Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ge-Mckinsey Nine-Box Matrix and Later Developed by Boston Consulting Group'S Growth Share Matrix
Загружено:
Naveen ChoudhuryОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ge-Mckinsey Nine-Box Matrix and Later Developed by Boston Consulting Group'S Growth Share Matrix
Загружено:
Naveen ChoudhuryАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
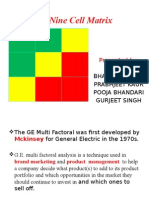
GE-McKinsey Nine-Box Matrix
The framework In the reading offers a systematic approach to prioritize the investments in an
organization. In multi-business enterprises, maintaining profitability is the real problem. This
dilemma was solved by GE-McKinsey nine-box matrix and later developed by Boston Consulting
Groups Growth share matrix.
GE-McKinsey nine-box matrix offers an approach for decentralized corporations to determine the best
areas to invest their cash. A business unit can be judged about its performance on following factors
1. Attractiveness of the relevant industry it consists of many factors like long run growth rate, industry
size, industry profitability, industry structure, demand changes, seasonality, availability of labor, etc.
2. Competitive strength within the industry. it has many factors like total market share, share growth
related to rivals, customer loyalty, brand strength, level of product differentiation, product flexibility,
etc.
The business units, placed within the matrix help in analyzing them by providing an analytical map.
Selective candidates lie on the diagonal while the ones above the diagonal, investment and growth
strategies may be adopted. The ones lying below can be sold, liquidated or run purely for cash. Sorting
units into these categories is an essential starting point for the analysis, but the trade offs need to be
weighed by judgement, for e.g. a strong unit in a weak industry is in a very different situation than a
weak unit in a strong industry. The criteria for assessing industry attractiveness and competitive
strength have growth more sophisticated. Most of large companies model their business referring to
nine-box matrix or its descendant.
Вам также может понравиться
- Ge MckinseyДокумент9 страницGe MckinseyAnjaliMoreОценок пока нет
- GE-McKinsey Nine-Box Matrix Framework for Prioritizing Business InvestmentsДокумент1 страницаGE-McKinsey Nine-Box Matrix Framework for Prioritizing Business InvestmentsNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Competition Demystified (Review and Analysis of Greenwald and Kahn's Book)От EverandCompetition Demystified (Review and Analysis of Greenwald and Kahn's Book)Оценок пока нет
- GE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsДокумент15 страницGE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsPratyay DasОценок пока нет
- Analyse Using GE/McKinsey and BCG MatricesДокумент12 страницAnalyse Using GE/McKinsey and BCG MatricesRian WallaceОценок пока нет
- GE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio AnalysisДокумент13 страницGE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio AnalysisRabia MalikОценок пока нет
- GE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio AnalysisДокумент13 страницGE Matrix or McKinsey Matrix Is A Strategic Tool For Portfolio Analysisadnanulhaq12963650% (2)
- Ge Matrix: Presented By: Sadia Nasir Student Id: 20181-23584Документ18 страницGe Matrix: Presented By: Sadia Nasir Student Id: 20181-23584Hassan AhmedОценок пока нет
- GE Nine Cell Matrix Model for Analyzing Business Unit Strength and Industry AttractivenessДокумент3 страницыGE Nine Cell Matrix Model for Analyzing Business Unit Strength and Industry AttractivenessJite PiteОценок пока нет
- GE McKinsey MatrixДокумент5 страницGE McKinsey Matrixkaartik123Оценок пока нет
- Dog Products: The Usual Marketing Advice Here Is To Aim To Remove Any Dogs From Your ProductДокумент6 страницDog Products: The Usual Marketing Advice Here Is To Aim To Remove Any Dogs From Your ProductIstiaque AhmedОценок пока нет
- GE Nine-Cell Planning Grid TechniqueДокумент10 страницGE Nine-Cell Planning Grid Techniquevarun rajОценок пока нет
- 23 - GE Nine Cell MatrixДокумент24 страницы23 - GE Nine Cell Matrixlali62100% (1)
- GE Nine MatrixДокумент12 страницGE Nine MatrixmysterioussurferОценок пока нет
- GE McKinsey Matrix: A 9-Box Tool for Strategic Portfolio AnalysisДокумент4 страницыGE McKinsey Matrix: A 9-Box Tool for Strategic Portfolio AnalysisMaaryaAslamОценок пока нет
