Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fenner Wedge & V-Belt Tensioning Instructions PDF
Загружено:
Alejandro RosetteОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fenner Wedge & V-Belt Tensioning Instructions PDF
Загружено:
Alejandro RosetteАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
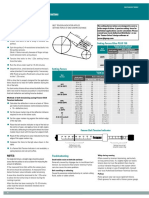
FRICTION BELT DRIVES
3 Fenner Wedge & V-Belt Tensioning Instructions
"ONE SHOT" TENSIONING
Fenner belts are Precision Built to ensure BELT TENSION INDICATOR APPLIES
inherent length stability and matching during SETTING FORCE AT MID CENTRE
storage and on the drive. Over many years, the DISTANCE
principle of "one-shot" tensioning has been
veried by successful drives the world over.
16
Install the belts to be a snug fit d mm
m eec
around the pulleys. dis etre tio
tan of n p
ce cen er 1 The setting forces below are
Spin the pulleys 3-4 revolutions to tre
bed belts into the pulley grooves. designed to cover a wide range
(Note: if done manually, beware of of drives. A precise setting
finger entrapment between belts force for individual applications
and pulleys) can be calculated. Please
consult your local Authorised
Tension the belts to the 1.25x setting Distributor or use the 'Fenner
forces from the table. Select' design software at
Run the drive under load for 15-20 www.fptgroup.com
SETTING FORCES
minutes.
Stop the drive, check tension & reset Setting force to deect belt
Belt 16 mm per metre of span
to the basic value (standard V and Section
wedge belts) if necessary.
Small pulley Basic setting forces 1.25 x setting forces
CRE Plus & Quattro Plus belts should diameter (mm) Newtons (N) kilograms (kgf) Newtons (N) kilograms (kgf)
be reset to the 1.25x value. 56 to 71 16 1.6 20 2.0
SPZ 75 to 90 18 1.8 22 2.2
With a drive that is properly designed for the 95 to 125 20 2.0 25 2.5
application there should be no need for further XPZ & QXPZ over 125 22 2.2 28 2.8
attention during the life of the belts. 80 to 100 22 2.2 28 2.8
SPA 106 to 140 30 3.0 38 3.9
For short centre distance drives where the 150 to 200 36 3.7 45 4.6
deection of the belt is too small to measure XPA & QXPA over 200 40 4.0 50 5.1
accurately it is recommended that both 112 to 160 40 4.0 50 5.1
deection and setting force be doubled. SPB 170 to 224 50 5.1 62 6.3
236 to 355 62 6.3 77 7.9
XPB& QXPB over 355 65 6.6 81 8.3
Method of belt tensioning using
224 to 250 70 7.1 87 8.9
Fenner Belt Tension Indicator SPC 265 to 355 92 9.4 115 12.0
Calculate the deection in mm on a & QXPC over 375 115 12.0 144 15.0
basis of 16mm per metre of centre dis- 8V 335 & above 150 15.0 190 19.0
Z 56 to 100 5 to 7.5 0.5 to 0.8
tance. Centre distance (metres) x 16 = A (& HA banded) 80 to 140 10 to 15 1.0 to 1.5
deection (mm). B 125 to 200 20 to 30 2.0 to 3.1
C 200 to 400 40 to 60 4.1 to 6.1
Set the lower marker ring at the deec- D 355 to 600 70 to 105 7.1 to 10.7
tion distance required in mm on the
lower scale. FENNER BELT TENSION INDICATOR
Set the upper marker ring against the
bottom edge of the top tube.
Place the belt tension indicator on top
of the belt at the centre of span, and
apply a force at right angles to the
belt, deecting it to the point where the Deection Setting force Product Code 230A0000
lower marker ring is level with the top in mm in kgf
of an adjacent belt.
NOTES: heat and/or chemical fumes can also
Read off the setting force value indi- cause the same problem.
For single belt drives a straight edge should be
cated by the top edge of the upper
placed across the two pulleys to act as a datum Belt swelling or softening
marker ring.
for measuring the amount of deection.
