Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Knowledge: Examples: Dates, Events, Places, Vocabulary, Key Ideas, Parts of Diagram, 5Ws
Загружено:
Dessy RismayatiОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Knowledge: Examples: Dates, Events, Places, Vocabulary, Key Ideas, Parts of Diagram, 5Ws
Загружено:
Dessy RismayatiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
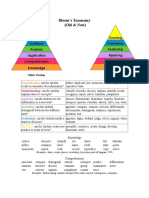
Benjamin Bloom (1956) developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior in
learning. This taxonomy contained three overlapping domains: the cognitive, psychomotor, and
affective. Within the cognitive domain, he identified six levels: knowledge, comprehension,
application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Critical thinking involves logical thinking and
reasoning including skills such as comparison, classification, sequencing, cause/effect,
patterning, webbing, analogies, deductive and inductive reasoning, forecasting, planning,
hypothesizing, and critiquing. Creative thinking involves creating something new or original. It
involves the skills of flexibility, originality, fluency, elaboration, brainstorming, modification,
imagery, associative thinking, attribute listing, metaphorical thinking, forced relationships. The
aim of creative thinking is to stimulate curiosity and promote divergence. While critical thinking
can be thought of as more left-brain and creative thinking more right brain, they both involve
"thinking." When we talk about HOTS "higher-order thinking skills" we're concentrating on the
top three levels of Bloom's Taxonomy: analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
Knowledge
collect describe identify list show tell tabulate
define examine label name retell state quote
enumerate match read record reproduce copy select
Examples: dates, events, places, vocabulary, key ideas, parts of diagram, 5Ws
Comprehension
associate compare distinguish extend interpret predict
contrast describe discuss estimate group summarize order
cite convert explain paraphrase restate trace differentiate
Analysis
analyze arrange connect divide infer separate
classify compare contrast explain select order
breakdown correlate diagram discriminate focus illustrate
infer outline prioritize subdivide points out prioritize
Examples: recognize and explain patterns and meaning, see parts and wholes
Synthesis
combine plan compose generalize modify invent substitute
create formulate integrate rearrange design speculate rewrite
adapt anticipate collaborate compile devise express facilitate
reinforce validate structure substitute intervene negotiate reorganize
Examples: discuss "what if" situations, create new ideas, predict and draw conclusions
Evaluation
assess compare decide discriminate measure rank test
convince conclude explain grade judge summarize support
appraise criticize defend persuade justify reframe
Affective Domain
Domain Attributes: interpersonal relations, emotions, attitudes, appreciations, values
accepts attempts challenges defends disputes joins judges
contributes praises questions shares supports volunteers
Вам также может понравиться
- Critical Thinking ListsДокумент2 страницыCritical Thinking ListsShannon HallОценок пока нет
- Critical and Creative ThinkingДокумент3 страницыCritical and Creative ThinkingAndRos Chin Yong Keat100% (1)
- Critical and Creative Thinking - Bloom's TaxonomyДокумент6 страницCritical and Creative Thinking - Bloom's TaxonomyAnonymous j8LfkG2Оценок пока нет
- List of Critical and Creative Thinking Skills and Relevant ActivitiesДокумент5 страницList of Critical and Creative Thinking Skills and Relevant ActivitiesLing Ching RouОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain: KnowledgeДокумент2 страницыBloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain: KnowledgeKlara Alexandra JuraОценок пока нет
- Critical and Creative Thinking SkillsДокумент1 страницаCritical and Creative Thinking SkillseilamieraОценок пока нет
- Domains of LearningДокумент19 страницDomains of LearningJoshua Olufemi100% (1)
- Critical Thinking TermsДокумент2 страницыCritical Thinking Termsnonono2451Оценок пока нет
- Assessment of Learning in The Cognitive Domain Handout 3Документ11 страницAssessment of Learning in The Cognitive Domain Handout 3Rizaldy GarciaОценок пока нет
- Critical and Creative Thinking - 1Документ3 страницыCritical and Creative Thinking - 1Luis Alonso Luna RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Rethorical 3Документ38 страницRethorical 3Raissa FebrinaОценок пока нет
- Action Verb List For Writing Student OutcomesДокумент3 страницыAction Verb List For Writing Student OutcomesanwarussaeedОценок пока нет
