Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Plate 2 (A Quantitative Approach of Seepage Analysis)
Загружено:
Robert Michael TampusОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Plate 2 (A Quantitative Approach of Seepage Analysis)
Загружено:
Robert Michael TampusАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Subject: GEO133P, Application of Quantitative Analysis in Geological Engineering pg.
Subject: GEO133P, Application of Quantitative Analysis in Geological Engineering
Plate No. 2
A QUANTITATIVE APPROACH OF SEEPAGE
ANALYSIS
Submitted by: Tampus, Robert Michael Rating:
Student No.: 2013140129
Course: B.S. GSE Date Submitted:
Year: 3
Faculty/Instructor: Engr. Celestino Avis
Plate Exercises of C. C. Avis Mapua Institute of Technology, 2016
Subject: GEO133P, Application of Quantitative Analysis in Geological Engineering pg. 2
1. Description
The principles of water flow through soils are used to determine seepage quantities, pressures, and forces.
There are approximate solutions for specific boundary conditions. These are generally limited to the solution of
one value, usually seepage quantity. The process of determining boundary conditions, selecting permeability
values, and making the analysis is a logical approach for evaluating structure and foundation performance and
for selecting appropriate control measures.
Seepage analysis is done by preparing cross sections to scale showing the boundaries of the structure,
entrance and discharge faces, and boundaries of seepage parallel to the direction of flow. These cross sections
are called flow nets. A flow net is a graphical solution to the equations of steady groundwater flow. A flow net
consists of two sets of lines which must always be orthogonal (perpendicular to each other): flow lines, which
show the direction of groundwater flow, and equipotential lines of constant head, which show the distribution of
potential energy. Flow nets are usually constructed through trial-and-error sketching. From the flow net, the
seepage quantity can be computed.
2. Objectives/Purpose
The main objective of this plate is to perform a quantitative approach of seepage analysis. Specifically, it
aims to:
a. Construct a flow net,
b. Interpret the constructed flow net, and
c. Compute the seepage quantity (Q).
3. Formula
Seepage Quantity (Isotropic Soil Condition)
Seepage Quantity (Anisotropic Soil Condition)
where:
Q = seepage quantity (cm3/sec)
k = coefficient of permeability (cm/s)
kx = coefficient of permeability in the horizontal axis
ky = coefficient of permeability in the vertical axis
h = net head
nf = number of flow channels = number of flow lines minus one
nd = number of equipotential (pressure) drops
is called the shape factor
4. Application to Geological Engineering Course:
As future geological engineers, embankments, dams, mine tailings, slopes and other earthworks need the
assessment for seepage conditions. Water, either surficial or groundwater, can extracted due to difficulties in
construction or for economic purposes. It is considered to be poor design practice to permit the water, which will
inevitably seep through the homogeneous earth fill, to discharge along the downstream face of the dam. Water
causes internal erosion on the soil around foundations. Hypothetical problems of common structures (such as
mine tailings) were given in this plate.
5. Problem Exercise:
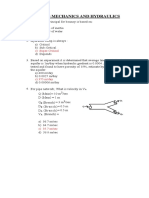
1. For the hypothetical mine tailing dam shown in Figure 1, k = 5 m/day. Determine the seepage flow per
meter width of dam in liters per minute.
Given:
W = 30 m
H = 18 m
T=1m
Plate Exercises of C. C. Avis Mapua Institute of Technology, 2016
Subject: GEO133P, Application of Quantitative Analysis in Geological Engineering pg. 3
Illustration:
Figure 1
Solution:
Flow per unit width:
Number of pressure drops, Nd = 9
Number of flow channels, Nf = 4
Seepage flow: ( )
Seepage flow:
2. For the hypothetical mine tailing dam shown in Figure 2, k = 10 m/day. Determine the seepage flow per
meter width of dam in liters per minute.
Given:
W = 20 m
H = 15 m
T=1m
Plate Exercises of C. C. Avis Mapua Institute of Technology, 2016
Subject: GEO133P, Application of Quantitative Analysis in Geological Engineering pg. 4
Illustration:
Figure 2
Solution:
Flow per unit width:
Number of pressure drops, Nd = 9
Number of flow channels, Nf = 4
Seepage flow: ( )
Seepage flow:
3. For the hypothetical mine tailing dam shown in Figure 3, k = 20 m/day. Determine the seepage flow per
meter width of dam in liters per minute.