Caused by excessive contamination by oil,
Compare this force to the kgf value If the measured force falls within certain cutting uids, water or rubber solvent.
shown in the table. the values given, the drive should be
satisfactory. A measured force below the Whip during running
If a Fenner BeltTension Indicator is not
available, a spring balance and rule basic value indicates under-tensioning. Often caused by incorrect tensioning,
will sufce. A new drive should be tensioned to the particularly on long centre drives. If a
1.25x value to allow for the normal drop in slightly higher (or lower) tension does not
With banded belts (pages 68 and 69) tension during the running-in period. cure the problem there may be a critical
use a bar across the band width to vibration frequency in the system which
ensure even distribution of the force After the drive has been running for 1520
requires re-design or use of banded belts.
and DIVIDE the force measured by the minutes, under load the tension should be
Consult your local Authorised Distributor
number of belts in the band for compar- checked and re-adjusted, if necessary.
Technical Services.
ison with the values in the table above.
TROUBLE SHOOTING Pulleys
Alternatively, for the same deection,
use a setting force from the table above Small radial cracks on belt side and base Pulley groove wear can cause rapid belt
MULTIPLIED by the number of belts in failure. Check grooves for wear with a
the band. Generally caused by slippage due to
insufcient belt tension, but excessive Fenner groove gauge.
74 Drive Design & Maintenance Manual - 2006
Installation and Operaton of Wedge & V-Belt Drives
FRICTION BELT DRIVES
Section
Although comparatively old in principle TENSIONING PULLEYS
today's belt drive is an extremely efcient Tensioning pulley movemement must
method of transmitting power between If tensioning (jockey) pulleys are to be
used on wedge belt drives, they must be allow for passing the belts over the
prime mover and machinery. outside diameter of one of the drive
grooved pulleys working on the inside of
It owes its present high performance the drive, preferably on the slack side. The pulleys on installation, and should also
standards to many years of research pulley should be positioned as close as allow for belt stretch/bedding in.
and development by engineers and possible to the large pulley. Flat tensioning
technologists, leading to signicant pulleys, bearing on the outside of the drive The modern wedge belt drive
renements in materials and processes. are permissible only with V and not with is a highly efcient power
To derive maximum benet from such wedge belts. They should be positioned transmission medium, but
advances it is important that the simple within one third of the centre distance optimum performance will not be
FRICTION BELT DRIVES
installation and operation procedures set from the small pulley. achieved without correct tension
out here are closely followed. Making The tensioning pulley must have at least and alignment.
these routines standard practice will the same diameter as the small pulley of
ensure optimum performance and long, the drive.
trouble-free life from Fenner belt drives.
INSTALLATION 1 2 3 4
Angular Composite Axial Correct installation -
PULLEYS misalignment misalignment misalignment both shafts and pulleys
are parallel and in
Before assembling the drive, check the
alignment.
pulley grooves are free from scores
or sharp edges, and all dimensions
conform to the relevant standard.
Drive installation is straightforward with
Taper Lock but follow all steps on the
installation leaet provided with every
Taper Lock bush.
ALIGNMENT
Good alignment of pulleys is important
to avoid belt ank wear. The diagrams
opposite show some of the common
alignment faults.
Pulley misalignment should not exceed
1/2 0 angular and 10mm / metre drive
centre distance, axial.
A laser alignment device is available, INSTALLATION AND
which facilitates quick, easy and TAKE-UP ALLOWANCE
accurate pulley alignment - consult your
local Authorised Distributor. Belt Installation Allowances Take
Pitch Length -up
BELT INSTALLATION SPZ SPA SPB SPC 8V
(mm) (mm)
When the pulleys have been correctly Z A B C D
positioned on the shafts, the belts can be 410 to 530 5
installed to complete the drive.
530 to 840 10
The drive centre distance should be
reduced prior to the installation of the 850 to 1160 15
belts so that they may be tted without 1170 to 1500 20
the use of force. Under no circumstances
1510 to 1830 20 25
must belts be prised into the grooves.