- WEEK 6 Rizal Iza TigonДокумент6 страницWEEK 6 Rizal Iza TigonVanesa AgootОценок пока нет
- STG MNGMNTДокумент10 страницSTG MNGMNTChandan DevОценок пока нет
- General ElectricДокумент12 страницGeneral ElectricAitm Mba BelagaviОценок пока нет
- Module 2Документ15 страницModule 2Omkar MulekarОценок пока нет
- GE Nine Cell MatrixДокумент21 страницаGE Nine Cell MatrixMadhuri Bhojwani67% (3)
- Name: Saptarshi Das Mba - 4 Semester Reg. No. 511010222Документ16 страницName: Saptarshi Das Mba - 4 Semester Reg. No. 511010222Nayan DasОценок пока нет
- Assignment - 1 Strategic Management: Submitted ToДокумент14 страницAssignment - 1 Strategic Management: Submitted ToNakulОценок пока нет
- UNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolДокумент12 страницUNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolNishath NawazОценок пока нет
- BPSM Avi AssingmentДокумент9 страницBPSM Avi AssingmentAvi JainОценок пока нет
- GE MatrixДокумент6 страницGE MatrixManish JhaОценок пока нет
- Multibusiness Strategy Portfolio ApproachesДокумент30 страницMultibusiness Strategy Portfolio Approachespreetimutiaray100% (1)
- STRATEGYДокумент21 страницаSTRATEGYSikendra KushwahaОценок пока нет
- GE NINE-CELL PLANNING GRID AS A GRAND STRATEGY TOOLДокумент3 страницыGE NINE-CELL PLANNING GRID AS A GRAND STRATEGY TOOLRenge Geevarghese100% (1)
- Assignment: Strategic ManagementДокумент17 страницAssignment: Strategic ManagementajoОценок пока нет
- GE McKinsey 9 BoxДокумент2 страницыGE McKinsey 9 BoxprashantpaperОценок пока нет
- Mckinsey 9 Model GridДокумент3 страницыMckinsey 9 Model Gridliam3deckerОценок пока нет
- BCG Growth-Share MatrixДокумент9 страницBCG Growth-Share MatrixSaurabh ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Comparing Growth Models: BCG, Ansoff, and GE MatricesДокумент34 страницыComparing Growth Models: BCG, Ansoff, and GE MatricesArti RahejaОценок пока нет
- Comparing Growth Models: BCG, Ansoff, and GE MatricesДокумент34 страницыComparing Growth Models: BCG, Ansoff, and GE MatricesPPriyaTechОценок пока нет
- BCG GrowthДокумент5 страницBCG GrowthAmol NirgudkarОценок пока нет
- SMU A S: Strategic Management & Business PolicyДокумент20 страницSMU A S: Strategic Management & Business PolicySantosh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Q.1 What Similarities and Differences Do You Find in BCG Business Portfolio Matrix, Ansoff Growth Matrix and GE Growth PyramidДокумент34 страницыQ.1 What Similarities and Differences Do You Find in BCG Business Portfolio Matrix, Ansoff Growth Matrix and GE Growth PyramidAboobacker NmОценок пока нет
- BCG Matrix Portfolio Analysis Definition: Portfolio Analysis Is An Examination of The Components Included in A Mix of Products With TheДокумент6 страницBCG Matrix Portfolio Analysis Definition: Portfolio Analysis Is An Examination of The Components Included in A Mix of Products With TheJite PiteОценок пока нет
- Nhóm 1-Cô Hoàng Anh-Phương Uyên-Dot 7Документ5 страницNhóm 1-Cô Hoàng Anh-Phương Uyên-Dot 7Nguyễn Ngọc YếnОценок пока нет
- GE MatrixДокумент3 страницыGE Matrixr.jeyashankar9550Оценок пока нет
- Strategies For Multi-Business Corporations Strategic ReviewДокумент31 страницаStrategies For Multi-Business Corporations Strategic ReviewwordssmithОценок пока нет
- Gec Model Industry AnalysisДокумент3 страницыGec Model Industry AnalysisHina Singhvi0% (1)
- Ge Nine Cell Matrix: Submitted To Ms. Sakshi Mam Submitted by TammanaДокумент12 страницGe Nine Cell Matrix: Submitted To Ms. Sakshi Mam Submitted by TammanaTamannaОценок пока нет
- GE Nine Cell MatrixДокумент12 страницGE Nine Cell MatrixIsha BhattОценок пока нет
- GE Nine CellДокумент3 страницыGE Nine CellVandana SharmaОценок пока нет
- Bmt1035-Strategic Management: FALL SEMESTER: 2021-22 Digital Assignment-07Документ8 страницBmt1035-Strategic Management: FALL SEMESTER: 2021-22 Digital Assignment-07Vasu Dev KanchetiОценок пока нет
- MB0052Документ34 страницыMB0052Prateek TutejaОценок пока нет
- GE Matrix Explained: Analyzing Business Units by Strength and Market AttractivenessДокумент26 страницGE Matrix Explained: Analyzing Business Units by Strength and Market AttractivenessFijo JoseОценок пока нет
- Analysing Strategy (BCG Matrix)Документ6 страницAnalysing Strategy (BCG Matrix)yadavpankaj1992Оценок пока нет
- Business Portfolio AnalysisДокумент20 страницBusiness Portfolio AnalysissoumitrabehuraОценок пока нет
