Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
11690119
Загружено:
Tytler Samuel Abiodun Olayinka0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров3 страницыassignment
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документassignment
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров3 страницы11690119
Загружено:
Tytler Samuel Abiodun Olayinkaassignment
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
MATRIC NO:- 11/69/0330
LEVEL:-HND II
COURSE CODE:-COM414 (COMPILER CONTRUCTION PRACTICAL)
ASSIGNMENT
QUESTION
1. LIST 5 COMPILERS EXAMPLES
Batch Compilers
C# Compilers
Basic compilers
Common Lisp Compilers
C ++ Compilers
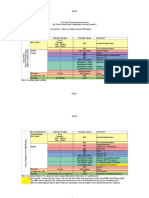
2. MENTION THE DIFFERENT BETWEEN COMPILER
AND INTERPRETER
S/ COMPILER INTERPRETER
N
1. Compiler works on the Interpreter program
complete program at works line-by-line. It
once. It takes the entire takes one statement
program as input. at a time as input.
2. Compiler generates Interpreter does not
intermediate code, called generate intermediate
the object code or object code or machine
machine code code.
3. Compiler executes Interpreter executes
conditional control conditional control
statements (like if-else statements at a
and switch-case) and much slower speed.
logical constructs faster
than interpreter.
4. Compiled programs Interpreter does not
take generate intermediate
more memory because object code. As a
the entire object code result, interpreted
has to reside in memory programs are more
memory efficient.
5. Compile once and run Interpreted programs
anytime. Compiled are interpreted line-by-
program does not need line every time they
to be compiled every are run.
time.
3. DOCUMENT 5 IMPORTANT COMPONENT OF
COMPILER
A compiler works with what are sometimes called 3GL and
higher-level languages. An assembler works on programs written
using a processor's assembler language.
A program that translates between high-level languages is
usually called a source-to-source compiler or transpiler. A
language rewriter is usually a program that translates the form of
expressions without a change of language.
When executing (running), the compiler first parses (or analyzes)
all of the language statements syntactically one after the other
and then, in one or more successive stages or "passes", builds
the output code, making sure that statements that refer to other
statements are referred to correctly in the final code.
A native or hosted compiler is one which output is intended to
directly run on the same type of computer and operating system
that the compiler itself runs on. The output of a cross compiler is
designed to run on a different platform. Cross compilers are often
used when developing software for embedded systems that are
not intended to support a software development environment.
Traditionally in some operating systems, an additional step was
required after compilation - that of resolving the relative location
of instructions and data when more than one object module was
to be run at the same time and they cross-referred to each
other's instruction sequences or data. This process was
sometimes called linkage editing and the output known as a load
module.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- A Harmony HospitalДокумент16 страницA Harmony HospitalTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Small and Medium Scale Industries On The Economic Growth of Nigeria (1986 - 2010)Документ82 страницыThe Impact of Small and Medium Scale Industries On The Economic Growth of Nigeria (1986 - 2010)Tytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- Siwes UrbanДокумент14 страницSiwes UrbanTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- The Ideology of MMM: Presentation by Samuel TytlerДокумент13 страницThe Ideology of MMM: Presentation by Samuel TytlerTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- Bukola Practical AssignmentДокумент8 страницBukola Practical AssignmentTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- Introduction WS2016Документ34 страницыIntroduction