Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
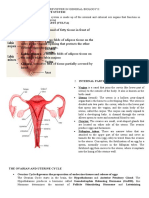
Structure and Function of The Ovaries
Загружено:
Anonymous FfdoEX0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
87 просмотров3 страницыThe ovaries are almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus that produce eggs and hormones. They contain thousands of primordial follicles containing immature eggs. During maturation, the follicles develop multiple layers of cells and a fluid-filled cavity in stages from primordial to primary to secondary to Graafian follicle. The ovaries are also responsible for producing the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and fertility. Common diseases of the ovaries include ovarian cancer, with symptoms appearing at later stages, and ovarian cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs of varying sizes that are usually harmless.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Structure and Function of the Ovaries.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe ovaries are almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus that produce eggs and hormones. They contain thousands of primordial follicles containing immature eggs. During maturation, the follicles develop multiple layers of cells and a fluid-filled cavity in stages from primordial to primary to secondary to Graafian follicle. The ovaries are also responsible for producing the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and fertility. Common diseases of the ovaries include ovarian cancer, with symptoms appearing at later stages, and ovarian cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs of varying sizes that are usually harmless.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
87 просмотров3 страницыStructure and Function of The Ovaries
Загружено:
Anonymous FfdoEXThe ovaries are almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus that produce eggs and hormones. They contain thousands of primordial follicles containing immature eggs. During maturation, the follicles develop multiple layers of cells and a fluid-filled cavity in stages from primordial to primary to secondary to Graafian follicle. The ovaries are also responsible for producing the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and fertility. Common diseases of the ovaries include ovarian cancer, with symptoms appearing at later stages, and ovarian cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs of varying sizes that are usually harmless.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
Structure and Function of the Ovaries
Overview:
The ovaries are the organs in a females
reproductive system that produces eggs, or
ova necessary for reproduction. They are
about 1.5 inches (3.5 centimeters) long. The
ovaries are deep in a females pelvis, on both
sides of the uterus, close to the ends of the
Fallopian tubes. At birth, a female has
approximately 1-2 million eggs, but only 300
of these eggs ever mature and are released
for the purpose of fertilization. Ovaries are
also responsible for the production of the
hormones estrogen and progesterone.
These are vital to normal reproductive
development and fertility.
Structure:
1. The surface layer of the
ovary is formed by
simple cuboidal
epithelium.
2. Cortex: The cortex
(outer part) of the
ovary is largely
comprised of
a connective tissue
stroma. It supports
thousands of follicles.
Each primordial follicle
contains an oocyte
surrounded by a single
layer of follicular cells.
3. Medulla: The medulla (inner part) is composed of supporting stroma
and contains a rich neurovascular network which enters the hilum of
ovary from the mesovarium.
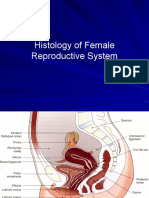
Primordial Follicle: These follicles consist of
oocytes surrounded by a single layer of
squamous follicular cells.
Primary Follicle: The primary follicle stage is
reached when the follicular cells proliferate into
a stratified epithelium known as the zona
granulosa.
Secondary Follicle: The characteristic feature
that distinguishes secondary from primary
follicles is the appearance of a follicular antrum
within the granulosa layer. At this stage, a layer
of cells outside the follicle become evident.
Graafian Follicle: The Graafian follicle is the
stage after the first meiotic division has
completed but before ovulation. The follicle is
characterized by a large follicular antrum that
makes up most of the follicle.
Oocyte: An oocyte is a
female gametocyte or germ cell involved
in reproduction. The formation of an oocyte is
called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the
formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and
of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation.
Diseases and Disorders of the Ovaries:
Ovarian Cancer:
Ovarian cancer is a serious
disease whose symptoms
dont become apparent until
the cancer has progressed
into the later stages.
Symptoms include:
Abdominal pain, abnormal
uterine bleeding, and pain
during intercourse. In
majority, the presence of
these symptoms does not
indicate cancer.
Ovarian Cysts: These
are fluid filled sacs that affect
women of all ages, though
mostly women of child
bearing age. Cysts are
common and they can vary in size from a pea to a grapefruit. The majority of
cysts are harmless, though larger cysts may need to be surgically removed.
Larger cysts can disrupt the blood supply to the ovaries.