Belts and pulley grooves can easily be 1840 to 2170 30
damaged by using sharp tools to stretch 2180 to 2830 25 40
the belts over the pulley rim.
2840 to 3500 30 50
The installation allowance given in
the table opposite is the minimum 3520 to 4160 50 60
recommended reduction in centre 4170 to 5140 65 70
distance for the various belt sections
and lengths to allow for correct tting. 5220 to 6150 85
The take-up allowance given in the 6180 to 7500 105
same table should be added on to the 7600 to 8500 125
calculated centre distance to allow for
8880 to 10170 145
belt stretch/bedding in.
GUARDS 10600 to 12500 175
Where guards are necessary it is
desirable to use mesh materials to TAPER LOCK
permit adequate ventilation. All Fenner V and wedge belt pulleys use
Guards should be generously sized to Taper Lock shaft xing.
allow for incidental belt ap. Detailed instructions for tting and
dismounting Taper Lock products are
included with Taper Lock bushes.
Drive Design & Maintenance Manual - 2006 75
Вам также может понравиться
- Fenner Belt Tension Pen Data Sheet PDFДокумент2 страницыFenner Belt Tension Pen Data Sheet PDFSadi KutkutОценок пока нет
- Fenner 471 Friction Belt Installation Guide by CBC AustraliaДокумент2 страницыFenner 471 Friction Belt Installation Guide by CBC AustraliaFanir ZОценок пока нет
- France TransfoTransformers Installation GuideДокумент27 страницFrance TransfoTransformers Installation GuideTarek FawzyОценок пока нет
- Pull Wire and Trip Switch PDFДокумент76 страницPull Wire and Trip Switch PDF450gasgas100% (1)
- T Verter n2 Series User Manual PDFДокумент4 страницыT Verter n2 Series User Manual PDFرفيفان النشمي0% (1)
- Rim and Face - Alignment KnowledgeДокумент19 страницRim and Face - Alignment Knowledgevj kumarОценок пока нет
- Torque Wrenches - Guidelines - 0Документ7 страницTorque Wrenches - Guidelines - 0Jellyn Base100% (1)
- Specification For Air Craft Warning LightsДокумент5 страницSpecification For Air Craft Warning Lightsgeverett2765Оценок пока нет
- 8DJH - ST, 12 KV Montaje en CubiculoДокумент112 страниц8DJH - ST, 12 KV Montaje en CubiculoSebastian Soto NacharОценок пока нет
- Wire Feeder: Owner'S ManualДокумент25 страницWire Feeder: Owner'S ManualPhạm Hoài Anh100% (1)
- Waukesha Knock Index (WKI ) 12V275GL+ Waukesha Knock Index Power and Timing Curve 750-1000 RPM 130°F (54°C) Intercooler WaterДокумент1 страницаWaukesha Knock Index (WKI ) 12V275GL+ Waukesha Knock Index Power and Timing Curve 750-1000 RPM 130°F (54°C) Intercooler WaterarasОценок пока нет
- Electrical Bus Bar Ampacity ChartДокумент4 страницыElectrical Bus Bar Ampacity ChartSemaj Eel0% (1)
- Hazardous Area Classifications (SANS10108)Документ4 страницыHazardous Area Classifications (SANS10108)cvbns0% (1)
- BS 5345-4 1977 PDFДокумент18 страницBS 5345-4 1977 PDFArt JamesОценок пока нет
- Motores Siemens PDFДокумент237 страницMotores Siemens PDFare_reeОценок пока нет
- Spare Part List MNS 2.0 and MNS 3.0 R0Документ12 страницSpare Part List MNS 2.0 and MNS 3.0 R0Jatupol Pongsirisart33% (3)
- Actuators Price ListДокумент2 страницыActuators Price ListJack ChavanОценок пока нет