Given:
W = 27 m
H = 40 m
T=1m
Plate Exercises of C. C. Avis Mapua Institute of Technology, 2016
Subject: GEO133P, Application of Quantitative Analysis in Geological Engineering pg. 5
Illustration:
Figure 3
Solution:
Flow per unit width:
Number of pressure drops, Nd = 9
Number of flow channels, Nf = 4
Seepage flow: ( )
Seepage flow:
Plate Exercises of C. C. Avis Mapua Institute of Technology, 2016
Subject: GEO133P, Application of Quantitative Analysis in Geological Engineering pg. 6
APPENDIX 1 (REFERENCES)
http://www2.humboldt.edu/geology/courses/geology556/556_handouts/constructing_flow_nets.pdf
http://people.eng.unimelb.edu.au/stsy/geomechanics_text/Ch6_SeepDam.pdf
Cedergren, H. R. (1997). Seepage, Drainage, and Flow Nets. John Wiley & Sons
Plate Exercises of C. C. Avis Mapua Institute of Technology, 2016
Вам также может понравиться
- Banawe 3 PDFДокумент1 страницаBanawe 3 PDFkrimeo0% (1)
- Komatsu Pc75uu 2 Shop ManualДокумент20 страницKomatsu Pc75uu 2 Shop Manualthomas100% (50)
- QB 103442Документ47 страницQB 103442Sri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 IrrigДокумент5 страницLab 7 IrrigAJ mnОценок пока нет
- Effect of Storage Capacity On Vertical Drains, LiquefactionДокумент12 страницEffect of Storage Capacity On Vertical Drains, LiquefactionMarco Dos Santos NevesОценок пока нет
- Surface Water Hydrology 8 PDFДокумент11 страницSurface Water Hydrology 8 PDFgladОценок пока нет
- Three-Dimensional in Uence Zone of New Tunnel Excavation Crossing Underneath Existing TunnelДокумент7 страницThree-Dimensional in Uence Zone of New Tunnel Excavation Crossing Underneath Existing Tunneljuan muneraОценок пока нет
- CFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave MakerДокумент7 страницCFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave MakerTrần Văn CườngОценок пока нет
- Two Phase Level Set COMSOL TutorialДокумент27 страницTwo Phase Level Set COMSOL Tutorialunomas9579100% (1)
- CFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave-Maker: Anant Lal, and M. ElangovanДокумент7 страницCFD Simulation and Validation of Flap Type Wave-Maker: Anant Lal, and M. Elangovanghanbari8668Оценок пока нет
- The Institution of Engineers, Sri Lanka:) W V W (I I y T Ac The C I T e e W UДокумент5 страницThe Institution of Engineers, Sri Lanka:) W V W (I I y T Ac The C I T e e W UUmange RanasingheОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Channel Roughness To The Flow Veloci PDFДокумент9 страницThe Effect of Channel Roughness To The Flow Veloci PDFrisman ramliОценок пока нет
- Irrig MSC2012Документ6 страницIrrig MSC2012Abubakr MuhammadОценок пока нет
- Numerical Simulation of Inflow Performance For Perforated Horizontal WellsДокумент7 страницNumerical Simulation of Inflow Performance For Perforated Horizontal Wellssaholans2000Оценок пока нет
- Y. F. Yao and N. D. Sandham - Direct Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Trailing-Edge Flow With Base Flow ControlДокумент9 страницY. F. Yao and N. D. Sandham - Direct Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Trailing-Edge Flow With Base Flow ControlWhiteLighteОценок пока нет
- Experimental Study For Determine Manning's Coefficient With Different Slops and Channel Bed MaterialsДокумент15 страницExperimental Study For Determine Manning's Coefficient With Different Slops and Channel Bed MaterialsMd. FizОценок пока нет
- 10 1680@p3is 15562 0030Документ9 страниц10 1680@p3is 15562 0030taher ahmedОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsДокумент2 страницыGujarat Technological University: Instructionssameer_m_daniОценок пока нет
