Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Antiarrhythmics
Загружено:
Solomon Seth SallforsАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Antiarrhythmics
Загружено:
Solomon Seth SallforsАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Antiarrhythmics
no longer used for rhythm control, modestly effective, very Increased TdP = hypotension syncope
toxic and sudden death within the 1st few
Moderate Na channel Blocker which supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias like atrial days; Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal
also blocks K channelsprolongs fibrillation & atrial flutter (moderately effective), ventricular cramping; Cinchonism = vertigo, HA,
QRS&QTaction potential; reduce extrasystoles and VT(poorly effective) tinnitus, psychosis, blurred vision; rash, Do not use in pt with long QT Rarely used;has a vasodilator effect so can be used in reduced
Quinidine (Antiarrhythmic automaticity and conduction velocity Major clinical use: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, & thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia;lupoid syndrom, TdP history, or vent function or HF; also has a indirect anticholinergic effect that
Class IA) (Phase 0 and phase 3) ventricular tachcycardia hepatitis and 2X to 3X increase in mortality hypokalemia (increases TdP) Put Na in your tonic and call it quinidine will decrease vagal tone and may facilitate condion in the AV node
Na channel blocker; Prolongs APD
and refractoriness (K channel effect);
slows conduction and decreases
automaticity and excitability of the
myocardium and Purkinje fibers. N- Used for Supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias;
acetyl-procainamide (procainamide acute re-entrant supraventricluar tachycardia and atrial fib and Salty (Na) old man weiding his cain in NAPA
metabolite) prolongs APD and flutter associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome valley, whacking hot Lupus chick, giving her Absorbed rapidly and is 100% orally bioaviable; i.v. loading
Procainamide refractoriness in atrial and venticular (see extra notes) lupus-like syndrome!! arrhythmia may be Do not use in pt with long QT butterfly rash; Rem: its not HIPP to get drug dose must be given slowly, so limited to clinical situations with
(Antiarrhythmic mixed myocardium and prolongs the QT Major clinical use: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, & aggravated, development of TdP; syndrom, TdP history, or induced-LE - (Hydralizine, INH, Phenytoin, adequate time available; Does not increase digoxin levels;
Class IA & III) interval. (Phase 0 and phase 3) ventricular tachcycardia agranulocytosis, BM depression hypokalemia Procainamide) cimetidine and ranitidine decrease clearance 10-50%
moderate Na channel blocker: Increase Broad range of supraventricular and ventricular
venticular refractoriness and prolong the arrhythmias (similar to procainamide and quinidine) Loading dose not recommented, risk of HF or anticholinergic SE;
QT inverval (reduces automaticity and Moderately effective for atrial arrhythmia and poorly effective rapid fluctuations in plasma concentration; Phenytoin, rifampicin,
conduction velocity - phase 0), also for ventricular arrhythmia Remember: dis o' pyramid sitting in sand of Na, and phenobarbital increase hepatic metabolism (elimination);
Disopyramide increases AP duration. (Phase 0 and Major clinical use: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, & anticholinergic SE - stops peeing, can't piss or poop (anticholinergic), just wants 1 depression of contractility from co-admin with beta-adrenergic of
(Antiarrhythmic Class IA) phase 3) ventricular tachcycardia pooping, salivating impaired ventricular function Ass (1A) movement CCB
Class 1B
Reduce automaticity
CNS symptoms: seizures!! (mental Shorten APD (narrow QRS)
modest Na channel blockers (both acute rapid suppression of V arrhythmias, raises status changes), drowsiness, dyarthria, Slow conduction velocity
active and inactive Na channels) ventricular fibrillation threshold as well as suppresses dysesthesi, and coma; can depress cardiac Remember: class I be (B) ventin (works only on Have little or no effect on atrial tissue
Reduce automaticity arrhythmias caused by abnormal automaticity (observed pt function leading to decreased clearance, ventricle) with the short fuse temper (shortens all other classes work above ventricles
Lidocaine (Antiarrhythmic Shorten APD (narrow QRS) continuoulsy for SE), no atria effect; very effective membrane and produce greater SE; sinus node AP) Moderately effective for ventricular arrhythmia
Class IB) Slow conduction velocity stabilizer (numbing) dysfunction only used for V!!
