Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Clinical Points: at The End of Your Study, You Should Be Able To
Загружено:
Mihaela0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров1 страницаThis document provides an overview of the upper limb, including:
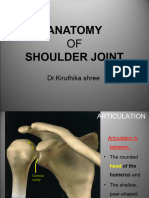
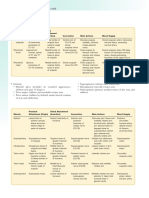
1) The glenoid cavity and suprascapular notch are important parts of the scapula. Damage to the long thoracic nerve can cause winging of the scapula.
2) The sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, and glenohumeral joints allow movement of the shoulder and connect the clavicle and scapula. Important ligaments support these joints.
3) The document describes bones of the upper limb like the clavicle and scapula, as well as muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and contents of the axilla.
Исходное описание:
Anatomie
Оригинальное название
pg_0691
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document provides an overview of the upper limb, including:
1) The glenoid cavity and suprascapular notch are important parts of the scapula. Damage to the long thoracic nerve can cause winging of the scapula.
2) The sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, and glenohumeral joints allow movement of the shoulder and connect the clavicle and scapula. Important ligaments support these joints.
3) The document describes bones of the upper limb like the clavicle and scapula, as well as muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and contents of the axilla.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров1 страницаClinical Points: at The End of Your Study, You Should Be Able To
Загружено:
MihaelaThis document provides an overview of the upper limb, including:
1) The glenoid cavity and suprascapular notch are important parts of the scapula. Damage to the long thoracic nerve can cause winging of the scapula.
2) The sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, and glenohumeral joints allow movement of the shoulder and connect the clavicle and scapula. Important ligaments support these joints.
3) The document describes bones of the upper limb like the clavicle and scapula, as well as muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and contents of the axilla.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
e104
SECTION 6 Upper Limb Study Guide
CLINICAL POINTS Glenoid cavity = socket for head of humerus
Suprascapular notch (scapular notch) = notch found
WINGED SCAPULA on superior border, two thirds of way along
Normally the scapula is held closely against the posterior laterally
thoracic wall. Damage to the long thoracic nerve to serratus Capable of considerable movement over thoracic wall
anterior (which courses superficially over the muscle) causes
winging of the scapula as its medial border lifts away from JOINTS
the thorax when the arm is raised. This is accentuated when Sternoclavicular joint
the individual leans on the hand or pushes the upper limb Saddle-type, synovial joint
against a wall. Most importantly, the arm cannot be abducted Divided into two compartments by an articular disc
above the horizontal plane because glenoid cavity cannot Movements
be rotated upward without the action of the serratus Elevation with posterior rotation
anterior. Protraction
Depression
Articulation between concave facet of manubrium and
6.2 SHOULDER AND AXILLA concave facet of clavicle
Strengthened by anterior and posterior sternoclavicu-
lar, costoclavicular, and interclavicular ligaments
Study Aims Blood supply: branches of suprascapular and internal
thoracic arteries
At the end of your study, you should be able to: Nerve supply: branches of supraclavicular nerve and
Identify the different parts and surface markings of the nerve to subclavius
clavicle and scapula Acromioclavicular joint
Describe the sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, and gleno- Plane-type, synovial joint
humeral joints, their movements, and supporting No demonstrable movement; muscles moving scapula
ligaments cause acromion to move on clavicle
Understand the organization of the scapular muscles Articulation between concave facet of acromion and
Know the origins, insertions, and actions of the intrinsic convex facet of clavicle
scapular muscles Strengthened by acromioclavicular and coracoclavicu-