- Exp 4-Manning's Rugosity CoefficientДокумент2 страницыExp 4-Manning's Rugosity Coefficientadityain2003Оценок пока нет
- 3) Cut Throat FlumeДокумент19 страниц3) Cut Throat FlumeMd Sajedul Islam SetuОценок пока нет
- Pump and Open Channel flow-CE3711Документ5 страницPump and Open Channel flow-CE3711Fearless HeroОценок пока нет
- Beeraspat&Park ZM-2020 ManuscriptДокумент9 страницBeeraspat&Park ZM-2020 Manuscriptneil beeraspatОценок пока нет
- An Analytical Soln For Wave Propagation in Pipe Pile With Mul. DefectsДокумент17 страницAn Analytical Soln For Wave Propagation in Pipe Pile With Mul. DefectsRAJ KARANОценок пока нет
- Falling Head Permeability Lab TestДокумент6 страницFalling Head Permeability Lab TestHamierul MohamadОценок пока нет
- Jcoengadmin, 1348-9Документ12 страницJcoengadmin, 1348-9ريان الحربيОценок пока нет
- Chowdhury 2019Документ7 страницChowdhury 2019niloОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual 3.2 - LEVEL 1 - Determination of Hydraulic Parameters in Uniform Flow For Open Channels.Документ4 страницыLab Manual 3.2 - LEVEL 1 - Determination of Hydraulic Parameters in Uniform Flow For Open Channels.Muhamad IzzanОценок пока нет
- Comparative Study For Designing The Horizontal Thrust Blocks in Pipelines For Water and Sewage NetworksДокумент7 страницComparative Study For Designing The Horizontal Thrust Blocks in Pipelines For Water and Sewage NetworksKuziva JaziОценок пока нет
- One Degree of Freedom Resonance Wave Energy ConvertorДокумент11 страницOne Degree of Freedom Resonance Wave Energy ConvertorMr PolashОценок пока нет
- Seismic Deformation Gina Gasket Inmersed TunnelsДокумент12 страницSeismic Deformation Gina Gasket Inmersed TunnelsCristian Menéndez FernándezОценок пока нет
- An Investigation Into Efficient Drainage Layouts For The Stabilization of Tunnel Faces in Homogeneous Ground PDFДокумент25 страницAn Investigation Into Efficient Drainage Layouts For The Stabilization of Tunnel Faces in Homogeneous Ground PDFPuthut Omar SatriawanОценок пока нет
- CHEY Dina E20130055Документ31 страницаCHEY Dina E20130055Sopheareak ChhanОценок пока нет
- EMCHIE2023 RRUPCv6 RRДокумент3 страницыEMCHIE2023 RRUPCv6 RRRosember RamirezОценок пока нет
- 9-2 Runoff - Rating Curves, Discharge Computation, and Rainfall-Runoff RelationsДокумент12 страниц9-2 Runoff - Rating Curves, Discharge Computation, and Rainfall-Runoff RelationsChadColemanОценок пока нет
- 4 Design StormsДокумент7 страниц4 Design StormsOndari HesbonОценок пока нет
- Flood Inundation Mapping of Babai Basin Using: Hec-Ras & GISДокумент13 страницFlood Inundation Mapping of Babai Basin Using: Hec-Ras & GISSunil MaharjanОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Ship Squat in Shallow Water Using CFDДокумент10 страницAssessment of Ship Squat in Shallow Water Using CFDSushant PandurangiОценок пока нет
- Btech Ce 3 Sem Fluid Mechanics Rce303 2019Документ3 страницыBtech Ce 3 Sem Fluid Mechanics Rce303 2019shivchauhan0507Оценок пока нет
- A Numerical Case Study On Pier Shape Coefficient oДокумент7 страницA Numerical Case Study On Pier Shape Coefficient oFk FeОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics Hydraulic Machine Lab ManualДокумент33 страницыHydraulics Hydraulic Machine Lab ManualAlcazar HyundaiОценок пока нет
- Radial Consolidation TheoriesДокумент13 страницRadial Consolidation TheoriesSidi Yéhia SounfountéraОценок пока нет
- Control of Seepage Through Earth Dams Based On PerДокумент18 страницControl of Seepage Through Earth Dams Based On PerGemechis BekeleОценок пока нет
