Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2005v04 Steel Plate PDF
Загружено:
MUBASОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2005v04 Steel Plate PDF
Загружено:
MUBASАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
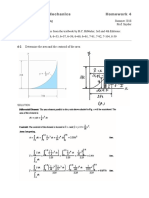
THE STEEL CONFERENCE
Steel Plate Shear Walls:
Practical Design and Construction
By Ignasius F. Seilie, P.E. and John D. Hooper, P.E.
Used for more than three decades as a primary lateral force resisting system, steel
plate shear walls are a good choice for a variety of building applications.
teel plate shear walls (SPSW)
S have been used, to a limited
extent, as the primary lateral
force resisting system in build-
ings for more than three
decades. There have been numerous
SPSW research programs in this time-
frame in the United States, Canada, and
Japan to help foster a better understand-
ing of the systems behavior, particularly
as it relates to earthquake-resistant
design. Some major building projects that
utilized SPSW as the primary lateral force
resisting system include the following:
United States Federal Courthouse,
Seattle, WA 23-story building (350)
Sylmar Hospital, Los Angeles, CA
six-story building
Canam-Manac Headquarters Expan-
sion, St. George, Quebec six-story
U.S. Federal Courthouse, Seattle (left) and The Century, San Francisco (right).
building
Hyatt Regency Hotel at Reunion, Dal-
las, TX 50-story building (562)
The Century, San Francisco, CA 46-
story building (465; the project was
cancelled after the completion of
design and permit)
Nippon Steel Building, Tokyo,
Japan 20-story building
Shinjuku Nomura Building, Tokyo,
Japan 51-story building (693)
Kobe Office Building, Kobe, Japan
35-story building (425)
The SPSW systems in the Kobe Office
Building and Sylmar Hospital have been
tested, having withstood fairly signifi-
cant earthquakes. The Sylmar Hospital
went through the Northridge Earth- Ignasius F. Seilie is an Associate with Mag- John D. Hooper is a Principal and the Direc-
nusson Klemencic Associates in Seattle. tor of Earthquake Engineering with Mag-
quake in 1994 and survived without any nusson Klemencic Associates in Seattle.
structural damage; however, there was
April 2005 Modern Steel Construction
cant structural damage (Astaneh & Zhao,
2002). The system also has been tested
since the 1970s. The system has been rec-
ognized in the National Building Code of
Canada (NBCC) since 1994 and will be
included in the American Institute of
Steel Construction (AISC) Seismic Provi-
sions in 2005.
Disadvantages of SPSW
Stiffness. SPSW systems are usually
more flexible in comparison to concrete
shear walls, primarily due to their flex-
ural flexibility. Therefore, when using
SPSW in tall buildings, the engineer
must provide additional flexural stiff-
ness. In both The Century and the U.S.
Federal Courthouse projects, large
composite concrete infill steel pipe
Planar SPSW (Canam HQ). See the September 2001 issue of MSC at www.modernsteel.com.
columns were used at all corners of the
core wall to improve the systems flex-
ural stiffness as well as its overturning
wide-ranging non-structural damage lesser building weight in comparison to capacity.
(Astaneh & Zhao, 2002). The Kobe Office buildings that use concrete shear walls. A Construction Sequence. Excessive
Building survived the Kobe Earthquake study performed for The Century project initial compressive force in the steel
in 1995 with minor damage (Astaneh & indicated that the total weight of the plate panel may delay the development
Zhao, 2002). building as designed using SPSW was of the tension-field action. It is impor-
There are three different SPSW systems: approximately 18% less than that of the tant that the construction sequence be
1. Un-stiffened, thin SPSW building designed using a concrete shear designed to avoid excessive compres-
2. Stiffened SPSW wall core system, which results in a sion in the panel. In the U.S. Federal
3. Composite concrete SPSW reduction of foundation loads due to Courthouse project, the welding of the
This paper will focus on the un-stiff- gravity and overall building seismic plate splice connections was delayed
ened, thin SPSW system, which is com- loads. until most of the dead load deformation
monly used in North America. Fast Construction. The use of a SPSW occurred in order to relieve the pre-com-
system reduces construction time. Not pression within the steel plate shear wall
Why Steel Plate Shear Walls? only is it fast to erect, but there also is no panel.
SPSW systems have been researched curing period. A scheduling study per- New System. Due to unfamiliarity
since the early 1970s. The most common formed by a contractor for The Century with the system, a contractor will typi-
research and application of SPSW in project indicated a one-month reduction cally estimate a relatively high erected
North America is the un-stiffened, thin in construction time. The steel erector for cost. This may be solved by engaging the
SPSW system. In Japan, the stiffened the U.S. Federal Courthouse indicated contractor early in the design phase.