Identify the boundaries of the axilla and describe its lar (conoid and trapezoid) ligaments
contents
Coracoclavicular
Describe the organization of the deep fascia
Unites coracoid process and clavicle
Two component ligaments: conoid: vertical, in shape
of inverted pyramid; trapezoid: horizontal, extends
laterally to inferior surface of clavicle
GUIDE Blood supply: branches of suprascapular and thoraco-
acromial arteries
BONES Nerve supply: branches of supraclavicular, lateral pec-
Clavicle: sternal and acromial ends toral, and axillary nerves
Double-curved long bone Shoulder (glenohumeral) joint
Sternal end articulates with manubrium of sternum Multiaxial, synovial ball-and-socket joint
Acromial end articulates with acromion Movements
Osteological features Flexion/extension
Deltoid tubercle for attachment of deltoid muscle Abduction/adduction
Conoid tubercle for attachment of conoid ligament Internal/external (medial/lateral) rotation
Subclavian groove for attachment of subclavius Circumduction
muscle Articulation of head of humerus with shallow glenoid
Trapezoid line where trapezoid ligament attaches cavity of scapula
Serves as a strut suspending scapula and limb with Joint socket deepened by glenoid labrum (fibrocarti-
maximum freedom laginous ring) and supported by the rotator cuff
Scapula: lying against posterolateral thorax muscles (see below)
Triangular, flat bone Loose fibrous capsule encloses and contains two
Lies posterolateral on 2nd through 7th ribs apertures
Osteological features Between tubercles of humerus for passage of long
Concave costal surface = subscapular fossa head of biceps brachii, which attaches to supragle-
Posterior surface divided by spine = transverse ridge noid tubercle within joint
of bone Anterior opening, inferior to coracoid process, for
Supraspinous fossa communication between subscapular bursa and
Infraspinous fossa synovial cavity of joint
Acromion = flattened lateral end of spine Blood supply: branches of anterior and posterior cir-
Coracoid process = anterior projection above glenoid cumflex humeral arteries from axillary and suprascapu-
cavity lar artery from subclavian
Вам также может понравиться
- MMB (018) Elbow Joint Cubital Fossa (Practical) 2022Документ39 страницMMB (018) Elbow Joint Cubital Fossa (Practical) 2022Mohamed AhmedОценок пока нет
- 1 Shoulder Region, Shoulder Joint and Superficial Back - 2 FebДокумент28 страниц1 Shoulder Region, Shoulder Joint and Superficial Back - 2 FebImkita MngqundanisoОценок пока нет
- Shoulder GirdleДокумент38 страницShoulder GirdleAnigha PrasadОценок пока нет
- The Shoulder Anatomy & Approaches: Abdulaziz F. Ahmed, MBBS PGY-2Документ61 страницаThe Shoulder Anatomy & Approaches: Abdulaziz F. Ahmed, MBBS PGY-2Abdulaziz Al-Akhras100% (1)
- Anatomy of The ARMДокумент17 страницAnatomy of The ARMJacob MasikaОценок пока нет
- 5.back and Scapular RegionДокумент72 страницы5.back and Scapular RegionGish KioiОценок пока нет
- Katz Sandor enДокумент49 страницKatz Sandor enAlexОценок пока нет
- 5 Joints of The Upper Limb MB 2Документ24 страницы5 Joints of The Upper Limb MB 2sandyОценок пока нет
- Imaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesДокумент12 страницImaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesChristian ToalongoОценок пока нет
- BonesДокумент27 страницBonesADELAJA SAMUELОценок пока нет
- Muscles of Pectoral RegionДокумент11 страницMuscles of Pectoral RegionTomar PrabhakarОценок пока нет
- An Breast and PectoralisДокумент36 страницAn Breast and PectoralisTom TsouОценок пока нет
- Shoulder JTДокумент30 страницShoulder JTEVELYN EZEKWEОценок пока нет
- Joints of Upper Limb: Pectoral GirdleДокумент34 страницыJoints of Upper Limb: Pectoral GirdleCupid MohОценок пока нет
- Pectoral Region & AxillaДокумент18 страницPectoral Region & AxillaMohammad PharaonОценок пока нет
- Vertebral Column and ContentsДокумент5 страницVertebral Column and ContentsJewelОценок пока нет
- Dissector Answers - Deep Back & Spinal CordДокумент9 страницDissector Answers - Deep Back & Spinal CordUloko ChristopherОценок пока нет
- Joints of Upper LimbДокумент70 страницJoints of Upper LimbHaania KhanОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The ArmДокумент38 страницAnatomy of The ArmAkomolede AbosedeОценок пока нет