Вам также может понравиться
- Ection I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALДокумент9 страницEction I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALNheil_Christop_4211Оценок пока нет
- Overview of The Female Reproductive SystemДокумент3 страницыOverview of The Female Reproductive SystemMonica J Ortiz PereiraОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент28 страницFemale Reproductive System1-LUMALANG Ashley Anne A.Оценок пока нет
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Документ11 страницCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudОценок пока нет
- The Female Reproductive System: 1-1. GENERALДокумент5 страницThe Female Reproductive System: 1-1. GENERALgladz25Оценок пока нет
- Spermatogenesis and OogenesisДокумент17 страницSpermatogenesis and Oogenesisanju kumawatОценок пока нет
- Cattle Reproducive SystemДокумент12 страницCattle Reproducive SystemSurajОценок пока нет
- Reproductive SystemДокумент26 страницReproductive SystemMuhammad naveedОценок пока нет
- FemrepnotesДокумент38 страницFemrepnotesLibi FarrellОценок пока нет
- GametesДокумент28 страницGametesJay PornelaОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentДокумент25 страницModule 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentKatie HolmesОценок пока нет
- Embryology IДокумент94 страницыEmbryology Imasemola koketsoОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент8 страницFemale Reproductive SystemNanen CaminceОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology GCSДокумент7 страницAnatomy and Physiology GCSSherry Ann FayeОценок пока нет
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMДокумент127 страницScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gОценок пока нет
- 12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionДокумент16 страниц12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionNishant ShahОценок пока нет
- CLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFДокумент30 страницCLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFmike RОценок пока нет
- UNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Документ12 страницUNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент64 страницыFemale Reproductive SystemJoryll AtienzaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент10 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyBurni GuevaraОценок пока нет
- ExplainerДокумент21 страницаExplainerfarahkhater106Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 Reproductive SystemДокумент8 страницChapter 16 Reproductive SystemfrommeyerjamesОценок пока нет
- Module 1..lesson 1,2&3Документ26 страницModule 1..lesson 1,2&3Carlyn100% (1)
- Human Embryology: Presenting By: Ms.G.Nivedhapriya M, SC ., Nursing Sripms-Con CoimbatoreДокумент74 страницыHuman Embryology: Presenting By: Ms.G.Nivedhapriya M, SC ., Nursing Sripms-Con CoimbatoreKavipriyaОценок пока нет
- Kanda - Histology of The Male Reproductive Organs-1Документ3 страницыKanda - Histology of The Male Reproductive Organs-1y yasminОценок пока нет
- Reproductive Biology and Technology in Animals PDFДокумент126 страницReproductive Biology and Technology in Animals PDFJuan CaroОценок пока нет
- Reproductive SystemДокумент6 страницReproductive Systemsubi100% (1)
- Reproductive Anatomy: Chapter 34 Lesson 1 Page 958Документ13 страницReproductive Anatomy: Chapter 34 Lesson 1 Page 958JanaОценок пока нет
- Histo Female ReproductiveДокумент3 страницыHisto Female ReproductiveAkachukwu ObunikeОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент6 страницFemale Reproductive SystemAlyanna L. ArquillanoОценок пока нет
- Soft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofДокумент6 страницSoft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofKhristin Joy GamponiaОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент7 страницFemale Reproductive SystemyannieОценок пока нет
- Human Reproduction Unit Review WorksheetДокумент25 страницHuman Reproduction Unit Review Worksheetmofid monirОценок пока нет
- Female ReproductiveДокумент34 страницыFemale ReproductiveAbdallah A. Abu Mattar100% (2)
- Developmental GeneticsДокумент20 страницDevelopmental GeneticsProjjal SanyalОценок пока нет
- First Week of Human DevelopmentДокумент81 страницаFirst Week of Human DevelopmentAsfoor gake10% (1)
- Ovarian Cyst FinalДокумент26 страницOvarian Cyst FinalReicy Aquino SacularОценок пока нет
- Hormones and ReproductionДокумент4 страницыHormones and ReproductionJОценок пока нет
- Chapter-3 Human ReproductionДокумент8 страницChapter-3 Human ReproductionbpmbhamoraОценок пока нет
- Histology of Female Genital System For Reproductive ModuleДокумент35 страницHistology of Female Genital System For Reproductive ModuleTeklemuz KahsayОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemДокумент6 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemJazmin Venice LasalaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 6.3 Human ReproductionДокумент39 страницLesson 6.3 Human ReproductionJohn Victor MalupaОценок пока нет
- Fertilization 1 1Документ219 страницFertilization 1 1Edwin TiuОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент25 страницFemale Reproductive SystemJay PornelaОценок пока нет
- Applied Animal ReproductionДокумент91 страницаApplied Animal ReproductionArslan AzizОценок пока нет
