Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Color Changing Flowers For The Classroom PDF
Загружено:
Alexander Arredondo SánchezОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Color Changing Flowers For The Classroom PDF
Загружено:
Alexander Arredondo SánchezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Color Changing Flowers for the Classroom
Overview: In this game, the player can design their own flower by expressing or knocking down genes.
A simplified metabolic pathway is shown on the left, and the resulting flower is shown on the right.
Background Information:
Flowers are colored by anthocyanins, a family of small molecules that absorb in the visible light range.
Each flower has its own unique mixture of anthocyanins, resulting in unique flower shades.
Anthocyanins arent limited to flowers either, they also give color to fruits and vegetables. Plants use
them to protect themselves from sunburn, generating anthocyanins in the presence of intense light.
Examples of plants containing Anthocyanins
Petunias Snapdragons Roses Blueberries
Plants manufacture anthocyanins in a process known as
biosynthesis. In this process, enzymes convert one small
molecule into another, generating colorful anthocyanins from
non-colorful molecules. This process is long, but is very similar in
every plant. We have simplified these pathways (example
below) in the game to five enzymes, each representing a portion
of the anthocyanin pathway.
Each enzyme is a protein. Each protein starts as a set of
instructions in DNA. You can change the instructions in the DNA
to change the enzyme levels in the plant. If you instruct the
plant to produce more enzyme, that is called overexpression, if
it produces less, that is repression.
Anthocyanin Pathway. For full
paper/image size, click here
Color Changing Flowers for the Classroom
In the game, we represent overexpression by plus signs, and repression by signs. You can click each
colored button in the pathway to over- or under-express the enzymes that make the next step. In order
for the pathway to work, the entire pathway must be functional: if you turn off an enzyme at the top of
the pathway, it wont make any molecules for the next enzyme in the pathway.
Incomplete anthocyanin biosynthesis Complete anthocyanin biosynthesis
You can also change the environment of the anthocyanins using the bottom button labeled pH.
Anthocyanins are sensitive to their environment metal ions, other molecules, and pH can all have an
impact on the absorbance of the molecules. A famous example of this is the hydrangea in acidic soil, it
is able to take up more aluminum , which combines with the existing anthocyanins in the flowers to turn
them blue.
Change the environment, change the color Differently colored hydrangeas
Color Changing Flowers for the Classroom
Every part of the flower can produce different levels of anthocyanins in different environments, just like
real flowers. Turn on the big green advanced mode button, and select the flower part that you want to
color in.
This flower was created by knocking out anthocyanin biosynthesis only on the rim of the flower (white)
and changing the environment of the core to make those pigments redder.
Hope you enjoy the game! Questions, comments, concerns, please send to keira@revolutionbio.co
Looking forward to hearing from you!
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Flexural Design Procedure For Singly Reinforced Rectangular BeamsДокумент3 страницыFlexural Design Procedure For Singly Reinforced Rectangular BeamstvelasquezОценок пока нет
- Zam ZamДокумент4 страницыZam ZamtahirmaqpkОценок пока нет
- 1.2.0 Drilling Ref. PFMEAДокумент12 страниц1.2.0 Drilling Ref. PFMEAMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Vacuum Super Insulated Heat Storage Up To 400 °C: January 2015Документ11 страницVacuum Super Insulated Heat Storage Up To 400 °C: January 2015Arvin SlayerОценок пока нет
- Decarburization of SteelДокумент7 страницDecarburization of SteelSadeep MadhushanОценок пока нет
- Bfs4063 & Bfs 40603 Concrete EngineeringДокумент4 страницыBfs4063 & Bfs 40603 Concrete EngineeringUtaya Kumar VeelmuruganОценок пока нет
- 10 - Chapter 2 PDFДокумент72 страницы10 - Chapter 2 PDFAwais SargodianОценок пока нет
- A Reviewof Studies On Central Receiver Solar Thermal Power PlantsДокумент28 страницA Reviewof Studies On Central Receiver Solar Thermal Power PlantsValeria Rueda100% (1)
- Ladle Furnace Refractory Lining: A Review: Dashrath Singh KathaitДокумент8 страницLadle Furnace Refractory Lining: A Review: Dashrath Singh KathaitHameedОценок пока нет
- Marcet BoilerДокумент8 страницMarcet BoilerOjiSofttouchCharlesОценок пока нет
- Science 7 ExamДокумент5 страницScience 7 Examangge21Оценок пока нет
- Chevron Specification PVM-MS-1322-EДокумент17 страницChevron Specification PVM-MS-1322-EmmemhdОценок пока нет
- Is 439 1989Документ11 страницIs 439 1989rajpd28Оценок пока нет
- Pressure Equipment Directive 97/23/EC Essential Safety Requirements Annex I ChecklistДокумент18 страницPressure Equipment Directive 97/23/EC Essential Safety Requirements Annex I ChecklistsergioОценок пока нет
- Butyl Diglycol Acetate ManufacturersДокумент4 страницыButyl Diglycol Acetate ManufacturersSomuSolventsОценок пока нет
- Increasing The Performance of Chain Sprocket by Using Cryogenic Treated and Normalizing in Superficial Heat TreatmentДокумент25 страницIncreasing The Performance of Chain Sprocket by Using Cryogenic Treated and Normalizing in Superficial Heat Treatmentthai avvaiОценок пока нет
- ReportДокумент20 страницReportAidaFarzanaNanaОценок пока нет
- Indian Standard: Code of Practice For Design in Tunnels Conveying WaterДокумент29 страницIndian Standard: Code of Practice For Design in Tunnels Conveying WaterswabrightОценок пока нет
- Petroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFДокумент28 страницPetroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFWahyu Probo Ananto HadiОценок пока нет
- 6 - Durma Laser User InterfaceДокумент30 страниц6 - Durma Laser User Interfacesciuc0% (1)
- Voe Main2Документ4 страницыVoe Main2prevrtljivacОценок пока нет
- 12 Types of Bearing DefectsДокумент5 страниц12 Types of Bearing Defectsjameel babooramОценок пока нет
- Solar and Stellar Magnetic Activity - ISBN0521582865 PDFДокумент402 страницыSolar and Stellar Magnetic Activity - ISBN0521582865 PDFOmar Musalem100% (1)
- Environmentally Friendly Cooling With Heat: Ecoo 2.0: The Classic of Adsorption RefrigerationДокумент3 страницыEnvironmentally Friendly Cooling With Heat: Ecoo 2.0: The Classic of Adsorption RefrigerationGokulSubramanianОценок пока нет
- (Anderson Poul) Satan's World (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFДокумент128 страниц(Anderson Poul) Satan's World (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFFüleki Eszter100% (1)
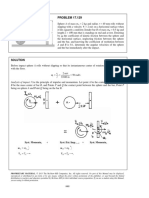
- PROBLEM 17.129: SolutionДокумент14 страницPROBLEM 17.129: SolutiontaОценок пока нет
- Metalcraft 4Документ90 страницMetalcraft 4Ana DuranОценок пока нет
- Adsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuДокумент7 страницAdsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuZhu Chen ChuanОценок пока нет
- Ceramic Engineering: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент6 страницCeramic Engineering: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaFaiz AbdullahОценок пока нет