Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CHECKMATE User Manual
Загружено:
brahm2009Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHECKMATE User Manual
Загружено:
brahm2009Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
CheckMATE
Strategic Planning Software
User Manual (Full)
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -1-
WELCOME ..................................................................................................... 4
FEATURES..................................................................................................... 4
INTUITIVE INTERFACE ...................................................................................................... 4
NETWORK APPLICATION .................................................................................................. 4
ADMINISTRATOR INTERFACE............................................................................................ 4
COMPREHENSIVE REPORTS .............................................................................................. 4
BENEFITS OF STRATEGIC PLANNING............................................................ 5
REASONS WHY SOME ORGANIZATIONS DO NO STRATEGIC PLANNING ........ 5
PITFALLS IN DOING STRATEGIC PLANNING................................................. 6
STEPS IN THE CHECKMATE STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCESS ....................... 6
I. STEP 1 - DEVELOP A VISION AND MISSION STATEMENT .............................................. 7
II. STEP 2 - PERFORM EXTERNAL AUDIT ......................................................................... 8
III. STEP 3 - PERFORM INTERNAL AUDIT ........................................................................ 9
IV. STEP 4 - ESTABLISH OBJECTIVES .............................................................................. 9
V. STEP 5 - ESTABLISH STRATEGIES ............................................................................. 10
VI. STEP 6 - IMPLEMENT STRATEGIES ........................................................................... 11
VII. STEP 7 - EVALUATE STRATEGIES ........................................................................... 11
CONCLUSION .................................................................................................................. 11
GETTING STARTED ..................................................................................... 12
INSTALLATION................................................................................................................ 12
Network Setup ............................................................................................................... 12
Single-User Setup ........................................................................................................... 14
LOGIN INSTRUCTIONS..................................................................................................... 14
ADD A NEW USER .......................................................................................................... 14
DELETE A USER .............................................................................................................. 15
EDIT USER PROPERTIES .................................................................................................. 15
RESET USER PASSWORD ................................................................................................. 16
CHOOSE USER STATUS ................................................................................................... 16
SET "REPORTS ENABLED" OPTION ................................................................................. 16
SET "NOTIFY FOR RANKINGS" OPTION........................................................................... 16
START A NEW STRATEGIC PLAN .................................................................................... 17
OPEN A STRATEGIC PLAN ............................................................................................... 17
COMPILE A STRATEGIC PLAN ..................................................................... 18
CHECKMATE NAVIGATION........................................................................................... 18
VISION STATEMENT ....................................................................................................... 18
MISSION STATEMENT ..................................................................................................... 19
INTERNAL AUDIT ........................................................................................................... 20
EXTERNAL AUDIT .......................................................................................................... 21
OBJECTIVES .................................................................................................................... 22
IE ANALYSIS .................................................................................................................. 23
SPACE MATRIX ............................................................................................................ 25
GRAND MATRIX .......................................................................................................... 28
TOWS MATRIX ............................................................................................................. 30
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -2-
REFINE STRATEGIES ....................................................................................................... 31
SELECT STRATEGIES....................................................................................................... 32
ADMINISTRATIVE TOOLS ........................................................................... 33
SECURITY INTERFACE .................................................................................................... 33
ADMINISTRATOR INTERFACE.......................................................................................... 34
Review User Entered Data ....................................................................................... 35
Delete Duplicate Entries........................................................................................... 35
Send data back to users .......................................................................................... 35
COMPLETE STRATEGIC PLAN INTERFACE ....................................................................... 38
Review User Entered Data ....................................................................................... 38
Rank the Data ........................................................................................................... 38
CHECKMATE EDITOR ................................................................................................... 41
Create a New Report ................................................................................................ 42
Open an Existing Report .......................................................................................... 42
Save A Report ........................................................................................................... 42
Print A Report ........................................................................................................... 42
CHECKMATE EDITOR TOOLBAR ................................................................................... 45
CHECKMATE REPORTS ................................................................................................. 46
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -3-
CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software
Welcome
A Strategic Plan is a document that reveals an organization's vision, mission,
objectives, and strategies for the future as well as resources needed for successful
implementation. The CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software has been used for
strategic planning in hundreds of organizations and was developed by Dr. Fred
David, author of the best selling book Strategic Management published by Prentice
Hall and has assisted hundreds of organizations in doing strategic planning. As
indicated on the CheckMATE website (http://www.checkmateplan.com/), Dr. David's
popular strategic management book is published in six different languages and is
widely used for strategic planning worldwide. The book can be ordered online at
Barnes & Noble. The book is used at more than 400 colleges and universities, so
perhaps is in a college bookstore near you.