CNS symptoms: seizures!! (mental
modest Na channel blockers (both status changes); dose related tremor, Remember: the Mexican (Mexiletine) injected
active and inactive Na channels) ventricular arrhythmias & refractory arrhythmias; useful in visual blurring, dizziness, dysphoria, and his toe (tocainamide) with lidocaine to numb Typically hepatic metabolism (CYP2D6), can be increased with
Reduce automaticity pts with torsades de pointes (TdP) or long QT syndrome (if nausea; thrombocytopenia and postivie the 1 Bee sting (class IB), but goes into a phenobarbital, phenytoin, or rifampicin; Pts with hepatic CYP2D6
Mexiletine (Antiarrhythmic Shorten APD (narrow QRS) other drugs contra), no effect in atrium; very effective ANA; worsen heart block with high seizure and wishes he'd injected dilantin deficiency are dependent on renal excretion. (notice, quinidine
Class IB) Slow conduction velocity membrane stabilizer (numbing) concentration instead inhibits the CYP2D6 Ez)
modest Na channel blockers (both
active and inactive Na channels)
Reduce automaticity
Tocainamide Shorten APD (narrow QRS)
(Antiarrhythmic Class IB) Slow conduction velocity similar to lidocaine
Effective for Atypical Ventricular Tachycardia;
Phenytoin [Dilantin] more typically used for seizures (also a membrane stabilizer,
(Antiarrhythmic Class IB ) Na channel blocker arrthymia in brain) Remember: die laughing so had a seizure
highly effective Na channel blocker; proarrhythmia!!; CHF; CNS=blurred drug interactions: cimetidine
Prolongs PR and QRS (prolongs AP), Potent inhibitor of ventricular arrhythmia; effective vision, headache, ataxia;decreases LV its clearance its half-life;
Flecainide (Antiarrhythmic reduces automaticity and conduction stabilization of atrial rhythm; supraventricular arrhythmias in function and depresses the SA node in pt digoxin, propranolol, & Remember: flick a cain in someones one eye eliminated by the liver (CYP2D6) and kidney(so not effected by
Class IC) velocity in A and V; negative inotrope pt with no structural heart dz with SA node dysfunction amiodarone its levels and they can't see (1C) CYP2D6 deficiency except in renal insufficiency)
highly effective Na channel blocker;
Prolongs PR and QRS (prolongs AP),
Encainide (Antiarrhythmic reduces automaticity and conduction Potent inhibitor of ventricular arrhythmia; effective
Class IC) velocity in A and V; negative inotrope stabilization of atrial rhythm; proarrhythmia!!