- Motor Data SheetДокумент4 страницыMotor Data Sheetlbc123100% (2)
- Sleeve Vs Antifriction Bearings Selection of The Optimal BearingДокумент13 страницSleeve Vs Antifriction Bearings Selection of The Optimal BearingKamal Arab0% (1)
- Preconisation Kerui2Документ12 страницPreconisation Kerui2zinouОценок пока нет
- ABB Motor Catalog Frame 315 & 355 PDFДокумент6 страницABB Motor Catalog Frame 315 & 355 PDFSUBHASHОценок пока нет
- Ampacity Chart For Copper Bus Bar DesignДокумент2 страницыAmpacity Chart For Copper Bus Bar DesignfaberromeroОценок пока нет
- ER2 Owners ManualДокумент164 страницыER2 Owners ManualKito Canada100% (5)
- Dol Starter With Remote Start and StopДокумент1 страницаDol Starter With Remote Start and StopAthul AОценок пока нет
- Omm - GK-X Manual 2-0Документ57 страницOmm - GK-X Manual 2-0fredy.arenas6175Оценок пока нет
- Weg W21 Fastening Bolt Torque Settings: Calculation DataДокумент1 страницаWeg W21 Fastening Bolt Torque Settings: Calculation Datajuanqui20Оценок пока нет
- Operation Manual: Multifunction Frequency Relay TypeДокумент35 страницOperation Manual: Multifunction Frequency Relay TypeLazyo RahmandoОценок пока нет
- Ringmaster Nov07 SE6251 PDFДокумент92 страницыRingmaster Nov07 SE6251 PDFosmpot100% (1)
- Operating Instructions: Brake Accessories, ZB. Motor RangeДокумент24 страницыOperating Instructions: Brake Accessories, ZB. Motor RangeAlfonso Vásquez100% (2)
- 3 Waukesha Gas Engine Maintenance ManualДокумент75 страниц3 Waukesha Gas Engine Maintenance ManualMamunОценок пока нет
- 01 Rockbreaker Systems 1 MRHДокумент50 страниц01 Rockbreaker Systems 1 MRHJuan Diego ArizabalОценок пока нет
- Alignment Tolerance TableДокумент1 страницаAlignment Tolerance TableAlagar Samy AОценок пока нет
- Is Standards Equivalent To IEC Standards Applicable To The Products We ManufactureДокумент1 страницаIs Standards Equivalent To IEC Standards Applicable To The Products We ManufactureGirish Rai100% (1)
- Electric Fence TH-2008 ManualДокумент13 страницElectric Fence TH-2008 ManualRap FigueroaОценок пока нет
- Operating Instructions Accessories Component Parts DC Pro Demag Chain HoistsДокумент144 страницыOperating Instructions Accessories Component Parts DC Pro Demag Chain HoistsAristideОценок пока нет
- Sub: Multipurpose Hall - Lusail Sports Club - Package 2Документ12 страницSub: Multipurpose Hall - Lusail Sports Club - Package 2Seyed IbrahimОценок пока нет
- 03-Etl+wz 1210174GBДокумент20 страниц03-Etl+wz 1210174GBAshraful HasanОценок пока нет
- Technical Specifications of Gear BoxДокумент6 страницTechnical Specifications of Gear Boxsagarkali100% (1)
- Greatork IOM ... MANUALДокумент36 страницGreatork IOM ... MANUALRAMESH RAMASAMY100% (1)
- Equipment Brochure AdorДокумент84 страницыEquipment Brochure AdorHum Hum0% (1)
- Elum ePowerControl HFS Datasheet 102019Документ4 страницыElum ePowerControl HFS Datasheet 102019CyrilColin100% (1)
- Sae J1231-2011Документ14 страницSae J1231-2011Ace LeeОценок пока нет
- Meter ItronДокумент2 страницыMeter ItronSumar Sono67% (3)
- 25.rotary Actuator CalculationДокумент12 страниц25.rotary Actuator Calculationcarthik_babu100% (1)
