Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Exercise I
Загружено:
jurieskАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Exercise I
Загружено:
jurieskАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EXERCISE 1
DATA
Conductor Pile:
OD = 30 inch = 762 mm
WT = 1 inch = 25.4 mm
ID = 28 inch = 711.2 mm
Rfs = 30 m
30 m 30 x 1 Fy = 345 MPa
True Batter = 1
Hammer:
Type = MHU 270T
mh = 444.4 kN
C.o.G. = 2.5 m
Cantilever Section
Calculate manually:
a. Actual and allowable stress acting on cantilever section
b. Unity check based on API 2000 section 3.3.1.
c. Residual Dynamic Stress
EXERCISE 2
DATA
Main Pile:
20 x 2 WT L2=5 m Fy = 345 MPa
True Batter =1:8
= 7.13
Hammer:
20 x 1 WT Type = MHU 270 T
L1=5 m
Weight (mh) = 444.4 kN
C.o.G. = 2.5 m
Cantilever Section
Calculate manually:
a. Actual and allowable stress acting on cantilever section
b. Unity check based on API 2000 section 3.3.1.
c. Residual Dynamic Stress
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 1 of 22
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 2 of 22
EXERCISE 3
DATA
Skirt Pile:
OD = 20 inch = 508 mm
WT = 1 inch = 25.4 mm
20 m I AIR
ID = 18 inch = 457.2 mm
Rfs = 40 m
Fy = 345 MPa
True Batter = 1
20 m II WATER Hammer:
Type = MHU 270T + under water ballast
mh + mub = 513 kN
C.o.G. = 1.970 m
Calculate manually:
a. Actual and allowable stress acting on cantilever section
b. Unity check based on API 2000 section 3.3.1.
c. Residual Dynamic Stress
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 3 of 22
Static Pile Stick-Up (Calculation Method)
The evaluation of static pile stick-up is performed in accordance with API-RP 2A 21st
edition (WSD) Section 3.2 3.3.
Allowable Axial Compressive Stress
D
a. For 60 ,
t
( Kl / r ) 2
1 Fy
2Cc2
Fa = for Kl / r < Cc
3( Kl / r ) ( Kl / r )3
5/3 +
8 Cc 8 Cc3
12 2 E
Fa = for Kl / r Cc
23 ( Kl / r ) 2
where :
1/ 2
2 2 E
Cc =
Fy
E = Youngs Modulus of elasticity, ksi (MPa)
K = Effectifve Length Factor (K=2.1 in accordance API section 6.10.4)
l = unbraced length, in. (m)
r = radius of gyration, in. (m)
D
b. For 60 < 300 and Wall Thickness 6 mm.
t
Substitute Fy with the following value :
b.1. Elastic Local Buckling Stress
Fxe = 2 C E t/D
b.2. In-Elastic Local Buckling Stress
Fxc = Fy x [1,64 0,23 (D/t)1/4] Fxe
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 4 of 22
D
Fxc = Fy for ( ) 60.
t
Allowable Bending Stress
D 1500 D 10,340
a. For or , SI units
t Fy t Fy
Fb = 0.75 Fy
1500 D 3000 10,340 D 20,680
b. For < or < , SI units
Fy t Fy Fy t Fy
FyD
Fb = 0.84 1.74 Fy
Et
3000 D 20,680 D
c. For < 300 or < 300, SI units
Fy t Fy t
FyD
Fb = 0.72 0.58 Fy
Et
Evaluation of Actual And Allowable Stress Through :
fa
a. 1.0
Fa
fa
b. For > 0.15
Fa
fa Cm. fb
+ 1.0 (I.R. 1) and
Fa fa
1 Fb
Fe'
fa fb
+ 1.0 (I.R. 2)
0.6 Fy Fb
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 5 of 22
where :
12 2 E
Fe =
23 (kl / r )
2
Cm = Minimum reduction factor = 1.0 (API section 6.10.4)
K = Minimum effective length factor = 2.1 (API section 6.10.4)
fa
c. For 0.15
Fa
fa fb
+ 1.0 (I.R. 3)
Fa Fb
Minimum Bending Moment (API Section 6.10.4)
Bending moment and axial loads should be calculated using the full weight of the pile
hammer, cap, and leads acting through the center of gravity of their combined masses,
and the weight of the pile add-on section with due consideration to pile batter
eccentricities. The bending moment so determined should not be less than that
corresponding to a load equal to 2% of the combined weight of the hammer,cap, and
leads applied at the pile head and perpendicular to its centerline. Therefore,
Minimum Bending Moment = 0.02 x W x Lfs
Where : W = weight of hammer and cap
Lfs = Free standing length
Stresses During Driving
It is recommended by the API (Section 6.10.5) to verify that at cantilever section :
Static Stress (fa + fb) + fdyn 100 SMYS
Dynamic Compressive Stress, fdyn 80 90% SMYS.