WS2016Tytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- The Establishment of The New Testament ChurchДокумент7 страницThe Establishment of The New Testament ChurchTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- Andrew Biemba ThesisДокумент92 страницыAndrew Biemba ThesisTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- Question: - Write The Working Pascal Code For This Flowchart Show Your ResultsДокумент3 страницыQuestion: - Write The Working Pascal Code For This Flowchart Show Your ResultsTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- Fiber Optics ContentДокумент2 страницыFiber Optics ContentTytler Samuel Abiodun OlayinkaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- E3276s-150 V200R002 Software Upgrade GuideДокумент15 страницE3276s-150 V200R002 Software Upgrade GuideAjit KumarОценок пока нет
- BASE24 DR With AutoTMF and RDF WhitepaperДокумент38 страницBASE24 DR With AutoTMF and RDF WhitepaperMohan RajОценок пока нет
- Registering Database Service With ListenerДокумент17 страницRegistering Database Service With ListenerG.R.THIYAGU ; Oracle DBA100% (4)
- Design and Development of Embedded Multimedia TerminalДокумент6 страницDesign and Development of Embedded Multimedia TerminalseventhsensegroupОценок пока нет
- Oric Tap File FormatДокумент4 страницыOric Tap File Formatrc3molinaОценок пока нет
- SAAD. System AnalysisДокумент49 страницSAAD. System AnalysisAvinash KarmacharyaОценок пока нет
- Stryker - SDC Ultra - User Manual GuideДокумент61 страницаStryker - SDC Ultra - User Manual GuideJoel GrullonОценок пока нет
- 2010 Firmware Upgrade Instruction For LCD TV T-VALAUSCДокумент4 страницы2010 Firmware Upgrade Instruction For LCD TV T-VALAUSCfoh8Оценок пока нет
- Revision History: Desktop DVD Player SOC General DatasheetДокумент40 страницRevision History: Desktop DVD Player SOC General DatasheetReady matinОценок пока нет
- VeritasДокумент194 страницыVeritasJames AndersonОценок пока нет
- Switcher ProДокумент7 страницSwitcher ProDino van RensburgОценок пока нет
- Appsense Environment Manager Enterprise Design GuideДокумент15 страницAppsense Environment Manager Enterprise Design GuideGaurav PhutelaОценок пока нет
- Umts CodesДокумент1 страницаUmts CodesacidwarriorОценок пока нет
- API TutorialДокумент8 страницAPI TutorialpassionsaurabhОценок пока нет
- Quotation: Jumo GMBH & Co. KG "Dubai Branch"Документ2 страницыQuotation: Jumo GMBH & Co. KG "Dubai Branch"Renato AbalosОценок пока нет
- Dsa Up LD 00002449Документ49 страницDsa Up LD 00002449Adrian Mircea TutuianuОценок пока нет
- 2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmДокумент17 страниц2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmForu MophiliaОценок пока нет
- FSP 150-GE100Pro Series: Programmable Carrier Ethernet and IP DemarcationДокумент5 страницFSP 150-GE100Pro Series: Programmable Carrier Ethernet and IP DemarcationedirobertОценок пока нет
- Bods InterviewДокумент61 страницаBods InterviewKishore Dammavalam100% (3)
- Technical Code: MCMC MTSFB TC T015:2017Документ14 страницTechnical Code: MCMC MTSFB TC T015:2017seanОценок пока нет
- Tegangan Pin Sirkuit TerpaduДокумент4 страницыTegangan Pin Sirkuit TerpaduDuan Dwi HargianОценок пока нет
- DX DiagДокумент28 страницDX DiagMohammad SulaimanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Digital Signal ProcessingДокумент284 страницыIntroduction To Digital Signal Processingrandombrein67% (3)
- Flash Lite Getting StartedДокумент44 страницыFlash Lite Getting Starteddr90308889034Оценок пока нет
- 01 08 CHIP Do Everything OnlineДокумент103 страницы01 08 CHIP Do Everything Onlineavi_alld9778100% (3)
- iDoctorV7R1 PDFДокумент636 страницiDoctorV7R1 PDFmennaammarОценок пока нет
- FilesДокумент12 страницFilesGoran Gero VukovicОценок пока нет
- Isd4004 + Pic16f877aДокумент38 страницIsd4004 + Pic16f877aSteven Howard100% (1)
- ISD1700 Design Guide - pdf1Документ83 страницыISD1700 Design Guide - pdf1leomancaОценок пока нет
- Template - Change Request Process and Description Requirements FinalДокумент1 страницаTemplate - Change Request Process and Description Requirements FinalSantu ChatterjeeОценок пока нет