Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CE566
Загружено:
Oso OsoАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CE566
Загружено:
Oso OsoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CE 566 Soil Stabilization (3 - 0:3)
Description: Clay mineralogy, mechanical stabilization, stabilization with additives (lime, cement, asphalt, etc), collapsible soils and their stabilization, swelling-shrinking soils,
foundation heave prediction and method of soil treatments, preloading and methods of stabilizing highly compressible soils, vertical sand drains, reinforced earth and reinforced
earth retaining walls, thermal stabilization, electrokinetic processes and their use in soil remediation and improvement.
Pre-requisite: CE 461 Soil Mechanics I.
Student Assessment and Grading: Assignments (10%), Projects (10), 2 Exams @ 20% each (40%), Final Exam (40%)
Learning outcomes, delivery and assessment methods- Cross Reference Table:
ABET 2000
Student Learning Outcome Method of Delivery Assessment Methods
Criterion 3
1. Clay mineralogy, types of clay minerals, diffuse double layer theory. Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, d
2. Mechanical stabilization; influence soil structure, permeability, swellability, shear
Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d
strength, and soil compressibility.
3. Stabilization with additives (lime, cement, asphalt, etc). Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d
4. Collapsible soils; identification and their stabilization. Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d
5. Dispersive soils; identification and their stabilization. Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d
6. Swelling-shrinking soils, foundation heave prediction and method of soil treatments. Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d ,e, k
7. Preloading and methods of stabilizing highly compressible soils. Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d ,e, k
8. Vertical sand drains. Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d ,e, k
9. Reinforced earth and reinforced earth retaining walls Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d ,e, k
10. Electrokinetic processes and their use in soil remediation and improvement. Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams a, b, c, d ,e, k
ABET a-k Engineering and Technology program objectives
(a) An ability to apply knowledge of (e) An ability to identify, formulate, and solve (i) A recognition of the need for, and an
mathematics, science, and engineering engineering problems ability to engage in life-long learning
(b) An ability to design and conduct (f) An understanding of professional and (j) A knowledge of contemporary issues
experiments, to analyze and interpret data ethical responsibility (k) An ability to use the techniques, skills,
(c) An ability to design a system, component, (g) An ability to communicate effectively and modern engineering tools necessary
or process to meet desired needs (h) The broad education necessary to for engineering practice
(d) An ability to function on multi-disciplinary understand the impact of engineering
teams solutions in a global and societal context
CE 566 Soil Stabilization
Catalog Data CE566 Soil Stabilization (3 0 : 3)
Clay mineralogy, mechanical stabilization, stabilization with additives (lime, cement, asphalt, etc),
collapsible soils and their stabilization, swelling-shrinking soils, foundation heave prediction and
method of soil treatments, preloading and methods of stabilizing highly compressible soils, vertical
sand drains, reinforced earth and reinforced earth retaining walls, thermal stabilization,
electrokinetic processes and their use in soil remediation and improvement ,
Textbook Various scientific papers, theses, and ASCE and ASTM special publications, International conferences on
expansive soils and unsaturated soils, state-of-the-Art-articles and handouts.
Reference 1. Clay Mineralogy, R.E. Grim, McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1968.
2. Clays, Muds, and Shales, Charles E. Weaver, Elsevier, 1989
Coordinator Dr. Waddah Abdullah
Goals Furnish the student with detailed knowledge of clay mineralogy, the diffuse double layer theory and the
factors influencing the DDL thickness. Conduct soil stabilization with various types of additives. Identify
and stabilize problematic soils such as collapsing soils, dispersive soils, and expansive soils. Design
foundations on swelling/shrinking soils including underreamed pile foundations. Design preloading to
reduce soil compressibility. Design reinforced earth retaining walls. Implementation of the EK principle
for soil remediation.
Learning After successfully completing this course, the students should be able to:
Outc 1. Comprehend the principles of clay mineralogy and their influence on soil behavior.
omes 2. Perform soil stabilization with or without additives in accordance with the nature of the
: problem at hand.
3. Identify and stabilize collapsing soils.
4. Identify and stabilize dispersive soils.
5. Identify, stabilize, predict soil heave, and method of treating expansive soils and best
foundation type of the situation to be dealt with.
