not related to the HPI) Dates, describe symptoms felt,
name of hospital, number of days admitted, give the diagnosis, laboratories done/results, complications, medications
given and the disposition upon discharge
B. Surgeries and Other Procedures Full details including type, date, results, and complications
C. Accidents and Injuries Type of injury, date, time, disabilities
D. Gynecologic Diseases affecting the female reproductive organs
E. Medications Prescribed, over-the-counter medications, and homeopathic remedies; and any adverse reactions
F. Blood Transfusion Date received, indications and transfusion reactions
G. Allergies Note the allergen and the reaction
H. Psychiatric History of violence, suicidal attempts, drug overdose, and substance abuse
FAMILY MEDICAL HISTORY:
Health status, age, if deceased: age and time of death and cause of death of immediate family members:
Father:
Mother:
Siblings:
Children:
Grandparents (Maternal):
Grandparents (Paternal):
Grandchildren:
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 2
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Disease with Heredo-Familial Tendency Stroke, Cancer, Hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus, Heart Diseases, Blood Disorders,
Allergies, Arthritis, Obesity, Alcoholism, Psychiatric Illnesses, Seizure Disorder, Kidney Diseases, etc.
Communicable Diseases Tuberculosis, Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI), etc.
Any member of the family member with similar symptoms:
PERSONAL AND SOCIAL HISTORY (PSH) OR FUNCTIONAL ASSESSMENT OR PERSONAL ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIVING (ADL):
Education Attainment:
Marital Status Health condition of spouse:
Occupational History
Nature of Work:
Number of Hours of Exposure to Hazards:
Safety Measures Used (Past and Present):
Interpersonal Relationships and Financial Resources Within and Outside the Family:
Living Conditions:
Source of Water:
Waste Disposal:
Relevant Travel History:
Habits:
Sleep and Rest Pattern:
Nutrition and Elimination:
Smoking History (Passive and Active Smoker):
Number of Sticks Smoked Per Day:
Number of Years of Smoking:
History of Alcohol and Coffee Intake:
Age When He/She Started Drinking Alcohol
Type of Alcohol:
Quantity:
Frequency of Alcohol Intake:
Illicit Drug Use:
Self-Care:
Activities:
Exercise:
Sexual History:
Exposure and History of STI:
Number and Variety of Partners:
MENSTRUAL AND OBSTETRICAL HISTORY:
Age at Menarche:
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 3
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Regularity, Interval, Duration, and Amount of Flow of the Succeeding Menses:
Premenstrual Symptoms:
Last Menstrual Period (LMP):
Previous Menstrual Period (PRP):
Age and Symptoms at Menopause:
Use of Hormonal Replacement:
Gravity:
Parity:
Manner of Delivery Spontaneous, Cesarean Section, Forceps Extraction
Use of Birth Control Methods:
REVIEW OF SYSTEMS:
1. CONSTITUTIONAL SYMPTOMS: 2. SKIN: 3. HEAD:
___ Significant Change in Weight ___ Itchiness ___ Headache
___ Generalized Body Weakness ___ Excessive dryness or sweating ___ Dizziness
___ Fatigue ___ Cyanosis ___ Vertigo
___ Fever ___ Pallor
___ Chills ___ Jaundice
___ Increased Appetite ___ Erythema
4. EYES: 5. EARS: 6. NOSE AND SINUSES:
___ Pain ___ Earache ___ Changes in Smell
___ Blurring of Vision ___ Deafness ___ Nose Bleeding
___ Double Vision ___ Tinnitus ___ Nasal Obstruction
___ Lacrimation ___ Ear discharge ___ Nasal Discharge
___ Photophobia ___ Pain Over Paranasal Sinuses
___ Use of Eye glasses
7. MOUTH AND THROAT: 8. NECK: 9. BREAST:
___ Toothache ___ Pain ___ Pain
___ Gum Bleeding ___ Limitation of Movement ___ Lumps
___ Disturbance in Taste ___ Mass ___ Nipple Discharge
___ Sore Throat
___ Hoarseness
10. RESPIRATORY: 11. CARDIOVASCULAR: 12. GASTROINTESTINAL:
___ Pleuritic Chest Pain ___ Palpitations ___ Abdominal Pain
___ Cough ___ Syncope ___ Nausea
___ Sputum Production ___ Easy Fatigability ___ Vomiting
___ Hemoptysis ___ Dysphagia
___ Audible Wheezing ___ Diarrhea
___ Constipation
___ Hematemesis
___ Melena
___ Hematochezia
___ Regurgitation
13. GENITOURINARY: 14. EXTREMITIES: 15. NERVOUS:
___ Dysuria ___ Edema ___ Loss of Consciousness
___ Urinary Frequency ___ Swelling of Joints ___ Focal Weakness
___ Urgency ___ Stiffness ___ Parethesia
___ Hematuria ___ Numbness ___ Speech Disorder
___ Incontinence ___ Intermittent Claudication ___ Loss of Memory
___ Genital Pruritus ___ Limitation of Movement ___ Confusion
___ Urethral Discharge
16. HEMATOLOGIC: 17. ENDOCRINE:
___ Bleeding Tendency ___ Intolerance to Heat and Cold
___ Easy Bruising ___ Polydipsia
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 4
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
GENERAL SURVEY:
A. Assess the LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS
Normal: Awake, alert, responds appropriate to verbal, tactile, and painful stimuli
Impaired: Agitated, restless, drowsy, stuporous, lethargic
May obtain Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
B. ORIENTATION to time, place, and person
C. APPEARANCE
Assess the relationship of the biologic age with the chronological age (Does patient look his stated age? Younger or older?)