- Six LevelsДокумент10 страницSix LevelsBlesilda MallillinОценок пока нет
- Blooms Taxonomy SlosДокумент5 страницBlooms Taxonomy SlosEjaz hussainОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsДокумент10 страницBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsJose JosephОценок пока нет
- Bloom's TaxonomyДокумент19 страницBloom's TaxonomyZubair KhanОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsДокумент10 страницBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsKellor NiohОценок пока нет
- Blooms TaxonomyДокумент39 страницBlooms TaxonomyAnonymous cl6f9sZ100% (1)
- Bloom's TaxonomyДокумент2 страницыBloom's Taxonomygoduke1Оценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsДокумент5 страницBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsHeksi Putri SutrisnoОценок пока нет
- Knowledge: ComprehensionДокумент2 страницыKnowledge: Comprehensionjanice alquizarОценок пока нет
- How To Construct A Table of SpecificationДокумент48 страницHow To Construct A Table of SpecificationPearl Marie Guilaran Palma82% (11)
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsДокумент5 страницBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domainsthanu_2010Оценок пока нет
- Bloom HandoutДокумент11 страницBloom HandoutRuth HerrinОценок пока нет
- Verba in BloomsДокумент29 страницVerba in BloomsJayakumarОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Competence Skills Demonstrated KnowledgeДокумент4 страницыBloom's Taxonomy: Competence Skills Demonstrated KnowledgeCnette S. LumboОценок пока нет
- Blooms Taxonomy of Learning Domains The PDFДокумент12 страницBlooms Taxonomy of Learning Domains The PDFLin Coloma Viernes WagayenОценок пока нет
- Learning ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыLearning Objectivesjessa marie marevilesОценок пока нет
- Assessment 1 Power Point 2Документ20 страницAssessment 1 Power Point 2dhamiltonNGCSUОценок пока нет
- Slide DeckДокумент30 страницSlide DeckJoseph BirungОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains - VikaspediaДокумент4 страницыBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domains - VikaspediaNAZIRA SANTIAGO ESCAMILLAОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsДокумент9 страницBloom's Taxonomy of Learning Domainsvansick007Оценок пока нет
- Bloom - S TaxonomyДокумент40 страницBloom - S TaxonomyRutadharmadhikariОценок пока нет
- Assessment Form - Bloom's TaxonomyДокумент3 страницыAssessment Form - Bloom's TaxonomyDavid Woo75% (4)
- Revised Category #1: Knowledge RememberДокумент3 страницыRevised Category #1: Knowledge RememberCikgu SiaОценок пока нет
- Blooms Domains 2Документ9 страницBlooms Domains 2Cherry-Ann C. OlajayОценок пока нет
- Blooms VerbsДокумент2 страницыBlooms VerbsMd. Arif HassanОценок пока нет
- Three Domains of LearningДокумент7 страницThree Domains of LearningMelОценок пока нет
- Benjamin Bloom: (Bloom, Englehart, Furst, Hill, & Krathwohl, 1956)Документ7 страницBenjamin Bloom: (Bloom, Englehart, Furst, Hill, & Krathwohl, 1956)Paula Tanseco SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy: A Focus On Higher-Order Thinking SkillsДокумент9 страницBloom's Taxonomy: A Focus On Higher-Order Thinking SkillsHeidi JorxОценок пока нет
- BloomДокумент3 страницыBloomwaqar AhmedОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy (Old & New) : Older Version Newer Version: Can The StudentДокумент2 страницыBloom's Taxonomy (Old & New) : Older Version Newer Version: Can The StudentjamesvillenaОценок пока нет
- Safari - 23 Oct 2018 at 7:07 AM PDFДокумент1 страницаSafari - 23 Oct 2018 at 7:07 AM PDFhr187Оценок пока нет
- 4233-Article Text-12144-1-10-20180608Документ6 страниц4233-Article Text-12144-1-10-20180608Peter McManusОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of LearningДокумент8 страницBloom's Taxonomy of LearningXiena Rose BaniquedОценок пока нет
- Bloom's TaxonomyДокумент38 страницBloom's Taxonomyas.stationers.7Оценок пока нет
- Cognitive DomainДокумент12 страницCognitive Domainpj501Оценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsДокумент8 страницBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsSakura MyristicОценок пока нет
- Bloom S TaxonomyДокумент40 страницBloom S TaxonomygauravОценок пока нет
- Bloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of LearningДокумент19 страницBloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of Learningiq_mzj9892Оценок пока нет
- Blooms TaxonomyДокумент13 страницBlooms Taxonomyapi-382387880% (5)
- All 3 Blooms 2015Документ4 страницыAll 3 Blooms 2015Lenie Sang-olanОценок пока нет
- The Three Types of LearningДокумент10 страницThe Three Types of Learningmary heart baldemoroОценок пока нет
