Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
What Is Explanation?: 1. Definition and Purposes of Explanation
Загружено:
Iswardi HidayatИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What Is Explanation?: 1. Definition and Purposes of Explanation
Загружено:
Iswardi HidayatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What is Explanation?
1. 1. Definition and purposes of Explanation
Explanation is a text which tells processes relating to forming of natural, social,
scientific and cultural phenomena. Explanation text is to say why and how of the
forming of the phenomena. It is often found in science, geography and history text
books.
1. 2. Generic structure of Explanation
General statement; stating the phenomenon issues which are to be explained.
Sequenced explanation; stating a series of steps which explain the
phenomena.
1. 3. Language Feature
Featuring generic participant; sun, rain, etc
Using chronological connection; to begin with, next, etc
Using passive voice pattern
Using simple present tense
1. 4. Examples and structures of the text
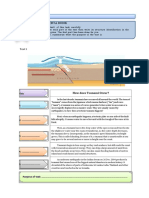
Making Paper from Woodchips
A general Woodchipping is a process used to obtain
statement pulp and paper products from forest trees.
The woodchipping process begins when the
trees are cut down in a selected area of the
forest called a coupe.
A Next the tops and branches of the trees are
sequencedexplanati cut out and then the logs are taken to the
on of mill.
At the mill the bark of the logs is removed
and the logs are taken to a chipper which
cuts them into small pieces called
woodchips.
The woodchips are then screened to remove
dirt and otherimpurities.At this stage they
why or how are either exported in this form or changed
something occurs into pulp by chemicals and heat.
The pulp is then bleached and the water
content is removed.
Closing Finally the pulp is rolled out to make paper.
Example of Explanation Text
1. A. Tsunami
The term of tsunami comes from the Japanese which means harbour (tsu) and
wave (nami). A tsunamigk is a series of waves generated when water in a lake or
the sea is rapidly displaced on a massive scale.
A tsunami can be generated when the sea floor abruptly deforms and vertically
displaces the overlying water. Such large vertical movements of the earths crust can
occur at plate boundaries.
Subduction of earthquakes are particularly effective in generating tsunamis, and
occur where denser oceanic plates slip under continental plates.
As the displaced water mass moves under the influence of gravity to regain its
equilibrium, it radiates across the ocean like ripples on a pond.
Tsunami always bring great damage. Most of the damage is caused by the huge mass
of water behind the initial wave front, as the height of the sea keeps rising fast and
floods powerfully into the coastal area.
(simplified from www.panda.org)
1. B. How Day and Night Happen
The sun seems to rise in the morning, crosses the sky during the day and sets at
night. However the sun does not actually move around the earth. Earths turning on
its axis makes it look as if the sun is moves.
The earth makes a complete turn on its axis for 24 hours. It is called as rotation. It
causes day and night. The earth also moves around the sun. It takes 365 days or a
year. This process is called revolution. The revolution process causes the changes of
the season
1. C. Why Summer Daylight is Longger than Winter Daylight
In the summer, the amount of daylight that we get is more than we get in winter. This
is not because as much people think we are closer to the sun but because of the tilt of
the earth.
The earth is actually closer to the sun in winter than it is in summer but you would be
forgiven for thinking that this can not be true after looking out of your window on a
cold and frosty morning.
It seems strange that as the earth get closer to the sun during its orbit then the
amount of daylight that we get decrease. But that is the case. It is the tilt of the earth
that determine the amount of daylight that we get and so the length of time that for
us the sun is above the horizon.
(Taken from: www.ictteachers.co.uk)
Generic Structure Analysis
General statement; stating the phenomenon whic daylight in summer is longer than
in winter.
Explanation; it is the tilt of the earth that determines the amount of daylight not the
distance of the earth from the sun.
Language Feature Analysis
Focusing generic participant; daylight.
Using chronological connection; then, so, but.
Using pasive voice; you would be forgiven.
Using present tense; the earth is actually closer to the sun.