- Greg Melling, Justin Dix, Stephen Turnock, University of Southampton - Gjm1v07@noc - Soton.ac - Uk Richard Whitehouse, HR WallingfordДокумент6 страницGreg Melling, Justin Dix, Stephen Turnock, University of Southampton - Gjm1v07@noc - Soton.ac - Uk Richard Whitehouse, HR WallingfordMahmoud Abd El LateefОценок пока нет
- Experiment Computation of Manning's N - EP1Документ5 страницExperiment Computation of Manning's N - EP1Md. FizОценок пока нет
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsДокумент15 страницFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsAngelica Joyce BenitoОценок пока нет
- Urban Surface Characteristics Study Using Time-Area Function Model: A Case Study in Saudi ArabiaДокумент8 страницUrban Surface Characteristics Study Using Time-Area Function Model: A Case Study in Saudi ArabiaMoh Hussain FarzamОценок пока нет
- Discharge Coefficient For Sharp-Crested Side Weir in Supercritical Flow PDFДокумент8 страницDischarge Coefficient For Sharp-Crested Side Weir in Supercritical Flow PDFNacera BenslimaneОценок пока нет
- Analytical-Numerical Coupling Analysis of Submarine Pipeline in J-Lay ProblemДокумент9 страницAnalytical-Numerical Coupling Analysis of Submarine Pipeline in J-Lay Problemnicholas_j_vaughanОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydralauics Engineering (Qwoa)Документ11 страницFluid Mechanics and Hydralauics Engineering (Qwoa)Kip ClayОценок пока нет
- Numerical Modelling of Subcritical Open Channel Flow Using The K-E Turbulence Model and The Penalty Function Finite Element TechniqueДокумент7 страницNumerical Modelling of Subcritical Open Channel Flow Using The K-E Turbulence Model and The Penalty Function Finite Element TechniquechrissbansОценок пока нет
- Kuchuk, F. J. - Well Testing and Interpretation For Horizontal WellsДокумент6 страницKuchuk, F. J. - Well Testing and Interpretation For Horizontal WellsJulio MontecinosОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual of Hydraulics PDFДокумент40 страницLab Manual of Hydraulics PDFJULIUS CESAR G. CADAOОценок пока нет
- Gradually Varied FlowДокумент42 страницыGradually Varied FlowJuan Manuel Sanabria GuioОценок пока нет
- 06 Ekinci Indd PDFДокумент8 страниц06 Ekinci Indd PDFkeeesaОценок пока нет
- Computers and Geotechnics: Pengpeng Ni, Sujith Mangalathu, Guoxiong Mei, Yanlin ZhaoДокумент10 страницComputers and Geotechnics: Pengpeng Ni, Sujith Mangalathu, Guoxiong Mei, Yanlin ZhaoManaswini VadlamaniОценок пока нет
- 44C PDFДокумент16 страниц44C PDFLokesh Yadav100% (1)
- Oh Ko (Oh) : Recession Flow Analysis For Aquifer Parameter DeterminationДокумент7 страницOh Ko (Oh) : Recession Flow Analysis For Aquifer Parameter Determinationdurga sharmaОценок пока нет
- Transient Seepage Flow in Angular Reservoirs: Liu Yuewu, Ouyang Weiping Wang Jianxiong Wu Lihua Chang HuaДокумент7 страницTransient Seepage Flow in Angular Reservoirs: Liu Yuewu, Ouyang Weiping Wang Jianxiong Wu Lihua Chang HuaPablo JarrinОценок пока нет
- JPSC04 SolutionsДокумент19 страницJPSC04 SolutionsAshish VermaОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydralaucis (Qwawh) PDFДокумент12 страницFluid Mechanics and Hydralaucis (Qwawh) PDFMohammed AnwhazОценок пока нет
- L1 Linear EquationsДокумент50 страницL1 Linear EquationsRobert Michael TampusОценок пока нет
- TAMPUS - Plate 3 (A Quantitative Approach of Landslide Assessment and Mitigating Measures)Документ12 страницTAMPUS - Plate 3 (A Quantitative Approach of Landslide Assessment and Mitigating Measures)Robert Michael TampusОценок пока нет
- Sedimentary BasinsДокумент49 страницSedimentary BasinsRobert Michael TampusОценок пока нет