A Strategic Plan is not something to nail together in slap-dash fashion by
sitting around a conference table. Many organizations unfortunately rely too heavily
on emotion, politics, opinion, subjectivity, and intuition in formulating strategies,
rather than conducting some research, collecting some facts and information, and
performing some analyses. The penalty for pursuing the wrong strategies can be
disastrous, so research and analysis is needed to formulate strategies effectively.
The CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software is an excellent tool for assimilating your
managers' research, analysis, opinions, and knowledge.
Features
Intuitive Interface
CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software intuitive interface has been designed to be
easy to use. With in-program instruction and a complete help file, anyone can
complete a Strategic Plan using CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software.
Network Application
CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software can be run as a shared network application.
The software is designed to run on an unlimited number of computers with one
shared database. CheckMATE is designed as a 2-Tier Application securing a flawless
connection between the application and the data.
Administrator Interface
CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software includes an administrator interface, which
enables a lead person to administer all of the data that is entered by the users. This
interface allows the administrator to analyze, clean, and prepare data for the final
Strategic Plan.
Comprehensive Reports
CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software includes a comprehensive set of reports to
display the input data and resultant documents. These reports are used for data
analysis and compilation of the final Strategic Plan.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -4-
Benefits of Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is a process by which an organization may turn empty dreams into
achievements. People and organizations that plan ahead are much more likely to
become what they want to become than those who do not plan at all. A good
manager plans and controls the plans, while a bad manager never plans and then
tries to control people. Without a Strategic Plan, an organization is like a ship without
a rudder. Strategic planning provides direction and purpose. When employees are
given the opportunity to participate in strategic planning, they become more
motivated and committed to the organization. They understand more fully what the
organization is trying to accomplish and why. Those who implement the plan must
feel it is their plan.
Constituencies of any organization expect that entity to have a clear Strategic Plan.
Constituency groups include employees, managers, creditors, staff, potential
acquirers, suppliers, and others. Any or all of these groups may ask, "What is the
plan" and expect a good answer.
Strategic planning may yield the following benefits for your organization:
Enable the organization to be prepared for internal and external changes.
Enable the organization to influence, initiate, anticipate, and be proactive,
rather than simply reacting to events as they occur.
Enable the organization to achieve maximum effect from a given effort.
Enable the organization to identify, prioritize, and exploit opportunities.
Enable more effective allocation of time and resources.
Creates a framework for internal communication among personnel.
Encourages forward thinking and a favorable attitude towards change.
Provides discipline and formality to managing a business.
Enable the organization to obtain the resources needed and carry out tasks in
the most efficient manner possible.
Enable the organization to conserve its own resources and be seen as an
effective, useful entity.
Enable the organization to identify the who, what, when, where, and why
operational details needed to achieve desired objectives.
Enable the organization to assess whether the effort, costs, and implications
associated with achieving desired objectives are warranted.
Enable the organization to avoid the trap of working hard but achieving little.
Enable the organization to obtain and keep accreditation, certification, or
licenses.
Reasons Why Some Organizations Do No Strategic Planning
Unfortunately, some organizations do no strategic planning, for some of the following
reasons:
No Rewards - There may be few or no rewards for engaging in strategic
planning or achieving objectives.
Fire Fighting - Managers may be so deeply embroiled in crisis resolution and
fire fighting that no time remains for planning.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -5-
Waste of Time - Managers may see planning as a waste of time since no
marketable product is produced. Time spent on planning actually is an
investment.
Lack of Effort - Managers may not want to put forth the effort needed to
gather and assimilate information needed to formulate a plan.