- Clinical Examination of The ShoulderДокумент78 страницClinical Examination of The ShoulderAbcabc34 AbaОценок пока нет
- Spine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiДокумент59 страницSpine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiJho AggasidОценок пока нет
- 8 - Pectoral Region & AxillaДокумент21 страница8 - Pectoral Region & AxillaRaj BahiramkarОценок пока нет
- Lecture On Elbow JointДокумент17 страницLecture On Elbow JointManvi MishraОценок пока нет
- Lec 2 The Shoulder Girdle and Upper Arm 2020Документ49 страницLec 2 The Shoulder Girdle and Upper Arm 2020Diane Lois ManicdaoОценок пока нет
- 02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEДокумент18 страниц02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEClaude ReyesОценок пока нет
- General Arthrology, Joints of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDДокумент33 страницыGeneral Arthrology, Joints of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDTodesengelОценок пока нет
- AtlasДокумент509 страницAtlasLasana Bayshawn SandyОценок пока нет
- (Week 7) Joints Part 2Документ29 страниц(Week 7) Joints Part 2TheLegendKiller337Оценок пока нет
- Epidural and Spinal AnesthesiaДокумент86 страницEpidural and Spinal Anesthesiasarguss1471% (7)
- Radioanatomy of Shoulder Joint-Dr - NaziyaДокумент82 страницыRadioanatomy of Shoulder Joint-Dr - Naziyaraghavmaster100% (1)
- Radiography of Shoulder and ArmДокумент81 страницаRadiography of Shoulder and ArmKristina ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Muscles of Scapular RegionДокумент62 страницыMuscles of Scapular RegionSanwan NaichОценок пока нет
- Ul PDFДокумент8 страницUl PDFNourhan ShabanОценок пока нет
- Elbow JointДокумент6 страницElbow JointDharm PatelОценок пока нет
- OsteologyДокумент38 страницOsteologyERIAS TENYWAОценок пока нет
- Knee Ankle JointsДокумент38 страницKnee Ankle JointsmaggieОценок пока нет
- Retinacula of Upper LimbДокумент35 страницRetinacula of Upper LimbDr. Janarthanan VОценок пока нет
- LABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Документ29 страницLABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Ian Mar ValenzuelaОценок пока нет
- Upper LimbДокумент84 страницыUpper LimbJinnah SheriffОценок пока нет
- Week 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesДокумент53 страницыWeek 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesCyril Jay G. OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Week 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesДокумент53 страницыWeek 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesHephzibah JaporОценок пока нет
- TrunkExam NurДокумент124 страницыTrunkExam Nuralina nguynОценок пока нет
- 5-Thoacolumbar SpineДокумент20 страниц5-Thoacolumbar SpineJULIOОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Shoulder JointДокумент44 страницыAnatomy of The Shoulder JointAuza Moses IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Appendicular SkeletonДокумент10 страницAppendicular SkeletonJoshua DanielОценок пока нет
- Aug15 1035 RasmussenДокумент35 страницAug15 1035 RasmussenPedro BragatoОценок пока нет
- Joints of Upper ExtremityДокумент28 страницJoints of Upper ExtremityIzabella MonteiroОценок пока нет
- Superior Extremities & Vertebrae OsteologyДокумент48 страницSuperior Extremities & Vertebrae OsteologyPokena EmaОценок пока нет
- 07-Shoulder JointДокумент42 страницы07-Shoulder JointVaishnaviОценок пока нет
- PDF Cervical Spine AnatomyДокумент71 страницаPDF Cervical Spine AnatomyAqilla Fadia HayaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and NeuralДокумент56 страницAnatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and Neuralvineet_ent100% (1)
- Chapter 21 Back of The Neck NewДокумент63 страницыChapter 21 Back of The Neck NewMohan PalanimalaiОценок пока нет
- Upper ExtremityДокумент216 страницUpper ExtremityChester VergilОценок пока нет
- Spine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineДокумент22 страницыSpine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineCris Soliven DucosОценок пока нет
- Arm and Cubital FossaДокумент40 страницArm and Cubital FossaAbdelrhman AbubakrОценок пока нет
- Subjects: - Introduction - Pelvic Girdle - Pelvic CavityДокумент39 страницSubjects: - Introduction - Pelvic Girdle - Pelvic CavityAshraf SidrahОценок пока нет
