Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: SEMICONDUCTORS, PN JUNCTION DIODE
Загружено:
muthai0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
55 просмотров4 страницыThe document discusses electronic devices and circuits, specifically pn junction diodes. It defines key terms related to semiconductors and pn junction diodes such as intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, drift current, diffusion current, depletion region, barrier potential, and recovery/storage/transition times. It provides expressions for drift current density and diode current. It describes applications of pn diodes such as rectification and uses of zener diodes for voltage regulation. Light emitting diodes are introduced as specialized pn junction diodes that convert electrical to light energy.
Исходное описание:
EDC unit I 2 marks
Оригинальное название
EDC Unit I 2 marks
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document discusses electronic devices and circuits, specifically pn junction diodes. It defines key terms related to semiconductors and pn junction diodes such as intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, drift current, diffusion current, depletion region, barrier potential, and recovery/storage/transition times. It provides expressions for drift current density and diode current. It describes applications of pn diodes such as rectification and uses of zener diodes for voltage regulation. Light emitting diodes are introduced as specialized pn junction diodes that convert electrical to light energy.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
55 просмотров4 страницыELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS: SEMICONDUCTORS, PN JUNCTION DIODE
Загружено:
muthaiThe document discusses electronic devices and circuits, specifically pn junction diodes. It defines key terms related to semiconductors and pn junction diodes such as intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, drift current, diffusion current, depletion region, barrier potential, and recovery/storage/transition times. It provides expressions for drift current density and diode current. It describes applications of pn diodes such as rectification and uses of zener diodes for voltage regulation. Light emitting diodes are introduced as specialized pn junction diodes that convert electrical to light energy.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
UNIT-I
TWO MARKS WITH ANSWER
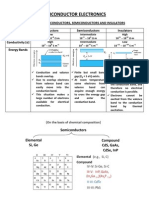
1. What are semiconductors?
The materials whose electrical property lies between those of conductors and insulators are
known as Semiconductors. Ex germanium, silicon.
It has two types.
1. Intrinsic semiconductor 2. Extrinsic semiconductor.
2.Differentiate between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor
Pure form of semiconductors are said to be intrinsic semiconductor.
Ex: germanium, silicon.
It has poor conductivity
If certain amount of impurity atom is added to intrinsic semiconductor the resulting
semiconductor is Extrinsic or impure Semiconductor
It has good conductivity.
3.Define drift current?
When an electric field is applied across the semiconductor, the holes move towards the negative
terminal of the battery and electron move towards the positive terminal of the battery. This drift
movement of charge carriers will result in a current termed as drift current.
4.Give the expression for drift current density
Drift current density due to electrons
Jn = q n nE
Where,
Jn - drift current density due to holes
q - Charge of holes
p - Mobility of holes
E - applied electric field
5.Define the term diffusion current?
A concentration gradient exists, if the number of either electrons or holes is greater in one
region of a semiconductor as compared to the rest of the region. The holes and electron
tend to move from region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration.
This process in called diffusion and the current produced due this movement is diffusion
current.
6. What is rectifier?
Rectifier is combination of diodes in a circuit, used to convert AC to DC supply.
Half and Full wave rectifiers are mostly employed for rectification purpose.
7.Differentiate between drift and diffusion currents.
Drift current
1. It is developed due to potential gradient.
2. This phenomenon is found both in metals and semiconductors
Diffusion current
1. It is developed due to charge concentration gradient.
2. This phenomenon is found only in metals
8.What is depletion region in PN junction?
The region around the junction from which the mobile charge carriers ( electrons and holes) are
depleted is called as depletion region.since this region has immobile ions, which are electrically
charged , the depletion region is also known as space charge region.
9.What is barrier potential?
Because of the oppositely charged ions present on both sides of PN junction an electric potential
is established across the junction even without any external voltage source which is termed as
barrier potential.
10.What is Reverse saturation current?
The current due to the minority carriers in reverse bias is said to be reverse saturation
current. This current is independent of the value of the reverse bias voltage.
11.What is the total current at the junction of pn junction diode?