Вам также может понравиться
- Definition and Purposes of ExplanationДокумент4 страницыDefinition and Purposes of ExplanationArka WiguaОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент4 страницыExplanation TextKuuharuRyuutaОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент5 страницExplanation TextRidhayani BurОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент3 страницыExplanation TextAskme AzmyОценок пока нет
- What Is Explanation?Документ10 страницWhat Is Explanation?Layly HariadiОценок пока нет
- Tugas 2 Pembuatan Bahan Ajar Bahasa Inggris Lilis SuryaniДокумент5 страницTugas 2 Pembuatan Bahan Ajar Bahasa Inggris Lilis Suryanililis suryaniОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент11 страницExplanation TextVespid MangoОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент10 страницExplanation TextYuyun Purwita SariОценок пока нет
- Definition and Purposes of ExplanationДокумент6 страницDefinition and Purposes of Explanation-Nduuh Newbie-100% (3)
- Unit 8 Explanation Text: GETTING STARTED................................................................Документ6 страницUnit 8 Explanation Text: GETTING STARTED................................................................Mutia ApriliyaniОценок пока нет
- Definition of Explanation TextДокумент2 страницыDefinition of Explanation TextSaniaОценок пока нет
- Contoh Explanation Text Beserta Generic Structure Dan Language FeaturesДокумент4 страницыContoh Explanation Text Beserta Generic Structure Dan Language FeaturesQoushy86% (43)
- Explanation: NAMA: Cindy Aprillia Kelas: X Mia 1Документ8 страницExplanation: NAMA: Cindy Aprillia Kelas: X Mia 1aryaivantaraОценок пока нет
- Explanation Text, Narrative, ProcedureДокумент11 страницExplanation Text, Narrative, ProcedureRashid Muthahar Hakim Al-MawahibОценок пока нет
- Distinguishing Text-Types According To Purpose and FeaturesДокумент20 страницDistinguishing Text-Types According To Purpose and Featuresrazle.jabeloОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент13 страницExplanation TextVucci VistaОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент7 страницExplanation Textdyansutraningsih99Оценок пока нет
- Explanation Text Is A Text Genre Which Tries To Explain How A Thing Happens or Why The Thing Is MadeДокумент9 страницExplanation Text Is A Text Genre Which Tries To Explain How A Thing Happens or Why The Thing Is MadeSyafaruddin MarpaungОценок пока нет
- Paragraph To ExplainДокумент13 страницParagraph To Explainagnes febrianti putriОценок пока нет
- 3.1. Explanation Text. LK - AKHMAL DUTA BAGASKARAДокумент5 страниц3.1. Explanation Text. LK - AKHMAL DUTA BAGASKARAAkhmal BagaskaraОценок пока нет
- Pathway To English SMA XI Wajib Chapter 8Документ15 страницPathway To English SMA XI Wajib Chapter 8charles dometianОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 MeteorologyДокумент17 страницLesson 3 MeteorologyCuadrado, Jeanen Grace C.Оценок пока нет
- English Version of Hydrospher PresentationДокумент8 страницEnglish Version of Hydrospher PresentationDara J.S.Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ4 страницыAssignment 1Amelia CahyaОценок пока нет
- Kliping Bahasa InggrisДокумент15 страницKliping Bahasa InggrisAnabel LuluОценок пока нет
- 20 Contoh Explanation Text WWW - Englishiana PRINTДокумент9 страниц20 Contoh Explanation Text WWW - Englishiana PRINTfaruq bawazir nur nizarОценок пока нет
- Elements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 41Документ89 страницElements of Weather Climate Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1-Day 41BENJ AMINОценок пока нет
- Hydrology Assignment 1Документ16 страницHydrology Assignment 1gtОценок пока нет
- How Earthquakes Happen: Contoh / Example of Explanation Text About EarthquakeДокумент5 страницHow Earthquakes Happen: Contoh / Example of Explanation Text About EarthquakeFitiyaОценок пока нет
- Power Point Explanation TextДокумент7 страницPower Point Explanation TextAghny AnjalyОценок пока нет
- Lessn 68 Day 2.beverly v. SantiagoДокумент32 страницыLessn 68 Day 2.beverly v. SantiagoCLARISSA TAGUBAОценок пока нет
- TX 5.8B TheSunandWaterCycle EXPLAIN STEMscopediaДокумент6 страницTX 5.8B TheSunandWaterCycle EXPLAIN STEMscopediaCinta KimiaОценок пока нет
- Gess 203Документ8 страницGess 203Kalpavriksha1974Оценок пока нет
- Explanation Text: Related Post in Text Types SamplesДокумент8 страницExplanation Text: Related Post in Text Types SamplesnanakukuОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент16 страницExplanation TextEgi NovarintaОценок пока нет
- GK-geo and ScienceДокумент28 страницGK-geo and Sciencevero1curziОценок пока нет
- Week 33 - Read and RespondДокумент12 страницWeek 33 - Read and RespondmmontoyaОценок пока нет
- LeavesДокумент1 страницаLeavesHartford CourantОценок пока нет
- Science 4 Q4 Week 3 Day 1 4Документ64 страницыScience 4 Q4 Week 3 Day 1 4LigieОценок пока нет
