Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ch-4 - Yoga P.Ed
Загружено:
Vineet SinghИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ch-4 - Yoga P.Ed
Загружено:
Vineet SinghАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4
Yoga
Meaning and Importance of Yoga: Meaning:
The term yoga is derived from a Sanskrit word Yuj which means join or union. Infact, joining
the individual self with the divine or universal spirit is called yoga.
Patanjali: Checking the impulses of mind is Yoga.
Mahrishi Ved Vyas: Yoga is attaining trance.
In Bhagwat Gita, Lord Krishna says, Skill in actions or efficiency alone is yoga.
Yoga as on Indian Heritage:
History of yoga is as old as the history of Indian culture. Although, there is no written proof in
this regard. Yoga is known as the heritage of India only should go through the related periods
of history.
Elements of yoga:
Around 147 Bc, Patanjali developed a system of yoga that contains Eight steps also known as
Astanga Yoga.
Introduction to Asanas, Pranayama, Mediation and yogic Kriyas:
Asanas:
Asana is to be seated in a position that is firm and relaxed for extended periods.
Pranayama:
Pranayam means extension of the breath of extension of the life force. Pranameans life force
and Ayama means control. There are three parts of Pranayama:
1. Purka - Means inhalation
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
2. Rechaka - Means exhalation
3. Kumbhaka - Means retaining the breath
Types of Pranayam: Suryabhedi, Ujjayi, Sheetkari, Sheetle, Bhastrika, Bhramari, Plavini,
Moorchha etc.
Meditation:
Meditation: means concentration of mind, resulting in Samadhi.
Yogic Kriya:
Yogic Kriya are cleansing techniques that cleanses various internal as well as external organs
of the body. There are six yogic kriyas also known as Khsatkarm Kriyas.
1. Neti Kriya 4. Kapalabhati Kriya
2. Dhayti Kriya 5. Trataka Kriya
3. Basti Kriya 6. Nauli Kriya
Body related benifits of Asana and Pranayam
Improves concentration power, correct body posture, Rehabitation of injuries, Increases
flexibility, Improves breathing system, Improves function of heart, Improves digestive system,
Improve overall health, Improves coordination of function between neurology and muscles.
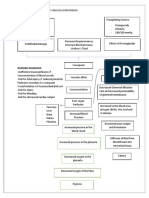
Prevention and Management of common Lifestyle diseases: obesity, Diabetes, Obesity:
Obesity is a medical condition when the body of a person contains 20% or more fat as
compared to ideal weight.
Weight in Kg.
According to WHO, the BMI =------------------------------------
(Height in Mtv)2
Classification BMI
Underweight <18.5
Normal Weight 18.5 - 24.9
Over Weight 25.0 - 29.9
Class I Obesity 30.0 - 34.9
Class II Obesity 35.0 - 39.9
Class III Obesity 40.0
Diabetes:
Diabetes is a metabolism disorder in which the person has high blood glucose may be either
due to inadequate production of insulin or the body cells do not respond properly to the
insulin produced by the pancreas. There are two types of diabetes.
1. Type I diabetes: In this type of diabetes, the body does not produce insulin.
2. Type II diabetes: In this stage of diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin for
proper functioning of the cells in the body and do not react to insulin.
