Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Linear Variable Differential Transformer
Загружено:
Vignesh SelvarajИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Linear Variable Differential Transformer
Загружено:
Vignesh SelvarajАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Linear variable differential transformer:
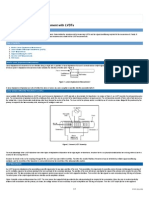
Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) is a type of electrical transformer used for
measuring linear displacement. The transformer has three solenoidal coils placed end-to-end
around a tube. The centre coil is the primary, and the two outer coils are the secondaries. A
cylindrical ferromagnetic core, attached to the object whose position is to be measured, slides
along the axis of the tube. An alternating current is driven through the primary, causing a voltage
to be induced in each secondary proportional to its mutual inductance with the primary. The
frequency is usually in the range 1 to 10 kHz.
LVDTs are commonly used for position feedback in servomechanisms, and for automated
measurement in machine tools and many other industrial and scientific applications.
Specifications
LVDT Range:50mm or total 100mm
Sensitivity: 25mV/cm
Operating frequency: 5KHz5%
Displacement measurement on a mm scale with fine Motion control
Carrier source (internal): 5KHz5%; 1.5V (nominal)
Built-in 3 digit DVM for output reading
IC based balanced demodulator circuit
IC controlled internal power supplies
Essential accessory - a CRO
Вам также может понравиться
- LVDT WhitePaperДокумент3 страницыLVDT WhitePaperdetrutamiОценок пока нет
- ENSC 387 Sensors and ActuatorsДокумент117 страницENSC 387 Sensors and ActuatorsMajed KawamОценок пока нет
- LVDT Lab ManualДокумент3 страницыLVDT Lab Manualguruabhay100% (2)
- What Is A Displacement Transducer?: Technical LearningДокумент4 страницыWhat Is A Displacement Transducer?: Technical LearningRamОценок пока нет
- Vibration and Monitoring Terms GlossaryДокумент12 страницVibration and Monitoring Terms Glossaryyaniprasetyo12Оценок пока нет
- Transistor and Voltage DividerДокумент10 страницTransistor and Voltage DividerAya SaleemОценок пока нет
- Variable Displacement Transformer, TransducerДокумент3 страницыVariable Displacement Transformer, TransducerArunОценок пока нет
- Presentation On CSEB Vocational Training by NAVNEET (RITEE, Raipur)Документ17 страницPresentation On CSEB Vocational Training by NAVNEET (RITEE, Raipur)Navneet Dewangan25% (4)
- Slip Ring: Ring Can Be Used in Any Electromechanical System That Requires RotationДокумент8 страницSlip Ring: Ring Can Be Used in Any Electromechanical System That Requires RotationMian UsmanОценок пока нет
- What is an LVDT? (Linear Variable Differential TransformerДокумент3 страницыWhat is an LVDT? (Linear Variable Differential Transformermuhammad aliОценок пока нет
- PEI Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inДокумент44 страницыPEI Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inBoban MathewsОценок пока нет
- LVDT ManualДокумент7 страницLVDT ManualShankar ArunmozhiОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 NotesДокумент9 страницUnit 4 NotesPrathamesh BhavsarОценок пока нет
- Displacement Sensors: 1. Resistance Based and Optical Incremental Sensors of Position TaskДокумент7 страницDisplacement Sensors: 1. Resistance Based and Optical Incremental Sensors of Position TaskBoobalan ThirugnanasambandamОценок пока нет
- Precision Power Analyzer: 1 To 8 Channels DC - 10 MHZ Accuracy 0.025 %Документ12 страницPrecision Power Analyzer: 1 To 8 Channels DC - 10 MHZ Accuracy 0.025 %tsampouriseОценок пока нет
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer Measurements: EET-027, Experiment # 9Документ4 страницыLinear Variable Differential Transformer Measurements: EET-027, Experiment # 9nainesh goteОценок пока нет
- Measuring Position and Displacement With LVDTS: TutorialДокумент5 страницMeasuring Position and Displacement With LVDTS: TutorialpeterhassanОценок пока нет
- Modeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorДокумент6 страницModeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorLelosPinelos123Оценок пока нет
- Transducer: Sonali Gome Asst. ProfessorДокумент16 страницTransducer: Sonali Gome Asst. ProfessorSunil KaramchandaniОценок пока нет
- SubstationДокумент7 страницSubstationSwati Sharma100% (1)
- Fault Detection in TM LineДокумент25 страницFault Detection in TM Linenaveen gОценок пока нет
