Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
All Meds List
Загружено:
jacky0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
86 просмотров7 страницThis document lists 11 medications including their classifications, dosages, physiological activities, purposes, side effects, and nursing implications. It provides a concise yet comprehensive reference for common orthopedic medications. Key drugs discussed include aspirin, iron supplements, vitamins, acetaminophen, celecoxib, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and famotidine. For each, the summary outlines its intended use, potential adverse effects, and factors nurses should monitor when administering or overseeing the medication.
Исходное описание:
medlist
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document lists 11 medications including their classifications, dosages, physiological activities, purposes, side effects, and nursing implications. It provides a concise yet comprehensive reference for common orthopedic medications. Key drugs discussed include aspirin, iron supplements, vitamins, acetaminophen, celecoxib, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and famotidine. For each, the summary outlines its intended use, potential adverse effects, and factors nurses should monitor when administering or overseeing the medication.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
86 просмотров7 страницAll Meds List
Загружено:
jackyThis document lists 11 medications including their classifications, dosages, physiological activities, purposes, side effects, and nursing implications. It provides a concise yet comprehensive reference for common orthopedic medications. Key drugs discussed include aspirin, iron supplements, vitamins, acetaminophen, celecoxib, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and famotidine. For each, the summary outlines its intended use, potential adverse effects, and factors nurses should monitor when administering or overseeing the medication.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 7
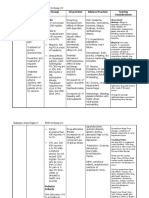
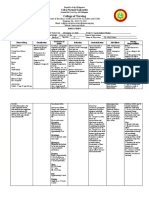
HOI: Hoag Orthopedic Institute Medications List p.
Range: Deficiency 2 3 mg/kg/day in
1. Aspirin, Chewable Aspirin tablet 2 4 divided doses or 60 100 mg
Classification: Antipyretic, non-opioid elemental iron twice daily. Prophylaxis
analgesic 60 100 mg elemental iron daily.
Dosage: 80-325 mg/daily Physiologic activity: An essential mineral
Physiological Activity: Inhibit the found in hemoglobin, myoglobin, and
production of prostaglandins and many enzymes.
decreases platelet aggregation Purpose: A type of Iron that is an
Side effect: EENT: Tinnitus, GI: essential body mineral. Used to treat
increased bleeding, dyspepsia, Iron deficiencies, anemia (Lack of RBC
epigastric distress, HEMAT: Anemia, bc of little Iron in the body)
hemolysis, DERM: rash, urticaria Side Effects: CNS: dizziness, headache,
Nursing Implications: Assess renal and syncope. GI: nausea, constipation, dark
liver functions for long term use, assess stools, epigastric pain
pain and limitation of movement, Nursing Implications: Assess bowel
monitor hematocrit for prolonged use for function for constipation or diarrhea,
GI blood loss Assess nutritional status and dietary
history to determine possible cause of
2. docusate sodium, Senokot S. anemia and need for pt. teaching
-Classification: Laxative, stool softener 5. Multivitamins and Chloraseptic Throat
-Dosage: 2 tablets once daily at Lozenges (Menthol, Benzocaine,
bedtime, not to exceed 4 tablets twice daily Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide)
Physiological Activity: local irritant in the Multivitamins
colon to stimulate peristalsis, promotes Purpose: Supplementing people,
incorporation of water in stool resulting particularly the elderly, with additional
in softer fecal mass vitamins and minerals not taken in
Side effect: GI: abdominal cramps, through the diet.
nausea, vomiting, DERM: rashes, GI: Side Effects: Mild diarrhea, Upset
urine discoloration stomach, Nausea
Nursing Implications: Assess bowel Nursing Implications: Prevent vitamin
sounds, check for abdominal distention, overdose / watch dosage, Assess bowel
assess color, consistency, and amount sounds
of stool produced Chloraseptic Throat Lozenges
Purpose: Oral Anesthetic / Analgesic
3. Ascorbic acid, Vitamin C Side Effects: Dizziness, Nausea
-Classification: Water-soluble vitamin Nursing Implications: Assess frequency
-Dosage: 500 mg/day for 14 days and nature of cough, lung sounds, and
-Physiological Activity: Involved in amount and type of sputum
oxidation reduction reactions: iron,
carbohydrate metabolism, lipid and 6. Acetaminophen / Tylenol
protein synthesis. Purpose: Pain reliever and fever
-Side Effects: CNS: headache, reducer. Used to treat headache,
insomnia, GI: Cramps, diarrhea, nausea, muscle aches, arthritis, back ache,
vomiting, GU: kidney stones, HEMAT: toothache, colds, and fevers
deep vein thrombosis Side Effects: Nausea, Upper stomach
-Nursing Implications: Assess for signs pain, Itching, Loss of appetite, Dark
of vitamin C deficiency; (gingivitis, urine, Jaundice, Skin rashdexa
bleeding gums, loose tooth), Mega Nursing Implications: Assess overall
doses may cause false-negative results for health status and alcohol use of pt.
occult blood stool test. before administering the drug as it can
cause serious problems if the pt. is
4. ferrous Sulfate EC / FeSO4 malnourished and an alcohol abuser.