- Preventive Maintenance Kits For ABB Industrial Drives, ACS800Документ2 страницыPreventive Maintenance Kits For ABB Industrial Drives, ACS800Jhon RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Weight For Bolt With Nut PDFДокумент1 страницаWeight For Bolt With Nut PDFRam RajaramanОценок пока нет
- Dcon5114853 PDFДокумент91 страницаDcon5114853 PDFAmrit KumarОценок пока нет
- CMG - Sga Series BrochureДокумент40 страницCMG - Sga Series BrochureIee XpОценок пока нет
- Drivecon XT Series Instruktion ManualДокумент120 страницDrivecon XT Series Instruktion ManualJoss Maykol Mundaca VasquezОценок пока нет
- MC600 Modular Conveyor: Revision 12 January 2014 Document Number: PCM-03-02-02Документ60 страницMC600 Modular Conveyor: Revision 12 January 2014 Document Number: PCM-03-02-02Carl RichterОценок пока нет
- Siemens Motors LP CatalogueДокумент32 страницыSiemens Motors LP Cataloguedabburinku100% (1)
- Fitting & Acc PDFДокумент663 страницыFitting & Acc PDFUncorrectableNameОценок пока нет
- Fitting & Acc.Документ595 страницFitting & Acc.jarekОценок пока нет
- 3MZ-FE Engine Belt Tension SpecificationsДокумент1 страница3MZ-FE Engine Belt Tension SpecificationsdilanОценок пока нет
- Belt Tension RequiredДокумент2 страницыBelt Tension RequiredJinto A J100% (3)
- CLP en PDFДокумент2 страницыCLP en PDFAnthony FuОценок пока нет
- SafetyДокумент3 страницыSafetykorkieОценок пока нет
- 106.5 - BeltsДокумент10 страниц106.5 - BeltsHassan GDOURAОценок пока нет
- LN Belt DriveДокумент45 страницLN Belt DriveDesri AfrilianiОценок пока нет
- Design Envelope 4300 A 4380 Vertical Inline PumpingДокумент44 страницыDesign Envelope 4300 A 4380 Vertical Inline PumpingsergiotrОценок пока нет
- TroubleshootTipsArmRew 0403 PDFДокумент3 страницыTroubleshootTipsArmRew 0403 PDFAlejandro RosetteОценок пока нет
- Allen Bradley TLY-A120P-BJ62AA Tamagawa TS5669Документ1 страницаAllen Bradley TLY-A120P-BJ62AA Tamagawa TS5669Alejandro RosetteОценок пока нет
- S120 3party Motors Sys Man 0121 en-USДокумент216 страницS120 3party Motors Sys Man 0121 en-USCRISENTENAОценок пока нет
- Ms Megachem A2740 8e 3Документ23 страницыMs Megachem A2740 8e 3nata siagianОценок пока нет
- Panduit Marcaje en Acero Inoxidable PermanenteДокумент8 страницPanduit Marcaje en Acero Inoxidable PermanenteAlejandro RosetteОценок пока нет
- MT Megachem A2740 0e 5Документ22 страницыMT Megachem A2740 0e 5rafael batista de paulaОценок пока нет
- Ms Megachem A2740 8e 3Документ23 страницыMs Megachem A2740 8e 3nata siagianОценок пока нет
- Effects of High or Low Voltage PDFДокумент2 страницыEffects of High or Low Voltage PDFAlejandro RosetteОценок пока нет
- Electric Motor TestingДокумент3 страницыElectric Motor TestingAlejandro RosetteОценок пока нет
- Manual Fag Trummy2 PDFДокумент6 страницManual Fag Trummy2 PDFAlejandro RosetteОценок пока нет
- Sleeve Bearing Specification For MotorДокумент45 страницSleeve Bearing Specification For MotorThiMinhKhuyen100% (2)
- KarcherДокумент60 страницKarcherAlfonso Martinez RomanОценок пока нет
- Tps 53014Документ27 страницTps 53014nebiyu mulugetaОценок пока нет
- Lab3 BJT Current MirrorsДокумент5 страницLab3 BJT Current MirrorsaublysodonОценок пока нет