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaДокумент24 страницыAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossakiranОценок пока нет
- Osteology of The Upper ExtremityДокумент75 страницOsteology of The Upper ExtremityKevo YoungОценок пока нет
- Kennedy Axis VДокумент10 страницKennedy Axis VMihaelaОценок пока нет
- James A. Kennedy - Mastering The Kennedy Axis V - A New Psychiatric Assessment of Patient Functioning (2003) - 1-15Документ15 страницJames A. Kennedy - Mastering The Kennedy Axis V - A New Psychiatric Assessment of Patient Functioning (2003) - 1-15MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Janofsky 1992Документ5 страницJanofsky 1992MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Kennedy Axis VДокумент24 страницыKennedy Axis VMihaelaОценок пока нет
- Kennedy Axis VДокумент18 страницKennedy Axis VMihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 258Документ1 страницаPG 258MihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0336Документ1 страницаPG 0336Mihaela100% (1)
- Autonomic Reflex Pathways: Schema : Innervation Plate 304Документ1 страницаAutonomic Reflex Pathways: Schema : Innervation Plate 304MihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0394Документ1 страницаPG 0394MihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0290Документ1 страницаPG 0290MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Atlas of Human Anatomy I-37Документ1 страницаAtlas of Human Anatomy I-37MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Sectional Anatomy Muscle Table: AbdomenДокумент1 страницаSectional Anatomy Muscle Table: AbdomenMihaelaОценок пока нет
- Vertebral Ligaments: Lumbosacral Region : Left Lateral ViewДокумент1 страницаVertebral Ligaments: Lumbosacral Region : Left Lateral ViewMihaelaОценок пока нет
- Autonomic Nerves in Thorax : Lungs Plate 206Документ1 страницаAutonomic Nerves in Thorax : Lungs Plate 206MihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0093Документ1 страницаPG 0093MihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0357Документ1 страницаPG 0357MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Thoracic Vertebrae : T6 Vertebra: Superior View T6 Vertebra: Lateral ViewДокумент1 страницаThoracic Vertebrae : T6 Vertebra: Superior View T6 Vertebra: Lateral ViewMihaelaОценок пока нет
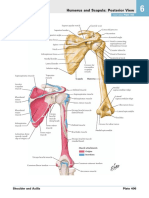
- Humerus and Scapula: Posterior View : See Also Plate 183Документ1 страницаHumerus and Scapula: Posterior View : See Also Plate 183MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Uterus and Adnexa : Posterior ViewДокумент1 страницаUterus and Adnexa : Posterior ViewMihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0257Документ1 страницаPG 0257MihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0334Документ1 страницаPG 0334Mihaela100% (1)
- PG 0469Документ1 страницаPG 0469MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Lymphatic Drainage of Breast : See AlsoДокумент1 страницаLymphatic Drainage of Breast : See AlsoMihaelaОценок пока нет
- Back and Spinal Cord Study Guide: 2.1 Topographic Anatomy Study AimsДокумент1 страницаBack and Spinal Cord Study Guide: 2.1 Topographic Anatomy Study AimsMihaelaОценок пока нет
- Psoas and Iliacus Muscles : See Also Plates 253, 258, 262Документ1 страницаPsoas and Iliacus Muscles : See Also Plates 253, 258, 262MihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0471Документ1 страницаPG 0471MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Clavicular Part: Flexes and Acromial Part: AbductsДокумент1 страницаClavicular Part: Flexes and Acromial Part: AbductsMihaelaОценок пока нет
- Bony Framework of Pelvis : Plate 330 Bones and LigamentsДокумент1 страницаBony Framework of Pelvis : Plate 330 Bones and LigamentsMihaelaОценок пока нет
- Wrist and Hand: Deep Dorsal Dissection : See AlsoДокумент1 страницаWrist and Hand: Deep Dorsal Dissection : See AlsoMihaelaОценок пока нет
- PG 0441Документ1 страницаPG 0441MihaelaОценок пока нет
- Uace Biology Rat Dissection GuideДокумент15 страницUace Biology Rat Dissection Guidemajanga johnОценок пока нет
- Cat MusclesДокумент8 страницCat MusclesPattyОценок пока нет
- Physical Therapy Protocols For Conditions of Shoulder RegionДокумент111 страницPhysical Therapy Protocols For Conditions of Shoulder RegionPieng Napa100% (1)
