Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chemistry Form 4 Definition List
Загружено:
Aliif Ismail0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
168 просмотров3 страницыChemistry Form 4 Definition List defines key terms:
1. An element consists of one type of atom, a compound consists of two or more elements chemically bonded. The atom is the smallest particle of an element.
2. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms, an ion is a positively or negatively charged particle, and isotopes are atoms of the same element with different nucleon numbers.
3. Terms also define relative atomic/molecular mass, empirical and molecular formulas, moles, valence electrons, and bond types like ionic and covalent.
Исходное описание:
chemistry definition list
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документChemistry Form 4 Definition List defines key terms:
1. An element consists of one type of atom, a compound consists of two or more elements chemically bonded. The atom is the smallest particle of an element.
2. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms, an ion is a positively or negatively charged particle, and isotopes are atoms of the same element with different nucleon numbers.
3. Terms also define relative atomic/molecular mass, empirical and molecular formulas, moles, valence electrons, and bond types like ionic and covalent.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
168 просмотров3 страницыChemistry Form 4 Definition List
Загружено:
Aliif IsmailChemistry Form 4 Definition List defines key terms:
1. An element consists of one type of atom, a compound consists of two or more elements chemically bonded. The atom is the smallest particle of an element.
2. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms, an ion is a positively or negatively charged particle, and isotopes are atoms of the same element with different nucleon numbers.
3. Terms also define relative atomic/molecular mass, empirical and molecular formulas, moles, valence electrons, and bond types like ionic and covalent.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
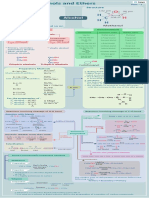
Chemistry Form 4 Definition List
Element a substance Compound a substance Atom smallest particle of an
consists of one type consists two or more elemen element.
of atom. ts that are chemically
bonded(molecule or ions).
Molecule a group Ion Isotopes atoms of the same
of two or more atoms. a positively charged / negati element with same
vely charged particle. proton number but different
nucleonnumbers.
Relative atomic mass Relative molecular mass of Molecule formula compound
of an element = the an element = the average shows the actual number of
average mass of one mass of one atom of an atoms of each element that are
atom of an element/ molecule/((1/12) x the mass present in a molecule of the
((1/12) x the mass of of one carbon-12 atom) compound
one carbon-12 atom)
Empirical formula Mole amount of substance One mole Avogadro constant
compound shows that contains as many 6.02 x 1023
the simplest whole particles as the number of
number ratio of atoms atoms inexactly 12 g of
of each element in the carbon-12 the symbol of
compound mole is mol.
Group (Periodic Table) Periods (Periodic Table) Valence electrons electrons
vertical columns of horizontal rows of that occupy the outermost shell.
element (similar element.
chemical properties).
Ionic bond bond Ionic compound consist Covalent bond bond formed
formed through the of positive ions through the sharing of non-
transfer of electrons and negative ions which are metal electrons to achieve the
between atoms held by strong electrostatic stable duplet or octet electron
of metal andnon-metal t forces of attraction. arrangement.
o achieve the stable
octet electron
arrangement.
Covalent Alkali (base) chemical Acid chemical substance
compound (also simple substance which ionizes in which ionizes in water to
molecular structure) water to produce hydroxide produce hydrogen ions, H+ or
consists of neutral ions, OH-. hydroxonium ions, H3O+.
molecules which are
held by weak
intermolecular forces
(Van der Waals).
pH degree of acidity pH value measure of the Strong alkali ionises
or alkalinity of a concentration of hydrogen (dissociates) completely in
solution. Scale ranges ions, H+. water to form hydroxide ions,
from 0 to 14. OH- of high concentration.
Weak alkali ionises Strong acid ionises Weak acid ionises
(dissociates) partially in (dissociates) completely in (dissociates) partially in water
water to water to to form hydrogen ions, H+ of
form hydroxide ions, form hydrogen ions, H+ of low concentration.
OH- of low high concentration.
concentration.
Polymer long chain
molecules made up by
monomer (repeating
unit).
SPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition List
Effective Homologous series Catalyst a chemical that alter the rate
collision (Collision organic compounds of reaction.
theory) collision (families)
that results in a with similar
chemical reaction formulae and
where the particles properties.
collide with
the correct
orientation and are
able to achieve
the activation energy.
Positive Negative Organic compounds carbon-containing
catalyst increases th catalyst decreases t compound. Carbon atoms
e rate of reaction he rate of reaction form covalent bonds.
& lower the & higher the
activation energy. activation energy
Inorganic Saturated Unsaturated hydrocarbons
compounds hydrocarbons hydrocarbons containing at least one
compounds from non- hydrocarbons carbon-carbon doubleor triple bond.
living things which containing
do not contain the only single bonds
element carbon. between all carbon
atoms.
Esterification esters Vulcanisation Redox reaction chemical reactions
are produced process which makes involving oxidation and reduction occurr
the natural rubber ing simultaneously.
harder and increases
its elasticity by
adding sulphur.
Flavouring improve Stabilisers help to Thickeners substances that thicken
the taste or smell of mix two liquids that food and give the food a firm, smooth
food and restore taste usually do not mix and uniform texture.
loss due to food together so that they
processing. form an emulsion.
Precipitation the Displacement the Neutralisation the heat change
heat change when one heat change when one mole of water is formed from
mole of a when one mole of a the reaction between an acid and an
precipitate is formed metal is displaced alkali.
from their ions in from its salt solution
aqueous solution. by a more
electropositive metal.
Combustion the
heat change when one
mole of a
substance is complete
ly burnt in oxygen
under standard
conditions.
Вам также может понравиться
- SPM Chemistry Definition ListДокумент3 страницыSPM Chemistry Definition ListLooiОценок пока нет
- DefinitionsДокумент6 страницDefinitionsali ahsan khanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryДокумент29 страницChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryNabindra RuwaliОценок пока нет
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxДокумент96 страницAlkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxEgbebessemenow oben ashuОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry NotesДокумент6 страницOrganic Chemistry NotesAzib ZararОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Paper 3 SampleДокумент3 страницыChemistry Paper 3 Samplerihdus2100% (2)
- Matriculation Chemistry Introduction To Organic Compound Part 1 PDFДокумент24 страницыMatriculation Chemistry Introduction To Organic Compound Part 1 PDFiki292Оценок пока нет
- Chemical BondingДокумент51 страницаChemical BondingDaniel MaglalangОценок пока нет
- VSEPR Handout PDFДокумент2 страницыVSEPR Handout PDFAriel ChenОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Syllabus Final VersionДокумент5 страницOrganic Chemistry Syllabus Final VersionYseemaz AzeeraОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemistryДокумент60 страницOrganic ChemistryddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- 19 - Electrochemistry - BДокумент83 страницы19 - Electrochemistry - BLissa HannahОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Notes For Technical SchoolsДокумент44 страницыOrganic Chemistry Notes For Technical SchoolsSheambom NelsonОценок пока нет
- GCE A Levels H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 2Документ20 страницGCE A Levels H2 Chemistry Prelim Paper 2Chong56Оценок пока нет
- Module Acids, Bases, SaltsДокумент7 страницModule Acids, Bases, SaltsAndy TanОценок пока нет
- Quick Revision Paper 3 Section B Physics SPMДокумент7 страницQuick Revision Paper 3 Section B Physics SPMTeoh MilayОценок пока нет
- Al KynesДокумент19 страницAl KynesAnkit JaipuriaОценок пока нет
- Topic 11 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryДокумент102 страницыTopic 11 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryMohamad AzzmerОценок пока нет