- Froth Flush ProcessДокумент33 страницыFroth Flush ProcessnivasssvОценок пока нет
- California Bearing Ratio, Evaluation and Estimation: A Study On ComparisonsДокумент4 страницыCalifornia Bearing Ratio, Evaluation and Estimation: A Study On ComparisonsAmyra MiaОценок пока нет
- Chip Scale Atomic Magnetometer Based On SERFДокумент4 страницыChip Scale Atomic Magnetometer Based On SERFluckystar83100% (2)
- Centrifugal PumpДокумент56 страницCentrifugal Pumpchandraa2208Оценок пока нет
- Literature ReviewДокумент2 страницыLiterature ReviewkhairulОценок пока нет
- CS1 Course OutlineДокумент2 страницыCS1 Course Outlineapi-27149177Оценок пока нет
- Die Casting Process & Design Gate & ParametersДокумент113 страницDie Casting Process & Design Gate & ParametersEr Tarun Patel100% (1)
- Depth of InvestigationДокумент8 страницDepth of InvestigationGogot Pantja ParijogoОценок пока нет
- Slum FinalДокумент46 страницSlum FinalSanghita Bhowmick83% (6)
- Nauticus 3D BeamДокумент114 страницNauticus 3D BeamMinca AndreiОценок пока нет
- SG-05 Safety Guideline For Illumination at WorkplaceДокумент5 страницSG-05 Safety Guideline For Illumination at WorkplacebsrchandruОценок пока нет
- Reason Key CommandsДокумент6 страницReason Key CommandsVijay KumarОценок пока нет
- Cryogenics Handbook PDFДокумент227 страницCryogenics Handbook PDFmangyanОценок пока нет
- SavcaEugeniu (CV) byДокумент4 страницыSavcaEugeniu (CV) bySavcaОценок пока нет
- PR 1-2Документ7 страницPR 1-2mech bhabhaОценок пока нет
- CND - Clinical Round ChecklistДокумент2 страницыCND - Clinical Round ChecklistMona Ismail AlsomaliОценок пока нет
- Demineralization Mechanism and Influence of Parameters On High Ash Indian Coal by Chemical Leaching of Acid and Alkali SolutionДокумент1 страницаDemineralization Mechanism and Influence of Parameters On High Ash Indian Coal by Chemical Leaching of Acid and Alkali SolutionSushanta Kumar BeheraОценок пока нет
- 01 40 00 - Quality RequirementsДокумент27 страниц01 40 00 - Quality RequirementsshauhramОценок пока нет
- 33R 15Документ10 страниц33R 15Ingenieria Ec100% (5)
- 04 Rociador Tyco K11.2 SRДокумент6 страниц04 Rociador Tyco K11.2 SRRuben Saucedo JacomeОценок пока нет
- Safety Is Your Top Priority: Explosion-Proof LED LightingДокумент62 страницыSafety Is Your Top Priority: Explosion-Proof LED LightingPhi LongОценок пока нет
- Torsion MEДокумент24 страницыTorsion MEmohamed.hassan031Оценок пока нет
- D Praveen Kumar ChaubeyДокумент2 страницыD Praveen Kumar ChaubeyyouvsyouОценок пока нет
- Safety in The Kitchen - 1Документ36 страницSafety in The Kitchen - 1Roxanne OquendoОценок пока нет
- Clevo d900c Sager Np9260 Np9261Документ100 страницClevo d900c Sager Np9260 Np9261Doru RazvanОценок пока нет
- Formulation of Immediate Release Dosage Form of Ranitidine HCL Tabletsusing HPMC and Starch Acetate Film FormerДокумент11 страницFormulation of Immediate Release Dosage Form of Ranitidine HCL Tabletsusing HPMC and Starch Acetate Film Formersunaina agarwalОценок пока нет
- f77 f55 User ManualДокумент36 страницf77 f55 User ManualGabi GabrielОценок пока нет
- Catalogo CMCДокумент145 страницCatalogo CMCalyboscanОценок пока нет