6. Design and perform preloading to improve highly compressible soils.
7. Design reinforced earth retaining walls and reinforced earthdams.
8. Design system of vertical sand drains to meet the requirement of time and settlement.
9. Comprehend the principles of electrokinetic processes and apply them to remediate contaminated sites
Pre-Requisites 1. Soil Mechanics 2. Foundation Engineering
by Topic 3. Material Science. 4. Computer skills
Topics 1. Clay mineralogy and diffuse double layer theory. 4 Lecture (50 min. each)
2. Mechanical stabilization. 3 Lecture
3. Stabilization with additives. 5 Lectures
4. Collapsible soils and dispersive soils. 4 Lectures
5. Swelling-shrinking soils. 7 Lectures
6. Preloading and methods for highly compressible soils. 5 Lectures
7. Vertical sand drains. 4 Lectures
8. Reinforced earth and reinforced earth retaining walls. 10 Lectures
9. Electrokinetic processes. 3 Lectures
Computer Usage Mathcad is used to solve problems involved in engineering practice
Assessment and Assignments.. 10% 2 exams @ 20% each 40%
Grad Projects.. 10% Final Exam . 40%
ing
Estimated Engineering Science 1 Credit
Content Engineering Design 2 Credit
Prepared by Dr. Waddah Abdullah Date: Feb 2007
Вам также может понравиться
- FancyДокумент16 страницFancyOso OsoОценок пока нет
- RA055B PPR KaubДокумент13 страницRA055B PPR KaubOso OsoОценок пока нет
- 39 TransportationДокумент7 страниц39 Transportationmpe1Оценок пока нет
- Dynamic Compaction Project SpecificationДокумент10 страницDynamic Compaction Project SpecificationOso OsoОценок пока нет
- An Evaluation of Signalized Intersection System Analysis TechniquesДокумент16 страницAn Evaluation of Signalized Intersection System Analysis TechniquesOso OsoОценок пока нет
- Footpath ErosionДокумент2 страницыFootpath Erosionnikhaacke100% (6)
- Προτυπα -Chapters IndexДокумент15 страницΠροτυπα -Chapters IndexOso OsoОценок пока нет
- Development of Unsignalised Intersection Analysis Procedure for Malaysian Highway Capacity ManualДокумент45 страницDevelopment of Unsignalised Intersection Analysis Procedure for Malaysian Highway Capacity ManualNizam MohamadОценок пока нет
- Cete 37Документ13 страницCete 37NSBMRОценок пока нет
- Intersection CalculatorДокумент8 страницIntersection CalculatorOso OsoОценок пока нет
- Modern Ground Improvement TechniquesДокумент17 страницModern Ground Improvement TechniquesOso OsoОценок пока нет
- Deep Dynamic Compaction: Basic Function Geologic ApplicabilityДокумент2 страницыDeep Dynamic Compaction: Basic Function Geologic ApplicabilityOso OsoОценок пока нет
- WGB 2 Dynamic Compaction June 2008Документ3 страницыWGB 2 Dynamic Compaction June 2008Oso OsoОценок пока нет
- WGB 2 Dynamic Compaction June 2008Документ3 страницыWGB 2 Dynamic Compaction June 2008Oso OsoОценок пока нет
- Bio Enzyme Stabilization Literature ReviewДокумент17 страницBio Enzyme Stabilization Literature Reviewaprabhusolanki100% (2)
- Specialisation Modules For Soil MechanicsДокумент5 страницSpecialisation Modules For Soil MechanicsOso OsoОценок пока нет
- CE1206 Construction Materials Bituminous GuideДокумент22 страницыCE1206 Construction Materials Bituminous Guidevarunsingh214761100% (1)
- Soil Compression and Compaction GuideДокумент30 страницSoil Compression and Compaction GuideOso OsoОценок пока нет
- Deterioration of Bituminous RoadsДокумент84 страницыDeterioration of Bituminous RoadsOso OsoОценок пока нет
- CEN/TC 227 Road Construction and Maintenance Materials: Resolution BT 312/1989Документ29 страницCEN/TC 227 Road Construction and Maintenance Materials: Resolution BT 312/1989Oso OsoОценок пока нет
- Bituminous MaterialsДокумент15 страницBituminous MaterialsPrashant YadavОценок пока нет
- Asphalt and Asphalt Concrete: History Asphalt and Tar Material Engineered Asphalt CementsДокумент29 страницAsphalt and Asphalt Concrete: History Asphalt and Tar Material Engineered Asphalt CementsEldwin Jay L MonteroОценок пока нет
- This Paper Has Been Mechanically Scanned. Some Errors May Have Been Inadvertently IntroducedДокумент12 страницThis Paper Has Been Mechanically Scanned. Some Errors May Have Been Inadvertently IntroducedOso OsoОценок пока нет
- BitumenДокумент35 страницBitumenamanbhu1991100% (5)
- 5 - Pavement Types (Compatibility Mode)Документ16 страниц5 - Pavement Types (Compatibility Mode)Eng-farah Ali AldajaahОценок пока нет
- 3496 9384 1 SMДокумент6 страниц3496 9384 1 SMOso OsoОценок пока нет