Classification: antianemic, iron
supplements
7. celecoxib / Celebrex
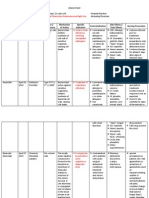
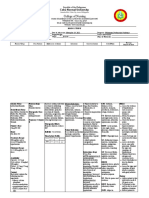
HOI: Hoag Orthopedic Institute Medications List p. 2
Classification: NSAID Purpose: Heal and prevent stress-
Range: 50 mg twice daily induced upper GI bleeding in critically ill
Physiological activity: Inhibits the pt
enzyme COX-2. This enzyme is required Side Effects: CNS: confusion, dizziness,
for the synthesis of prostaglan- dins. drowsiness, Endo: gynecomastia.
Purpose: decreases pain and Hemat: AGRANULOCYTOSIS,
inflammation caused by arthritis or APLASTIC ANEMIA
ankylosing spondylitis. Also relieves Nursing Implications: Assess for
menstrual pain (primary dysmenorrhea) epigastric or abdominal pain, frank or
Side Effects: CNS: dizziness, headache, occult blood in stool, emesis, or gastric
insomnia, CV: MYOCARDIAL aspirate. In geriatric pts, assess for
INFARCTION, STROKE, confusion. Administer with meals and at
THROMBOSIS, edema. GI: GI bedtime to prolong effect.
BLEEDING, abdominal pain, diarrhea,
Nursing Implications: Assess ROM, 10. Oxycodone CR / Oxycontin
degree of swelling and pain in joints - Purpose: control of moderate to severe
before and periodically throughout pain
therapy. Assess for skin rash frequently - Side effect: severe stomach pain,
and d/c at first sign of rash. Advise pt to constipation, vomiting, black, bloody, or tarry
notify HCP if pregnancy planned or stools, coughing up blood or vomit that
suspected. looks like coffee grounds, weak or shallow
breathing, tachycardia, bradycardia,
8. Hydrocodone w/ Acetaminophen / Norco confusion, hallucinations, feeling like you
might pass out, easy bruising or bleeding,
Classification: opioid agonists/nonopioid
seizures,
analgesic combinations
decreased hearing, tinnitus
Range: 2.510 mg q 36 hr as needed
Nursing implication: Assess pain prior
Physiological Activity: Bind to opiate and 1 hour post administration, assess
receptors in the CNS. BP, HR, respiration prior and periodically
Purpose: manages moderate to severe after administration, assess for
pain. Also suppresses cough reflex constipation, assess risk for opioid
Side Effects: CNS: confusion, dizziness, addiction
sedation, Resp: respiratory depression.
CV: hypotension, bradycardia. GI: 11. Oxycodone with Acetaminophen /
constipation, dyspepsia, nausea, Percocet
Nursing Implications: Assess BP, pulse Purpose: control of moderate to severe
and respiration before and periodically pain
during administration. Assess bowel Side effect: severe stomach pain,
function routinely. Assess pain type, constipation, vomiting, black, bloody, or
location and intensity prior and following tarry
administration. Assess risk for stools, coughing up blood or vomit that
addiction. Assess cough and lung looks like coffee grounds, weak or shallow
sounds during antitussive use. breathing, tachycardia, bradycardia,
confusion, hallucinations, feeling like you
9. Famotidine / Pepcid might pass out, easy bruising or
Classification: Histamine H2 antagonist bleeding, seizures,
Range: 40 mg/day at bedtime or 20 mg decreased hearing, tinnitus
twice daily for up to 8 wk Nursing implication: Assess pain prior
Physiological Activity: Inhibits the action and 1 hour post administration, assess
of histamine at the H2-receptor site BP,
located primarily in gastric parietal cells, HR, respiration prior and periodically
resulting in inhibition of gastric acid after administration, assess for constipation,
secretion. assess risk for opioid addiction
HOI: Hoag Orthopedic Institute Medications List p. 3
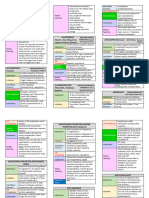
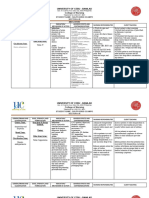
12. Hydroxyzinehydrochloride / Vistaril Monitor for peripheral edema or steady
Purpose: Treatment of anxiety, weight gain.
preoperative sedation, antiemetic effect,
antipruritic
effect
Side effect: restless muscle movements 15. Diazepam / Valium
in eyes, tongue, jaw or neck, tremors, Purpose: Adjunct in the management of
confusion, seizures, dizziness, anxiety disorder. Treatment of status
drowsiness, blurred vision, dry mouth, stomach epilepticus/uncontrolled seizures.