SPSW system is more common. Regard- that the erection of the SPSW was much
less of which system is used, the determi- easier than that of the special concentri- Steel Plate Shear Wall
nation of whether a SPSW system is the cally braced frames. Configuration
right application in general is important. Ductility. A relatively thin steel There are two distinct SPSW configu-
The advantages and disadvantages of plate has excellent post-buckling capac- rations: core systems and planar systems.
SPSW systems depend on the type of ity. Research performed on the SPSW Depending on the building layout, size,
building being considered, as indicated system indicates that the system can and height, one type may be more advan-
below. survive up to 4% drift without experi- tageous than the other.
encing significant damage, even though SPSW core systems are best suited
Advantages of SPSW most of the tests showed damage out- for medium- to high-rise buildings. This
Wall Thickness. SPSW allow for less side the steel plate panel. There was configuration provides better torsional
structural wall thickness in comparison some pinching and tearing close to the and overturning stiffness and capacity.
to the thickness of concrete shear walls. corners of the panel due to bending. Multiple planar SPSW are more suit-
A study performed for The Century proj- However, this tearing did not reduce able for low-rise buildings and also for
ect indicated an average wall thickness, the plate capacity and stiffness (Astaneh rehabilitating existing buildings. These
including the furring, of 18 as opposed & Zhao, 2002). walls will provide sufficient shear capac-
to a concrete shear wall thickness with an Tested System. At least two buildings ity with somewhat limited overturning
average of 28 (refer to Figure 2). This that use SPSW as their primary lateral moment capacity.
resulted in a savings of approximately force resisting system have undergone
2% in gross square footage. significant earthquake ground shaking. Analysis and Design Approach
Building Weight. SPSW result in a Both buildings survived with insignifi- The typical SPSW system is com-
Modern Steel Construction April 2005
prised of steel plate panels, vertical Vertical
boundary elements, and horizontal Boundary
boundary elements. Elements
The general procedure in the design Horizontal
of the SPSW system is as follows: Boundary
Element Steel
Plate
Gravity Framing Panel
The building frames, including the
SPSW boundary elements, should be
designed to carry gravity loadings while
neglecting the contribution of the SPSW
panels. This is an important factor, done
to ensure that the building frames have
sufficient capacity to support the gravity
loads during seismic events, during
which the plate experiences buckling
due to the development of its tension-
field action.
Steel Plate Panel SPSW panel assemblage (The Century, San Francisco).
The steel plate panel is designed to
handle both wind and seismic loads. All
lateral shear loads in the SPSW panel are
resisted by the steel plate, utilizing ten-
sion-field action. There are many differ-
ent approaches that can be used to ana-
lyze the plate. The most common
approach is the tension-field strut model,
oriented in the direction of the tension
field a. Plate elements with orthotropic
properties oriented in the a direction
may be used in the lateral model as a
substitute for the struts. These tension
struts are designed as tension members.
This approach is represented by the fol-
lowing equation:
2 1
+
wL Ac
tan 4 =
2 2h h4 Gravity framing analysis, The Century, San Francisco.
+ +
wL AbL 180 I c L2
important to the proper performance of Alternative Modeling Techniques
Where: SPSW systems. For boundary elements Comparative studies between actual
L = steel plate panel length with plate walls on one side only (edge physical SPSW tests at the University of
h = steel plate panel height boundary elements), the boundary ele- California, Berkeley (Astaneh & Zhao,
w = steel plate thickness ment should be designed based on the 2002), tension-field strut models, and
Ac, Ic = vertical boundary element mem- capacity of the steel plate wall. This elastic orthotropic plate element models
ber area and moment of inertia demand is based on the panels aspect indicate that both modeling techniques
Ab = horizontal boundary element ratio, the steel plates thickness, and the are suitable for use. The NBCC suggests
member area steel plates expected strength. the use of the tension-field strut model,
The suggested maximum height/ The vertical boundary elements, with a minimum of ten struts per panel
length aspect ratio (h/L) is 1. A large whether built-up or comprised of stan- oriented in the a direction. However,
height/length ratio means the vertical dard W shapes, should meet the AISC for high-rise building design, this
boundary elements stiffness and capac- compactness criteria. approach can be very tedious. The use of
ity will have more influence on the sys- elastic orthotropic plate elements simpli-
tem quality. The suggested minimum Hinging Sequence fies the analysis for high-rise buildings.
length/thickness ratio is 180. Thicker The desirable hinging sequence for The stiffness property in the direction
plates will delay the development of ten- the SPSW system is as follows: of the tension-field should be the full
sion-field action. 1. Steel plate walls steel stiffness property, while the stiffness
2. Coupling beams property in the perpendicular direction
Boundary Elements 3. Horizontal boundary elements to the tension-field should be a fraction
The boundary elements are very 4. Vertical boundary elements
April 2005 Modern Steel Construction
Core walls with composite concrete infill steel pipe columns.