The total in the junction is due to the hole current entering the n material and the electron current
entering the p material. Total current is given by
I = Ipn(0) + Inp(0)
Where,
I Total current
Ipn(0) - hole current entering the n material
Inp(0) - electron current entering the p material
12.Give the diode current equation?
The diode current equation relating the voltage V and current I is given by
where
I diode current
Io diode reverse saturation current at room temperature
V external voltage applied to the diode
- a constant, 1 for Ge and 2 for Si
VT = kT/q = T/11600, thermal voltage
K Boltzmanns constant (1.38066x10^-23 J/K)
q charge of electron (1.6x10^-19 C)
T temperature of the diode junction
13.what is recovery time? Give its types.
When a diode has its state changed from one type of bias to other a transient accompanies the
diode response, i.e., the diode reaches steady state only after an interval of time tr called as
recovery time. The recovery time can be divided in to two types such as
(i) forward recovery time
(ii) reverse recovery time
14.Define storage time.
The interval time for the stored minority charge to become zero is called storage time. It is
represented as ts.
15.Define transition time.
The time when the diode has normally recovered and the diode reverse current reaches reverse
saturation current Io is called as transition time. It is represented as t t
16.Define PIV. Peak inverse voltage is the maximum reverse voltage that can be applied to the
PN junction without damage to the junction.
17.Draw V-I characteristics of pn diode
18.Write the application of pn diode
Can be used as rectifier in DC Power Supplies.
In Demodulation or Detector Circuits.
In clamping networks used as DC Restorers
In clipping circuits used for waveform generation.
As switches in digital logic circuits.
In demodulation circuits.
19. What is application of zener diode?
Zener diode is used for voltage regulator at the power supply unit. Used for reverse bias operation
and used for in series with signal diode for temperature coefficients.
20. What is LED?
"Light Emitting Diode" or LED as it is more commonly called, is basically just a specialised
type of PN junction diode, made from a very thin layer of fairly heavily doped semiconductor
material. LED are semiconductor devices that convert electrical energy into light energy.
Вам также может понравиться
- Ec-8261 Electronic Devices: Two Mark Questions and AnswersДокумент21 страницаEc-8261 Electronic Devices: Two Mark Questions and Answersmadhupavi_2007100% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearДокумент27 страницElectronic Devices and Circuits - Ii YearT ThirumuruganОценок пока нет
- 2 Mark (ED Questions)Документ26 страниц2 Mark (ED Questions)Pradeep ravichanderОценок пока нет
- PN Junction Devices and Diode CharacteristicsДокумент41 страницаPN Junction Devices and Diode CharacteristicsNagendran100% (1)
- EDC Question BankДокумент44 страницыEDC Question BankKRCT EEE HODОценок пока нет
- Chapter: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits (One Mark Questions)Документ19 страницChapter: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits (One Mark Questions)khannapuneetОценок пока нет
- EDC 2markДокумент15 страницEDC 2markavv456Оценок пока нет
- Edc 2 Marks QBДокумент18 страницEdc 2 Marks QBAnonymous lt2LFZHОценок пока нет
- Senkottai Village, Madurai - Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution)Документ23 страницыSenkottai Village, Madurai - Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution)Raji SharmiОценок пока нет
- ED Unit 1Документ38 страницED Unit 1Gowrishankark EEE-Associate ProfessorОценок пока нет
- Pn Junctions and Diode ApplicationsДокумент13 страницPn Junctions and Diode ApplicationsJai GaizinОценок пока нет