highly effective Na channel blocker; drug interactions: increases
Prolongs PR and QRS (prolongs action digoxin, theophylline,
potential), reduces automaticity and (similar to Flecainide) many arrhythmias, supraventricular cyclosporine levels and warafin
conduction velocity in atria and arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation in pt w/o structural heart dz; effects;cimetidine increases its eliminated by the liver CYP2D6; if CYP2D6 deficiency have slow
Propafenone ventricles; negative inotrope; structurally potent inhibitor of ventricular arrhythmia; effective proarrhythmia!! nausea, vomiting, metallic levels;phenobarbital, phenytoin, Prop a phone against Kofi in one sea (1C), the elimination of propafenone and develop significant receptor
(Antiarrhythmic Class IC) similar to propanolol so= blocker stabilization of atrial rhythm taste to food rifampin decreases its levels sea is rough (proarrhythmia) antagonism at low doses
Dofetilide (Antiarrhythmic
mixed Class IC & III) similar to Flecainide similar to Flecainide similar to Flecainide
See adrenergics; indirect effect via
reduction of sympathetic receptor activity
and membrane stabilizing activity; mild Severe systolic heart failure
effect on automaticity and conduction ventricular tachycardia, supraventricular arrhythmias, also (from massive myocardial
velocity; greatest effect is to slow AV AV node re-entry, atrial fibrillation, and atrial flutter; congenital damage, RV infarction, or acute
node conduction, also decrease SA long QT syndrome; prevents recurrent episodes of high doses=fatigue and depression; valvular regurgitation) and
node automaticity and increase AV node ventricular tachycardia and reduces symptoms of bronchospasm, bradycardia and AV block, active wheezing from reactive esmolol, ultra short half life=9min, used for atrial fibrillation and
refractory period palpitations and sudden death in pt w/ prior MI myocardial contractility, impotence, CHF airway dz atrial flutter after surgery
proarrhythmia, bronchospasm, worsens
heart failure;instability in pt w vent Remember: Jaba the Hut saying Sotolol
& K & Na & Ca channel blocker; arrhythmias post MI;TdP in those w (meaning solo) for Han Solo, who is a master
prolongs QT interval and cardiac bradycardia, prolonged QT intervals, and bounty hunter and will pull in any criminal,
Sotolol (Antiarrhythmic refractoriness;slows sinus rate and all types of arrhythmias ie supravent and vent arrhythmias, hypokalemia;normal side effects of including & K & Na & Ca channel blocker almost as good as amiodarone; eliminated by the kidney w half life
Class III) negative inotrope (slows repolarization) cannot be used in patients with heart failure blockers criminals of 12hrs
Irreversible pulm fibrosis!!
Hepatotoxicity (jaundice and cirrhosis);
hype- & hyporthyroidism, corneal
deposits; agranulocytosis, bluish
discoloration of skin & photodermatitis,
nausea, constipation, bradycardia, Remember: Amy and Yoda sitting together
& K & Na & Ca channel blocker; ONLY used for life-threatening (refractory) Ventricular hypotension with IV due to contractility eatting bananas (K), yoda got corneal deposits
Amiodarone prolongs PR and QT; slows sinus rate arrhythmias or Atrial fibrillation unresponsive to other and peripheral vascular resistance in eyes and is bitch'n because he has
(Antiarrhythmic Class III; (slows repolarization); prolongs AP in antiarrhythmatics (AV nodal re-entrant tach and Wolff- 1-2% chance proarrhythmia (long QT drug interactions: digoxin and pulmonary fibrosis and toxic liver, but stoked
has class I, II, III, and IV fast-response AP and prolongs effective Parkinson-White syndrome and sudden death post MI or HF) syndrome; should first be started on an inpt cyclosporine levels and cause he can have a prolonged orgasm (half metabolized to desethyl metabolite (DEA) in the liver; half life of
activity) refractory period Most efficacy of rhythm control among the antiarrhythmics basis) wafarin effects life) 5hrs to 30days (Cecil says 103days); IV HAS A RAPID EFFECT
dont give to those w
TdP (esp in women w vent function or hypokalemia,
Ibutilide (Antiarrhythmic K channel blocker; prolongs PR and QT electrolyte disoders--all TdP), heart hypomagnesemia or a QTc
class III) (slows repolarization) atrial fibrillation or flutter block, hypotension, nausea >440msec oxidative hepatic metabolism and cleared by the kidney
TdP; drug interactions which increase Rem: Do fret, I lied (Do-fet-i-lide)
levels: erythromycin, diltiazem, cimetidine, - though your heart can be fixed