Manner of dressing and personal hygiene (appropriate, well-kempt neat and clean, unkempt dirty)
D. ATTITUDE AND BEHAVIOUR (cooperative/uncooperative, rational/irrational, friendly/hostile, interested/indifferent)
E. SPEECH AND LANGUAGE
Assess the quantity, rate, loudness (tone), fluency, slurring
Possible findings: aphasia/dysphasia, dysphonia, dysarthria
F. MEMORY, MOOD AND AFFECT
Memory (immediate, recent, remote)
Mood (euthymic/normal, dysphoric/sad, euphoric/elated, angry, anxious, apathetic, etc.)
Affect (appropriate or inappropriate)
G. NUTRITIONAL STATUS (underweight, normal weight/well-nourished, overweight, obese)
BMI = weight in kg/(height in m)2
H. GAIT AND POSTURE
Ask the patient to stand straight and observe posture (normal erect and straight, abnormal stooping)
Ask the patient to walk and observe gait (normal, abnormal limping, shuffling, staggering)
If unable to walk (wheelchair-borne)
I. BODY BUILT (slender, short, tall, lanky, stout)
Sthenic Type (Athletic type)
Hypersthenic (short and stocky)
Hyposthenic (thin and developed)
Asthenic (malnourished marasmus or kwashiorkor)
J. SIGNS OF DISTRESS
Check for objective evidence of:
Dyspnea (flaring od alae nasi, use of accessory muscles of respiration, intercostal retractions, active contractions of the SCM)
Cyanosis
Agitation or restlessness
Pallor
Cold-clammy respiration
Chest pain
VITAL SIGNS:
A. BLOOD PRESSURE
B. CARDIAC RATE (beats per minute)
Assess rate and rhythm
C. PULSE RATE (beats per minute)
Assess rate, volume, and rhythm
Amplitude (strong or weak)
D. RESPIRATORY RATE (cycles per minute)
E. BODY TEMPERATURE
F. WEIGHT (kg)
G. HEIGHT (cm)
EXAMINATION OF THE HEAD
A. Inspect and palpate the HAIR:
1. Color (black, brown, gray; natural or dyed?)
2. Quantity (thin, thick or fairly abundant)
3. Distribution (evenly distributed, pattern of hair loss if any, receding hairline)
4. Texture (fine or course)
5. Moisture (dry or oil)
B. Examine the SCALP for skin lesions (scars, scales, masses, etc.) and lice
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 5
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
C. Inspect and palpate the CRANIUM:
1. Size/Shape (normocephalic, microcephalic, macrocephalic)
2. Symmetry (symmetric, asymmetric)
3. Scalp (describe lesions if present, tenderness)
4. Temporal Arteries (tortuous or not, describe amplitude and equality of pulsations, consistency of the walls soft or hard?)
Sample Recording of Findings:
Head: Thick, black hair, evenly distributed, course and dry; clean scalp; normocephalic, no mass or tenderness. Temporal arteries are not visible but palpable with
strong, equal puslations, walls not thickened
EXAMINATION OF THE FACE
Inspect the FACE:
1. SKIN
a. Color (fair, brown, black)
b. Lesions (describe type macule, papule, patch, wheals, etc; color changes erythematous, hyperpigmented,
hypopigmented, depigmented, etc; distribution)
2. SHAPE (oval, triangular, round, square, etc.)
3. SYMMETRY (symmetric or asymmetric; describe shallow right nasolabial fold, drooping right angle of mouth, etc)
4. FACIAL EXPRESSION (FACIE) AND INVOLUNTARY FACIAL MOVEMENTS
Sample Recording of Findings:
Face: Oval, symmetrical, fair-skinned with several hyperpigmented papules scattered over the face, no masses, normal facie, no involuntary movements
EXAMINATION OF EYES
A. EYEBROWS (amount, distribution, lesion)
B. EYELIDS (swelling, edema, erythematous rim, ptosis lesions)
C. PALPEBRAL FISSURES (normal, widened, or narrowed)
D. EYEBALLS
1. Exopthalmos (protruding eyeballs) or Enopthalmos (sunken eyeballs)
2. Lid Lag Test
With your finger or holding a penlight as a target in the midline above the eye level, about 20 inches (50 cm) away, move the target rapidly downward in
the midline, watching for the appearance of white sclera between the iris and the upper eye lid margin.