upset, headache Skeletal muscle relaxant. Management
Nursing implication: Assess for over of alcohol withdrawals
sedation and provide safety precautions, Side Effects: Dizziness, drowsiness,
geriatric pts more sensitive to CNS and lethargy, respiratory depression, blurred
anti-cholinergic effects vision, constipation, rashes, pain
Nursing Implications: Monitor BP, pulse
13. oxycodone IR / Roxicodone and respiratory rate prior to and
Classification: opioid agonists, opioid periodically throughout therapy. Assess
mental status. Assess for falls risk and
agonists/nonopioid analgesic
institute fall precautions for elderly.
combinations
Range: 510 mg q 34 hr initially, as
needed. 16. Gabapentin/ Neurotonin
Purpose: Analgesic adjuncts,
Physiological Activity: Binds to opiate
anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers
receptors in the CNS. Alters the
perception of and response to painful Side Effects: suicidal thoughts,
stimuli, while producing generalized confusion, depression, dizziness,
CNS depression. drowsiness, rhabdomyolysis, ataxia,
Purpose: Opiod analgesic for moderate multiorgan hypersensitivity reactions
to severe pain Nursing Implications: Monitor closely for
Side effects: CNS: confusion, sedation, notable changes in behavior that could
CV: orthostatic hypotension. GI: indicate the emergence or worsening of
constipation, dry mouth suicidal thoughts or behavior or
Nursing implication: Assess type, depression
locations, and intensity of pain prior to
and 1 hour after administration. Assess 17. Warfarin/ Coumadin
BP, pulse and respirations before and Purpose: Anticoagulation
periodically after administration. Assess Side Effects: bleeding, cramps, nausea,
for constipation. Assess risk for opiod dermal necrosis, fever
addiction Nursing Implications: Assess for signs of
bleeding and hemorrhage (bleeding
14. Dexamethasone / Decadron gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising;
Purpose: Corticosteroid that prevents tarry, black stools; hematuria; fall of
the release of substances in the body hematocrit or BP; guaiacpositive stools,
that cause inflammation urine, or nasogastric aspirate)
Side Effects: Aggression, agitation,
anxiety, blurred vision, decrease in the 18. Prochlorperazine/ Compazine
amount of urine, dizziness, irregular Purpose: Antiemetics, antipsychotics
heartbeat or pulse, headache,
Side Effects: Neuroleptic Malignant
irritability, mental depression, mood
changes, nervousness, shortness of syndrome, extrapyramidal reactions,
breath, swelling of the fingers, hands, blurred vision, dry eyes, constipation,
feet, or lower legs dry mouth
Nursing Implications: Monitor intake Nursing Implications: Monitor for
and output of patient. Assess breath development of neuroleptic malignant
sounds for rales, crackles or dyspnea. syndrome (fever, respiratory distress,
tachycardia, seizures, diaphoresis,
HOI: Hoag Orthopedic Institute Medications List p. 4
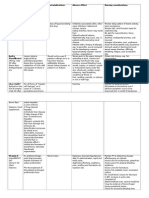
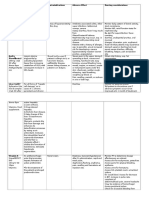
hypertension or hypotension, pallor, Implication: monitor bp, pulse, signs of
tiredness, severe muscle stiffness, loss angioedema, monitor weight, jugular
of bladder control). CBC and liver vein distention, HF.
function tests should be evaluated
periodically during therapy. May cause 22. Calcium Channel Blockers for
blood dyscrasias, especially between wk Hypertension such as (Amlodipine) Norvasc
4 and 10 of therapy. Hepatotoxicity is or
more likely to occur between wk 2 and 4 Diltiazem
of therapy. May recur if medication is Purpose - For hypertension
restarted. LIver function abnormalities
Side Effects - Peripheral edema,
may require discontinuation of therapy.
bradycardia, hypotension, nausea
Implications - Monitor BP and pulse
19. Meloxicam / Mobic
before drug therapy, monitor I & O,
Purpose: Relief of osteoarthritis and
assess for dyspnea
rheumatoid arthritis (including juvenile
rheumatoid arthritis)
23. Dulcolax Suppository (bisacodyl)
Side effect: HF, MI, CVA, edema, HTN,
Classification: Stimulant laxative
increased liver enzymes, diarrhea, GI
bleeding, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens- Range: 515 mg/day (up to 30 mg/day)
johnsons syndrome, toxic epidermal as a single dose.
necrolysis. Physiological activity: Stimulates
Implications: Pts. With asthma, ASA peristalsis. Alters fluid and electrolyte
allergies, nasal polyps are at risk for transport, producing fluid accumulation
hypersensitivity reactions. Assess for in the colon.
rhinitis, asthma, urticaria. Assess for Side Effects: GI: abdominal cramps,
rash periodically during tx. Discontinue if nausea, Misc: protein-losing
S&S associated with Stevens-Johnson enteropathy
syndrome occur along with fever, Nursing Implications - Assess pt for
malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, abdominal distention, presence of bowel
blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis. sounds, usual pattern of bowel function.