Height/length aspect ratio.
of the steel stiffness in order to represent ness, which can create difficulties for
limited steel stiffness under compression. stick building/erection of the system.
The engineer should plan the panel seg-
Construction Considerations ment size and details to mitigate this con-
There are several important factors struction issue. Sufficient out-of-plane
that need to be considered by the engi- stiffness should be provided.
Forces supported by vertical boundary ele- neer in order to produce good SPSW Careful Construction Sequence Plan.
ment. behavior and an efficient construction The engineer, with assistance from the
process. contractor, should plan the construction
SPSW Fabricated Panel Size and sequence to alleviate gravity-load
Details. SPSW panels can consist of large induced axial compression in the steel
steel panels with low out-of-plane stiff- plate panels. Axial pre-compression in
Modern Steel Construction April 2005
the steel plate wall may delay the devel- This paper has been edited for space consider- Handbook of Steel Construction, Sixth Edi-
opment of the tension-field action. One ations. To learn more about practical design tion. Canadian Institute of Steel Con-
approach to overcome this is to delay the and construction of steel plate shear walls, struction. December 1995.
tightening/fixing of the steel plate splice read the complete text online at www.mod- Patent Problems, Challenge Spawn Steel
connection. This will allow shortening of ernsteel.com or in the 2005 NASCC Pro- Seismic Walls, Engineering News
the vertical elements prior to fixing the ceedings. Record. January 26, 1978.
steel plate splice. Quake-Proof Hospital Has Battleship-
Stability During Construction. One References Like Walls, Engineering News Record.
of the advantages of using the SPSW sys- Astaneh, Abolhassan. Seismic Behavior September 21, 1978.
tem is speed of construction. The engi- and Design of Steel Plate Shear Shear Walls and Slipforming Speed Dal-
neer needs to make sure that the assem- Walls, Structural Steel Educational las Reunion Project, Engineering
bled system has sufficient out-of-plane Council Steel Tips. January 2001. News Record. July 28, 1977.
stiffness during construction. The SPSW Astaneh, Abolhassan; Zhao, Quihong. Timler, Peter. Design Procedure Devel-
has less out-of-plane stiffness in compar- Cyclic Test of Steel Shear Walls opment, Analytical Verification, and
ison to a concrete wall. Final Report. Department of Civil Cost Evaluation of Steel Plate Shear
and Environmental Engineering, Col- Wall Structures. Department of Civil
Summary lege of Engineering, University of Cal- Engineering, University of British
SPSW systems have been used, to a ifornia at Berkeley. August 2002. Columbia. March 1998.
limited extent, as the primary lateral Driver, Robert G.; Grondin, Gilbert Y.;
force resisting system in buildings for Behbahanifard, Mohammad R.; Hus-
more than three decades. Their recent sain, Munawar A. Recent Develop-
good performance in major earthquakes, ments and Future Directions in Steel
their robust performance in the labora- Plate Shear Wall Research, NASCC
tory, and their recent inclusion in codes Proceedings. Department of Civil and
and standards suggest that SPSW sys- Environmental Engineering, Univer-
tems are here to stay. sity of Alberta. May 2001.