E. EYELASHES
1. Direction of Growth
2. Matting of Eyelashes
F. CONJUNCTIVAE AND SCLERAE
1. Color of Sclerae (white or icteric)
2. Color of Palpebral Conjunctivae (pinkish, congested, injected, pale)
3. Look for any growth or edema
G. CORNEA (transparency or clarity, scars, abrasions and ulcers of the cornea)
H. IRIS, PUPILS AND LENS
1. Color of IRIS
2. PUPILS
a. Size (measure the diameter of each pupil in mm)
b. Shape
c. Symmetry
d. Reaction to Light
Pupillary Light Reflex (Direct and Indirect/Consensual Response)
Swinging Flashlight Test (Move the light from one pupil to the other, back and forth)
Accomodation Reflex
3. LENS (transparency, opacity)
I. EXTRAOCULAR MOVEMENTS
H Pattern
Observe for Nystagmus
J. OPHTHALMOSCOPIC EXAMINATION
Note for the following:
1. Clarity of the disc outline (Nasal outline may be normally somewhat blurred)
2. Color of the disc (Normally yellowish orange to creamy pink)
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 6
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
3. Presence of normal white or pigmented rings or crescents around the discs
4. Size of the central physiologic cup (If present, this cup is normally yellowish white)
5. Symmetry of the eyes (In terms of these observations)
K. TESTING VISUAL ACUITY
1. Distant Vision: Snellen Chart at 10 or 20 feet
2. Near Vision: Near Vision Card at 14 inches
Abnormal Response:
20/30-1: The patient missed a letter of the 20/30 line
20/200: Legally blind (At 20 feet the patients reads a line that a normal eye could see at 200 feet)
CF (Counting Fingers): If a patient is unable to read the top line, have him count fingers at maximal distance
HM (Hand Motion): If a patient cannot count fingers, ask them to determine direction of hand motion
LP (Light Perception): If a patient cannot perceive hand motion, see if they can perceive a light
NLP (No Light Perception)
L. VISUAL FIELDS
Confrontation
Peripheral Visual Fields (White Pin)
- Wiggling Fingers
- Counting Fingers
Central Visual Fields (Red Pin)
EXAMINATION OF THE EARS:
A. AURICLE
1.Inspect each auricle and surrounding tissues for size, deformities, lumps, or skin lesions
2.If with ear ache, discharge or inflammation are present, move the auricle up and down, press the tragus and press firmly
behind the ear. Note for tenderness.
B. OTOSCOPIC EXAMINATION
Observe for the following:
1. Patency of the ear canal
2. Identify any discharge
3. Describe the walls of the ear canal. Note any tenderness or swelling.
4. Inspect the tympanic membrane and note for the following:
a. Color (pearly white or pinkish grey; hyperemic in myringitis)
b.Intact or Perforated
c. Contour (bulging: fluid in the middle ear; flat: normal; retracted: pulled upward due to a block in the Eustachian tube)
d.Cone of Light (a change in the normal contour suggests middle ear disease)
e. Identify the Malleus (visible or not)
EXAMINATION OF THE NOSE:
A. Inspect the nose for symmetry and deformity
B. Palpate for tenderness
C. Test for patency of the nasal cavities
D. Asses the INTERNAL STRUCTURES of the nose using a penlight or otoscope without a speculum
1. Visualize SEPTUM (Normal: Pink mucosa, straight at the midline and intact; Deviated; Perforated)
2. Visualize TURBINATES (Normal: Flat and dry with the same pink color as the surrounding mucosa; Congested; Red; Pale; Wet
with mucus)
E. Assessment of the FRONTAL AND MAXILLARY SINUSES
1. Palpate for tenderness
2. Transillumination using a penlight
EXAMINATION OF THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX:
EXAMINATION OF THE ORAL CAVITY
A. LIPS
1. Color
2. Moisture
3. Lesions (fissures, ulcers)
4. Symmetry
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 7
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
5. Deformities
B. BUCCAL MUCOSA
1. Color
2. Pigmentation
3. Ulcers
4. Patches
5. Nodules
C. GUMS
1. Color
2. Swelling
3. Bleeding
4. Retraction
5. Discoloration
6. Recession of the Gingival Margins
7. Pus in the Margins
8. Presence of lead and bismuth line
D. TEETH
1. Absence of one or more teeth
2. Presence of carries
3. Discoloration
4. Fillings
5. Bridges and braces
E. ROOF (PALATE) AND FLOOR OF THE MOUTH
1. Color
2. Deformities
3. Any lesions and masses
4. Odor (alcohol, ammonia, sweetish fruity odor of acetone, musty odor, halitosis)
F. TONGUE
1. Observe for abnormal movements (fasciculations, tremors)
2. Observe for the following:
a. Size
b. Color
c. Surface
d. Moisture
e. Symmetry
f. Lesions
G. SOFT PALATE, UVULA, TONSILLAR PILLARS, TONSIL, AND POSTERIOR PHARYNGEAL WALL
1. Color
2. Symmetry
3. Any evidence of exudates
4. Swelling
5. Ulcerations
6. Tonsillar enlargement
7. Induration or tenderness
Description of Normal Findings:
Lips: pinkish, moist, symmetrical, no lesions
Buccal Mucosa and Gums: pink, smooth, no lesions
Teeth: complete set, no dental carries, good oral hygiene
Roof, Floor and Palate: pinkish, no lesion
Uvula in midline, tonsils not enlarged, pharynx is pink, no lesions, no exudates
EXAMINATION OF THE NECK:
INSPECTION AND RANGE OF MOTION
A. Inspect the NECK
1. Symmetry
2. Size (unusually long or short)
3. Deformity, mass and swelling
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 8
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
B. Observe how the patient carries his head (position: tilted, rotated) and note the tone of the neck muscles
C. Range of Motion
1. Flexion (chin to chest)
2. Extension (look at the ceiling)
3. Lateral Rotation (chin to shoulder)
4. Lateral Flexion/Bending (ear to shoulder)
PALPATION OF THE NECK
A. In front of patient: posterior cervical spine, mastoid process, trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
B. Behind the patient: thyroid gland, lymph nodes
If a mass is palpable, describe its location, consistency, size, and mobility
PALPATION OF TRACHEA
Palpate the trachea for any deviation
PALPATION LYMPH NODES
1. Preauricular
2. Posterior auricular
3. Occipital
4. Tonsillar
5. Submandibular
6. Submental
7. Superficial cervical
8. Posterior Cervical Chain
9. Deep Cervical Chain
10. Supraclavicular
Describe palpable lymph nodes
A. Size
B. Shape
C. Surface/Texture (smooth, irregular)
D. Delimitation (discrete, matted)
E. Mobility (fixed or movable)
F. Consistency (soft, firm, hard)
G. Tenderness
THYROID GLAND
A. Inspection (normally rise as the person swallows)
B. Palpation
C. Auscultation (Done if thyroid is visible and palpable)
Use bell of stethoscope Listen for bruit while the patient holds his breath
D. Describe as to:
1. Size
2. Shape
3. Symmetry
4. Consistency
5. Presence of nodules
6. Tenderness
7. Bruit
EXAMINATION OF THE THORAX AND LUNGS
INSPECTION
A. CHEST WALL
1. Skin
a. Color
b. Lesions
c. Dilated Blood Vessels
2. Bony Thorax
a. Shape and Symmetry
b. Deformity (pectus carinatum, pectus excavatum, scoliosis, kyphosis, kyphoscoliosis, gibbus)