20. Atenolol / tenormin Assess color, consistency, amount of
Purpose: management of Hypertension. stool produced.
Side effect: bradycardia, HF, pulmonary
edema, fatigue, weakness, erectile 24. Miralax (polyethylene glycol)
dysfunction, hypotension, Purpose - Treatment of occasional
bronchospasm, wheezing. constipation
Implications: monitor bp, ecg, pulse, Side effects - Urticaria, abdominal
I&Os, daily weight, assess for HF, bloating, cramping, flatulence, nausea
(dyspnea, rales/crackles, weight gain, Implications - Assess pt for abdominal
peripheral edema, Jugular vein distention, presence of bowel sounds,
distention(JVD). Monitor for signs of usual pattern of bowel function. Assess
overdose (bradycardia, severe color, consistency, amount of stool
dizziness, fainting, drowsiness, produced.
dyspnea, bluish fingernails, palms,
seizures).
21. Lisinopril / Prinivil 24-1. (Hydromorphone) Dilaudid, Dilaudid-HP,
Purpose: management of hypertension. Exalgo, Hydrostat IR, Jurnista
Reduction of risk of death or Classification: opioid agonists
development of HF following MI. Range: 4 8 mg q 3 4 hr initially
Side effect: agranulosis, angioedema, Physiological Activity: Binds to opiate
cough, hypotention, taste disturbances, receptors in the CNS.
erectile dysfunction.
Purpose: - Moderate to severe pain
(alone and in combination with
HOI: Hoag Orthopedic Institute Medications List p. 5
nonopioid analgesics); extended release concomitant use of two heparin
product for opioid-tolerant patients products. Do not aspirate or massage.
requiring around-the-clock management
of persistent pain. Antitussive (lower
doses). 26. Morphine Sulfate:
Side Effects: - CNS: confusion, Purpose: treat severe pain, pulmonary
sedation, dizziness, dysphoria, edema, pain associated with MI
euphoria, floating feeling, hallucinations, Side effects: confusion, sedation,
headache, unusual dreams. EENT: dizziness, dysphoria, euphoria, floating
blurred vision, diplopia, miosis. Resp: feeling, hallucinations, headache,
respiratory depression. CV: unusual dreams. EENT: blurred vision,
hypotension, bradycardia. GI: diplopia, miosis. Resp: RESPIRATORY
constipation, dry mouth, nausea, DEPRESSION. CV: hypotension,
vomiting. GU: urinary retention. Derm: bradycardia. GI: constipation, nausea,
flushing, sweating. Misc: physical vomiting. GU: urinary retention. Derm:
dependenc flushing, itching, sweating. Misc:
Implications: - Assess BP, pulse, and physical dependence, psychological
respirations before and periodically dependence, tolerance.
during administration. If respiratory rate Implications: High Alert: Do not confuse
is 10/min, assess level of sedation. with other drugs! Duh! Extra precautions
Dose may need to be decreased by 25 for children. Have second practitioner
50%. Initial drowsiness will diminish with independently check original order, dose
continued use. calculations, and infusion pump settings.
25. (Enoxaparin) Lovenox (subcu)
Purpose: Prevention of venous 27. Cefazolin/Ancef
thromboembolism (VTE) (deep vein Purpose: Treatment of perioperative prophylaxis,
thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary biliary tract infections, genital infections,
embolism (PE)) in surgical or medical bacterial endocarditis prophylaxis for dental and
patients. Treatment of DVT with or upper respiratory tract procedures.
without PE (with warfarin). Prevention of Adverse Rxns/ Side Effects: Seizures
ischemic complications (with aspirin) (high doses), diarrhea, nausea,
from unstable angina and non- vomiting, rashes, hemolytic anemia,
STsegment-elevation MI. Treatment of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, pain at
acute ST-segment-elevation MI (with IM site, phlebitis at IV site
thrombolytics or percutaneous coronary Nursing Implications: Observe pt. for
intervention). s/sy of anaphylaxis. Monitor bowel
Side Effects: CNS: dizziness, headache, function. Assess pt. for skin rash
insomnia. CV: edema. GI: constipation, frequently during therapy.
qliver enzymes, nausea, vomiting. GU:
urinary retention. Derm: ecchymoses, 28. Vancomycin/ Vancocin (IVPB)
pruritus, rash, urticaria. Hemat:
Purpose: Useful in staphylococcal
BLEEDING, anemia, thrombocytopenia.
infections: endocarditis, meningitis,
Local: erythema at injection site,
osteomyelitis, pneumonia, septicemia,
hematoma, irritation, pain. Misc: fever.
soft-tissue infection
Implications: Assess for signs of
Adverse Rxns/ Side Effects: ototoxicity,
bleeding and hemorrhage (bleeding
hypotension, nausea, vomiting,
gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising;
nephrotoxicity, rashes, phlebitis, back
black, tarry stools; hematuria; fall in
and neck pain, chills, fever, anaphylaxis,
hematocrit or BP; guaiac-positive
superinfection
stools); bleeding from surgical site.