- SpaДокумент5 страницSpamillionОценок пока нет
- Current Transformer: Electrical EngineeringДокумент5 страницCurrent Transformer: Electrical EngineeringKallempudi MeenakshiОценок пока нет
- Seminar Project LVDT: - To Study The Basics, ConstructionДокумент9 страницSeminar Project LVDT: - To Study The Basics, ConstructionNaeem SaifОценок пока нет
- LVDTДокумент8 страницLVDTAnirban GhoshОценок пока нет
- LVDT - Working Principle Construction Types, Advantages and ApplicationsДокумент11 страницLVDT - Working Principle Construction Types, Advantages and ApplicationsKunal AhiwaleОценок пока нет
- TransducerДокумент30 страницTransducerVishal GuptaОценок пока нет
- Electronic Workshop 2nd Experiment3Документ9 страницElectronic Workshop 2nd Experiment3chinnuОценок пока нет
- Electronics workshop lab instruments guideДокумент9 страницElectronics workshop lab instruments guidechinnu0% (1)
- Measuring Electrical Potential with VoltmetersДокумент5 страницMeasuring Electrical Potential with Voltmetershumaid15Оценок пока нет
- Module 6Документ78 страницModule 6JASPER PAYAPAYAОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Power ElectronicsДокумент37 страницIntroduction to Power ElectronicsEngr Muhammad Faisal YaqoobОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Instrument TransformersДокумент6 страницIntroduction To Instrument Transformersadi nugrohoОценок пока нет
- Inductive Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiДокумент26 страницInductive Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamОценок пока нет
- Railway Current Voltage TransducersДокумент25 страницRailway Current Voltage TransducersThasnimFathimaОценок пока нет
- Instrumentation and Measurement Chapter on Transducers and Measuring InstrumentsДокумент30 страницInstrumentation and Measurement Chapter on Transducers and Measuring InstrumentsYab TadОценок пока нет
- Switching Converters ExplainedДокумент470 страницSwitching Converters ExplainedAyushmaanОценок пока нет
- Linear Variable Differntial Transformer AssainmentДокумент2 страницыLinear Variable Differntial Transformer AssainmentMohan PrasadОценок пока нет
- Measure Linear Displacement with LVDT SensorsДокумент7 страницMeasure Linear Displacement with LVDT Sensorsஹரி கிருஷ்ணன் வாசுОценок пока нет
- Oa1-Two MarksДокумент28 страницOa1-Two MarksMEIVELJ 19EE025Оценок пока нет
- Basics of Electrical Ep - 6Документ10 страницBasics of Electrical Ep - 6Dheeraj ChopraОценок пока нет
- Function GeneratorДокумент78 страницFunction GeneratorVishali Chowdary100% (1)
- Mkm1133 Instrumentation and Control SystemДокумент19 страницMkm1133 Instrumentation and Control SystemNurul Nadia Mohd ZawawiОценок пока нет
- A Project Report On Inverter Using IC 4093 NAND Gate & MOSFET SwitchingДокумент3 страницыA Project Report On Inverter Using IC 4093 NAND Gate & MOSFET SwitchingPranav BahalkarОценок пока нет
- Presentation - On-Chip Current Sensing Technique For Cmos Monolithic Switch-ModeДокумент30 страницPresentation - On-Chip Current Sensing Technique For Cmos Monolithic Switch-Modesohailasghar_tОценок пока нет
- Power InvertersДокумент13 страницPower InvertersCaHyaUTamaPNОценок пока нет
- A Low Cost High Efficiency Inverter For Photovoltaic ApplicationsДокумент6 страницA Low Cost High Efficiency Inverter For Photovoltaic ApplicationsbpchimeraОценок пока нет
- TransducerДокумент11 страницTransducerRohit WayamОценок пока нет
- Selective Harmonic Elimination by Programmable Pulse Width Modulation in InvertersДокумент6 страницSelective Harmonic Elimination by Programmable Pulse Width Modulation in InvertersseventhsensegroupОценок пока нет
- Signal Flow - Instrument Sensor Transducer PLC - jpg1653x483 56.9 KBДокумент7 страницSignal Flow - Instrument Sensor Transducer PLC - jpg1653x483 56.9 KBsakthisriniОценок пока нет
- Micro Inverter For CFL LampsДокумент27 страницMicro Inverter For CFL LampsHamed RazaОценок пока нет
- Inverting Subtractor and Voltage Controlled OscillatorДокумент10 страницInverting Subtractor and Voltage Controlled OscillatorKartheek KonaОценок пока нет
- Contactless Liquid Level ControllerДокумент37 страницContactless Liquid Level ControllerSai KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Measuring Position and Displacement With LVDTS: 1. What Is Linear Displacement MeasurementДокумент4 страницыMeasuring Position and Displacement With LVDTS: 1. What Is Linear Displacement MeasurementJelena GavanskiОценок пока нет