One third increase is not allowed.
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 6 of 22
Others (API Section 6.11)
Consideration that should be taken in determine length of pile section, for instance :
Capability of lift equipment to raise, lower, and stab.
Capability of lift equipment to place hammer on the section
Possibility of immediate downward pile movement
Pile stresses during lifting
Wall thickness and material properties at field welds.
Interference with adjacent piles
Type of soil in which the pile tip is positioned during field welding
Cut off length, normally 0.5 1.5 meters.
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 7 of 22
EXERCISE 1
DATA
Conductor Pile
OD = 30 inch = 762 mm
WT = 1 inch = 25.4 mm
ID = 28 inch = 711.2 mm
Rfs = 30 m
30 m 30 x 1 Fy = 345 MPa
True Batter = 1
Hammer
Type = MHU 270T
mh = 444.4 kN
C.o.G. = 2.5 m
Cantilever Section
o CALCULATE LOADS
mh.sin
COG
mh.cos
mh mh
mL.sin
= 1
mL mL.cos
mL
- Bending Moment
M = mh . (Rfs + C.o.G.) . sin 1 + mL . (Rfs / 2) . sin 1
Where : mL = weight of pile (kN)
= 0.25 (OD2 ID2) . Rfs . 7850 kg/m3
= 0.25 (0.7622 0.71122) . 30 . 7850
= 13842.23 kg
mL = 135.792 kN
M = 444.4 (30 + 2.5) sin 1 + 135.792 (30 / 2 ) sin 1
M = 287.387 kNm
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 8 of 22
Minimum bending moment based on API requirement:
M = 2% mh R fs
= 2% 444.4 30
M = 266.64 kNm
Therefore, adopt M = 287.387 kNm
- Axial Load
N = (mh + mL) . cos 1
= (444.4 + 135.792) . cos 1
N = 580.104 kN
o CALCULATE ACTUAL STRESS
- Bending Stress
fb =
M
S
, where S =
1
32 OD
(
OD 4 ID 4 )
=
1
32 0.762
(
0.762 4 0.7112 4 )
S = 0.0105 m3
287.387
fb = = 27,370.190 kN/m2
0.0105
f b = 27.370 MPa
- Axial Stress
N 580.104
fa = = = 9869.396 kN/m2
(
A 0.25 0.762 0.7112
2 2
)
f a = 9.869 MPa
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 9 of 22
o CALCULATE ALLOWABLE STRESS
- Allowable Bending Stress
D 30
= = 30
t 1
10,340
= 29.97 10,340 D 20,680
Fy < <
Fy t Fy
20,680
= 59.94
Fy
therefore,
Fy D
Fb = 0.84 1.74 Fy
Et
345 0.762
= 0.84 1.74 345
200,000 0.0254
Fb = 258.734 MPa
- Allowable Axial Stress
D
= 30 60
t
r=
I
A
, where: I =
1
64
(
0.762 4 0.7112 4 )
I = 0.00399 m4
A = 0.25 (0.7622 0.71122)
A = 0.0588 m2
0.00399
r= = 0.260 m
0.0588
Kl 2.1 30
= = 242.307
r 0.260
Kl
> Cc
r
2 2 E 2 2 200,000
Cc = = = 106.972
Fy 345
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 10 of 22
therefore,
12 2 E 12 2 200,000
Fa = = = 17.619 MPa
23(Kl/r ) 23 242.307 2
2
o CALCULATE UNITY CHECK
fa 9.869
a. = = 0.560 <1
Fa 17.619
fa Cm fb 12 2 E 12 2 200,000
b. + , where : Fe' = =
Fa f a 23 (Kl/r ) 23 242.307 2
2
1 ' Fb
Fe
Fe' = 17.619 MPa
9.869 1 27.370
+ = 0.803 <1 (I.R 1)
17.619 9.869
1 258.734
17.619
fa f 9.869 27.370
c. + b = + = 0.154 <1 (I.R 2)
0.6Fy Fb 0.6 345 258.734
fa fb 9.869 27.370
d. + = + = 0.668 <1 (I.R 3)
Fa Fb 17.619 258.734
o CALCULATE RESIDUAL DYNAMIC STRESS
Total Static Stress:
Fs = fa + fb