April 2005 Modern Steel Construction
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Urban Transportation PlanningДокумент4 страницыUrban Transportation PlanningMUBASОценок пока нет
- 1409043391.0502M3 L3 PDFДокумент10 страниц1409043391.0502M3 L3 PDFMohit RajaiОценок пока нет
- SedmentationДокумент6 страницSedmentationJorge Olortiga OrtizОценок пока нет
- L Inverted Siphon 3rd CДокумент6 страницL Inverted Siphon 3rd CPreston VargheseОценок пока нет
- Water Resource Engineering NotesДокумент5 страницWater Resource Engineering NotesMUBASОценок пока нет
- Test ScribdДокумент1 страницаTest ScribdMUBASОценок пока нет
- Raw WaterДокумент5 страницRaw WaterMUBASОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Job Number Sheet Continuous Beam CalculationsДокумент4 страницыJob Number Sheet Continuous Beam CalculationsJONHCENA13Оценок пока нет
- Karpurapu & Bathurst C&G v17 n3 1995Документ21 страницаKarpurapu & Bathurst C&G v17 n3 1995lollazzoОценок пока нет
- EarthquakeДокумент8 страницEarthquakeKinjal ShahОценок пока нет
- ANSYS Mechanical APDL Fracture Analysis GuideДокумент160 страницANSYS Mechanical APDL Fracture Analysis GuideAlejandra Hernandez Sanchez100% (4)
- Early Thermal Cracking in Concrete ExplainedДокумент5 страницEarly Thermal Cracking in Concrete ExplainedAshrafОценок пока нет
- ChairДокумент7 страницChairapi-487109487Оценок пока нет
- Common Mistakes in Fatigue AnalysisДокумент14 страницCommon Mistakes in Fatigue AnalysismuhannedОценок пока нет
- MIDAS MCT File Quick ReferenceДокумент90 страницMIDAS MCT File Quick ReferenceromanoscotchОценок пока нет
- Foundation Consultants LTD.: M/S Kakoli Dying and Printing Works Ltd. Report OnДокумент53 страницыFoundation Consultants LTD.: M/S Kakoli Dying and Printing Works Ltd. Report Onপ্রিয়দীপ প্রিয়মОценок пока нет
- Key Design NumericalsДокумент2 страницыKey Design NumericalsMuhammad Azeem SheikhОценок пока нет
- The Influence of Reinforcement Geometry and Soil Types On The Interface Behaviour in Pullout ConditionsДокумент7 страницThe Influence of Reinforcement Geometry and Soil Types On The Interface Behaviour in Pullout Conditionskunalji_jainОценок пока нет
- Fracture Mechanics of Concrete StructuresДокумент71 страницаFracture Mechanics of Concrete StructuresHowo4Die100% (1)
- Engineering Materials and Testing IIДокумент37 страницEngineering Materials and Testing IILorie Mae BelloОценок пока нет
- Shear Stress PDFДокумент6 страницShear Stress PDFengineer bilalОценок пока нет
- Ghateh, Razmyar PDFДокумент271 страницаGhateh, Razmyar PDFDaVishur WthОценок пока нет
- COLUMN BASE PLATE DESIGN CALCULATIONS (BS5950-1:2000Документ7 страницCOLUMN BASE PLATE DESIGN CALCULATIONS (BS5950-1:2000Shakil Akhter100% (1)
- Design of Steel Purlins AnalysisДокумент6 страницDesign of Steel Purlins AnalysisSayavi Nicole Sayavi Nick100% (2)
- FCE 431 - Lecture 5 - 2022-2023Документ12 страницFCE 431 - Lecture 5 - 2022-2023melissakiptooОценок пока нет
- HW4 Solutions ENGS 33Документ8 страницHW4 Solutions ENGS 33Brayan LozanoОценок пока нет
- Design of Precast and Prestressed Double Tee Beam CalculationДокумент20 страницDesign of Precast and Prestressed Double Tee Beam CalculationLim Wee BengОценок пока нет
- Project: Dog Legged Stair Design Constant: OK Under ReinforcedДокумент4 страницыProject: Dog Legged Stair Design Constant: OK Under ReinforcedlakshminarayanstrОценок пока нет
- New Era University: Foundation Engineering (Lab)Документ6 страницNew Era University: Foundation Engineering (Lab)Hailley DensonОценок пока нет
- Steel Beam Design Flowchart EUROCODEДокумент7 страницSteel Beam Design Flowchart EUROCODELong Live TauОценок пока нет
- 5-1 13 3/8" Surface Casing DesignДокумент10 страниц5-1 13 3/8" Surface Casing Designeng20072007Оценок пока нет
- 2010 - Strasser - Scaling of The Source Dimensions of Interface and Intraslab Subduction-Zone Earthquakes With Moment MagnitudeДокумент10 страниц2010 - Strasser - Scaling of The Source Dimensions of Interface and Intraslab Subduction-Zone Earthquakes With Moment Magnitudecjmentor1279Оценок пока нет
- Typical Cross Girder DesignДокумент81 страницаTypical Cross Girder Designsushil deshmukhОценок пока нет
- STPDF1 - Subtopic PDF 1 Flexural and Shear Stresses in BeamsДокумент22 страницыSTPDF1 - Subtopic PDF 1 Flexural and Shear Stresses in Beamsnaughty dela cruzОценок пока нет
- ASME VIII A13 - Vessels of Noncircular Cross Section (Type 13-2 (A) (6) )Документ14 страницASME VIII A13 - Vessels of Noncircular Cross Section (Type 13-2 (A) (6) )hardik5818100% (1)
- Ce511 Tabinas HW02 PDFДокумент17 страницCe511 Tabinas HW02 PDFKathlyn Kit TabinasОценок пока нет
- Chopra, Dynamic Stiffness Matrices For Homogeneous ViscoelasticДокумент134 страницыChopra, Dynamic Stiffness Matrices For Homogeneous ViscoelasticCarlos Eduardo Cueva CallerОценок пока нет