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2Документ6 страницLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHOОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Module 3Документ14 страницChemistry Module 3MASHОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsДокумент25 страницChemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsSharmini RajagopalОценок пока нет
- History of Atomic TheoryДокумент16 страницHistory of Atomic TheorySkylar Gevirah100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryДокумент102 страницыChapter 1 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryMELVINDO JACOBОценок пока нет
- Algebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationДокумент3 страницыAlgebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationBruce WalkerОценок пока нет
- Worksheet-Nernst Equation PDFДокумент4 страницыWorksheet-Nernst Equation PDFLedd SleddОценок пока нет
- CH 6 - Organic ReactionsДокумент18 страницCH 6 - Organic Reactionskevincai96Оценок пока нет
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: AtomsДокумент52 страницыSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: AtomsSuyash A.100% (1)
- Worksheet 1 - Chemical BondingДокумент4 страницыWorksheet 1 - Chemical BondingFahd KhanОценок пока нет
- A-Level Chemistry NotesДокумент16 страницA-Level Chemistry NotesMuradОценок пока нет
- 11.alcohol, Phenol & Ethers Colour BookletДокумент84 страницы11.alcohol, Phenol & Ethers Colour BookletVishal Malik100% (1)
- 01.coordination Chemistry Class Notes Part I-1 PDFДокумент86 страниц01.coordination Chemistry Class Notes Part I-1 PDFShadrack Peter100% (1)
- Periodic Table MCQДокумент3 страницыPeriodic Table MCQAbhay Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Chemical Nomenclature For Use in Matriculation Examinations: October 2003Документ13 страницChemical Nomenclature For Use in Matriculation Examinations: October 2003Noni Iranaya NoniОценок пока нет
- Analytical Chem Exam 1 (CH1-3) 4Документ6 страницAnalytical Chem Exam 1 (CH1-3) 4Jules BrunoОценок пока нет
- Notes Functional GroupsДокумент5 страницNotes Functional GroupsFrank GaoОценок пока нет
- 15 Unique Nature of CarbonДокумент17 страниц15 Unique Nature of CarbonlairinОценок пока нет
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersДокумент3 страницыAlcohols Phenols and EthersSubath KumarОценок пока нет
- Alkane, Alkene, AlkyneДокумент36 страницAlkane, Alkene, AlkyneJia ChiОценок пока нет
- Acids Bases and Salts WksheetДокумент2 страницыAcids Bases and Salts WksheetShakwan WatermanОценок пока нет
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationДокумент22 страницыForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationChew Han Hoong0% (2)
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryДокумент41 страницаHard Soft Acid Base TheorythinhbuОценок пока нет
- Guide To SN1 SN2 E1 and E2Документ7 страницGuide To SN1 SN2 E1 and E2كوفيتي رمز اصالتيОценок пока нет
- Alkane Alkene Alkyne Isomer Practice QuizДокумент3 страницыAlkane Alkene Alkyne Isomer Practice QuizJoby Chen100% (1)
- Chem TB PDFДокумент173 страницыChem TB PDFPrudence SitholeОценок пока нет
- Engineering Materials PDFДокумент55 страницEngineering Materials PDFChin MandatoОценок пока нет
- Mgo LabДокумент3 страницыMgo Labapi-336093393Оценок пока нет
- Lab Report Corrosion-1Документ10 страницLab Report Corrosion-1areniqwardiah_918730100% (1)
- Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsДокумент9 страницSummary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compoundsstreetcribdealer100% (1)
- 110 Oxidation NumberДокумент3 страницы110 Oxidation NumberTerry100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Question and AnswerДокумент53 страницыOrganic Chemistry Question and Answergoi_pin100% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Документ18 страницSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Exercise (Tricky)Документ10 страницOrganic Chemistry Exercise (Tricky)chong56Оценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаOrganic Chemistry Cheat SheetGagan Nd0% (2)
- Revision of IsomerismДокумент20 страницRevision of IsomerismAjnish GuptaОценок пока нет