Dofetilide (Antiarrhythmic atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation; maintenance of sinus or ketoconazole; causes massive by bananas (K), it causes eliminated by liver (CYP3A4) and kidney; half life=8-10 hrs but
class III) K channel blocker; prolongs QT rhythm after reversion diarrhea! massive diarrhea 12% to 18% lower in women
Dihydropyridine group
(nifedipine, amlodipine,
nitrendipine, isradipine, Ca channel blockers (CCB), SM
nisoldipine -- selective; see renal CCB; slow reflex tach due to vasodilation; edema
Antiarrhythmic class IVs) conduction velocity, phase 0 of node small effect on AV conduction and arrhythmia and orthostatic hypotension
Ca channel blocker; slows AV node
Diltiazem (non- conduction (moderately), myocardial
dihydropyridine selective; slows conduction velocity, slows vent rate with atrial fibrillation or flutter and moderate in LV contractility,
antiarrhythmic class IV) phase 0 of node prevents AV nodal re-entrant tach bradycardia and hypotension
CCB: Most potent to AV node
conduction (also SA node); negative
inotrope; myocardial selective; slows Indicated for atrial fibrillatoin and atrial flutter; V response peripheral edema, moderate in LV
Verapamil (non- conduction velocity (phase 0) and in SVT and slows V rate w/ A fib or flutter and prevents AV contractility (V. Fib.) and hypotension
dihydropyridine increase refractoriness in tissues with nodal re-entrant tach; HTN and peripheral vasospasm (peripheral vasodilation); constipation; CHF (because of decreased
antiarrhythmic class IV) slow-response AP disorders hemodynamic collapse inotropic effect)
promotes atrial and vent irritability;
slows AV node conduction (Vagotonic hypokalemia, loss of appetite, nausea,
action), and depress SA node; vomiting, diarrhea, blurred vision & yellow-
conduction velocity and slows V green halos (xanthopsia), confusion,
response to SVT; force of heart drowsiness, dizziness, nightmares, Wolff-Parkinson-White
contraction via inhibition of the Na+/K+ agitation,depression; do not give with syndrome (direct
Digoxin (digitalis) see also ATPase pump less Na to trade for Ca Atrial fibrillation & atrial flutter; and CHF not be controlled quinidine (displaces digoxin from binding connection/reentry tachy - dig
above - cardiac glycosides to exit cell by other med (not antiarrhythmic) sites on albumin) would exacerbate) derived from digitalis
facial flushing, dyspnea, or chest pressure dont use for AFib, sick sinus
DOC for acute Paroxysmal SVT caused by re-entry thru AV lasts <60 sec; sometimes nausea, syndrome, or 2 and 3 heart
Adenosine (antiarrhythmic Slows AV node conduction - causes node; lightheadedness, headache, sweating, block unless they have a Half life of 1.5 to 10 sec (shortest half life of any drug);
class V) transient heart block in the AV node diagnostic tool (see extra notes) palpitation, hypotension and blurred vision pacemaker metabolized in the plasma
Prolongs APD and refractoriness (K
channel effect); slows conduction and
decreasses automaticity and excitability
of atrial and ventricular myocardium and
Purkinje fibers. N-acetyl-procainamide
(aka NAPA, procainamide metabolite)
prolongs APD and refractoriness in atrial
and venticular myocardium and polongs Used for Supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias Absorbed rapidly and is 100% orally bioaviable; i.v. loading
the QT interval (Reduce automaticity (similar to quinidine, used if quinidine not effective); acute re- Arrhythmia may be aggravated, Do not use in pt with long QT dose must be given slowly, so limited to clinical situations with
Procainamide and conduction velocity effects phase entrant supraventricluar tachycardia and atrial fib and development of TdP; lupus-like syndrome, TdP history, or adequate time available; Does not increase digoxin levels;
(Antiarrhythmic Class III) 4 and 0) flutter associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome syndrome; agranulocytosis hypokalemia cimetidine and ranitidine decrease clearance 10-50%
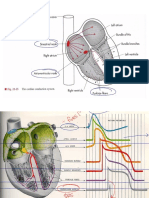
Action Potential All phases common to nodal and non-nodal Electrolyte shift in Atrial or Ventricular tissue (non-nodal) Electrolyte shift in Nodal Tissue
Class 1A: Electrolyte shifts create electrical activity Phase 0: Rapid depolarization Phase 0: Sodium Phase 0: Calcium and Sodium
1. Reduce automaticity (phase 4, reduce slope of upstroke, ALL Antiarrhythmic drugs have narrow therapeutic Four phase action potential demonstrates the various Phase 1: Depolarization overshoot Phase 1: Sodium channel closes Phase 1: Sodium channel????????