Hypertension:
High blood pressure or hypertension means high pressure in arteries. It is measured in
mm/Hg.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Back pain:
Back pain is a pain felt in the back that usually originates from the muscles, nerves, bones,
joints or other structures in the spine. Main causes of back pain are lack of physical activities,
lack of flexibility, smoking, excessive pressure on back etc.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Вам также может понравиться
- Ancient Yoga and Kundalini Fundamentals: Your First Steps to Experiencing Kundalini AwakeningОт EverandAncient Yoga and Kundalini Fundamentals: Your First Steps to Experiencing Kundalini AwakeningОценок пока нет
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Документ4 страницыMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 4AbhishekОценок пока нет
- Physical Education Class 11 Long Answers Chapter 4Документ5 страницPhysical Education Class 11 Long Answers Chapter 4Aditya kumarОценок пока нет
- CLASS-11 - PHY-ED. - CHAPTER-5. - Physical Fitness AndwellnessДокумент13 страницCLASS-11 - PHY-ED. - CHAPTER-5. - Physical Fitness AndwellnessIshmeet KaurОценок пока нет
- Yoga Therapy Full BookДокумент207 страницYoga Therapy Full BookHarriesh Gomahan93% (41)
- CH-3 YogaДокумент36 страницCH-3 YogaSTARTED GAMINGОценок пока нет
- Chen Style Tai Chi Cultivating Internal Energy MethodДокумент11 страницChen Style Tai Chi Cultivating Internal Energy Methodjns198Оценок пока нет
- The Five-Fold Moral CultureДокумент31 страницаThe Five-Fold Moral CultureSam SonОценок пока нет
- Yoga: Its History and Emergence Through TimeДокумент9 страницYoga: Its History and Emergence Through TimeCla BelenОценок пока нет
- NZLVW 7 Kab STC Ru CTW Wo IДокумент10 страницNZLVW 7 Kab STC Ru CTW Wo IDhruv RajputОценок пока нет
- Class Notes: Class: XI Topic: YOGA/SKV Subject: Physical EducationДокумент8 страницClass Notes: Class: XI Topic: YOGA/SKV Subject: Physical EducationDisney DoreamonОценок пока нет
- 3 Yoga XiДокумент20 страниц3 Yoga XiICSE BOARDОценок пока нет
- CBSE Chapter 3 Yoga and Lifestyle DiseasesДокумент54 страницыCBSE Chapter 3 Yoga and Lifestyle DiseasesShagnik BasuОценок пока нет
- Yoga, Class XI, SynopsisДокумент6 страницYoga, Class XI, SynopsisOcean WavesОценок пока нет
- 5 "S" of yoga: A Yoga book for adults to learn about 5 "S" s of yoga - Self-discipline, Self-control, Self-motivation, Self-healing and Self-realization.От Everand5 "S" of yoga: A Yoga book for adults to learn about 5 "S" s of yoga - Self-discipline, Self-control, Self-motivation, Self-healing and Self-realization.Оценок пока нет
- Notes On Anatomy and Physiology For Yoga PDFДокумент195 страницNotes On Anatomy and Physiology For Yoga PDFPetar MogilskiОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 YogaДокумент55 страницUnit 5 Yogashreyavjha2020Оценок пока нет
- 11 Physical Education - Yoga-NotesДокумент11 страниц11 Physical Education - Yoga-NotesAbhinav KumarОценок пока нет
- 11 Physical Education - Yoga-NotesДокумент11 страниц11 Physical Education - Yoga-NotesAtu Kaushal100% (1)
- Lesson 12Документ33 страницыLesson 12Marykris CamachoОценок пока нет
- Yoga Therapy Full Book PDFДокумент207 страницYoga Therapy Full Book PDFEma Ghinter100% (2)
- Yoga Notes PDFДокумент24 страницыYoga Notes PDFdhruv jainОценок пока нет
- Yoga TherapyДокумент95 страницYoga TherapyRozze AngelОценок пока нет
- Art of Living Practice of Sudarshan KriyaДокумент2 страницыArt of Living Practice of Sudarshan Kriyajeevaka100% (3)
- Sambhav GsДокумент13 страницSambhav GsAditya BhardwajОценок пока нет
- YogaДокумент10 страницYogariotech455Оценок пока нет
- VishalДокумент17 страницVishalVishal SharmaОценок пока нет
- DeshpandeДокумент17 страницDeshpandedeekshithОценок пока нет
- 11th YogaДокумент3 страницы11th Yogatyagigame10Оценок пока нет
- SKY Introduction EnglishДокумент18 страницSKY Introduction Englishdinakaran20200% (1)
- Studyguide360: Yoga Meaning and Importance of Yoga: MeaningДокумент3 страницыStudyguide360: Yoga Meaning and Importance of Yoga: MeaningAnuj BhaiОценок пока нет