= 9.869 + 27.370
= 37.239 MPa
Residual Dynamic Stress:
Rfdyn = Fy fs
= 345 37.379
= 307.761 MPa
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 11 of 22
Percentage of Residual Dynamic Stress,
307.761
% R f dyn = 100%
345
= 89.21 %
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 12 of 22
EXERCISE 2
Main Pile :
Fy = 345 MPa
True Batter =1:8
508 x 50.8 L2=5 m = 7.13
Hammer :
Type = MHU 270 T
Weight (mh) = 444.4 kN
508 x 25.4 C.o.G. = 2.5 m
L1=5 m
Cantilever Section
mh.sin
mh.cos
2.5 m COG
mh
mL2.sin
5m
mh
mL2.cos
mL2
mL2
5m
= 7.13
mL1.sin
mL1 mL1.cos
mL1
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 13 of 22
LOAD CALCULATION
Bending Moment,
L1 L2
M = [ mh . (Rfs + C.o.G.) . sin + mL1. . sin + mL2. L1 + . sin ]
2 2
where : mL1 = weight of segment pile 1
(OD 2 ID 2 )
= R fs 7850 kg/m3
4
(0.5082 0.457 2 )
= 5 7850 kg/m3
4
= 1511.48 kg = 14.83 kN
mL2 = weight of segment pile 2
(OD 2 ID 2 )
= R fs 7850 kg/m3
4
=
(
0.5082 0.4062 ) 5 7850 kg/m3
4
= 2863.72 kg = 28.09 kN
5 5
M = 444.4 (10 + 2.5) sin 7.13 + 14.83 sin 7.13 + 28.09 5 + sin 7.13
2 2
M = 720.24 kNm
Minimum bending moment based on API Section 6.10.4 :
M = 2% mh R fs
= 2% 444.4 10
M = 88.88 kNm
Therefore, actual bending moment govern.
Adopt M = 720.24 kNm
Axial Load,
N = (mh + mL1 + mL2) . cos
= (444.4 + 14.83 + 28.09) . cos 7.13
N = 483.55 kN
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 14 of 22
ACTUAL STRESSES AT CANTILEVER SECTION
- Bending Stress,
(OD3 ID3 )
S =
32
(5083 4573 )
=
32
S = 4,425,982 mm3
M
fb =
S
720.24 106
fb =
4,452,982
f b = 162.73 MPa
- Axial Stress,
N
fa =
A
483.55 103
fa =
1 (5082 457 2 )
4
f a = 12.56 MPa
ALLOWABLE STRESSES
- Allowable Bending Stress ( API Section 3.2.3 )
D 20 10,340
For = = 20 = 30
t 1 Fy
Fb = 0.75 Fy
Fb = 0.75 x 345 = 258.75 MPa
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 15 of 22
- Allowable Axial Stress ( API Section 3.2.2 )
D
= 20 60
t
(5084 457 4 )
I 1
r= , where : I =
A 64
= 1,127,985,077 mm4
A = 0.25 (5082 4572)
= 38,653 mm2
1,127,985,077
r =
38,653
= 170.83 mm
kl 2.1 (10 1000 )
= = 122.93 (K = 2.1 in accordance API 6.10.4)
r 170.83
1/ 2 1/ 2
2 2 E 2 2 200,000
Cc = = = 106.9
Fy 345
D kl
For 60 and > Cc ,
t r
12 2 E
Fa =
23(Kl/r )
2
12 2 200,000
=
23(122.93)
2
= 68.15 MPa
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 16 of 22
UNITY CHECK
f a 12.56
a. = = 0.184 <1
Fa 68.15
fa Cm fb
b. + , where : Cm = 1.0 (API Section 6.10.4)
Fa f a
1 ' Fb
Fe
12 2 E 12 2 200,000
Fe' = =
23 (Kl/r ) 23 122.932
2
Fe' = 68.15 MPa
12.56 1 162.73
+ = 0.955 < 1 (I.R 1)
68.15 12.56
1 258.75
68.15
fa f 12.56 162.73
c. + b = + = 0.689 < 1 (I.R 2)
0.6Fy Fb 0.6 345 258.75
f a f b 12.56 162.73
d. + = + = 0.813 < 1 (I.R 3)
Fa Fb 68.15 258.75
RESIDUAL DYNAMIC STRESS
Total Static Stress:
Fs = fa + fb
= 12.56 + 162.73
= 175.29 MPa
Residual Dynamic Stress:
Fres dyn = Fy Fs
= 345 175.29
= 169.71 MPa
Percentage of Residual Dynamic Stress,
169.71