- The Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisОт EverandThe Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListДокумент3 страницыChemistry Form 4 Definition ListSyazana Mohd RosliОценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListДокумент3 страницыSPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListNursafika Bahira100% (1)
- SPM Definition ListДокумент3 страницыSPM Definition ListWong Weng SiongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 24: Fiber Optics: True/FalseДокумент6 страницChapter 24: Fiber Optics: True/FalseChristopher Inoval Paril100% (1)
- Standard Hydrogen Electrode, SHE: © 2017 Pearson Education, LTDДокумент7 страницStandard Hydrogen Electrode, SHE: © 2017 Pearson Education, LTDWilfredОценок пока нет
- BS 3Документ58 страницBS 3abhishekОценок пока нет
- Sebatian AromatikДокумент100 страницSebatian AromatikGanthimathi SugumaranОценок пока нет
- انتاج اوكسيد الاثيلينДокумент53 страницыانتاج اوكسيد الاثيلينسرى العبيديОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Modeling and Process Optimization of Sulfuric Acid PlantДокумент9 страницDynamic Modeling and Process Optimization of Sulfuric Acid PlantchikukotwalОценок пока нет
- Charged Water Gas ElectrolyzersДокумент139 страницCharged Water Gas Electrolyzersmalte1134100% (1)
- Ultrahigh Piezoelectricity in Ferroelectric Ceramics by DesignДокумент7 страницUltrahigh Piezoelectricity in Ferroelectric Ceramics by DesignGabriel MoreiraОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Financial Statement Analysis 11th Edition by Subramanyam PDFДокумент61 страницаSolution Manual For Financial Statement Analysis 11th Edition by Subramanyam PDFMNHS67% (3)
- Gel Permeation ChromatographyДокумент37 страницGel Permeation ChromatographyNofrizalОценок пока нет
- Frank N. Trager - Springer Handbook of Lasers and Optics-Springer (2007) PDFДокумент1 342 страницыFrank N. Trager - Springer Handbook of Lasers and Optics-Springer (2007) PDFNguyễn TúОценок пока нет
- 4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics Spring 2013: Homework #9Документ2 страницы4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics Spring 2013: Homework #9Henry NgoОценок пока нет
- Coal GasificationДокумент11 страницCoal GasificationPratik RanjanОценок пока нет
- GCSE Practical Guide Chemistry ElectrolysisДокумент12 страницGCSE Practical Guide Chemistry Electrolysisr aОценок пока нет
- Performance Characterization of Sunpower Free-Piston Stirling EnginesДокумент6 страницPerformance Characterization of Sunpower Free-Piston Stirling EnginesDanny DurhamОценок пока нет
- CH U3 A1 Atomic History WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCH U3 A1 Atomic History WorksheetАбдурахман Псикс0% (1)
- Surface TensionДокумент50 страницSurface TensionbagheldhirendraОценок пока нет
- Ekstraksi Palladium Dari PCB Dengan Asam Nitrat - Solvent Ekstraksi Dan Precipitasi AmoniaДокумент10 страницEkstraksi Palladium Dari PCB Dengan Asam Nitrat - Solvent Ekstraksi Dan Precipitasi AmoniaAde SatriaОценок пока нет
- Industrial Refrigeration TrainerДокумент2 страницыIndustrial Refrigeration TrainerEugine BalomagaОценок пока нет
- Radial Heat Conduction ExperimentДокумент13 страницRadial Heat Conduction ExperimentqwertyasdОценок пока нет
- Study On The Heat Load Characteristics of Underground StructuresДокумент9 страницStudy On The Heat Load Characteristics of Underground StructureskylealamangoОценок пока нет
- 02 - Les Differents Voix Du SynthéseДокумент312 страниц02 - Les Differents Voix Du SynthéseChërchěf DjămiīlåОценок пока нет
- Gas - Dynamics Turrell 1997Документ164 страницыGas - Dynamics Turrell 1997B Rajha BharathiОценок пока нет
- SpectrosДокумент71 страницаSpectrosAshraf MambalamОценок пока нет
- Ice CH3 2019 2020Документ38 страницIce CH3 2019 2020مصطفى سعيد سعد برغوث 201810526Оценок пока нет
- Nov 24th 2014 Monday: Products DetailsДокумент1 страницаNov 24th 2014 Monday: Products DetailsXuân Giang NguyễnОценок пока нет
- To Study Rate of DiffusionДокумент17 страницTo Study Rate of DiffusionShlok Singh100% (1)
- SMJC 2701 Exp2Документ14 страницSMJC 2701 Exp2norsiahОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Polymer BlendsДокумент612 страницHandbook of Polymer BlendsKaihuanZhangОценок пока нет
- RTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 6Документ11 страницRTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 6Vincent Vetter100% (1)