- Path To Enlightenment: A Guide To Meditation Techniques Practiced in ThailandДокумент65 страницPath To Enlightenment: A Guide To Meditation Techniques Practiced in ThailandShubham InfinityОценок пока нет
- Yoga MergedДокумент12 страницYoga Mergedmitrasupratik42Оценок пока нет
- The Five Points of YogaДокумент11 страницThe Five Points of Yogaanattā100% (1)
- 30 Journal enДокумент4 страницы30 Journal enM. Abdullah AhmedОценок пока нет
- Yoga Open NotesДокумент8 страницYoga Open NotesInsight MndyОценок пока нет
- YogaДокумент128 страницYogaALMIRA JENNAОценок пока нет
- PE PROJECT OgДокумент32 страницыPE PROJECT OgLEGALОценок пока нет
- QigongДокумент7 страницQigongFrank ValenzuelaОценок пока нет
- Science of YogaДокумент5 страницScience of YogaoluОценок пока нет
- The Koshas - 5 Layers of BeingДокумент9 страницThe Koshas - 5 Layers of Beinggeorgina_notОценок пока нет
- Assignment Asthanga Yoga PranayamaДокумент9 страницAssignment Asthanga Yoga PranayamaVenkateswara Rao DoodalaОценок пока нет
- YOGAДокумент10 страницYOGAdeepthikamichetty336Оценок пока нет
- Role of Sky Yoga in Overcoming Fear of Death and Enhancing Quality of LifeДокумент7 страницRole of Sky Yoga in Overcoming Fear of Death and Enhancing Quality of LifeBrock StonОценок пока нет
- Physiotherapy For HealthДокумент30 страницPhysiotherapy For HealthAnuj MehtaОценок пока нет
- Sudarshan Kriya ANovel Breathing Technique 1Документ9 страницSudarshan Kriya ANovel Breathing Technique 1Ankit LatiyanОценок пока нет
- Yoga AssignmentДокумент9 страницYoga AssignmentSharunieRavikumar77% (13)
- 5 Points of YogaДокумент24 страницы5 Points of YogamangaldasОценок пока нет
- Effect of Sky Yoga On Blood Sugar Levels of Diabetic PatientsДокумент8 страницEffect of Sky Yoga On Blood Sugar Levels of Diabetic PatientsGopal KrishnanОценок пока нет
- BreathingДокумент85 страницBreathingrhvenkat100% (1)
- General Yoga InformationДокумент4 страницыGeneral Yoga InformationmuruganananОценок пока нет
- Bronchial Asthma And Respiratory Disorders & It's Management Through YogaОт EverandBronchial Asthma And Respiratory Disorders & It's Management Through YogaОценок пока нет
- Meridian Exercise for Self Healing: Classified by Common SymptomsОт EverandMeridian Exercise for Self Healing: Classified by Common SymptomsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Yoga for Beginners With Over 100 Yoga Poses (Boxed Set): Helps with Weight Loss, Meditation, Mindfulness and Chakras: Helps with Weight Loss, Meditation, Mindfulness and ChakrasОт EverandYoga for Beginners With Over 100 Yoga Poses (Boxed Set): Helps with Weight Loss, Meditation, Mindfulness and Chakras: Helps with Weight Loss, Meditation, Mindfulness and ChakrasРейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (6)
- Mindful Yoga: Cultivating Presence and Well-Being Through Yoga Practice (2024 Beginner Guide)От EverandMindful Yoga: Cultivating Presence and Well-Being Through Yoga Practice (2024 Beginner Guide)Оценок пока нет
- CH 3 Olympic MovmentДокумент2 страницыCH 3 Olympic MovmentVineet Singh0% (1)
- 11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch09 Biomechanics in SportsДокумент2 страницы11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch09 Biomechanics in SportsAkash33% (3)
- Material Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksДокумент3 страницыMaterial Downloaded From and Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksAkashОценок пока нет
- Ch-11 - Training in SportsДокумент1 страницаCh-11 - Training in SportsVineet SinghОценок пока нет
- Air PollutionДокумент3 страницыAir PollutionVineet SinghОценок пока нет
- Resetting USB Drive Using Windows Diskpart-V1Документ16 страницResetting USB Drive Using Windows Diskpart-V1y_satyapОценок пока нет
- 16 17 UTSC International From UTSCДокумент17 страниц16 17 UTSC International From UTSCVineet SinghОценок пока нет
- Accounts 11th Class Sample PaperДокумент8 страницAccounts 11th Class Sample PaperVineet SinghОценок пока нет
- Air PollutionДокумент3 страницыAir PollutionVineet SinghОценок пока нет
- News On ChemistryДокумент4 страницыNews On ChemistryVineet SinghОценок пока нет
- DefinitionsДокумент2 страницыDefinitionsRoxenette Gil Bernales PangilinanОценок пока нет