% Fres dyn = 100%
345
= 49.19 %
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 17 of 22
EXERCISE 3
DATA
Skirt Pile
OD = 20 inch = 508 mm
WT = 1 inch = 25.4 mm
20 m I AIR
ID = 18 inch = 457.2 mm
Rfs = 40 m
Fy = 345 MPa
True Batter = 1
20 m II WATER Hammer
Type = MHU 270T + Under water ballast
mh + mub = 513 kN
C.o.G. = 1.970 m
o WEIGHT OF PILE
- Section I (Above water)
mL1 = 0.25 (OD2 ID2) . Rfs . 7850 kg/m3
= 0.25 (0.5082 0.45722) . 20 . 7850
= 6046.034 kg
mL1 = 59.312 kN, C.o.G. from cantilever section = 30 m
- Section II (Under Water)
mL2 = mL1 buoyancy
= 6046.034 . v
[ ]
= 6046.034 1025 0.25(0.508 2 0.4572 2 ) 20
= 5256.583 kg
mL2 = 51.567 kN, C.o.G. from cantilever section = 10 m
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 18 of 22
o CALCULATE LOADS
Mh+mub.sin
Mh+mub.cos
1.97 m COG
Mh+mub
mL1.sin
20 m
Mh+mub
mL1.cos
mL1
mL1
20 m
= 1
mL2.sin
mL2 mL2.cos
mL2
- Bending Moment
[ ]
M = (mh + mub ) (R fs + C.o.G.) sin 1 + (mL1 30 sin 1) + (mL2 10 sin 1)
= [513 (40 + 1.970 ) sin 1] + (59.312 30 sin 1) + (51.567 10 sin 1)
M = 415.815 kNm
Minimum bending moment based on API requirement:
M = 2% (m h + m ub ) R fs
= 2% 513 40
M = 410.40 kNm
Therefore adopt M = 415.815 kNm
- Axial Load
N = (mh + mub + mL1 + mL2) . cos 1
= (513 + 59.312 + 51.567) . cos 1
N = 623.78 kN
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 19 of 22
o CALCULATE ACTUAL STRESSES
- Bending Stress
fb =
M
S
, where : S =
1
32 OD
(
OD 4 ID 4 )
=
1
32 0.508
(
0.5084 0.4572 4 )
S = 0.004426 m3
415.815
fb = = 93948.204 kN/m2
0.004426
f b = 93.948 MPa
- Axial Stress
N 623.78
fa = = = 16198.072 kN/m2
(
A 0.25 0.508 0.4572
2 2
)
f a = 16.198 MPa
o CALCULATE ALLOWABLE STRESS
- Allowable Bending Stress
D 20
= = 20
t 1
D 10,340
<
10,340 t Fy
= 29,97
Fy
therefore,
Fb = 0.75 Fy
= 258.75 MPa
- Allowable Axial Stress
D
= 20 60
t
r=
I
A
, where : I =
1
64
(
0.5084 0.4572 4)
I = 0.001124 m4
A = 0.25 (0.5082 0.45722)
A = 0.0385 m2
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 20 of 22
0.001124
r= = 0.171 m
0.0385
Kl 2.1 40
= = 491.228
r 0.171
Kl
> Cc
r
2 2 E 2 2 200,000
Cc = = = 106.972
Fy 345
D kl
For 60 and > Cc ,
t r
12 2 E 12 2 200,000
Fa = = = 4.268 MPa
23(Kl/r ) 23 491.2282
2
o CALCULATE UNITY CHECK
f a 16.198
a. = = 3.795 >1
Fa 4.268
fa Cm fb
b. + , Fe' = Fa = 4.268 MPa
Fa f a
1 ' Fb
F
e
16.198 1 93.948
+ = 3.665 >1 (I.R 1)
4.268 16.198
1 258.75
4.268
fa f 16.198 93.948
c. + b = + = 0.441 <1 (I.R 2)
0.6Fy Fb 0.6 345 258.75
f a f b 16.198 93.948
d. + = + = 4.158 >1 (I.R 3)
Fa Fb 4.268 258.75
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 21 of 22
o CALCULATE RESIDUAL DYNAMIC STRESS
Total Static Stress:
Fs = fa + fb
= 16.198 + 93.948
= 110.146 MPa
Residual Dynamic Stress:
Rfdyn = Fy fs
= 345 110.146
= 234.854 MPa (68.074% of Fy)
Static Pile Stick-up Exercise 22 of 22
Вам также может понравиться
- S PMT Best Practice GuideДокумент29 страницS PMT Best Practice Guidejuriesk100% (1)