- 11 Upper Limb Muscle Groups SmithДокумент3 страницы11 Upper Limb Muscle Groups SmithMatra Dutt SharmaОценок пока нет
- Human Anatomy 5Th Edition Mckinley Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент54 страницыHuman Anatomy 5Th Edition Mckinley Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJenniferWhitebctr100% (10)
- Avian Skeletal System - Robert Porter PDFДокумент16 страницAvian Skeletal System - Robert Porter PDFJohn MillerОценок пока нет
- Shoulder StabilityДокумент5 страницShoulder StabilityAshley WatsonОценок пока нет
- Voies D'abord MasqueletДокумент385 страницVoies D'abord MasqueletAlexandru MazurОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Concept Book AtfДокумент246 страницAnatomy Concept Book AtfRishi ShekharОценок пока нет
- One More RepДокумент35 страницOne More RepGeorgi Ignatov100% (5)
- 1 OsteologyДокумент115 страниц1 OsteologyAbhijith S. PОценок пока нет
- People Vs Urminita, G.R. No. L-33314Документ8 страницPeople Vs Urminita, G.R. No. L-33314Cyber QuestОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab FG 1011 1Документ11 страницIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab FG 1011 1CharmaineОценок пока нет
- Pectoral Region KJR (1) - 2Документ36 страницPectoral Region KJR (1) - 2MahiОценок пока нет
- Structural Balance of ShouldersДокумент51 страницаStructural Balance of ShouldersMark McKean100% (1)
- Bio Mechanics of The ShoulderДокумент106 страницBio Mechanics of The ShoulderOnwaree Ing100% (11)
- Labeled ItДокумент50 страницLabeled ItKaloy KamaoОценок пока нет
- Shoulder Application SolutionsДокумент3 страницыShoulder Application SolutionsDОценок пока нет
- Manual in Radiographic Positioning.Документ116 страницManual in Radiographic Positioning.Jestia Lyn EngracialОценок пока нет
- Shoulder ComplexДокумент64 страницыShoulder ComplexcpОценок пока нет
- Musculoskeletal SystemДокумент210 страницMusculoskeletal SystemDr. Serin KuriakoseОценок пока нет
- MANUAL OF LAB MSK WEEK One 2019Документ8 страницMANUAL OF LAB MSK WEEK One 2019Lisa OnoОценок пока нет
- 2018 Automated Three-Dimensional Measurement of Glenoid Version and Inclination in Arthritic ShouldersДокумент9 страниц2018 Automated Three-Dimensional Measurement of Glenoid Version and Inclination in Arthritic Shouldersusman khanОценок пока нет
- 3D Printed AnatomyДокумент52 страницы3D Printed AnatomyHaryono zhuОценок пока нет
- Anatomical Basis of The Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment, and Clinical Relevance of The Supraspinatus FasciaДокумент8 страницAnatomical Basis of The Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment, and Clinical Relevance of The Supraspinatus FasciaEleonora FondiОценок пока нет
- MFS)Документ47 страницMFS)SanthiyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Upper Limb Sameh DossДокумент143 страницыAnatomy Upper Limb Sameh DossStella JОценок пока нет
- 50 Best Calisthenic Exercises - CamEditДокумент68 страниц50 Best Calisthenic Exercises - CamEditPhoenix Phoenix100% (1)
- The Only Book A Teen Will EVER Need To Lose Fat & Build Muscle in The GymДокумент146 страницThe Only Book A Teen Will EVER Need To Lose Fat & Build Muscle in The GymJake Farrugia100% (1)
- Bridging Ortho NotesДокумент4 страницыBridging Ortho NotesJonathan TayОценок пока нет
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)От EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (82)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDОт EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesОт EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1412)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (42)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeОт EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (254)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.От EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceОт EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (51)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsОт EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (39)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlОт EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (60)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingОт EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1138)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessОт EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (328)