- Bhangarh Fort - Ajabgarh, Alwar, RajasthanДокумент8 страницBhangarh Fort - Ajabgarh, Alwar, RajasthanVineet SinghОценок пока нет
- Malnutrition AdimeДокумент2 страницыMalnutrition Adimeapi-508953960Оценок пока нет
- Retinal Vascular DisordersДокумент52 страницыRetinal Vascular Disorderssushma shresthaОценок пока нет
- Guias Hipertension 2023 Esc AnalisisДокумент12 страницGuias Hipertension 2023 Esc Analisismiguel contrerasОценок пока нет
- Nurleli: Program Studi Kesehatan Masyarakat, Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Kesehatan Makassar Korespondensi: (E-Mail)Документ7 страницNurleli: Program Studi Kesehatan Masyarakat, Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Kesehatan Makassar Korespondensi: (E-Mail)NURLELIОценок пока нет
- Ecg Echo LVHДокумент3 страницыEcg Echo LVHSoʋɭ ʜʌcĸɘʀОценок пока нет
- Family Nursing Care Plan FinalДокумент1 страницаFamily Nursing Care Plan FinalKhrisha Anne Davillo100% (1)
- Knowledge and Attitude Towards Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal at Kampala International University Teaching HospitalДокумент71 страницаKnowledge and Attitude Towards Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal at Kampala International University Teaching HospitalBALUKU YOSIAHОценок пока нет
- The Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease in Ilorin, NigeriaДокумент5 страницThe Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease in Ilorin, NigeriaMuhammad A MakusidiОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDareRaymondОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 2 - Reviewed by CommitteeДокумент14 страницSCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 2 - Reviewed by CommitteeBayani VicencioОценок пока нет
- Resistant Hypertension - Cleveland Clinic (2023)Документ11 страницResistant Hypertension - Cleveland Clinic (2023)Areli KamuiОценок пока нет
- Recalls 6Документ16 страницRecalls 6Charisse Caydan0% (1)
- Drugs Acting On Cardio Vascular SystemДокумент16 страницDrugs Acting On Cardio Vascular SystemANUSHYA B PSGRKCWОценок пока нет
- A Short History of The Metabolic Syndrome DefinitionsДокумент8 страницA Short History of The Metabolic Syndrome DefinitionsexraОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Benefits and Risks of Moderate Alcohol Consumption - UpToDateДокумент17 страницCardiovascular Benefits and Risks of Moderate Alcohol Consumption - UpToDateAnca StanОценок пока нет
- Badyal, 2003 - Animal Models of Hypertension and Effect of DrugsДокумент14 страницBadyal, 2003 - Animal Models of Hypertension and Effect of DrugsHo Yoke MeiОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Hypertension ': Case PresentationДокумент64 страницыPulmonary Hypertension ': Case PresentationYasha IchirouОценок пока нет
- Brisk Walking ExerciseДокумент8 страницBrisk Walking ExercisePerin Graha100% (1)
- Thiazide and Thiazide-Like DiureticsДокумент3 страницыThiazide and Thiazide-Like DiureticsYohanes SutrisnoОценок пока нет
- Aortic Coarctation Cardiology Clinics 2020Документ15 страницAortic Coarctation Cardiology Clinics 2020Angela OrozcoОценок пока нет
- Empr Prescriber's EditionДокумент420 страницEmpr Prescriber's EditionPatel Pratyk100% (1)
- GSIS v. CalumpianoДокумент2 страницыGSIS v. CalumpianoKei Sha100% (1)
- Diagnosis and Management of Cerebral Small Vessel.9Документ18 страницDiagnosis and Management of Cerebral Small Vessel.9Felipe MontorfanoОценок пока нет
- SCMHRD SM-4Документ42 страницыSCMHRD SM-4ruchit2809Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 1Документ2 страницыExercise 1April Mergelle LapuzОценок пока нет
- Case DM Type II + Gangrene Diabeticum +anemiaДокумент26 страницCase DM Type II + Gangrene Diabeticum +anemiaAAn NaОценок пока нет
- Cva Case StudyДокумент31 страницаCva Case StudyZoe AnnaОценок пока нет
- Blood Pressure Medications Lecture 2020 4 Pod CastsДокумент46 страницBlood Pressure Medications Lecture 2020 4 Pod CastsfbjsjdfhОценок пока нет
- 10 Ways To Improve Kidney Function NaturallyДокумент9 страниц10 Ways To Improve Kidney Function Naturallydreamyson1983Оценок пока нет
- Ghid CardiovascularДокумент78 страницGhid Cardiovasculardiudiu93Оценок пока нет