- Bahan Ajar PPG Siklus 2Документ3 страницыBahan Ajar PPG Siklus 2dzulОценок пока нет
- 12.water CycleДокумент4 страницы12.water CycleLius DonОценок пока нет
- Natural Science 2Документ8 страницNatural Science 2Manyaim ShahОценок пока нет
- Contoh Teks ExplanationДокумент40 страницContoh Teks ExplanationTelemedia GubugОценок пока нет
- Analytical Exposition: By: Fuad, Adam, Adri, Bobby, AudiДокумент12 страницAnalytical Exposition: By: Fuad, Adam, Adri, Bobby, AudiArdiRakunОценок пока нет
- Explanation 2 (Mazaya & Selvy)Документ3 страницыExplanation 2 (Mazaya & Selvy)Mazaya HakimОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент13 страницExplanation TextYenni YolandaОценок пока нет
- Krisna Prabowo (18) Tugas Explanation 2020Документ2 страницыKrisna Prabowo (18) Tugas Explanation 2020Kena KenokeniОценок пока нет
- Explanation Text: 3.3 Membedakan Fungsi Sosial, Struktur Teks, Dan UnsurДокумент7 страницExplanation Text: 3.3 Membedakan Fungsi Sosial, Struktur Teks, Dan UnsurNazwaaaОценок пока нет
- Explanation Text PrintДокумент8 страницExplanation Text PrintHonest Vania AsariОценок пока нет
- Explanation TextДокумент12 страницExplanation TextAdriel AcangОценок пока нет
- Metamorphis MДокумент37 страницMetamorphis MIswardi HidayatОценок пока нет
- Book 1 Iseng 2Документ1 страницаBook 1 Iseng 2Iswardi HidayatОценок пока нет
- 18 Maret 2017Документ8 страниц18 Maret 2017Iswardi HidayatОценок пока нет
- The Science of MiningДокумент170 страницThe Science of MiningOktay Türkyılmaz83% (6)
- Lamp IranДокумент1 страницаLamp IranIswardi HidayatОценок пока нет
- Bergson, The Philosophy of ChangeДокумент104 страницыBergson, The Philosophy of ChangeSoha Hassan Youssef100% (2)
- Listening Test 1.1Документ2 страницыListening Test 1.1momobear152Оценок пока нет
- Thermo SolДокумент9 страницThermo SolLugisaniMushavhanamadiОценок пока нет
- Sample Test Paper 2012 NucleusДокумент14 страницSample Test Paper 2012 NucleusVikramОценок пока нет
- Document 1 PetДокумент9 страницDocument 1 PetRoel Jr Pinaroc DolaypanОценок пока нет
- Healthcare ProfessionalismДокумент28 страницHealthcare ProfessionalismAnjo CincoОценок пока нет
- Tips Experiments With MatlabДокумент190 страницTips Experiments With MatlabVishalОценок пока нет
- Design BasisДокумент9 страницDesign BasisSamiksha RajdevОценок пока нет
- Brandi Jones-5e-Lesson-Plan 2Документ3 страницыBrandi Jones-5e-Lesson-Plan 2api-491136095Оценок пока нет
- Prelim Examination in Logic DesignДокумент5 страницPrelim Examination in Logic Designdj_eqc7227Оценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper-08 (For 2013)Документ11 страницCBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper-08 (For 2013)cbsesamplepaperОценок пока нет
- Project PlanДокумент8 страницProject PlanRodsheen100% (1)
- Spinning CalculationДокумент178 страницSpinning Calculationamboklate69% (16)
- Spirolab IIIДокумент1 страницаSpirolab IIIDzenan DelijaОценок пока нет
- My Home, My School: Meet and GreetДокумент2 страницыMy Home, My School: Meet and GreetAcebuque Arby Immanuel GopeteoОценок пока нет
- Pal and Lisa Senior Secondary School Senior Five End of Term Two ExaminationsДокумент3 страницыPal and Lisa Senior Secondary School Senior Five End of Term Two ExaminationsAthiyo MartinОценок пока нет
- BharathДокумент2 страницыBharathbharath kumarОценок пока нет
- Fendrick Govt 720 Global Problem EssayДокумент5 страницFendrick Govt 720 Global Problem Essayapi-283893191Оценок пока нет
- ESG Assignment Part 2: Shareholder ActivismДокумент6 страницESG Assignment Part 2: Shareholder ActivismParesh ShrivastavaОценок пока нет
- InheretanceДокумент8 страницInheretancefarhan.mukhtiarОценок пока нет
- Lp-7 2019-Ratio and ProportionДокумент5 страницLp-7 2019-Ratio and Proportionroy c. diocampoОценок пока нет
- Performing and Reporting Cost Analysis During The Design Phase of A ProjectДокумент4 страницыPerforming and Reporting Cost Analysis During The Design Phase of A ProjectAhmad Zubair RasulyОценок пока нет
- Contoh RefleksiДокумент7 страницContoh RefleksiIzzat HanifОценок пока нет
- 1 SMДокумент9 страниц1 SMSelly ManaluОценок пока нет
- Disneyland (Manish N Suraj)Документ27 страницDisneyland (Manish N Suraj)Suraj Kedia0% (1)
- Kolkata City Accident Report - 2018Документ48 страницKolkata City Accident Report - 2018anon_109699702Оценок пока нет
- Ieee Sight 2018 Call For PapersДокумент4 страницыIeee Sight 2018 Call For PapersThushar TomОценок пока нет
- Henderson 1Документ4 страницыHenderson 1danielОценок пока нет
- (Herbert Kitschelt, Steven I. Wilkinson) Patrons, PDFДокумент387 страниц(Herbert Kitschelt, Steven I. Wilkinson) Patrons, PDFClemente Tomás Sánchez BarjaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2: Question 1: Predator-Prey ModelДокумент2 страницыAssignment 2: Question 1: Predator-Prey ModelKhan Mohd SaalimОценок пока нет