Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Forces WEP
Загружено:
DhanBahadurАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Forces WEP
Загружено:
DhanBahadurАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Addu High School DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE 2. A student reads the following statement in a novel.
Hithadhoo/ Addu PHYSICS
A man weighing 70 kilograms will fall 100 metres in less than 5
Topic: Vectors and projectile motion Worksheet 1 seconds.
(a) Comment on the use of the word weighing.
1. The photograph shows a climber abseiling down a rock face. At
the instant shown the climber is in equilibrium. (b) Make an appropriate calculation to check whether the
statement is correct. Assume the man falls from rest.
(c) Calculate the kinetic energy of the man after falling
100m from rest.
3. The force produced by the engine of a car which drives it is
ultimately transmitted to the area of contact between the cars
tyres and the road surface. The diagram shows a wheel at an
instant during the motion of the car when it is being driven
forward in the direction indicated.
D ire c tio n o f m o tio n o f c a r
(a) Explain what is meant by equilibrium in this context. Ty re
(b) The climbers mass is 65 kg. Calculate his weight.
(c) Below is an incomplete free-body force diagram for the climber.
R o ad su rfac e
d ire c tio n o f ro p e
F 1 F2
C o n ta c t p o in t
b e tw e e n
ro a d a n d ty re
Two horizontal forces act at the point of contact between the
tyre and road due to the transmitted force from the engine.
These are shown as F1 and F2. Assume that the area of
(i) The rope is at an angle of 40 to the horizontal. Calculate the
contact between the tyre and road is very small.
tension in the rope.
Department of Science- Physics- unit 1/ Worksheet 1- Enrichment programme 1 of 5
(a) Complete the statements
(i) F1 is the force of the...................................... on
the ...................................... .
(ii) F2 is the force of the...................................... on
the ...................................... .
1. A girl is attempting to throw a ball across her bedroom onto a shelf.
(b) The total forward force on the car is 400 N when the car is The shelf is 2m above floor level and the horizontal distance from
1 the girl to the shelf is 5m The girl throws the ball with speed u ms-1 at
travelling at a constant speed of 10 m s along a level road. an angle of 30o to the horizontal. It lands on the nearest edge of the
Calculate the effective power driving the car forward. shelf.
(c) Hence calculate the total work done by the 400 N force in 5 minutes (a)
Show the time of flight of the ball is 5/u cos 300
1
in maintaining the speed of 10 m s .
(b) Find the value of u
(d) Although work is done on the car, it continues to move at a constant
speed. Explain why the car is not gaining kinetic energy. 2. A cricketer bowls a ball from a height of 2.3 m. The ball leaves the
hand horizontally with a velocity u. After bouncing once, it passes
4. A weightlifter raised a bar of mass of 110 kg through a height just over the stumps at the top of its bounce. The stumps are 0.71
of 2.22 m. The bar was then dropped and fell freely to the m high and are situated 20 m from where the bowler releases the
floor. ball.
u
(i) Show that the work done in raising the bar was about
2400J.
(ii) It took 3.0 s to raise the bar. Calculate the average
power used. 2 .3 m
(iii) State the principle of conservation of energy.
0 .7 1 m
(iv) Describe how the principle of conservation of energy S tu m p s
20 m
applies to
(1) lifting the bar
(a) Show that from the moment it is released, the ball takes about 0.7 s
to fall 2.3 m.
lifting the bar,
(b) How long does it take the ball to rise 0.71 m after bouncing?
(2) the bar falling to the floor. Do not include the
impact with the floor.
(c) Use your answers to parts (a) and (b) to calculate the initial
horizontal velocity u of the ball. You may assume that the horizontal
(v) Calculate the speed of the bar at the instant it reaches
velocity has remained constant.
the floor.
(d) In reality the horizontal velocity would not be constant. State one
reason why.
Department of Science- Physics- unit 1/ Worksheet 1- Enrichment programme 2 of 5
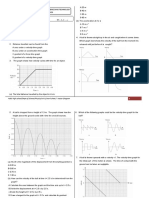
3. A ball is dropped from a high window onto a concrete floor. The S 1 A
velocitytime graph for part of its motion is shown. B
v /m s 1
A
30
20
10 x
0
0 2 4 6 t/s
10 C lo c k
20
30
T ra p d o o r s w itc h
(a) Calculate the gradient from the origin to A.
(b) Comment on the significance of your answer. (a) State what happens at the instant when the switch S1 is moved
from A to B.
(c) What happened to the ball at point A?
(b) The distance x is 1.00 m. Calculate the time for the ball to fall
(d) Calculate the height of the window above the ground. this distance.
4. A lamp is suspended from two wires as shown in the diagram. The (c) In a second experiment the ball is fired horizontally from the
tension in each wire is 4.5N. edge of a table 1.00 m high.
2 .0 0 m
4 .5 N 4 .5 N
40 40
1 .0 0 m
(a) Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force exerted on the lamp
by the wires. (d) State with a reason the time for the ball to reach the ground.