AP becomes broader) index, variable metabolism and clearance; many stages of activity Phase 2: Plateau Phase 2: Calcium channel open Phase 2: Calcium channel
2. Prolong action potential duration Drug interactions: increases digoxin level and warfarin (especially class I) inhibit Cytochrome P-450 (which is Electrolytes associated with each phase differ in nodal Phase 3: Repolarization Phase 3: Potassium rectifier Phase 3: Potassium rectifier All class I anti-arrhythmic agents are use-
3. Reduce conduction velocity (phase 0, slope also reduced) effect;heparin, verapamil, cimetidine increases its levels; absent in 7% caucasians and 2% blacks); many drug eliminated mainly by the liver and some by the kidney; elderly vs. non-nodal tissue Phase 4: Instrinsic depolarization Phase 4: Sodium leak Phase 4: Sodium leak dependent, meaning that they tend to be more acive
Note: (phase 3 affected, not 4, according to Lange) phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin decreases its level interactions requires lower dose due to reduced clearance at ion channels that are depolaring more frequently
Antiarrhythmic Class III: prolong duration of cardiac action
potential (AP) and refractoriness;most potent class of Class 1A effects also (procainamide is a mixed class drug) WPW syndrome is best txed with a class IA agent which increase refractoriness of the bypass track and "break" the reentry
antiarrhythmic drugs, effective for rhythm disturbances in all Reduce automaticity (phase 4, reduce slope of upstroke, AP tachyarrhythmia. Other agents (adenosine, BB, and digoxin (&CCB?) should be avoided in a wide complex preexcitation
tissues; combo of blocker, Ca channel blocker and Na becomes broader) syndrome such as WPW because they may accelerate the ventricular rate and cause the rhythm to degenerate to Vfib (these
Channel blocker along with primary effect on repolarization Prolong action potential duration agents act by inhibiting the AV node and thus increase conduction down accessory pathway; also class IB agents shorten the
current (basically does everything the other classes do put Reduce conduction velocity (phase 0, slope also reduced) repolarization by decreasing the AP duration and thus also can increase the ventricular response to an SVT). If a pt has
together) evidence of WPW on ECG and is hemodynamically unstable, DC cardioversion should be first-line therapy
Disopyramide:
Moderately effective for atrial arrhythmia and poorly effective for
Antiarrhythmics: limited usefulness because of toxicity and ventricular arrhythmia
lack of efficacy; may worsen mortality. Every agent has Antiarrhythmic Class I (A, B, & C): local anesthetic or Reduces automaticity and conduction velocity
Antiarrhythmic Class IA include quinidine, procainamide, potential for serious toxicity. Classified according to membrane-stabilizing activity; block fast inward Na Side effects include decreased contractility and urinary retention
and disopyramide - increase venticular refractoriness and electrophysiology (see Cecil 341) for Vaughan William s Class channel, decreasing maximum depolarization rate, Vmax, has anticholinergic effects - stops peeing, pooping, salivating
prolong the QT inverval (I, II, III, & IV) of the AP (phase 0); basically Na Channel Blockers
Antiarrhythmic Class Class IB include lidocain, mexiletine, Synergistic depression of myocardial function with combo of Lidocaine works on slightly depolarrized or ischemic tissue Note: Infiltration of inflammation mediators and necrotic materials
and tocainide - modest Na channel blockers that shorten other antiarrhythmic agents (especially propranolol). Pts with more so than normal tissue, due to its state-dependent lower tissue pH (eg abcess) and render lidocain anestheic less
the action potential duration (APD) and refractoriness with heart failure (HF) achieve lidocaine levels that are double blocking. Therefore, use lidocaine (IV) to suppress acute effective (lidocaine is a weak base, does not work when