- ECE I - Course Standard 5Документ10 страницECE I - Course Standard 5sadyia carmelОценок пока нет
- Taxonomy of Educational Objectives OutlineДокумент9 страницTaxonomy of Educational Objectives OutlineRexonChanОценок пока нет
- Bloom TaxonomyДокумент3 страницыBloom TaxonomySrinath Gm G MОценок пока нет
- Bloom's TaxonomyДокумент6 страницBloom's TaxonomyJisiamar GeromoОценок пока нет
- Planning For Instructional Objectives: Adibah Binti Abdul LatifДокумент71 страницаPlanning For Instructional Objectives: Adibah Binti Abdul Latifshahmi nordinОценок пока нет
- Determining Instructional ObjectivesДокумент20 страницDetermining Instructional ObjectivesAxielОценок пока нет
- Lateral Leading: A Very Brief Introduction to Power, Understanding and TrustОт EverandLateral Leading: A Very Brief Introduction to Power, Understanding and TrustОценок пока нет
- Field Study 1Документ37 страницField Study 1Anthony Caputol100% (15)
- Applications of Neural Networks - TutorialspointДокумент2 страницыApplications of Neural Networks - Tutorialspointprabhuraaj101Оценок пока нет
- Fodor, J. - Concepts. Where Cognitive Science Went Wrong PDFДокумент91 страницаFodor, J. - Concepts. Where Cognitive Science Went Wrong PDFLear NcmОценок пока нет
- Hearing Vs Listening Group 10Документ11 страницHearing Vs Listening Group 10Muhammad Ali KhalidОценок пока нет
- Developmental Coordination DisorderДокумент4 страницыDevelopmental Coordination DisorderAmmar-1996Оценок пока нет
- 602 12 The Effect of Music Tempo On Memory Retention1Документ9 страниц602 12 The Effect of Music Tempo On Memory Retention1Stenley JosephОценок пока нет
- De Haan Jackson SchenkДокумент7 страницDe Haan Jackson SchenkMatthew MalekОценок пока нет
- Oscar Alfredo Torres Apa Audiolingual MethodДокумент10 страницOscar Alfredo Torres Apa Audiolingual Methodoscar-30Оценок пока нет
- Field Study 4Документ6 страницField Study 4Jundee L. Carrillo38% (13)
- Chapter 3 Motor AbilitiesДокумент18 страницChapter 3 Motor AbilitiesRoszalina InaОценок пока нет
- Quarter: 1: Lesson Exemplar in EnglishДокумент5 страницQuarter: 1: Lesson Exemplar in EnglishJan Jan HazeОценок пока нет
- X Cooperative LearningДокумент2 страницыX Cooperative LearningJhay B. MagtibayОценок пока нет
- AP Psych Unit 6 VocabДокумент3 страницыAP Psych Unit 6 VocabBrooke EmisonОценок пока нет
- 2014 2016 Pennsylvania Learning Standards For Early ChildhoodДокумент52 страницы2014 2016 Pennsylvania Learning Standards For Early Childhoodapi-472974486Оценок пока нет
- Mind-Body Dualism - Are They Separate or The Same?Документ8 страницMind-Body Dualism - Are They Separate or The Same?barbarian27100% (1)
- Lesson Plan GagneДокумент2 страницыLesson Plan Gagnechiew gin siongОценок пока нет
- Memory and Learning: The Path To UnderstandingДокумент17 страницMemory and Learning: The Path To UnderstandingDavid HansonОценок пока нет
- 3annie Kim Lesson Plan 0Документ3 страницы3annie Kim Lesson Plan 0api-385649496Оценок пока нет
- Related Literature LocalДокумент4 страницыRelated Literature LocalDalynai86% (7)
- Reading and Writing For Individuals With Down SyndromeДокумент10 страницReading and Writing For Individuals With Down SyndromeClara BiancaОценок пока нет
- Psychology Test 1 Practice QuestionsДокумент6 страницPsychology Test 1 Practice Questionsshamim326180% (5)
- Food Mind-Set and Obesity: Stimulus PieceДокумент2 страницыFood Mind-Set and Obesity: Stimulus PieceShannen IbayОценок пока нет
- Stage Appropriate Teaching Strategies and Nursing InterventionsДокумент5 страницStage Appropriate Teaching Strategies and Nursing InterventionsMarie KitОценок пока нет
- Utilizing Ict Integration in Reading ProgramДокумент4 страницыUtilizing Ict Integration in Reading ProgramRyanKingjimDiezUyОценок пока нет
- The Directive Function of Speech in Development and Dissolution - A. R. LuriaДокумент13 страницThe Directive Function of Speech in Development and Dissolution - A. R. LuriaPamela CОценок пока нет
- Entrance Exam: Program in Teaching English As A Foreign Language (Tefl)Документ6 страницEntrance Exam: Program in Teaching English As A Foreign Language (Tefl)Olga Caicedo BazanОценок пока нет
- Victor Corpuz ThesisДокумент0 страницVictor Corpuz ThesisMarini BudiartiОценок пока нет
- Key ConceptsДокумент35 страницKey ConceptsxicotiuaОценок пока нет
- Thinking Preference: Hermann Brain Dominance InstrumentДокумент36 страницThinking Preference: Hermann Brain Dominance InstrumentDina RedaОценок пока нет
- Autism, Impulsivity and Inhibition A Review of The LiteratureДокумент52 страницыAutism, Impulsivity and Inhibition A Review of The Literaturecsepulveda10Оценок пока нет