- A Quantitative Approach of Liquefaction AnalysisДокумент10 страницA Quantitative Approach of Liquefaction AnalysisRobert Michael TampusОценок пока нет
- Modelling On The Water Balance of Mapúa Institute of Technology Intramuros CampusДокумент18 страницModelling On The Water Balance of Mapúa Institute of Technology Intramuros CampusRobert Michael TampusОценок пока нет
- Geomembranes For Geofoam Applications PDFДокумент22 страницыGeomembranes For Geofoam Applications PDFΘανάσης ΓεωργακόπουλοςОценок пока нет
- 01 The Law and Practice of Delay Claims A Practical Introduction TrainorДокумент19 страниц01 The Law and Practice of Delay Claims A Practical Introduction TrainorMOHОценок пока нет
- Problem No: 1: Submitted ToДокумент4 страницыProblem No: 1: Submitted ToLight HouseОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTIONДокумент5 страницINTRODUCTIONRaj KumarОценок пока нет
- Christopher Lyon ResumeДокумент2 страницыChristopher Lyon Resumeapi-353696827Оценок пока нет
- Proposed Wedding Hall and Garden DesignДокумент3 страницыProposed Wedding Hall and Garden DesignMendoza, Kyle S.Оценок пока нет
- Base Isolation For Multi Storey Buildings PDFДокумент311 страницBase Isolation For Multi Storey Buildings PDFRal GLОценок пока нет
- Contract TerminologyДокумент20 страницContract TerminologyMital DamaniОценок пока нет
- 02 01 Byg ClassicДокумент204 страницы02 01 Byg ClassicEscuela EntrenamientoОценок пока нет
- Ventilation WorksheetДокумент1 страницаVentilation WorksheetIskandar 'muda' AdeОценок пока нет
- (Catalogue) HTLSC Ver.2Документ28 страниц(Catalogue) HTLSC Ver.2Huy Thông NguyễnОценок пока нет
- New AVME EXPORT-20220530 - 090509Документ4 936 страницNew AVME EXPORT-20220530 - 090509Muthukumaran TОценок пока нет
- Conbextra EP10Документ4 страницыConbextra EP10Venkata Raju KalidindiОценок пока нет
- Valvulas CheckДокумент4 страницыValvulas CheckLAM AAAОценок пока нет
- Factors Influencing Project Delay: A Case Study of The Vale Malaysia Minerals Project (VMMP)Документ8 страницFactors Influencing Project Delay: A Case Study of The Vale Malaysia Minerals Project (VMMP)LOKESH KUMAR SINHAОценок пока нет
- Inspection & Test Plan: Project Name: Main Activity: Date: W Witness H Hold Point T Test R RandomДокумент1 страницаInspection & Test Plan: Project Name: Main Activity: Date: W Witness H Hold Point T Test R RandomKasinadh KarraОценок пока нет
- Marine Air Systems ManualДокумент32 страницыMarine Air Systems ManualKyaw MyoОценок пока нет
- Bowles J. E. - FDN - Analysis & DSNДокумент2 страницыBowles J. E. - FDN - Analysis & DSNharishОценок пока нет
- Production RateДокумент50 страницProduction RateFührer Magdi Badran100% (2)
- DQS258 20232 A1 - Part A - FinaleДокумент26 страницDQS258 20232 A1 - Part A - Finalenur asyiqinОценок пока нет
- Contoh Painting ReportДокумент1 страницаContoh Painting ReportYudha Andrie Sasi ZenОценок пока нет
- Glass Panel Under In-Plane Shear LoadingДокумент4 страницыGlass Panel Under In-Plane Shear LoadingTheAnh TranОценок пока нет
- Datasheet Hdpe 1-1.5-2-2.5Документ1 страницаDatasheet Hdpe 1-1.5-2-2.5மதன் குமார் முனியசாமிОценок пока нет
- Sample Architectural PlanДокумент1 страницаSample Architectural PlanAl DrinОценок пока нет
- Bridgette (OTC)Документ31 страницаBridgette (OTC)mhel vianney bariquitОценок пока нет
- Chain Crosby® Grade 100Документ1 страницаChain Crosby® Grade 100CROSBYОценок пока нет
- Fatigue Calculation of Concrete According To EC2: Severe or Not?Документ9 страницFatigue Calculation of Concrete According To EC2: Severe or Not?ShamaОценок пока нет
- Sources of Water (Water Supply Engineering)Документ9 страницSources of Water (Water Supply Engineering)Shuvanjan Dahal86% (7)