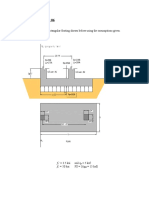
- F Ksi F Ksi Q KSF: Combined Footing - 01Документ7 страницF Ksi F Ksi Q KSF: Combined Footing - 01jurieskОценок пока нет
- Stab CalcДокумент4 страницыStab CalcjurieskОценок пока нет
- Combined Footings 06: Design The Combined Rectangular Footing Shown Below Using The Assumptions GivenДокумент6 страницCombined Footings 06: Design The Combined Rectangular Footing Shown Below Using The Assumptions GivenjurieskОценок пока нет
- H-L Series Crane Dimensional Data Sheet: ContactДокумент3 страницыH-L Series Crane Dimensional Data Sheet: ContactjurieskОценок пока нет
- Fencing Spec...Документ3 страницыFencing Spec...jurieskОценок пока нет
- Pilecap Mesh Specifications - : BRC Asia Limited. All Rights ReservedДокумент2 страницыPilecap Mesh Specifications - : BRC Asia Limited. All Rights ReservedjurieskОценок пока нет
- Menck MHU - New BrochureДокумент4 страницыMenck MHU - New BrochurejurieskОценок пока нет
- Prefabricated Column Reinforcement SpecificationsДокумент2 страницыPrefabricated Column Reinforcement SpecificationsjurieskОценок пока нет
- Pile Driving Record (Blow Count Record)Документ3 страницыPile Driving Record (Blow Count Record)jurieskОценок пока нет
- SRD Stevens ExampleДокумент9 страницSRD Stevens Examplejuriesk100% (1)
- EN1002 Steel GradeДокумент1 страницаEN1002 Steel GradejurieskОценок пока нет
- Hammer Data Sheet - Rev.iДокумент13 страницHammer Data Sheet - Rev.ijurieskОценок пока нет
- Pile Driveability Analysis Check List Rev.cДокумент1 страницаPile Driveability Analysis Check List Rev.cjuriesk100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Carbon Emissions Don't Cause Global Warming: BackgroundДокумент5 страницCarbon Emissions Don't Cause Global Warming: BackgroundLibertyAustraliaОценок пока нет
- Planetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaДокумент11 страницPlanetary Characteristics: © Sarajit Poddar, SJC AsiaVaraha Mihira100% (11)
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreДокумент10 страницInstitute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreMUmairQrОценок пока нет
- Kingdom Fungi: - Characteristics of Fungi - Oomycota - Zygomycota - Ascomycota - Basidiomycota - DeuteromycotaДокумент15 страницKingdom Fungi: - Characteristics of Fungi - Oomycota - Zygomycota - Ascomycota - Basidiomycota - DeuteromycotaLeah Rice100% (1)
- Sip Dissertation - Final - Final For CollegeДокумент17 страницSip Dissertation - Final - Final For Collegevikashirulkar922Оценок пока нет
- Bryophytes MorphologyДокумент9 страницBryophytes Morphologyrachna singh0% (1)
- R OR K C S V: EG Epair Its For Ylinder and Ervice AlvesДокумент5 страницR OR K C S V: EG Epair Its For Ylinder and Ervice AlvesLeonardoFabioCorredorОценок пока нет
- Weichai WP10 Euro IIIДокумент35 страницWeichai WP10 Euro IIIBakery HamzaОценок пока нет