Notify health care professional if these Nursing Implications: Monitor IV site
occur. Assess for thrombosis. Monitor closely, monitor BP throughout, monitor
neurological impairment. Monitor Labs I/O and daily weight, assess for
for abnormality. High Alert: Unintended superinfection, anaphylaxis, assess
HOI: Hoag Orthopedic Institute Medications List p. 6
bowel status throughout , monitor urine Physiological Activity: Skeletal muscle
lab tests relaxation, probably as a result of CNS
depression.
s/e: CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, light-
headedness. GI: anorexia, GI upset,
29. Ondansetron/ Zofran nausea. GU: brown, black, or green
Classification: antiemetics urine
Range: 24 mg 30 Nursing Implications: Assess pt for pain,
Physiological Activity: Blocks the effects muscle stiffness, ROM. Assess geriatric
of serotonin at 5-HT3 Blocks the pts for anticholinergic effects.
effects of serotonin at 5-HT3 sites
(selective antagonist) located in vagal 32. temazepam (Restoril)
nerve terminals and the chemoreceptor Classification: benzodiazepines
trigger zone in the CNS. Range: 1530 mg at bedtime initially if
s/e: CNS: headache, dizziness, GI: needed; some patients may require only
constipation, diarrhea 7.5 mg.
Purpose: Prevention of nausea and Physiological Activity: Acts at many
vomiting Adverse Rxns/ Side Effects: levels in the CNS, producing
serotonin syndrome, headache, generalized depression. Effects may be
dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, weaknes, mediated by GABA, an inhibitory
constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, neurotransmitter.
dry mouth s/e: CNS: abnormal thinking, behavior
Nursing Implications: Assess pt for changes, hangover, EENT: blurred
nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention vision. GI: constipation, diarrhea,
and bowel sounds prior to and following nausea, vomiting
treatment, assess pt for extrapyramidal Nursing Implications: Assess mental
effects periodically, monitor ECG pts., status and potential for abuse, assess
Monitor for s/sy of serotonin syndrome sleep pattern prior to administration
30. Insulin / Novolog (short acting), Insulin / 33. alprazolam (Xanax)
Lantus or Levimir (long acting) Classification: benzodiazepines
Novolog Range: .25-.5 mg 2-3 times daily not to
Purpose: Fast acting drug that treats exceed 4 mg/day
Type 1 (adults and children age 2) and Physiological activity: acts at many
Type 2 (adults) diabetes levels in the CNS to produce anxiolytic
Side Effects: Headache, Excessive effects. May produce CNS depression
hunger, Confusion, Shakiness, Cold s/e: CNS: Dizziness, lethargy,
sweats, Restlessness, Anxiety drowsiness, EENT: Blurred vision, GI:
Nursing Implications: Assess pt. for Diarrhea, vomiting, nausea
signs of Hypoglycemia, Monitor body
weight, Monitor blood glucose 34. cyclobenzaprine/Flexeril
Levimir Classification: skeletal muscle relaxants
Purpose: Man made form of Insulin. Range: 10 mg 3 times daily
Long acting Insulin that starts to work Physiological activity: Reduces tonic
several hours after injection somatic muscle activity at the level of
Side Effects: Same as above the brainstem.
Nursing Implications: Same as above s/e: CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, CV:
arrhythmias. GI: constipation
31. methocarbamol (Robaxin) Nursing implications: Assess geriatric pt
Classification: Skeletal muscle for anticholinergic effect, Assess for
relaxation serotonin syndrome like mental changes
Range: 1.5 g 4 times daily initially (up to
8 g/day) for 2 3 days, then 4 4.5 g/ 35. simvastatin/ Zocor
day in 3 6 divided doses
HOI: Hoag Orthopedic Institute Medications List p. 7
Classification: lipid-lowering agents s/e: CNS: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS,
Range: 5 40 mg once daily in the behavioral changes, drowsiness,
evening; Resp:secretions. CV: palpitations.