(b) What is the weight of the lamp? Explain your answer. (e) The ball hits the floor a horizontal distance of 2.00 m from the
edge of the table. Calculate the speed at which the ball was
5. The diagram shows an apparatus for timing a falling ball. fired.
Department of Science- Physics- unit 1/ Worksheet 1- Enrichment programme 3 of 5
6. The figure shows a rollercoaster train that is being accelerated
when it is pulled horizontally by a cable.
(a) The train accelerates from rest to a speed of 58ms1 in 3.5 s.
The mass of the fully loaded train is 5800 kg. Calculate the Explain why the ball can be caught even though it was thrown
average acceleration of the train. vertically upwards and the skateboarder is moving horizontally.
(b) Calculate the average tension in the cable as the train is Ignore the effect of air resistance.
accelerated, stating an appropriate unit.
(c) Calculate the distance the train moves while accelerating from 9. A student is required to measure the speed of a trolley rolling down
rest to 58ms1. a slope. This could be done using a ruler and stopwatch but the
student prefers a method using ICT.
7. The figure shows two different rifles being fired horizontally from a
height of 1.5m above ground level. (a) The student uses a light gate as shown in the diagram.
Assume the air resistance experienced by the bullets is negligible. Describe how the student obtains the measurements needed to
calculate speed.
(a) When rifle A is fired, the bullet has a horizontal velocity of 430ms1
as it leaves the rifle. Assume the ground is level.
(i) Calculate the time that the bullet is in the air before it hits the
ground.
(ii) Calculate the horizontal distance travelled by the bullet
before it hits the ground.
(b) Rifle B is fired and the bullet emerges with a smaller horizontal
velocity than the bullet from rifle A.
(i) Explain why the horizontal distance travelled by bullet B will (b) The student thinks that the stopwatch method is less reliable than
be less than bullet A. the ICT method.
Discuss what makes using a stopwatch less reliable
8. A skateboarder throws a ball vertically upwards, while travelling at
a constant horizontal speed. The skateboarder catches the ball 10. The photograph shows an arrangement used to launch a light,
moments later whilst still moving horizontally. foam rocket at a school science competition.
Department of Science- Physics- unit 1/ Worksheet 1- Enrichment programme 4 of 5
(a) The rocket travels 1.88 m in a time of 0.88 s.
(i) Show that the horizontal component of the initial velocity of
the rocket is about 2 m s1.
(ii) Show that the vertical component of the initial velocity of the
rocket is about 4 m s1.
(iii) Calculate the initial velocity of the rocket.
(b) The students obtained their data by filming the flight. When they
checked the maximum height reached by the rocket they found it
was less than the height predicted using this velocity.
(i) Suggest why the maximum height reached was less than
predicted.
The rocket is launched at the level of one end of a long table and lands at (ii) Give two advantages of filming the flight to obtain the data.
the other end at the same level. The students measure the horizontal
distance travelled by the rocket and the time of flight.
Department of Science- Physics- unit 1/ Worksheet 1- Enrichment programme 5 of 5
Вам также может понравиться
- Physics 22 - The Nuclear AtomДокумент60 страницPhysics 22 - The Nuclear AtomHakim AbbasОценок пока нет
- Bismuth-214 Half-Life and Radioactive DecayДокумент9 страницBismuth-214 Half-Life and Radioactive DecayAbhishek SinghОценок пока нет
- Speed, Acceleration and Motion GraphsДокумент5 страницSpeed, Acceleration and Motion GraphsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- 3.2 LightДокумент11 страниц3.2 LightDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Topic:: SolidsДокумент8 страницTopic:: SolidsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- 2.3 Transfer of Thermal EnergyДокумент7 страниц2.3 Transfer of Thermal EnergyDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Thermal Properties and TemperatureДокумент13 страниц2.2 Thermal Properties and TemperatureDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент4 страницы3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- States of Matter ExplainedДокумент10 страницStates of Matter ExplainedDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Waves Full TopicДокумент64 страницыWaves Full TopicDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- 3.4 SoundДокумент5 страниц3.4 SoundDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Understanding Sound WavesДокумент6 страницUnderstanding Sound WavesDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- B 2. D 3. A&B 4.: EitherДокумент2 страницыB 2. D 3. A&B 4.: EitherDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Materials 1Документ10 страницMaterials 1DhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Revision Worsheet MechanicsДокумент8 страницRevision Worsheet MechanicsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Topic: Circular MotionДокумент2 страницыTopic: Circular MotionDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Projectile motion worksheet calculationsДокумент9 страницProjectile motion worksheet calculationsAbdul AhadhОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion WorksheetДокумент5 страницProjectile Motion WorksheetDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Horizontal Projectile Motion - Past Paper Qns - MsДокумент5 страницHorizontal Projectile Motion - Past Paper Qns - MsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Topic:: SolidsДокумент8 страницTopic:: SolidsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Core Practical 1 QuestionsДокумент3 страницыCore Practical 1 QuestionsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Ms SolidsДокумент8 страницMs SolidsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Worksheet: Motion GraphДокумент5 страницWorksheet: Motion GraphDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Topic: Free Body Force Diagram WorksheetДокумент3 страницыTopic: Free Body Force Diagram WorksheetDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Addu High School Physics Worksheet on Quantities and UnitsДокумент3 страницыAddu High School Physics Worksheet on Quantities and UnitsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Magnetic FieldДокумент4 страницыMagnetic FieldDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Horizontal Projectile Motion - Past Paper Qns - MsДокумент5 страницHorizontal Projectile Motion - Past Paper Qns - MsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Quantities and Units WorksheetДокумент2 страницыQuantities and Units WorksheetDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Capacitor and Electric FieldДокумент5 страницCapacitor and Electric FieldDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Particles Universe: Physics Is The Study of Energy, Matter, and Their InteractionsДокумент2 страницыFundamental Particles Universe: Physics Is The Study of Energy, Matter, and Their InteractionsDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- EC6401-Electronic Circuits II 1Документ20 страницEC6401-Electronic Circuits II 1hod eceОценок пока нет
- (Paul E. Minton) Handbook of Evaporation Technology - 170-182Документ13 страниц(Paul E. Minton) Handbook of Evaporation Technology - 170-182Ahmad Asfahani100% (1)
- Survey ToolДокумент74 страницыSurvey Toolk saikiranОценок пока нет
- Airbase 13671Документ6 страницAirbase 13671ssarangОценок пока нет
- Lcra Drought Contingency Plan For Firm Water Customers Update Pres 2024-02-21Документ10 страницLcra Drought Contingency Plan For Firm Water Customers Update Pres 2024-02-21Anonymous Pb39klJОценок пока нет
- Epf 4802 Chap 10 Heat IntegДокумент92 страницыEpf 4802 Chap 10 Heat IntegMiaoluan ChanОценок пока нет
- CPA Process GuideДокумент58 страницCPA Process GuideUtkarsh RaiОценок пока нет
- Gta - Sa - Weapons - Gifts - ItemsДокумент24 страницыGta - Sa - Weapons - Gifts - ItemsSaikat DattaОценок пока нет
- XPol 806-960MHz 90° Fixed Tilt Sector Panel AntennaДокумент1 страницаXPol 806-960MHz 90° Fixed Tilt Sector Panel AntennaArif Noviardiansyah100% (1)
- Hydraulic TrainingДокумент132 страницыHydraulic TrainingJose Luis Rodriguez100% (3)
- Ece 230Документ4 страницыEce 230JackОценок пока нет
- 90202-1043DEA - RS003N Installation&Connection ManualДокумент20 страниц90202-1043DEA - RS003N Installation&Connection ManualIuliana SmarandaОценок пока нет
- Astm d4694 09 Def FWDДокумент3 страницыAstm d4694 09 Def FWDJuan Casia Boza100% (1)
- Programming a Synth for Wind Control (part 1Документ3 страницыProgramming a Synth for Wind Control (part 1CirrusStratusОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Kaedah Penunjuk Bentuk Permukaan Ukuran Had Terima Fit Simbol Bentuk PermukaanДокумент21 страницаChapter 4 Kaedah Penunjuk Bentuk Permukaan Ukuran Had Terima Fit Simbol Bentuk PermukaanhaziqismailОценок пока нет
- Pattern MatchingДокумент58 страницPattern Matchingamitavaghosh1Оценок пока нет
- A Steganography Intrusion Detection SystemДокумент21 страницаA Steganography Intrusion Detection SystemjamessomОценок пока нет
- Worksheet FlowДокумент18 страницWorksheet FlowRaymond VoongОценок пока нет
- Safety Swivel Lifting Eye Bolts Load CapacitiesДокумент1 страницаSafety Swivel Lifting Eye Bolts Load CapacitiesRaul G. MartinezОценок пока нет
- 7 FeedforwardДокумент12 страниц7 FeedforwardHamdi MakniОценок пока нет
- Fuji FCR 5000 Service ManualДокумент892 страницыFuji FCR 5000 Service Manualmasroork_270% (10)
- Digestive Chamber: Scale NTSДокумент1 страницаDigestive Chamber: Scale NTSRomeo Beding Densen Jr.Оценок пока нет
- EDI MessageДокумент3 страницыEDI Messagerameshkola1434Оценок пока нет
- UM4730 Integration GuideДокумент0 страницUM4730 Integration Guidenarse8488Оценок пока нет
- AdaptTo2016 Unit Testing With Sling and AEM Mocks Stefan SeifertДокумент32 страницыAdaptTo2016 Unit Testing With Sling and AEM Mocks Stefan SeifertkaranОценок пока нет
- Nanjing University of Science & Technology CGS-UPSP Supported ProgramДокумент6 страницNanjing University of Science & Technology CGS-UPSP Supported ProgramlankyrckОценок пока нет
- Human Resource BBPB2103 - English Module PDFДокумент290 страницHuman Resource BBPB2103 - English Module PDFVignash100% (1)
- Lean Accounting PDFДокумент303 страницыLean Accounting PDFAnushaОценок пока нет
- TorsionДокумент3 страницыTorsionTannyVaneОценок пока нет
- Vertical VTP Pump enДокумент8 страницVertical VTP Pump enJorgeОценок пока нет