- AN-PFC-TDA 4863-3 Calculation-Tool For PFC-Preconverter Using TDA 4863Документ9 страницAN-PFC-TDA 4863-3 Calculation-Tool For PFC-Preconverter Using TDA 4863NaciConSolОценок пока нет
- The Art of Logical ThinkingДокумент210 страницThe Art of Logical ThinkingAndyAyam100% (1)
- TSBДокумент3 страницыTSBnoe dela vegaОценок пока нет
- HART - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент3 страницыHART - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediakalyanupdownОценок пока нет
- Management Science - Lecture 2Документ9 страницManagement Science - Lecture 2Nicole SallanОценок пока нет
- Sample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Документ17 страницSample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Adam Michael GreenОценок пока нет
- Quiz Business MathДокумент5 страницQuiz Business MathMA. JEMARIS SOLISОценок пока нет
- The 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All TimeДокумент4 страницыThe 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All Timeungku1Оценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talks Working at Elevations English 1Документ1 страницаToolbox Talks Working at Elevations English 1AshpakОценок пока нет
- Practice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)Документ13 страницPractice Exam 3 KEY (Solutions)joseОценок пока нет
- Free Non Veg Nutrition Plan YSF PDFДокумент8 страницFree Non Veg Nutrition Plan YSF PDFAbhilash Wasekar100% (1)
- Unit-3 DC Machines IMP QuestionsДокумент30 страницUnit-3 DC Machines IMP Questionskrishna Sai Atla VenkataОценок пока нет
- Design and Management of Mettur Dam by Predicting Seepage Losses Using Remote SensingДокумент10 страницDesign and Management of Mettur Dam by Predicting Seepage Losses Using Remote SensingInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementОценок пока нет
- Modeling of Conducted EMI (Model Motor Simulink Bun)Документ8 страницModeling of Conducted EMI (Model Motor Simulink Bun)Ioan ŢileaОценок пока нет
- 300.91C - Fire Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test Checklist 3-27-14Документ2 страницы300.91C - Fire Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test Checklist 3-27-14mthuyaОценок пока нет
- BSN Curriculum 2012Документ1 страницаBSN Curriculum 2012Joana Bless PereyОценок пока нет
- Gilmour Price List Till 20 DecДокумент18 страницGilmour Price List Till 20 DecnhzaidiОценок пока нет
- Research Proposal PHDДокумент19 страницResearch Proposal PHDSuleiman Mukhtar100% (2)
- Union Fork & Hoe No. 19Документ68 страницUnion Fork & Hoe No. 19Jay SОценок пока нет
- Barilla SpaДокумент11 страницBarilla Spavariapratik100% (1)
- Flap Designs For Flap Advancement During Implant Therapy A Systematic Review 2016 PDFДокумент8 страницFlap Designs For Flap Advancement During Implant Therapy A Systematic Review 2016 PDFRohit ShahОценок пока нет
- Anti-Cellulite: Endermologie TreatmentДокумент8 страницAnti-Cellulite: Endermologie TreatmentMinu CatalinОценок пока нет