Physiological activity: Inhibits 3-hydroxy- Derm: rash. GI: constipation, diarrhea
3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG- Nursing Implications: Observe and
CoA) reductase, an enzyme which is record intensity, duration, and location of
responsible for catalyzing an early step seizure activity, monitor for changes in
in the synthesis of cholesterol. behavior, assess need for continued
s/e: GI: abdominal cramps, constipation, treatment regularly
diarrhea, flatus, heartburn, Derm:
rashes, pruritus. Endo: hyperglycemia. 37. escitalopram/ Lexapro
MS: RHABDOMYOLYSIS Classification: SSRI
Nursing Implications: Evaluate liver Range: 10 mg once daily
function test prior to start of therapy, Physiological activity: Selectively inhibits
Obtain a diet history in regard to fat the reuptake of serotonin in the CNS.
consumption s/e: CNS: NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT
SYNDROME, SUICIDAL THOUGHTS,
36. clonazepam/Klonopin insomnia, GI: diarrhea, nausea,
Classification: Benzodiazepines, abdominal pain,
anticonvulsant Nursing Implications: Advise patient to
Range: 0.5 mg 3 times daily; may q by look for signs of suicidality, may cause
0.5 1 mg q 3 days. dizziness, emphasize importance of
Physiological activity: Anticonvulsant follow up exams.
effects may be due to presynaptic
inhibition. Produces sedative effects in Uses: Major depressive disorder.
the CNS, probably by stimulating Generalized anxiety disorder
inhibitory GABA receptors.
Вам также может понравиться
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationДокумент4 страницыBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatОценок пока нет
- Magnesium SulfateДокумент6 страницMagnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateДокумент6 страницDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент33 страницыDrug Studyjefwy8Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug StudyKyle Margaret FloresОценок пока нет
- Nursing Drug CardsДокумент32 страницыNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyhitorixxivОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal AgentsДокумент40 страницGastrointestinal Agentse_sagadОценок пока нет
- AcetazolamideДокумент1 страницаAcetazolamideKyuSheenОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент12 страницDrug StudyFelecidario TaerОценок пока нет
- Autocids, Gout & R. ARTHRITIS-NursingДокумент36 страницAutocids, Gout & R. ARTHRITIS-NursingManikanta GupthaОценок пока нет
- 2NDДокумент176 страниц2NDArjay NasirinОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент9 страницDrug StudyChristy BerryОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент7 страницDrug StudyCheska Mae PalicОценок пока нет
- Urosepsis With Aki On CKD: By-Roli JalanДокумент79 страницUrosepsis With Aki On CKD: By-Roli JalanRoli JalanОценок пока нет
- Nursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriДокумент29 страницNursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriGlyssa CabarrubiasОценок пока нет
- 37 Thyroid and Parathyroid AgentsДокумент6 страниц37 Thyroid and Parathyroid AgentssenyorakathОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIAДокумент8 страницDRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIAKent Martin AmorosoОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessДокумент8 страницGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessMaricon BautistaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент8 страницDrug StudyJoel MadjosОценок пока нет
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureДокумент31 страницаOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420Оценок пока нет
- 2ND and 3RD Drug StudyДокумент16 страниц2ND and 3RD Drug Study황춘히Оценок пока нет
- I.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EДокумент176 страницI.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EFatima Doran PandaogОценок пока нет
- Drug LisinoprilДокумент1 страницаDrug LisinoprilSrkocherОценок пока нет
- NCP DS NCM114 RleДокумент12 страницNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study On PtuДокумент4 страницыDrug Study On PtuDizzy BualanОценок пока нет
- COMPILATIONSSSSДокумент976 страницCOMPILATIONSSSSANNooonynmousОценок пока нет
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsДокумент11 страницName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisДокумент19 страницDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaОценок пока нет
- Drug CardsДокумент10 страницDrug CardsMaria Robustelli100% (3)
- LisinoprilДокумент3 страницыLisinoprilLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOОценок пока нет
- Drug Study 2nd SemДокумент7 страницDrug Study 2nd SemKyla CarbonelОценок пока нет
- IbuprofenДокумент3 страницыIbuprofenapi-3797941100% (1)
- NLM MedicatingДокумент11 страницNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент9 страницDrug StudyKAROL MARIAE LUZ ERESОценок пока нет
- EnalaprilДокумент4 страницыEnalaprilGwyn RosalesОценок пока нет
- OB Drug StudyДокумент12 страницOB Drug StudyCj AttoОценок пока нет
- Med Cards Starting With A PDFДокумент7 страницMed Cards Starting With A PDFDonn Patrick AlegreОценок пока нет
- AcetazolamideДокумент3 страницыAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesОценок пока нет