- MARKETING MATRIX MODELS FOR BUSINESS ANALYSISДокумент26 страницMARKETING MATRIX MODELS FOR BUSINESS ANALYSISTerjani Khanna GoyalОценок пока нет
- GE Nine-Cell Matrix Strategic Tool Prioritize InvestmentsДокумент3 страницыGE Nine-Cell Matrix Strategic Tool Prioritize Investmentslatha loganathanОценок пока нет
- McKinsey matrix analysis model for strategic business unitsДокумент5 страницMcKinsey matrix analysis model for strategic business unitsFaiz Kazi100% (1)
- Master of Business Administration MBA Semester-4: Clearanc Certificate Number: 0013Документ45 страницMaster of Business Administration MBA Semester-4: Clearanc Certificate Number: 0013Apu MajumdarОценок пока нет
- SMU MBA 4th Sem Information Systems Management AssignmentsДокумент3 страницыSMU MBA 4th Sem Information Systems Management AssignmentsPooja Upreti PandeyОценок пока нет
- Ge MatrixДокумент11 страницGe MatrixBhaveen JoshiОценок пока нет
- GE 9 CellДокумент20 страницGE 9 CellakhilОценок пока нет
- SPM Ge MateДокумент10 страницSPM Ge Mateashutosh kankaneОценок пока нет
- GS Iii PDFДокумент70 страницGS Iii PDFjayalakshmi sujithОценок пока нет
- Rubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedДокумент1 страницаRubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedlottaОценок пока нет
- BSDFGBXCVBDZFB ZCNJFRNДокумент1 страницаBSDFGBXCVBDZFB ZCNJFRNNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Medieval India Satish ChandraДокумент139 страницMedieval India Satish ChandraPruthvi Kommu90% (10)
- ExampleAdjectivesДокумент17 страницExampleAdjectivesArielОценок пока нет
- Rubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedДокумент1 страницаRubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedlottaОценок пока нет
- GS I PDFДокумент28 страницGS I PDFsrikanta bagОценок пока нет
- GS Ii PDFДокумент76 страницGS Ii PDFtabishakhОценок пока нет
- History Key Words PDFДокумент20 страницHistory Key Words PDFNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Parts of Speech, English GrammarДокумент17 страницParts of Speech, English GrammarmaliknaseerОценок пока нет
- TESOL Mid-Term Assignment (After Phase 5)Документ3 страницыTESOL Mid-Term Assignment (After Phase 5)riyaОценок пока нет
- CV - Brian A. Hoey, Ph.D.Документ17 страницCV - Brian A. Hoey, Ph.D.Naveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- 120 Hours TESOL Instructions: Kindly Read The Following Instructions Before Attempting The AssignmentДокумент2 страницы120 Hours TESOL Instructions: Kindly Read The Following Instructions Before Attempting The AssignmentNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Rubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedДокумент1 страницаRubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedlottaОценок пока нет
- ExampleAdjectivesДокумент17 страницExampleAdjectivesArielОценок пока нет
- Rubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedДокумент1 страницаRubrics Answers Comprising of Plagiarized Content Will Not Be AcceptedlottaОценок пока нет
- Brief - Chennai District - 14.5.20Документ4 страницыBrief - Chennai District - 14.5.20Naveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Parts of Speech, English GrammarДокумент17 страницParts of Speech, English GrammarmaliknaseerОценок пока нет
- Quick&Reilly Consider Off-the-Shelf CRM Systems Like SiebelДокумент1 страницаQuick&Reilly Consider Off-the-Shelf CRM Systems Like SiebelNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Daniel Jordan Smith CV (2014)Документ19 страницDaniel Jordan Smith CV (2014)Naveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- CV Example PHD AnthroДокумент2 страницыCV Example PHD AnthroNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- 4 Days in Dharamsala + Prashar Lake: RouteДокумент8 страниц4 Days in Dharamsala + Prashar Lake: RouteNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- #Day Date Place Distance: 1 26-Apr 2 27-Apr 3 28-Apr 4 29-Apr 5 30-Apr 6 1-MayДокумент3 страницы#Day Date Place Distance: 1 26-Apr 2 27-Apr 3 28-Apr 4 29-Apr 5 30-Apr 6 1-MayNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- SUMMARY: Consumer Attitudes Revisited: Group 2Документ2 страницыSUMMARY: Consumer Attitudes Revisited: Group 2Naveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Learning From Perception-Session 1 and 2Документ1 страницаLearning From Perception-Session 1 and 2Naveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Iimn PGP IvДокумент8 страницIimn PGP IvNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Group 10 Poletown DilemmaДокумент3 страницыGroup 10 Poletown DilemmaNaveen Choudhury100% (1)