- Bitumen Properties 2Документ3 страницыBitumen Properties 2amanbhu1991Оценок пока нет
- An Evaluation of Signalized Intersection System Analysis TechniquesДокумент16 страницAn Evaluation of Signalized Intersection System Analysis TechniquesOso OsoОценок пока нет
- tgp0611 2015 06Документ5 страницtgp0611 2015 06Oso OsoОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Joint Memorandum Circular (JMC) No. 2021Документ49 страницJoint Memorandum Circular (JMC) No. 2021Nicey RubioОценок пока нет
- NDU Final Project SP23Документ2 страницыNDU Final Project SP23Jeanne DaherОценок пока нет
- PB Engine Kappa EngДокумент20 страницPB Engine Kappa EngOscar AraqueОценок пока нет
- M Series CylindersДокумент61 страницаM Series CylindersAndres SantanaОценок пока нет
- QDA Miner 3.2 (With WordStat & Simstat)Документ6 страницQDA Miner 3.2 (With WordStat & Simstat)ztanga7@yahoo.comОценок пока нет
- HealthFlex Dave BauzonДокумент10 страницHealthFlex Dave BauzonNino Dave Bauzon100% (1)
- Camera MatchingДокумент10 страницCamera MatchingcleristonmarquesОценок пока нет
- Bolsas Transfer FKДокумент7 страницBolsas Transfer FKBelèn Caridad Nelly Pajuelo YaipènОценок пока нет
- SC invalidates Ordinance allowing oil depots in Pandacan due to population densityДокумент2 страницыSC invalidates Ordinance allowing oil depots in Pandacan due to population densityMigs Raymundo100% (1)
- Enhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTДокумент10 страницEnhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTMohsin IamОценок пока нет
- Wordbank Restaurants 15Документ2 страницыWordbank Restaurants 15Obed AvelarОценок пока нет
- 2010 Yoshimura Book of SpeedДокумент83 страницы2010 Yoshimura Book of Speedacornwoods_brentОценок пока нет
- Perbandingan Sistem Pemerintahan Dalam Hal Pemilihan Kepala Negara Di Indonesia Dan SingapuraДокумент9 страницPerbandingan Sistem Pemerintahan Dalam Hal Pemilihan Kepala Negara Di Indonesia Dan SingapuraRendy SuryaОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Knowledge and SkillДокумент2 страницыDifference Between Knowledge and SkilljmОценок пока нет
- Nammo Bulletin 2014Документ13 страницNammo Bulletin 2014Dmitry Karpov0% (1)
- Product Catalog: Ductless Mini-Splits, Light Commercial and Multi-Zone SystemsДокумент72 страницыProduct Catalog: Ductless Mini-Splits, Light Commercial and Multi-Zone SystemsFernando ChaddadОценок пока нет
- Rust Experimental v2017 DevBlog 179 x64 #KnightsTableДокумент2 страницыRust Experimental v2017 DevBlog 179 x64 #KnightsTableIngrutinОценок пока нет
- ABN AMRO Holding N.V. 2009 Annual ReportДокумент243 страницыABN AMRO Holding N.V. 2009 Annual ReportF.N. HeinsiusОценок пока нет
- Product Data: Airstream™ 42BHC, BVC System Fan CoilsДокумент40 страницProduct Data: Airstream™ 42BHC, BVC System Fan CoilsMaxmore KarumamupiyoОценок пока нет
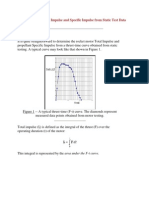
- Determining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test DataДокумент4 страницыDetermining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test Datajai_selvaОценок пока нет
- Business Advantage Pers Study Book Intermediate PDFДокумент98 страницBusiness Advantage Pers Study Book Intermediate PDFCool Nigga100% (1)
- Nmea Components: NMEA 2000® Signal Supply Cable NMEA 2000® Gauges, Gauge Kits, HarnessesДокумент2 страницыNmea Components: NMEA 2000® Signal Supply Cable NMEA 2000® Gauges, Gauge Kits, HarnessesNuty IonutОценок пока нет
- cp2021 Inf03p02Документ242 страницыcp2021 Inf03p02bahbaguruОценок пока нет
- Pass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppДокумент1 страницаPass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppAnoop SharmaОценок пока нет
- E200P Operation ManualДокумент26 страницE200P Operation ManualsharmasourabhОценок пока нет
- Dubai Healthcare Providers DirectoryДокумент30 страницDubai Healthcare Providers DirectoryBrave Ali KhatriОценок пока нет
- AP Statistics - 2014-2015 Semester 1 Test 3Документ4 страницыAP Statistics - 2014-2015 Semester 1 Test 3Camden BickelОценок пока нет
- CCTV8 PDFДокумент2 страницыCCTV8 PDFFelix John NuevaОценок пока нет
- Fleck 3150 Downflow: Service ManualДокумент40 страницFleck 3150 Downflow: Service ManualLund2016Оценок пока нет
- DS 20230629 SG3300UD-MV SG4400UD-MV Datasheet V16 ENДокумент2 страницыDS 20230629 SG3300UD-MV SG4400UD-MV Datasheet V16 ENDragana SkipinaОценок пока нет