- 3.1 Sensors and TransducersДокумент14 страниц3.1 Sensors and Transducersgopal sapkotaОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Sensors and ActuatorsДокумент115 страницPresentation On Sensors and ActuatorschibuikeОценок пока нет
- Module 29Документ4 страницыModule 29Denaiya Watton LeehОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Instrument TransformersДокумент4 страницыIntroduction To Instrument TransformersArnel Pascual LaquindanumОценок пока нет
- Welcome To The Presentation: The Name of Our Project IsДокумент24 страницыWelcome To The Presentation: The Name of Our Project IsDebalina PandaОценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Vibration Exciter (2N To 100N) : Use ScenariosДокумент1 страницаVibration Exciter (2N To 100N) : Use ScenariosVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- 1200W Smoke Generator:: Technical DetailsДокумент1 страница1200W Smoke Generator:: Technical DetailsVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Pitot Static Tube With Digital ManometerДокумент4 страницыPitot Static Tube With Digital ManometerVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- EI P L: Column Testing - Fixed-FixedДокумент3 страницыEI P L: Column Testing - Fixed-FixedVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- AA02 Supersonic Wind Tunnel ContinuousДокумент5 страницAA02 Supersonic Wind Tunnel ContinuousVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Carbon PDFДокумент4 страницыCarbon PDFVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Analysis of BladeДокумент3 страницыAnalysis of BladeVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- 1page 3Документ2 страницы1page 3Sajid MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Member Management System - MMS User GuideДокумент11 страницMember Management System - MMS User GuideVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Impact Testing Machine Make KedarДокумент3 страницыImpact Testing Machine Make KedarVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Newton's RingДокумент7 страницNewton's RingReddyvari VenugopalОценок пока нет
- Impact Test MachineДокумент2 страницыImpact Test MachineVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Service DetailsДокумент1 страницаService DetailsVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- TicДокумент1 страницаTicVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Analysis of An Inflatable Gossamer Device To Efficiently De-OrbitДокумент100 страницAnalysis of An Inflatable Gossamer Device To Efficiently De-OrbitVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Vocab Spot CheckДокумент9 страницVocab Spot CheckMr. Yogesh RamaniОценок пока нет
- ShivaДокумент6 страницShivaVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Form 1: Employee Personal Information Name of DepartmentДокумент12 страницForm 1: Employee Personal Information Name of DepartmentRajashree PatilОценок пока нет
- Achievements Summary-AadesДокумент1 страницаAchievements Summary-AadesVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Length-2.6 M Chord 0.15m No of Blade-5 Radius-1.2 M Max Torque - 150 N-M Rated Wind Speed-11 M/s Max Force - 500N, Operational Force-250 N NACA-4415Документ1 страницаLength-2.6 M Chord 0.15m No of Blade-5 Radius-1.2 M Max Torque - 150 N-M Rated Wind Speed-11 M/s Max Force - 500N, Operational Force-250 N NACA-4415Vignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Quantitative AptitudeДокумент2 страницыQuantitative AptitudeSivakumar MОценок пока нет
- Thulasi StotramДокумент2 страницыThulasi StotramVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Pre CompДокумент33 страницыPre CompVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Sample Employment Application FormДокумент4 страницыSample Employment Application Formapi-296940651Оценок пока нет
- Vinayakar-Subramanyar ThuthiДокумент1 страницаVinayakar-Subramanyar ThuthiVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Optimization Formulations For Composite Structures Subjected To Compression LoadsДокумент2 страницыOptimization Formulations For Composite Structures Subjected To Compression LoadsVignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Bottom view scale 1:3 doc 2Документ1 страницаBottom view scale 1:3 doc 2Vignesh SelvarajОценок пока нет
- Sample Employment Application FormДокумент4 страницыSample Employment Application Formapi-296940651Оценок пока нет