Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Diabetes - What S New - Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Загружено:
LinhTranОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Diabetes - What S New - Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Загружено:
LinhTranАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
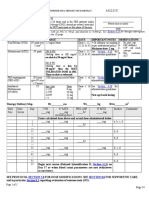
APPENDIX 2.
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERGLYCEMIA IN TYPE 2 DIABETES
Clinical Assessment
Lifestyle intervention (initiation of nutrition therapy and physical activity)
L A1C > 0.07 but < 0.09
after trial with lifestyle changes
A1C 0.09 Symptomatic hyperglycemia with metabolic
decompensation (e.g., diabetic ketoacidosis)
Initiate pharmacotherapy immediately without
Initiate waiting for effect from lifestyle interventions. Initiate insulin
I metformin Consider adding metformin concurrently
with another agent from a different class; or
metformin
Initiate insulin
F If not at target
Add an agent best suited to the individual based on
advantages/disadvantages listed below and information in Appendix 1.
E Class Expected in
A1C
Hypo-
glycemia
Advantages Disadvantages
Alpha-glucosidase Rare Improved postprandial control GI side effects
inhibitor Weight neutral
Incretin agent: to Rare Improved postprandial control Newer agent so long term
S DPP-4 inhibitor Weight neutral safety is unknown
Insulin Yes No dose ceiling, many types, Weight gain
flexible regimens
Insulin Improved postprandial control Requires TID to QID dosing,
T secretagogue:
Meglitinide to Yes*
Newer sulfonylureas (glicazide,
glimepiride) associated with less
weight gain
Sulfonylurea Yes hypoglycemia than glyburide
Requires 6 12 weeks for
Thiazolidinedione Rare Durable monotherapy maximal effect, weight gain,
Y edema, rare CHF, rare
fractures in women
GI side effects (orlistat)
Weight loss agent None Weight loss
L If not at target
Add another drug from a different class; or
E Add bedtime basal insulin to other agent(s); or
Intensify insulin regimen
Make timely adjustments to and/or add antihyperglycemic agents to attain target A1C within 6 to 12 months
: <0.01 reduction; : 0.01-0.02 reduction; : >0.02 reduction
DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4
* Less hypoglycemia in context of missed meals
See Info Point 19 for updated information
Adapted and Reprinted with Permission from: Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Canadian
Diabetes Association 2008 clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes in Canada. Pharmacologic Management
of Type 2 Diabetes. Can J Diabetes, 32 (suppl 1): S56.
The Foundation for Medical Practice Education, www.fmpe.org
August 2009
17
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Tuberculosis and NutritionДокумент14 страницTuberculosis and NutritionYenny PangaribuanОценок пока нет
- EMDR Scripted Protocols Index by Marilyn Luber PHDДокумент4 страницыEMDR Scripted Protocols Index by Marilyn Luber PHDcebanova1994Оценок пока нет
- "HIV Depletes T-Helper17, We Simply Stimulate It": by Prof. DR - Pichaet Wiriyachitra PH.D., F.R.A.C.IДокумент37 страниц"HIV Depletes T-Helper17, We Simply Stimulate It": by Prof. DR - Pichaet Wiriyachitra PH.D., F.R.A.C.IfroggyzzОценок пока нет
- Is Early Surgical Treatment For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Preferable Medical Therapy - Pros and ConsДокумент11 страницIs Early Surgical Treatment For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Preferable Medical Therapy - Pros and ConsClaudia FreyonaОценок пока нет
- NBEMS announces DNB/DrNB practical exam datesДокумент2 страницыNBEMS announces DNB/DrNB practical exam datesShivaraj S AОценок пока нет
- High Risk B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Interim Maintenance IIДокумент1 страницаHigh Risk B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Interim Maintenance IIRitush MadanОценок пока нет
- Web KFOG-jan-11Документ16 страницWeb KFOG-jan-11kutra3000Оценок пока нет
- Ultrasound-Guided Brachial Plexus BlockДокумент7 страницUltrasound-Guided Brachial Plexus BlockÇağdaş BaytarОценок пока нет
- Opsonin Pharma ListДокумент14 страницOpsonin Pharma ListDelegate Tech100% (1)
- DCMNTДокумент2 страницыDCMNTameenОценок пока нет
- Pre Final Exam NCM 118Документ26 страницPre Final Exam NCM 118Faith BugtongОценок пока нет
- Erectile DysfunctionДокумент31 страницаErectile Dysfunctionrahuldtc100% (1)
- Identificação Bacteriológica em Banheiros de Unidades Básicas de Saúde de Municípios Do Noroeste Paulista, BrasilДокумент5 страницIdentificação Bacteriológica em Banheiros de Unidades Básicas de Saúde de Municípios Do Noroeste Paulista, BrasilLiana Maia100% (1)
- Hip DislocationДокумент4 страницыHip DislocationcrunkestОценок пока нет
- Schedule FinalДокумент2 страницыSchedule Finalapi-360816970Оценок пока нет
- Starting Injectable RCN PDFДокумент40 страницStarting Injectable RCN PDFPhilip HartleyОценок пока нет
- High Output Renal FailureДокумент4 страницыHigh Output Renal Failuredrhiwaomer100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalsДокумент2 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalskyawОценок пока нет
- Bronchoscopy: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasДокумент17 страницBronchoscopy: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviОценок пока нет
- Social Participation of People With Chronic Wounds - A Systematic ReviewДокумент25 страницSocial Participation of People With Chronic Wounds - A Systematic ReviewcumbredinОценок пока нет
- Combination lipid therapy as first-line strategy for very high-risk patientsДокумент4 страницыCombination lipid therapy as first-line strategy for very high-risk patientsYo MeОценок пока нет
- Ten Rules For The Management of Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury During Pregnancy: An Expert ViewpointДокумент11 страницTen Rules For The Management of Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury During Pregnancy: An Expert ViewpointKaren Campos GonzalezОценок пока нет
- SRG Test BiologyДокумент156 страницSRG Test Biologypranayallen2006Оценок пока нет
- Dr. Ikar J. Kalogjera: Psychiatrist & Clinical Professor of PsychiatryДокумент1 страницаDr. Ikar J. Kalogjera: Psychiatrist & Clinical Professor of PsychiatryMWWОценок пока нет
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 2Документ3 страницыPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 2Milenka SalcedoОценок пока нет
- Microbiology of Clostridium Tetani and Wound ClassificationДокумент3 страницыMicrobiology of Clostridium Tetani and Wound ClassificationAZIZAH ARDINALОценок пока нет
- SepanskiДокумент13 страницSepanskiTammy Utami DewiОценок пока нет
- Emergency Medical Technician CPGs PDFДокумент121 страницаEmergency Medical Technician CPGs PDFAnonymous OdW7ev100% (1)
- Ace InhibitorsДокумент26 страницAce InhibitorsDeipa KunwarОценок пока нет
- Hyun-Yoon Ko - Management and Rehabilitation of Spinal Cord Injuries-Springer (2022)Документ915 страницHyun-Yoon Ko - Management and Rehabilitation of Spinal Cord Injuries-Springer (2022)JESSICA OQUENDO OROZCOОценок пока нет