- KedarДокумент2 страницыKedarNaveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- RHAPSODY - The Intramural Sports Tournament 2017Документ9 страницRHAPSODY - The Intramural Sports Tournament 2017Naveen ChoudhuryОценок пока нет
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinОт EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdОт EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (17)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewОт EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0От EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Оценок пока нет
- HBR's 10 Must Reads 2023: The Definitive Management Ideas of the Year from Harvard Business Review (with bonus article "Persuading the Unpersuadable" By Adam Grant)От EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads 2023: The Definitive Management Ideas of the Year from Harvard Business Review (with bonus article "Persuading the Unpersuadable" By Adam Grant)Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerОт EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (121)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessОт EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (80)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsОт EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (48)
- New Sales. Simplified.: The Essential Handbook for Prospecting and New Business DevelopmentОт EverandNew Sales. Simplified.: The Essential Handbook for Prospecting and New Business DevelopmentРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (44)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantОт EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (387)
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesОт EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesОценок пока нет
- Impact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeОт EverandImpact Networks: Create Connection, Spark Collaboration, and Catalyze Systemic ChangeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewОт EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (104)
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceОт EverandPower and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (38)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't (Rockefeller Habits 2.0 Revised Edition)От EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't (Rockefeller Habits 2.0 Revised Edition)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- Strategic Risk Management: New Tools for Competitive Advantage in an Uncertain AgeОт EverandStrategic Risk Management: New Tools for Competitive Advantage in an Uncertain AgeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- HBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyОт EverandHBR Guide to Setting Your StrategyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)От EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (11)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2От EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Managing Yourself, Vol. 2Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (11)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Business Model InnovationОт EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Business Model InnovationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (12)
- The Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeОт EverandThe Digital Transformation Playbook: Rethink Your Business for the Digital AgeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (48)
- Jim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryОт EverandJim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Strategy Legacy: How to Future-Proof a Business and Leave Your MarkОт EverandThe Strategy Legacy: How to Future-Proof a Business and Leave Your MarkОценок пока нет
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffОт EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffОценок пока нет
- Strategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewОт EverandStrategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (45)
- Understanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and StrategyОт EverandUnderstanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and StrategyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (24)