- Medication Cards Table Form Up To p.38Документ38 страницMedication Cards Table Form Up To p.38enf.mayara90Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Drug StudyДокумент16 страницChapter 5 Drug StudyRegee Rose LacsonОценок пока нет
- IndapamideДокумент2 страницыIndapamideNovi Yuliana100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDrug StudyLovely Saad TubañaОценок пока нет
- Furosemide (LASIX)Документ1 страницаFurosemide (LASIX)Amanda CoadОценок пока нет
- Effects On Lab Test ResultsДокумент18 страницEffects On Lab Test Resultsjay5ar5jamorabon5torОценок пока нет
- Ciprofloxacin CiproДокумент1 страницаCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayОценок пока нет
- Drug Study LosartanДокумент3 страницыDrug Study LosartanLouie Danielle SegarraОценок пока нет
- DRUg StudyДокумент11 страницDRUg StudyKathОценок пока нет
- Cebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesДокумент7 страницCebu Normal University: Republic of The PhilippinesdnllsgrraОценок пока нет
- Drug 25Документ17 страницDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Pharmacology Final: Week 1Документ9 страницPharmacology Final: Week 1Zoe RueОценок пока нет
- A Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletДокумент7 страницA Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletRaijenne VersolaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study TemplateДокумент3 страницыDrug Study Templateralphocampo53Оценок пока нет
- Docu - Tips Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDocu - Tips Drug StudyArdel LabadaОценок пока нет
- RandomДокумент2 страницыRandomAllen YnionОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDrug StudyJoshua KellyОценок пока нет
- Medication Brand Name and Generic NameДокумент12 страницMedication Brand Name and Generic Namexaliokoli127Оценок пока нет
- 220 Nursing Bullets Fundamentals of Nursing Reviewer 1 - NurseslabsДокумент35 страниц220 Nursing Bullets Fundamentals of Nursing Reviewer 1 - NurseslabsjackyОценок пока нет
- 220 Nursing Bullets Fundamentals of Nursing Reviewer 1 - NurseslabsДокумент35 страниц220 Nursing Bullets Fundamentals of Nursing Reviewer 1 - NurseslabsjackyОценок пока нет
- Order of OperationsДокумент1 страницаOrder of OperationsjackyОценок пока нет
- Lecture Outline - Chapter 5Документ5 страницLecture Outline - Chapter 5jackyОценок пока нет
- Breath Sounds WorksheetДокумент1 страницаBreath Sounds WorksheetjackyОценок пока нет
- IVT Procedure IДокумент47 страницIVT Procedure Izhallene813Оценок пока нет
- Chronic UrticariaДокумент40 страницChronic UrticariaeeeeewwwwwОценок пока нет
- Perspectives On Episodic and Semantic Memory Retrieval. Chaprer 1.1 of The Book Handbook of Episodic Memory.Документ2 страницыPerspectives On Episodic and Semantic Memory Retrieval. Chaprer 1.1 of The Book Handbook of Episodic Memory.Tahi GuzmánОценок пока нет
- Brosur & Spec - Carina System PDFДокумент8 страницBrosur & Spec - Carina System PDFHafid Sang PemimpiОценок пока нет
- Nawrin JahanДокумент82 страницыNawrin JahanMamanya Fadhil HaniОценок пока нет
- Uterine Sub Mucosal Leiomyoma (Fibroid) - A Case ReportДокумент5 страницUterine Sub Mucosal Leiomyoma (Fibroid) - A Case ReportInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Оценок пока нет
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureДокумент9 страницFulminant Hepatic FailurerazerxxxОценок пока нет
- Hands On: The Approach To The Patient Presenting With Multiple Joint PainДокумент12 страницHands On: The Approach To The Patient Presenting With Multiple Joint PainMithun CbОценок пока нет
- Elektrokardiograf: Prof. Dr. Peter KaboДокумент56 страницElektrokardiograf: Prof. Dr. Peter KaboAchmad DamnhuriОценок пока нет
- How To Be A Lab Director 2017Документ200 страницHow To Be A Lab Director 2017pieterinpretoria391Оценок пока нет
- Adaptive Method For SchizoidsДокумент3 страницыAdaptive Method For SchizoidsAntxon7850% (2)
- CH35 QuestionsДокумент8 страницCH35 QuestionsJharaОценок пока нет
- Hematology - Oncology GlossaryДокумент18 страницHematology - Oncology GlossaryFran CescaОценок пока нет
- The Auburn Plainsman 12-3-1998Документ32 страницыThe Auburn Plainsman 12-3-1998The Auburn PlainsmanОценок пока нет
- TessalonДокумент1 страницаTessalonSheri490100% (1)
- Agen HematinikДокумент77 страницAgen HematinikErinaGeraldiОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug StudyFloribelle SamaniegoОценок пока нет
- SBARДокумент4 страницыSBARIka AnggreIta SafitriОценок пока нет
- Good Witch Eng 01Документ6 страницGood Witch Eng 01Julio Bueno0% (1)
- Lecture Rickettsia Chlamydia, MycoplasmaДокумент49 страницLecture Rickettsia Chlamydia, MycoplasmaHabeeb Ali Baig100% (3)
- 4001 EconДокумент31 страница4001 EconAngus LeungОценок пока нет
- Control of Blood Glucose LevelДокумент21 страницаControl of Blood Glucose LevelalynnsakinaОценок пока нет
- Empyema CPGДокумент8 страницEmpyema CPGLe Vu AnhОценок пока нет
- Cellular AberrationДокумент2 страницыCellular AberrationFrances Gaviola100% (1)
- 58f6anesthesia For Laparoscopic SurgeriesДокумент56 страниц58f6anesthesia For Laparoscopic SurgeriesSayed NourОценок пока нет
- PDSA Examples: PlanДокумент6 страницPDSA Examples: PlanTrà My Lê MỹОценок пока нет
- Shock Syndromes and Sepsis PDFДокумент61 страницаShock Syndromes and Sepsis PDFhuong LОценок пока нет