c. Muscle Development
B. Observe RESPIRATION
1. Respiratory Rate
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 9
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
2. Timing of Inspiratory Phase and Expiratory Phase
3. Rhythm and Depth of Respiration
4. Abnormalities in Rate and Rhythm
a. Cheyn-Stokes Respiration
b. Biots Breathing
c. Kussmaul Respiration
d. Paradoxic Respiration
C. Contraction of the ACCESSORY MUSCLES OF RESPIRATION (sternocleidomastoid, intercostal, etc.)
D. Observe for EQUALITY OF CHEST MOVEMENT
PALPATION
A. Identify tender areas
B. Assess further lung expansion
C. Tactile fremitus or voiced sounds
PERCUSSION
AUSCULTATION
A. Determine the characteristics of the different breath
(lung) sounds
1. Vesicular
2. Bronchial
3. Bronchovesicular
4. Tracheal
B. Listen for and identify any adventitious (added) sounds
(crackles, wheezing)
C. Listen to the sounds of the patients spoken and
whispered voice as they are transmitted to the chest
wall
1. Bronchophony (99, 99 or tres tres)
2. Egophony (eee)
3. Whispered Pectoriloquy (Whisper 99, 99 or tres
tres)
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 10
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
EXAMINATION OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
INSEPCTION AND PALPATION OF THE NECK VESSELS
A. Inspect the neck for venous distention (Patient supine. Elevate trunk to about 30 degrees from the horizontal) Turn head slightly
to the left.
If with venous distention Measure Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) and Central Venous Pressure(CVP)
B. Inspect and Palpate the Carotid Arteries
1. Amplitude of pulsation (strong or weak)
2. Rhythm (regular or irregular)
3. Equality of pulsation
4. Consistency of the walls (soft or rigid)
INSPECTION AND PALPATION OF THE PRECORDIUM
A. Observe the precodium
B. Locate the apex beat or apical impulse
1. Location (usually 5th ICS or 1-2 cm medial to the LMCL or 7 cm from the midsternal line)
2. Size (1cm x 2cm or <2.5cm in diameter)
3. Amplitude (normally a gentle tap)
C. Describe the precordium (adynamic, dynamic, hyperdynamic)
D. Abnormal Precordial Pulsations
1. Thrust or Lift and Heave
2. Palpable Heart Sound
3. Thrills
AUSCULATION OF THE PRECORDIUM
A. Count Heart Rate and identify the Rhythm
B. Identify the 1st and 2nd Heart Sounds (S1 and S2)
S1: Closure of AV valves Louder at the APEX
S2: Close of Semilunar valves Louder at the BASE
C. Listen for Extra Heart Sounds (S3 and S4)
S3: Early Diastolic Sound (Closely follows S2)
S4: Late Diastolic Sound (Occurs before S1)
D. Auscultate for Murmurs
1. Location (area of maximum intensity)
2. Radiation (area of minimum intensity)
3. Timing (systolic or diastolic)
4. Intensity (grade 1 to 6)
Grade 1 Very faint, heard only after listener has tuned in; May not be heard
in all position
Grade 2 Faint, but hear immediately after placing the stethoscope on the
chest
Grade 3 Moderately loud
Grade 4 Loud with palpable thrill
Grade 5 Very loud, with thrill; May be heard when the stethoscope is partly
off the chest
Grade 6 Very loud, with thrill; May be heard with stethoscope entirely off
the chest
5. Quality (blowing, rumbling)
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 11
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
6. Pitch (high or low pitched)
7. Shape (crescendo, decrescendo, crescendo-decrescendo)
EXAMINATION OF THE VASCULAR SYSTEM
A. Assess function of the peripheral blood vessel (inspection and palpation) of the upper and lower extremities
1. Size of arms and legs
2. Symmetry
3. Swelling or edema (pitting or non-pitting)
4. Changes in the skin and soft tissue
a. Pigmentation
b. Pallor/Cyanosis
c. Hairloss
d. Dilated Veins/Varicosities
e. Lesions (ulcers)
5. Nails
B. Asses the peripheral arterial blood flow by palpating for:
1. Temperature of both upper and lower extremities
2. Peripheral Pulses
a. Brachial
b. Radial
c. Femoral
d. Popliteal
e. Dorsalis Pedis
3. Describe the Pulses
a. Amplitude
3+ Full or bounding
2+ Normal to strong
1+ Weak or thready
0 Absent
b. Rhythm (regular or irregular)
c. Equality
d. Consistency of the walls (soft, thickened, rigid)
EXAMINATION OF THE ABDOMEN
INSPECTION
A. Describe the abdomen (symmetry, skin, shape, appearance of umbilicus, visible pulsations in the epigastric region)
1. Symmetry
2. Skin (color, lesions, scars location,size, shape, shape, cause)
3. Shape (flat, globular, scaphoid, protuberant)
4. Appearance of the umbilicus ( flat, inverted, everted)
B. Observe for abnormal findings (bulging flanks, dilated superficial blood vessels, pulsations outside of the epigastric region,
peristaltic waves, mass)
Sample Recording of Findings:
On inspection, the abdomen, is symmetrical; the skin is brown, no lesions and no scar. The shape is flat and the umbilicus is inverted. No bulging flanks and no
localized bulges. No dilated blood vessels, no abnormal pulsations. No visible peristalsis and no mass.