little effect on PR, QRS, or QT intervals the levels of normal pts (reduce dose by half) MI-associated ventricular arrhythmias protonated)
Class 1C
Antiarrhythmic Class Class IC include flecainide and Reduce automaticity and conduction velocity in atria and Class IC do same thing as class1A, but more powerful
propalenone - potent Na channel blockers that slow ventricles very powerful side effects, the worst SE is accutally
conduction velocity, little effect on repolarization, and increase Prolong action potential duration worsening arrhythmia
PR and QRS intervals, little change on QT interval Major side effect is proarrhythmia Class IC kills people; thus, they are not used as first line agents
Benefits of IV BB therapy early in acute infarction
reduces myocardial O2 consumption (negative
Antiarrhythmic Class II: beta adrenergic antagonist, effective inotropic and chronotropic actions) and has a direct
for supraventricular arrhythmias and tachyarrhythmias caused Premature ventricular contraction (PVC) - common in pts antiarrhythmic effect. Do not withhold in pts with sinus
by excessive sympathetic activity; limited efficacy for severe, with and without HD (found in 60% of adults on Holter bradycardia, diabetes, or well-controlled asthma (all BB are beneficial in longterm tx of pts follwing MI if they have
life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias; mech unknown; only monitoring), do no specifically suggest any underlying dz, relavite contraindications) - rhythm disturbances tend to be evidence of recurrent ischemia or have sustained a Q-wave MI
drugs effective in preventing sudden cardiac death with usually requires no tx; beta blocker would be DOC if it effects reversibble and are easily treated with temoproary pacing (give BB, ACEI and ASA). Howevere, BB have no benefit in pts
MI survivors daily life of pt if symptomatic with small or non-Q-wave MI (give ACEI and ASA)
Most potent class of antiarrhythmic agents (meaning Class III)
Effective for rhythm disturbance in all tissues
Agents possess combination of mild beta blocker, calcium
channel blocker and sodium channel blocker activity along
with primary effect on repolarization current (K current)
Amiodarone:
prolonged half-life of 30 days - makes difficult to use to
reach steady state (4-5 half lives) requires half a year (3
months for effect), and if make a mistake, takes 5 half lives to
get ride of , must follow pt closely (have foresight)
Rapid effect when given IV
Side Effects
Hepatotoxicity
Hypo and hyperthyroidism
Corneal deposits hypothyrodism SE either as a result of its high iodine content Dose dependent toxicity especially with long-term use
Irreversible pulmonary fibrosis (permanent) or by inducing thyroiditis (avoid use in young pts) Increased AP duration causes the increase in QT interval
Antiarrhythmic Class IV: Ca channel antagonists; dont
affect the Phase2 plateau???; poor effect as direct
antiarrhythmic for atrial or vent arrhythmias, most effective
on slowing conduction velocity (Phase 0) in nodal
tissues; useful for the control of vent rate in SVT
CCB and beta blockers have ~same effect in heart - slow
conduction velocity in the AV node (prevent SVT from getting
to V)
When macula densa sense increase NaCl, they send signal (via extraglomerular mesanginum) to granular cells to secret
Used diagnostically to determine whether ventriclar drug interactions: carbamazepine and dipyridamole adenosine which vasoconstricts primarily the afferent a. (know that in most areas of the body adenosine is a vasodilator,
tachycardia was induced supraventricularly or pretreatment its potency; caffeine and theophylline not so in the kidneys), decreasing GFR (moderate constriction; if severe constriction then GFR decreases because blood
ventricularly antagonize it flow becomes so stagnant that proteins clog up on exam always assume moderate efferent a. constriction)
Procainamide:
Moderately effective for atrial or ventricular arrhythmia
Metabolized in liver to active component NAPA