- Paidepally Srinivas RaoДокумент9 страницPaidepally Srinivas RaoShyam KalavalapalliОценок пока нет
- Surgery Department: Emergency Case ReportsДокумент46 страницSurgery Department: Emergency Case ReportsMohamad ZulfikarОценок пока нет
- NCP ConstipationДокумент3 страницыNCP ConstipationNika LoОценок пока нет
- Redefining Anxiety: What It Is, What It Isn't, and How to Get Your Life BackОт EverandRedefining Anxiety: What It Is, What It Isn't, and How to Get Your Life BackРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (153)
- Rewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryОт EverandRewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (157)
- Somatic Therapy Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Experiencing Greater Mind-Body ConnectionОт EverandSomatic Therapy Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Experiencing Greater Mind-Body ConnectionОценок пока нет
- The Upward Spiral: Using Neuroscience to Reverse the Course of Depression, One Small Change at a TimeОт EverandThe Upward Spiral: Using Neuroscience to Reverse the Course of Depression, One Small Change at a TimeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (140)
- Summary of The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma by Bessel van der Kolk MDОт EverandSummary of The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma by Bessel van der Kolk MDРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (167)
- The Complex PTSD Workbook: A Mind-Body Approach to Regaining Emotional Control & Becoming WholeОт EverandThe Complex PTSD Workbook: A Mind-Body Approach to Regaining Emotional Control & Becoming WholeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (49)
- My Grandmother's Hands: Racialized Trauma and the Pathway to Mending Our Hearts and BodiesОт EverandMy Grandmother's Hands: Racialized Trauma and the Pathway to Mending Our Hearts and BodiesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (70)
- Feel the Fear… and Do It Anyway: Dynamic Techniques for Turning Fear, Indecision, and Anger into Power, Action, and LoveОт EverandFeel the Fear… and Do It Anyway: Dynamic Techniques for Turning Fear, Indecision, and Anger into Power, Action, and LoveРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (250)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsОт EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (39)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- A Profession Without Reason: The Crisis of Contemporary Psychiatry—Untangled and Solved by Spinoza, Freethinking, and Radical EnlightenmentОт EverandA Profession Without Reason: The Crisis of Contemporary Psychiatry—Untangled and Solved by Spinoza, Freethinking, and Radical EnlightenmentОценок пока нет
- Summary: No Bad Parts: Healing Trauma and Restoring Wholeness with the Internal Family Systems Model by Richard C. Schwartz PhD & Alanis Morissette: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: No Bad Parts: Healing Trauma and Restoring Wholeness with the Internal Family Systems Model by Richard C. Schwartz PhD & Alanis Morissette: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouОт EverandThe Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouОценок пока нет
- Happiness Hypothesis, The, by Jonathan Haidt - Book SummaryОт EverandHappiness Hypothesis, The, by Jonathan Haidt - Book SummaryРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (95)
- Rapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: How to Lose Weight with Self-Hypnosis, Positive Affirmations, Guided Meditations, and Hypnotherapy to Stop Emotional Eating, Food Addiction, Binge Eating and MoreОт EverandRapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: How to Lose Weight with Self-Hypnosis, Positive Affirmations, Guided Meditations, and Hypnotherapy to Stop Emotional Eating, Food Addiction, Binge Eating and MoreРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (17)
- The Anatomy of Loneliness: How to Find Your Way Back to ConnectionОт EverandThe Anatomy of Loneliness: How to Find Your Way Back to ConnectionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (163)
- It's All Too Much: An Easy Plan for Living a Richer Life with Less StuffОт EverandIt's All Too Much: An Easy Plan for Living a Richer Life with Less StuffРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (232)
- The Worry Trick: How Your Brain Tricks You into Expecting the Worst and What You Can Do About ItОт EverandThe Worry Trick: How Your Brain Tricks You into Expecting the Worst and What You Can Do About ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (107)
- Heal the Body, Heal the Mind: A Somatic Approach to Moving Beyond TraumaОт EverandHeal the Body, Heal the Mind: A Somatic Approach to Moving Beyond TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (56)
- I Don't Want to Talk About It: Overcoming the Secret Legacy of Male DepressionОт EverandI Don't Want to Talk About It: Overcoming the Secret Legacy of Male DepressionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (106)
- Winning the War in Your Mind: Change Your Thinking, Change Your LifeОт EverandWinning the War in Your Mind: Change Your Thinking, Change Your LifeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (559)