- Analog Circuits Lab Possible Viva QuestionsДокумент18 страницAnalog Circuits Lab Possible Viva Questionsarsp_0610198571% (14)
- Analog and Digital Electronics: S. M. Jahadun-NobiДокумент39 страницAnalog and Digital Electronics: S. M. Jahadun-NobiJune C. OsunaОценок пока нет
- 2 Mark 16 MarkedcДокумент18 страниц2 Mark 16 MarkedccoolrajeeeОценок пока нет
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент16 страницEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017Оценок пока нет
- EDC Question Bank 18Документ33 страницыEDC Question Bank 18kalaiselvanОценок пока нет
- EI2203 EDC 2marksДокумент14 страницEI2203 EDC 2marksBhanu KodaliОценок пока нет
- Ec8252 Electronic Devices 1971170102 Ec8252 Electronic Devices Ed Q.BДокумент26 страницEc8252 Electronic Devices 1971170102 Ec8252 Electronic Devices Ed Q.BHeny ShahОценок пока нет
- Experiment 10Документ7 страницExperiment 10Deepan AdakОценок пока нет
- PN Junction Diode: Electronic Circuits (18NPC304) Assignment 2 Part - 1Документ2 страницыPN Junction Diode: Electronic Circuits (18NPC304) Assignment 2 Part - 1Narendran SrinivasanОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices NotesДокумент19 страницElectronic Devices NotesShivam YadavОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices Question BankДокумент17 страницElectronic Devices Question BankrammanoharОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions-Semiconductor DevicesДокумент7 страницCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions-Semiconductor DevicesGanesh Dhyani0% (1)
- 9 - Electronic Devices PDFДокумент28 страниц9 - Electronic Devices PDFthinkiitОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics: PresentationДокумент46 страницBasic Electronics: PresentationdennyОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Electronics Notes: Intrinsic, Extrinsic, n-type, p-typeДокумент4 страницыSemiconductor Electronics Notes: Intrinsic, Extrinsic, n-type, p-typeADITYA MAHECHAОценок пока нет
- Eto Handout1 DiodeДокумент20 страницEto Handout1 DiodedawitОценок пока нет
- UNIT1 Question Bank EDДокумент7 страницUNIT1 Question Bank EDsuganya1190Оценок пока нет
- Electron Devices - 1Документ12 страницElectron Devices - 1rajshrimohanksОценок пока нет
- Ec6202-Electronic Devices and Circuits 2 Marks and 16 Marks (Q&A) Unit 1Документ31 страницаEc6202-Electronic Devices and Circuits 2 Marks and 16 Marks (Q&A) Unit 1SayiTisanShalomОценок пока нет
- Semiconductors: Materials that enable modern electronicsДокумент58 страницSemiconductors: Materials that enable modern electronicsadi_risingsun0% (1)
- Semiconductors 1Документ16 страницSemiconductors 1Rohit SwamiОценок пока нет
- EDC 2 Marks All Five UnitsДокумент31 страницаEDC 2 Marks All Five Unitsksreddy2002Оценок пока нет
- Ec3353 Electronic Devices and CircuitsДокумент28 страницEc3353 Electronic Devices and CircuitsParanthaman GОценок пока нет
- Full Summary (Floyd)Документ8 страницFull Summary (Floyd)Adrian BagayanОценок пока нет
- Bed Unit 1 Notes 17.7.18Документ49 страницBed Unit 1 Notes 17.7.18gunasekaran kОценок пока нет
- Bee r20 Questions & Answers UNIT1Документ6 страницBee r20 Questions & Answers UNIT1surya pratapОценок пока нет
- Ramco Institute of TechnologyДокумент5 страницRamco Institute of TechnologyVijayakumar SОценок пока нет
- EC 3353 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Unit 1: Semi Conductor DevicesДокумент57 страницEC 3353 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Unit 1: Semi Conductor DevicesAnusha PadmavathiОценок пока нет
- Semi ConductorДокумент8 страницSemi ConductorSunil KumarОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor NotesДокумент14 страницSemiconductor NotesBansariОценок пока нет
- ' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityДокумент8 страниц' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityVam ArmodiaОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Документ45 страницBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalОценок пока нет
- SemiconductorsДокумент8 страницSemiconductorsgoodspeedopayashОценок пока нет
- Presentation Applied PhysicsДокумент9 страницPresentation Applied PhysicsSamar ShahzadОценок пока нет
- SemiconductorsДокумент5 страницSemiconductorsManoj KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor NotesДокумент8 страницSemiconductor NotesAaryaОценок пока нет
- 2.basic ElectronicsДокумент209 страниц2.basic ElectronicsJayanthi Krishnasamy BalasundaramОценок пока нет
- PHY 311 Electronics Semiconductor DevicesДокумент27 страницPHY 311 Electronics Semiconductor DevicesHassan Badiru AbdulsalamОценок пока нет
- PH3256 DHДокумент19 страницPH3256 DHdigitalepcsОценок пока нет
- MODULE-I - PN Junction DiodeДокумент17 страницMODULE-I - PN Junction DiodeAnurag HodgeОценок пока нет
- EE3950 Class Notes Chapter 10 Hambley 1-21Документ67 страницEE3950 Class Notes Chapter 10 Hambley 1-21Austin WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesДокумент128 страницEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDilip TheLipОценок пока нет
- Semiconductors and DevicesДокумент5 страницSemiconductors and DevicesSajal MallikОценок пока нет
- P-N Junction DiodeДокумент32 страницыP-N Junction Diodesashi_s2Оценок пока нет
- PAMT101 Applied Mathematics For EngineersДокумент2 страницыPAMT101 Applied Mathematics For EngineersmuthaiОценок пока нет
- Vao 2011 GeДокумент50 страницVao 2011 GeMahendra Kumar K CОценок пока нет
- CH 7 Timers, Counters, T/C Applications 1Документ67 страницCH 7 Timers, Counters, T/C Applications 1tino pawОценок пока нет
- Static Electric City CrosswordsДокумент2 страницыStatic Electric City CrosswordsmuthaiОценок пока нет
- SPRДокумент4 страницыSPRmuthaiОценок пока нет
- ARM Architecture Overview: Processors, Modes & Instruction SetsДокумент20 страницARM Architecture Overview: Processors, Modes & Instruction SetsmuthaiОценок пока нет
- D. A. Lowther, P. P. Silvester (Auth.) - Computer-Aided Design in Magnetics-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1986)Документ329 страницD. A. Lowther, P. P. Silvester (Auth.) - Computer-Aided Design in Magnetics-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1986)muthaiОценок пока нет
- PAPS103 Offshore Renewable Energy Conversion SystemsДокумент2 страницыPAPS103 Offshore Renewable Energy Conversion SystemsmuthaiОценок пока нет
- BEEE - NotesДокумент57 страницBEEE - NotesmuthaiОценок пока нет
- PIC MicrocontrollerДокумент27 страницPIC Microcontrollermuthai100% (1)
- Gate SyllabusДокумент3 страницыGate Syllabusmurthy237Оценок пока нет
- SPRДокумент4 страницыSPRmuthaiОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Energ Storage Based On Flywheels EERA Report 2013Документ67 страницKinetic Energ Storage Based On Flywheels EERA Report 2013muthaiОценок пока нет
- Gate SyllabusДокумент3 страницыGate Syllabusmurthy237Оценок пока нет
- Timer & SerialДокумент19 страницTimer & SerialmuthaiОценок пока нет
- Micro Controller 8051Документ56 страницMicro Controller 8051muthaiОценок пока нет
- Rect 2 Combined Engineering Service Question PaperДокумент33 страницыRect 2 Combined Engineering Service Question PaperAnonymous 8pCXXsОценок пока нет
- Arm Processor Class NotesДокумент20 страницArm Processor Class NotesmuthaiОценок пока нет
- Arm Processor Class NotesДокумент20 страницArm Processor Class NotesmuthaiОценок пока нет
- Csse1 EngДокумент52 страницыCsse1 EngPonnaiyan MlkrОценок пока нет
- Microcontroller 8051 ProgrammingДокумент24 страницыMicrocontroller 8051 ProgrammingmuthaiОценок пока нет
- PIC ProgrammingДокумент19 страницPIC ProgrammingmuthaiОценок пока нет
- Ic1251 Control SystemsДокумент14 страницIc1251 Control SystemscsdtgrОценок пока нет