INSPECTION
A. Listen and describe the BOWEL SOUNDS (normoactive, hyperactive, hypoactive, absent)
Press the diaphragm firmly on the RLQ and listen for gurgling/bubbling/popping sounds
B. Auscultate for possible BRUIT
1. Aortic Aneurysm press the diaphragm firmly over the epigastrium
2. Renal Artery Stenosis position the diaphragm slightly above and lateral to the umbilicus (R and L paraumbilical hernia) then press firmly towards the
midline and listen
Sample Recording of Findings:
On auscultation, the bowel sounds are normoactive. No bruit heard over the epigastrium, right and left paraumbilical areas.
PERCUSSION
A. Assess DISTRIBUTION OF AIR in the bowel (tympanitic, dull) randomly percuss each of the four quadrants
B. Measure the LIVER SPAN (normal: 6-12cm)
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 12
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
C. Measure the SIZE OF SPLEEN
D. Detect PRESENCE OF FLUID ASCITES
1. Fluid Wave
2. Shifting Dullness
3.Elicit presence of COSTOVERTEBRAL ANGLE TENDERNESS (Kidney punch)
PALPATION
A. Light Palpation
1. Consistency of the abdomen (soft, firm, rigid), (voluntary, involuntary)
2. Palpable mass (location, size, shape, consistency, tenderness, pulsation, mobility)
3. Tenderness (location)
B. Deep Palpation (deep tenderness, deep masses, enlargement of liver, spleen, kidneys)
Single handed technique
Double handed technique
C. Palpation of Specific organs and structures
1.Liver (Hooking technique)
2.Spleen (Middleton technique)
3.Left and Right kidney (Capture technique)
4.Abdominal Masses
a. Location (intrabdominal or intramural mass)
b. Size (Small or big)
c. Mass with ascites (Ballottement maneuver)
Special Maneuvers
A. Test for localized peritonitis
Rebound tenderness (+) Result: pain intensifies upon withdrawal of the examining finger
Blumberg sign Rebound tenderness in the RLQ
Rovsing sign Rebound tenderness in the RLQ during LLQ pressure
Jar tenderness or Markles sign (+) Result: exacerbation of abdominal pain
Psoas sign (+) Result: exacerbation of pain the RLQ
Obturator sign (+) Result: exacerbation of pain the RLQ
B. Test for Possible Acute Cholecystitis
Murphys sign (+) Result: inspiratory arrest 20 to a sharp increase in tenderness over the RUQ
C. Test to Identify an Organ or a Mass Obscured by Ascites
Single handed (+) Result: A freely movable mass will rebound upward and is felt with fingers
Bimanual ballottement
THE NEUROLOGIC EVALUATION:
CEREBRAL FUNCTION
A. Assessment of GENERAL CEREBRAL FUNCTION
1. Level of Consciousness (GCS: E__V__M__)
2. General Behavior and Appearance
a. Appropriately groomed
b. Cooperative, hostile, indifferent
c. Hyperactive, agitated, violent, quiet, immobile
3. Intellectual Performance
a. Orientation to time, place, and person
b. Memory
i. Immediate memory or retention (repeat a series of 7
digits forward and 5 digits backward)
ii. Recent memory (ask what his last meal was)
iii. Remote memory (ask patients date of birth)
c. Calculation (subtract series of 3s or 7s from 100)
d. Abstract Reasoning or Thinking
e. Emotional Status
B. Assessment of SPECIFIC CEREBRAL FUNCTION
1. Language
a. Fluency (ability to talk spontaneously with or without sense)
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 13
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
b. Repetition (repeat a simple phrase or sentence or a series of numbers)
c. Comprehension (verbal request similar request but now written)
2. Cortical Sensory Interpretation or Object Recognition (Agnosia)
3. Cortical Motor Integration (Apraxia)
Ability to follow a 3-stage command
CRANIAL NERVES
A. CN I: OLFACTORY
Check patency of each nostril
B. CN II: OPTIC NERVE
1. Visual Acuity
2. Opthalmoscopic Examination
3. Examination of Visual Fields
Confrontation Test
C. CN III, IV, VI: OCCULOMOTOR NERVE, TROCHLEAR NERVE, AND ABDUCENS NERVE
1. Direct Light Reflex
2. Indirect or Consensual Light Reflex
3. Convergence or Accommodation Test
4. Levator Palpebrae Muscle (Lid Elevation)
Measure the size of the palpebral fissure in mm
5. Extra-ocular Muscle
6 Cardinal Gaze (H Pattern)
Superior Oblique Test (Note if there is symmetry in position of eyeballs)
Nystagmus
D. CN V: TRIGEMINAL NERVE
1. Test for Sensory Function
a. Facial Sensation (blunt and sharp forehead, cheeks, and jaw)
b. Corneal Reflex
2. Test for Motor Function
a. Contraction of temporalis and masseter muscle (clench teeth or bite)
b. Deviation of lower jaw (open and close mouth)
c. Resist force to close mouth (apply pressure on the chin)
3. Jaw Jerk Reflex
Open mouth, place top of your left index finger on his chin and tap with a reflex hammer
E. CN VII: FACIAL NERVE
1. Taste Sensation (Anterior 2/3 of the tongue)
Keep the tongue out until he identifies the test substance used
2. Motor Function (Facial Expression)
Frown/wrinkle forehead
Raise the eyebrow
Close the eyes tightly
Wrinkle the nose
Show teeth and smile
F. CN VIII: VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR NERVE
1. Auditory Function
a. Gross Hearing Acuity (128 or 256 Hz) Ask if sound is heard equally or better in one ear
b. Webers Test (256 Hz)
c. Rinnes Test (512 Hz)