this metabolite is more effective (acetly group)
must check prodrug and metabolite to prevent toxcity
Reduce automaticity and conduction velocity
effects phase 4 and 0
Antiarrhythmic Class III: prolong duration of cardiac action Universal adverse effect is lupus
potential (AP) and refractoriness
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Neuro Written I TablesДокумент6 страницNeuro Written I TablesSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Know The Risks: Opioid Addiction ResourcesДокумент17 страницKnow The Risks: Opioid Addiction ResourcesWKYC.comОценок пока нет
- Pfizer CSRДокумент68 страницPfizer CSRShawkat HaiderОценок пока нет
- Master Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery Knee11Документ1 139 страницMaster Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery Knee11hasla16Оценок пока нет
- Neuro Written II TablesДокумент10 страницNeuro Written II TablesSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Neuro Written II Tables AddendumДокумент3 страницыNeuro Written II Tables AddendumSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Learn Ejaculatory Control in 4 Easy StepsДокумент3 страницыLearn Ejaculatory Control in 4 Easy StepsWilliam PayneОценок пока нет
- Blood TransfusionДокумент52 страницыBlood TransfusionAnonymous GC8uMx367% (3)
- Documento15 Drug Calculation Practice AtriajobsДокумент21 страницаDocumento15 Drug Calculation Practice AtriajobsVendiОценок пока нет
- Peterson, Severin - A Catalog of The Ways People Grow PDFДокумент383 страницыPeterson, Severin - A Catalog of The Ways People Grow PDFvivaldioz100% (2)
- Hemodynamics CILДокумент42 страницыHemodynamics CILSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- 24 Valve DisordersДокумент3 страницы24 Valve DisordersSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- AnginaДокумент30 страницAnginaSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Shock ChartДокумент1 страницаShock ChartSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Cardio My Opa Thies ChartДокумент2 страницыCardio My Opa Thies ChartSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Cardiomyopathy Self StudyДокумент3 страницыCardiomyopathy Self StudySolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- AV Block Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент1 страницаAV Block Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Drug TableДокумент3 страницыDrug TableSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Ecg ReviewДокумент27 страницEcg ReviewSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- AtrialArrhythmias ChartДокумент4 страницыAtrialArrhythmias ChartSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure ChartДокумент3 страницыHeart Failure ChartSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Cardiovascular Radiography: Spencer M. Smith, M.D. August 24, 2007Документ49 страницIntroduction To Cardiovascular Radiography: Spencer M. Smith, M.D. August 24, 2007Solomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Classified Cardiac Arrhythmia MechanismsДокумент1 страницаClassified Cardiac Arrhythmia MechanismsSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Part of Aorta Main Branch: AscendingДокумент5 страницPart of Aorta Main Branch: AscendingSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Epidemiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment EndocarditisДокумент1 страницаEpidemiology Clinical Features Diagnosis Treatment EndocarditisSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Neuro Practical II TablesДокумент4 страницыNeuro Practical II TablesSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- SyncopeДокумент2 страницыSyncopeSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- FormulasДокумент3 страницыFormulasSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Reproductive Exam TablesДокумент6 страницReproductive Exam TablesSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Big Drugs!!