- Ic1251 Control SystemsДокумент14 страницIc1251 Control SystemscsdtgrОценок пока нет
- r05220205 Control SystemsДокумент9 страницr05220205 Control SystemsSrinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- Dap 1Документ2 страницыDap 1muthaiОценок пока нет
- Lesson PlanДокумент6 страницLesson PlanmuthaiОценок пока нет
- ScholarshipДокумент5 страницScholarshipmuthaiОценок пока нет
- SERB-CII Doctoral Fellowship GuidelinesДокумент3 страницыSERB-CII Doctoral Fellowship Guidelinesvicky_ani1986Оценок пока нет
- Exam SolutionДокумент12 страницExam SolutionEng GutaleОценок пока нет
- Master Thesis Photovoltaic Thermal System (PVT) PDFДокумент143 страницыMaster Thesis Photovoltaic Thermal System (PVT) PDFYandi Hidayat0% (1)
- Blue Boy Deluxe Overdrive Owner's ManualДокумент2 страницыBlue Boy Deluxe Overdrive Owner's ManualshredmanОценок пока нет
- HGJHGHJДокумент1 страницаHGJHGHJVenom GamingОценок пока нет
- Physics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniДокумент17 страницPhysics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniKrunalKapadiya1Оценок пока нет
- Apm9435 PDFДокумент9 страницApm9435 PDFMohamed SalamОценок пока нет
- 4T SRAM SIMULATION FOR IMCДокумент2 страницы4T SRAM SIMULATION FOR IMCPRANJAL RAJANОценок пока нет
- ICL7116, ICL7117: 3 / Digit, LCD/LED Display, A/D Converter With Display HoldДокумент14 страницICL7116, ICL7117: 3 / Digit, LCD/LED Display, A/D Converter With Display HoldСергей КолосовОценок пока нет
- Comtec PDFДокумент7 страницComtec PDFgeorgeОценок пока нет
- UNIT-I NewДокумент163 страницыUNIT-I NewSanjay Rajan VОценок пока нет
- Axial Flux Motor PDFДокумент27 страницAxial Flux Motor PDFRyan LagasseОценок пока нет
- R500 Series Wire Mesh Rail: R511 R517 R520 R521Документ1 страницаR500 Series Wire Mesh Rail: R511 R517 R520 R521PrakashОценок пока нет
- Amplitude ModulationДокумент10 страницAmplitude ModulationlakshmiОценок пока нет
- Study Guide With Out AnswesДокумент9 страницStudy Guide With Out AnswesyazeedОценок пока нет
- Finder 16A 12V DC Relay Datasheet.Документ10 страницFinder 16A 12V DC Relay Datasheet.velizarkoОценок пока нет
- Electronic DetonatorДокумент10 страницElectronic Detonatorjumpupdnbdj0% (1)
- Tiny Serial Digital Thermal Sensor: Features General DescriptionДокумент16 страницTiny Serial Digital Thermal Sensor: Features General DescriptionKrychaОценок пока нет
- Online Electronic Instruments ManufacturersДокумент8 страницOnline Electronic Instruments ManufacturersAnalysis Tech IncОценок пока нет
- RF IC Important Questions Unit 12 UpdatedДокумент10 страницRF IC Important Questions Unit 12 Updatedchandu prabhaОценок пока нет
- Speed Control of A Separately Excited DC MotorДокумент2 страницыSpeed Control of A Separately Excited DC MotorKashyap SrishaОценок пока нет
- Simulation of A Solar MPPT Charger Using Cuk Converter For Standalone ApplicationДокумент6 страницSimulation of A Solar MPPT Charger Using Cuk Converter For Standalone ApplicationcashnuiОценок пока нет
- Electronic - Components-EDM Diciembre PDFДокумент526 страницElectronic - Components-EDM Diciembre PDFalvaro marrugoОценок пока нет
- Automotive Microelectronics 2001Документ93 страницыAutomotive Microelectronics 2001sayapopai100% (16)
- Driver DFC MotorДокумент24 страницыDriver DFC Motorda.dientuhnОценок пока нет
- MSE Mono 60 - v3 (270-280)Документ2 страницыMSE Mono 60 - v3 (270-280)amitОценок пока нет
- Alesis Microverb 4 - 1Документ11 страницAlesis Microverb 4 - 1gustavoОценок пока нет
- Elec 5204 Review Quizzes AnsДокумент9 страницElec 5204 Review Quizzes Ansveljal6317Оценок пока нет
- ch03 PDFДокумент9 страницch03 PDFFaisal MumtazОценок пока нет
- Lasers and Their Many UsesДокумент27 страницLasers and Their Many UsesnawidОценок пока нет
- Tecniplast Ivc RatsДокумент4 страницыTecniplast Ivc RatsCaroline SilvaОценок пока нет