2. Vestibular Function (Nystagmus present?)
G. CN IX and X: GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE AND VAGUS NERVE
1. Dysphonia (abnormality in phonation or nasality in voice) or dysarthria (abnormality in articulation or pronunciation of
consonants)
2. Position of Uvula
3. Gag Reflex
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 14
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
H. CN XI: SPINAL ACCESSORY NERVE
1. Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Turn his head to one side against resistance of examiners hand
2. Trapezius Ask patient to elevate the shoulders Apply resistance
I. CN XII: HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE
1. Inspect tongue as it lies on the floor of the mouth Fasciculations?
2. Protruded tongue Look for asymmetry, atrophy, or deviation from midline
3. Move tongue from side to side
CEREBELLAR FUNCTION
A. Finger-Nose-Finger Test
B. Rapid Alternating Movement (RAM)
C. Heel to Shin Test
D. Tandem Walking Test
MOTOR FUNCTION
A. Muscle Size
Arm Circumference: 10 cm from the acromion process
Forearm Circumference: 10 cm from the olecranon process
Thigh Circumference: 15 cm from the midinguinal area
Leg Circumference: 15 cm from the fibular head
B. Muscle Tone (Resistance to passive movement)
C. Hypokinetic and Hyperkinetic Movement (Inspect for any involuntary movements: fasciculations, tremors, myoclonus, tics,
chorea, athetosis, dystonia or torsion spasm, ballismus, motor seizures)
D. Muscle Strength (Upper and Lower Extremities)
Grade 0 No visible muscle contractions
Grade 1 Flicker or trace of contraction but no joint movement
Grade 2 Active muscle movement with gravity eliminated
Grade 3 Active muscle movement against gravity
Grade 4 Active muscle movement against gravity and minimal to moderate resistance
Grade 5 Active muscle movement against full resistance without evident fatigue
SENSORY FUNCTION
A. Superficial Tactile Sensation
Touch with a wisp of a cotton
B. Superficial Pain
Alternate use of the dull and sharp part of a big safety pin
C. Sensitivity to Vibration
Vibrating tuning fork over bony prominences
D. Position Sense
Distal phalanx of the fourth digits of the hands and feet moved passively while lightly holding on the sides ( up, down,neutral)
REFLEXES
A. Superficial Reflexes (Corneal, Gag, Abdominal, Cremasteric, Anal)
B. Deep Tendon Reflexes (Biceps, Brachioradialis, Triceps, Patellar or Knee Jerk, Achilles or Ankle jerk)
Grading of Stretch Reflexes:
0 = absent
1+ = diminished
2+ = normal
3+ = increased or hyperactive
4+ = hyperactive with clonus
C. Release or Primitive Reflexes(Snout, Grasp, Palmomental, Rooting)
D. Pathological Reflexes (Babinski, Chaddock/Oppenheim/Gordon, Hoffman, Clonus)
STANCE AND GAIT
A. Observe for Posture, Balance, Swinging of the arms, Steps (Wide based gait, spasticity, rigidity)
Ask patient to walk back and forth several times across the room
B. Ask patient to turn as he walks (ataxic, shuffling)
C. Ask patient to walk on toes and on heels (plantar flexors or dorsiflexors weakness)
SIGNS OF MENINGEAL IRRITATION
A. Nuchal rigidity (+) Result: neck resists flexion and patient winces in pain.
B. Brudzinkis sign (+) Result: flexion of the hips and knees
C. Kernigs sign (+) Result: back pain or sciatic pain
LTRP + PAAD BATCH 2017 15
Вам также может понравиться
- Case Presentation - HerniaДокумент19 страницCase Presentation - HerniaElvin Louie Lisondra100% (1)
- Legal and Ethical Aspects of Genetic Screening and Counseling Role of Nurse in Genetic CounselingДокумент41 страницаLegal and Ethical Aspects of Genetic Screening and Counseling Role of Nurse in Genetic CounselingAmy Lalringhluani67% (3)
- Case Write Up 1: Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever Saarah Huurieyah BT Wan Rosli 1050024 Year 4 Internal MedicineДокумент16 страницCase Write Up 1: Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever Saarah Huurieyah BT Wan Rosli 1050024 Year 4 Internal MedicineRoshandiep GillОценок пока нет
- 2022 Oxford Handbook of Anaesthesia Oxford Press 5th Edition ExportДокумент2 страницы2022 Oxford Handbook of Anaesthesia Oxford Press 5th Edition ExportHany Elbarougy0% (3)
- Cagayan State University: Pediatrics 2 LaboratoryДокумент12 страницCagayan State University: Pediatrics 2 LaboratoryAmaetenОценок пока нет
- Epilepsy in ChildhoodДокумент20 страницEpilepsy in ChildhoodRizky Indah SorayaОценок пока нет
- Preterm ContractionДокумент19 страницPreterm ContractionAiman ArifinОценок пока нет
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)От EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Оценок пока нет
- Neonatal History and Physical ExamДокумент2 страницыNeonatal History and Physical ExamMuhammad Farhan KhaliqОценок пока нет
- Treating Lupus Using Tung PointstДокумент5 страницTreating Lupus Using Tung PointstOmer Binmahfooz100% (4)
- HTN Complicating PregnancyДокумент18 страницHTN Complicating PregnancyAiman ArifinОценок пока нет
- Pedia 1Документ8 страницPedia 1Jani MisterioОценок пока нет
- Gyni History TalkingДокумент61 страницаGyni History TalkingEthiopia TekdemОценок пока нет
- Dietician Referral Ms SmithДокумент3 страницыDietician Referral Ms SmithPrasoon Premraj0% (1)
- CP On AGEДокумент31 страницаCP On AGELeah CaressaОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics Case PresentationДокумент70 страницPediatrics Case PresentationRold Brio Sos100% (1)
- Bronchial AsthmaДокумент21 страницаBronchial AsthmashaitabliganОценок пока нет
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyОт EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisОценок пока нет
- Case Report 2 - Ovarian CystДокумент9 страницCase Report 2 - Ovarian CystA MОценок пока нет
- Antenatal Assessment 18Документ13 страницAntenatal Assessment 18naga mani100% (1)
- أدوية الطوارىءДокумент162 страницыأدوية الطوارىءManar22Оценок пока нет
- BernottiДокумент44 страницыBernottiAlexandra Alexandra100% (2)
- Bronchial AsthmaДокумент39 страницBronchial AsthmaSaeed mohamed100% (1)
- Schroth Basics EbookДокумент8 страницSchroth Basics EbookJo CacerОценок пока нет
- Lange Gynecology MCQ 2Документ5 страницLange Gynecology MCQ 2BassamSheryan0% (1)
- PneumoniaДокумент102 страницыPneumoniaJay Kumar100% (1)
- Chief ComplaintДокумент10 страницChief ComplaintVivekanandaОценок пока нет
- Case PresentationДокумент5 страницCase Presentationahmadhajjj100% (1)
- Case Presentation - Cholecystitis - DR - RikiДокумент14 страницCase Presentation - Cholecystitis - DR - RikiLevina AudreyОценок пока нет
- CASE 2 PneumoniaДокумент12 страницCASE 2 PneumoniaKenneth MiguelОценок пока нет
- HX and PX Obstetrics and GynecologyДокумент21 страницаHX and PX Obstetrics and GynecologyTadesse MuhammedОценок пока нет
- Fever Proforma and Assignment - 1Документ48 страницFever Proforma and Assignment - 1SivaОценок пока нет
- Case Report MartaДокумент10 страницCase Report MartadenekeОценок пока нет
- Placenta PreviaДокумент36 страницPlacenta Previaotartil_nimanОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprung NCM 109 Case PresentationДокумент10 страницHirschsprung NCM 109 Case PresentationValerie LeddaОценок пока нет
- CaseStudyTuberculosis Quindala TanoДокумент102 страницыCaseStudyTuberculosis Quindala TanoLiz G. QuindalaОценок пока нет
- Case AppendicitisДокумент30 страницCase AppendicitisSarahОценок пока нет
- History Taking OBS GYNДокумент10 страницHistory Taking OBS GYNzvkznhsw2tОценок пока нет
- Decompensated Liver DiseaseДокумент16 страницDecompensated Liver Diseasedk.clinicalresearchОценок пока нет
- Toaz - Info Case Study Pneumonia PRДокумент41 страницаToaz - Info Case Study Pneumonia PRTrixОценок пока нет
- Multinodular Goitre Case PresentationДокумент19 страницMultinodular Goitre Case PresentationTamilОценок пока нет
- Case Presentation On Copd: By, Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternДокумент32 страницыCase Presentation On Copd: By, Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternThomas EipeОценок пока нет
- Grand ReportsДокумент60 страницGrand ReportsfilchibuffОценок пока нет
- HERNIA - Case StudyДокумент8 страницHERNIA - Case StudyMa Jaimeliz Mae MuñizОценок пока нет