Документ2 145 страницBig Drugs!!Solomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Book ListДокумент3 страницыBook ListSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Listen (Echo, Repeat Back) Elicit Info (OLDCARTS) Give Info Respect Empathy ProfessionalismДокумент1 страницаListen (Echo, Repeat Back) Elicit Info (OLDCARTS) Give Info Respect Empathy ProfessionalismSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Neuro Practical I TablesДокумент9 страницNeuro Practical I TablesSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- Neuro Written III TablesДокумент5 страницNeuro Written III TablesSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Well Woman LabДокумент2 страницыWell Woman LabSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Cardiopulmonary I Tables PDFДокумент4 страницыCardiopulmonary I Tables PDFSolomon Seth SallforsОценок пока нет
- Top200PharmaceuticalProductsByWorldwideSalesin2009 PDFДокумент1 страницаTop200PharmaceuticalProductsByWorldwideSalesin2009 PDFLê Trịnh Hoàng DươngОценок пока нет
- The Role of Fathers in Childhood DevelopmentДокумент4 страницыThe Role of Fathers in Childhood DevelopmentRaúl HuapayaОценок пока нет
- Depression in Children and AdolescentsДокумент16 страницDepression in Children and AdolescentsAvimar JuniorОценок пока нет
- Israel Regardie, Initiation, and PsychotherapyДокумент9 страницIsrael Regardie, Initiation, and PsychotherapyMetcher Maa AkhiОценок пока нет
- Geriatopia: A Remediation ScapeДокумент4 страницыGeriatopia: A Remediation ScapeJoch CelestialОценок пока нет
- HCF Corporate Products BrochureДокумент15 страницHCF Corporate Products BrochureKrishnadas MОценок пока нет
- Stress Management: Estrella D. Brigole Chief - Regional Training Unit DSWD Field Office XIДокумент25 страницStress Management: Estrella D. Brigole Chief - Regional Training Unit DSWD Field Office XIRabhak Khal-Hadjj100% (1)
- EBM Prof Darwin 1. Introduction - Prof SudigdoДокумент49 страницEBM Prof Darwin 1. Introduction - Prof SudigdoMelda Amalia Sikumbang100% (1)
- Get Rid of StammeringДокумент8 страницGet Rid of StammeringRajveer RajОценок пока нет
- Q.P. Code: 302342Документ14 страницQ.P. Code: 302342srinivasanaОценок пока нет
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraДокумент57 страниц7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya ArhОценок пока нет
- ActelionДокумент124 страницыActelionSilviu CiocianuОценок пока нет
- 2013DRAFTMEMSProtocols062713 PDFДокумент134 страницы2013DRAFTMEMSProtocols062713 PDFMarian Ioan-LucianОценок пока нет
- revision 復健科Документ4 страницыrevision 復健科屏頂大Оценок пока нет
- Sense of TasteДокумент13 страницSense of TastefihaОценок пока нет
- NCP NSD 2Документ3 страницыNCP NSD 2Warren Bilog OleaОценок пока нет
- AchondroplasiaДокумент3 страницыAchondroplasiaramziaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study 8Документ3 страницыDrug Study 8Vicky RoqueОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Physical Agents Theory and Practice 3rd Edition Barbara J Behrens Holly Beinert DownloadДокумент11 страницTest Bank For Physical Agents Theory and Practice 3rd Edition Barbara J Behrens Holly Beinert Downloadryanparker18011988fno100% (20)
- Hematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsДокумент15 страницHematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsChompz MuMu PhantarsОценок пока нет
- Phytochemical and Pharmacological Screening of Combined Mimosa Pudica Linn and Tridax Procumbens For in Vitro Antimicrobial ActivityДокумент4 страницыPhytochemical and Pharmacological Screening of Combined Mimosa Pudica Linn and Tridax Procumbens For in Vitro Antimicrobial Activityimyourfan2001Оценок пока нет
- Oral Zinc Sulphate in Treatment of Alopecia Areata Double Blind Cross Over Study 2155 9554.1000150Документ4 страницыOral Zinc Sulphate in Treatment of Alopecia Areata Double Blind Cross Over Study 2155 9554.1000150ErtyWitalayaL.ToruanОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan & Drug Study Set #1: PneumoniaДокумент6 страницNursing Care Plan & Drug Study Set #1: PneumoniaBakushidoОценок пока нет