- 5.1 Female 2023 - JPДокумент89 страниц5.1 Female 2023 - JPtexasrepublican1976Оценок пока нет
- Point A Group 4Документ48 страницPoint A Group 4mama lilisОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemДокумент39 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemDevi Arine KusumawardaniОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 3 Human ReproductionДокумент3 страницыChapter - 3 Human ReproductionMr.Prashant SharmaОценок пока нет
- Human ReproductionДокумент6 страницHuman Reproductionlakshshah5116Оценок пока нет
- FertlizationДокумент5 страницFertlizationgallardo.bettinarose.iОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System Study GuideДокумент2 страницыFemale Reproductive System Study GuideRhea Jane SorillaОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент11 страницFemale Reproductive SystemArianna Jasmine MabungaОценок пока нет
- Reproductive System For ReviewerДокумент50 страницReproductive System For Reviewerzyrle (zayrieeo)Оценок пока нет
- 4 FertilizationДокумент389 страниц4 FertilizationAngel Gabriel Fornillos100% (1)
- Oogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in TheДокумент7 страницOogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in ThebarbacumlaudeОценок пока нет
- Reproductive Endocrine IntegumentaryДокумент94 страницыReproductive Endocrine IntegumentaryMilyn Mae PalganОценок пока нет
- Notes On The Human Female Reproductive SystemДокумент10 страницNotes On The Human Female Reproductive Systemfichte121Оценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System in Human - DocxenjelДокумент35 страницFemale Reproductive System in Human - DocxenjelAyusofilla ChipzzОценок пока нет
- Identifying - Explaining Brake System FunctionsДокумент39 страницIdentifying - Explaining Brake System FunctionsJestoni100% (1)
- Aabroo Recyclable Waste Program Survey: 1. Demographic InformationДокумент2 страницыAabroo Recyclable Waste Program Survey: 1. Demographic InformationIqra KhaliqОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFДокумент9 страниц1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFIfwat ThaqifОценок пока нет
- Ddrive Transmission ReportДокумент43 страницыDdrive Transmission Reportelah150% (2)
- Lexus JTJBT20X740057503 AllSystemDTC 20230702045631Документ2 страницыLexus JTJBT20X740057503 AllSystemDTC 20230702045631Venerable DezzyОценок пока нет
- Sensors & Transducers: (Code: EI 401)Документ4 страницыSensors & Transducers: (Code: EI 401)Mayukh BiswasОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 2 - Unit Hydrograph2Документ33 страницыChapter - 2 - Unit Hydrograph2Abhilekh PaudelОценок пока нет
- IbnTaymiyyah Theological EthicsДокумент361 страницаIbnTaymiyyah Theological EthicsDado Daki100% (1)
- UNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalДокумент4 страницыUNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalNirmal K.c.Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Cumulative Review: Multiple ChoiceДокумент2 страницыChapter 1 Cumulative Review: Multiple ChoiceJ. LeeОценок пока нет
- 31. (NÂNG CAO) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 31 - DươngДокумент15 страниц31. (NÂNG CAO) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 31 - DươngNguyễn Quế Anh100% (1)
- Energy Thesis StatementДокумент6 страницEnergy Thesis Statementnicoledixonmobile100% (2)
- Bahir Dar NDP UDP - Final ReportДокумент188 страницBahir Dar NDP UDP - Final ReportWorkuMamo100% (1)
- AE451 Aerospace Engineering Design: Team HДокумент140 страницAE451 Aerospace Engineering Design: Team HÖmer Uğur ZayıfoğluОценок пока нет
- SMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportДокумент6 страницSMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportFurqan HamidОценок пока нет
- The Pole and Zeros PDFДокумент24 страницыThe Pole and Zeros PDFKim KeatОценок пока нет
- Audio Spot LightingДокумент20 страницAudio Spot LightingLavanya Vaishnavi D.A.Оценок пока нет
- Complex Sentences For IELTS SpeakingДокумент16 страницComplex Sentences For IELTS SpeakingWill Go NalamОценок пока нет
- Toda People in IndiaДокумент9 страницToda People in IndiaAmoona KopiKoОценок пока нет
- BSN Curriculum 2012Документ1 страницаBSN Curriculum 2012Joana Bless PereyОценок пока нет
- Hydrostatic, Deviatoric StressesДокумент7 страницHydrostatic, Deviatoric StressespanbuОценок пока нет
- Fermat Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionДокумент4 страницыFermat Contest: Canadian Mathematics Competitionสฮาบูดีน สาและОценок пока нет
- Cutting Room Agility and ExcellenceДокумент8 страницCutting Room Agility and Excellenceperro perezОценок пока нет
- Dynamics Study MaterialДокумент57 страницDynamics Study Materialanik sarkerОценок пока нет
- Research Argumentative EssayДокумент6 страницResearch Argumentative EssayHoney LabajoОценок пока нет
- Computer From ScratchДокумент6 страницComputer From ScratchPaul NavedaОценок пока нет
- HCCI - Seminar Reports PPT PDF DOC PresentationДокумент3 страницыHCCI - Seminar Reports PPT PDF DOC PresentationVenkatesh MohanОценок пока нет
- Static CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsДокумент19 страницStatic CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsAbhijna MaiyaОценок пока нет
- TotSK 3.0Документ22 страницыTotSK 3.0PedroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 TurbineДокумент56 страницChapter 4 TurbineHabtamu Tkubet EbuyОценок пока нет