- Case Study of A Boy With HaemophiliaДокумент18 страницCase Study of A Boy With HaemophiliaImanuel Far-FarОценок пока нет
- Pat 2 Medsurg1Документ20 страницPat 2 Medsurg1api-300849832Оценок пока нет
- Case ReportДокумент19 страницCase ReportvivitaslimОценок пока нет
- Case Presentation 2Документ53 страницыCase Presentation 2Hussain AzharОценок пока нет
- Case Write UpsДокумент4 страницыCase Write UpsMuhammad AzmanОценок пока нет
- Scrub Typhus FeverДокумент20 страницScrub Typhus FeverDimpal ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- National Guidelines On Management of Dengue Fever & Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever in Children and Adolescents - Sri LankaДокумент53 страницыNational Guidelines On Management of Dengue Fever & Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever in Children and Adolescents - Sri LankaNational Dengue Control Unit,Sri Lanka100% (1)
- O and G Notes Notebank NumberedДокумент173 страницыO and G Notes Notebank NumberedPerscitus Ali القحطانيОценок пока нет
- Case 1 PediatricsДокумент5 страницCase 1 PediatricsEggy Pascual0% (1)
- Obg Prenatal Period Golden Points: Nursing CrashДокумент9 страницObg Prenatal Period Golden Points: Nursing CrashOmprakash SainiОценок пока нет
- Newborn NotesДокумент44 страницыNewborn NotesHaziq KamardinОценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент7 страницCase Studymark kennethОценок пока нет
- Session13 - Endometrial CaДокумент27 страницSession13 - Endometrial CaCHALIE MEQUОценок пока нет
- Toxic Multinodular Goiter Physical ExaminationДокумент2 страницыToxic Multinodular Goiter Physical ExaminationAngie MandeoyaОценок пока нет
- ARI - Final 2Документ62 страницыARI - Final 2BinayaОценок пока нет
- Obstetrics Case PresentationДокумент27 страницObstetrics Case PresentationMahaprasad sahoo 77Оценок пока нет
- SAMДокумент108 страницSAMAlimyon Abilar MontoloОценок пока нет
- Physical ExaminationДокумент39 страницPhysical ExaminationprashanthОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics 2 LaboratoryДокумент40 страницPediatrics 2 LaboratoryAmaetenОценок пока нет
- Case Presentation On MalariaДокумент13 страницCase Presentation On Malarialavate amol bhimraoОценок пока нет
- A Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutОт EverandA Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Screening For Health, Fitness and WellnessДокумент27 страницScreening For Health, Fitness and WellnessShimmering MoonОценок пока нет
- PatienthistoryformenglishДокумент4 страницыPatienthistoryformenglishRuriko IkusawaОценок пока нет
- National Consolidated Guidelines For PMTCT and The Management of HIV in Children, Adolescents and AdultsДокумент136 страницNational Consolidated Guidelines For PMTCT and The Management of HIV in Children, Adolescents and AdultsLaura Lopez Gonzalez100% (12)
- 014 Nursing (GNM) III Final RevaluationДокумент1 страница014 Nursing (GNM) III Final Revaluationhr7.bccnОценок пока нет
- 5 - DOWNLOAD Lactobacillus Acidophilus Rosell 52Документ6 страниц5 - DOWNLOAD Lactobacillus Acidophilus Rosell 52everstrongОценок пока нет
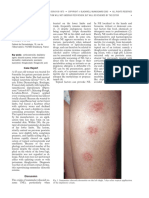
- Contact Nummular (Discoid) Eczema From Depilating Cream: Case ReportДокумент2 страницыContact Nummular (Discoid) Eczema From Depilating Cream: Case ReportMorindaОценок пока нет
- POT Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыPOT Lesson PlanMichelle ThereseОценок пока нет
- March 2012Документ28 страницMarch 2012Bill5199Оценок пока нет
- Abortion in CattleДокумент6 страницAbortion in CattlekumarpujariОценок пока нет
- The European Guideline On Management of Major Bleeding and Coagulopathy Following Trauma Sixth Edition (2023) PDFДокумент1 страницаThe European Guideline On Management of Major Bleeding and Coagulopathy Following Trauma Sixth Edition (2023) PDFMatheus LiraОценок пока нет
- Operational Guidelines On FBMC With Sam PDFДокумент84 страницыOperational Guidelines On FBMC With Sam PDFBalireddy NeeharikaОценок пока нет
- (BHU) DoneДокумент6 страниц(BHU) Donedr.venkat r singhОценок пока нет
- Types of Feeding-GastrostomyДокумент8 страницTypes of Feeding-GastrostomyElda KuizonОценок пока нет
- 2003 HemaДокумент19 страниц2003 Hemahavana1975Оценок пока нет
- IDL Tubex TestДокумент5 страницIDL Tubex TestMaya RustamОценок пока нет
- Typhon PAST WorksheetДокумент2 страницыTyphon PAST WorksheetKa Chun NgОценок пока нет
- Safe Working EnvironmentДокумент16 страницSafe Working EnvironmentDawud AsnakewОценок пока нет
- Thesis Synopsis - Naveen ReddyДокумент16 страницThesis Synopsis - Naveen ReddyNaveen ReddyОценок пока нет
- Radiographic Aids in The Diagnosis of Periodontal Diseases: Presented By: DR: Abdullah AliДокумент27 страницRadiographic Aids in The Diagnosis of Periodontal Diseases: Presented By: DR: Abdullah AliMugahed Abdo Al-gahdariОценок пока нет
- Cells in The PBSДокумент31 страницаCells in The PBSDelzell Dame CasaneОценок пока нет
- Immuno Oncology Therapies White Paper PPDДокумент12 страницImmuno Oncology Therapies White Paper PPDkevalОценок пока нет
- Prittie-2006-Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical CareДокумент11 страницPrittie-2006-Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Carejose fdoОценок пока нет
- Oral MedicationДокумент4 страницыOral MedicationnonameОценок пока нет
- Summer PromoДокумент1 страницаSummer PromobarilesОценок пока нет
- Gambaran Penemuan Kasus Tuberkulosis Paru Oleh Petugas Puskesmas Di Kabupaten SukoharjoДокумент8 страницGambaran Penemuan Kasus Tuberkulosis Paru Oleh Petugas Puskesmas Di Kabupaten SukoharjoBenti Eka WatiОценок пока нет