Content With Success - Managers may feel there is no need to plan because
things are fine as they stand. However, success today is no guarantee for
success tomorrow.
Fear of Failure - By not having a clear Strategic Plan, there are no clear
objectives to evaluate success or failure.
Overconfidence - As top managers amass experience, they may rely less on
formal planning. Being overconfident and overvaluing one's experience can
bring demise. Forethought is rarely wasted and is often the mark of
professionalism.
Pitfalls In Doing Strategic Planning
In doing strategic planning, the following pitfalls should be avoided:
Too hastily moving from vision/mission development to strategy formulation.
Failing to communicate the plan to constituencies who continue working in the
dark.
Top management making too many intuitive decisions that conflict with the
formal plan.
Top management not actively supporting the strategic planning process.
Failing to use plans as a standard for measuring performance.
Delegating planning to a "planner" rather than involving all managers.
Failing to create a collaborative climate supportive of change.
Viewing planning to be unnecessary or unimportant.
Rushing through planning. The stakes are too high to plan haphazardly.
Being so formal in planning that flexibility and creativity are stifled.
Steps in the CheckMATE Strategic Planning Process
As listed below, there are logical, distinct steps in the strategic planning process.
The steps listed coincide with the steps to be followed in using the CheckMATE
Strategic Planning Software. Planners should complete one step before moving to
the next, even though they may occasionally need to go back and make changes to
earlier steps. The seven steps listed below represent a systematic, rational, objective
approach for developing a Strategic Plan, rather than relying upon politics, emotions,
opinions, and subjectivity to determine a organization's future:
I. Develop a Vision and Mission Statement
II. Perform External Audit
III. Perform Internal Audit
IV. Establish Objectives
V. Establish Strategies
VI. Implement Strategies
VII. Evaluate Strategies
VIII. Conclusion
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -6-
The CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software focuses on the first five steps because
implementation and evaluation of strategies involve detailed financial statement
analysis and projection, resource allocation, budgets, and personnel decisions which
vary considerably among companies.
I. Step 1 - Develop a Vision and Mission Statement
Step 1 in strategic planning and this software is to "Develop a Vision and Mission
Statement." These are enduring statements of purpose that distinguish one
organization from other similar enterprises. Sometimes called a creed statement or
statement of purpose, vision and mission statements are important to insure
unanimity of purpose, arouse positive feelings about the organization, provide
direction, provide a basis for objectives and strategies, serve as a focal point, and
resolve divergent views among managers. In every organization, there are
divergent views regarding direction and strategies. Discussing issues in developing a
vision and mission statement can help resolve divergent views and pave the way for
consensus on more specific strategies and objectives.
Vision Statement
A "vision statement" answers the question "What Do We Want To Become?"
Developing a vision statement is often considered the first step in strategic planning,
preceding even development of a mission statement. It is especially important for
managers to agree upon the basic vision for which the organization strives to achieve
long term. A clear vision provides the foundation for development of a
comprehensive mission statement. The vision statement should be short, preferably
one sentence. All managers should have input into developing the statement.
Vision defines the organization's sense of future direction, its dream for an ideal
state, and why it should be doing what it is doing. The vision should be meaningful
enough to instigate and inspire action and achievement among employees. All
actions of the organization should be directed toward this vision.
The vision statement is a concise declaration of the direction that an organization is
planning to take into the future.
Using the CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software, write a vision statement for your
firm. If you are part of a team using CheckMATE, then you will have the opportunity
to see and assess the vision statements proposed by the other members of the
team. In this manner, the team, led by an administrator, can then decide upon the
vision statement for the firm.
Mission Statement
The "mission statement" should define the organization in a concise and clear
manner. A lay reader, after viewing the statement, should have a vivid picture of
what is unique about the organization and should be inspired to support the
organization. Further, every program and activity in the organization should tie to its
mission.
A mission statement should be less than 200 words. The statement needs to be
longer than a phrase or sentence, but not a two page document. A mission
statement also should not be too specific. Do not include $'s, %'s, #'s, goals, or
strategies. In a Strategic Plan, objectives, and strategies should be specific, but not
the mission statement. Too much detail in a mission statement can alienate
managers and stifle creativity. A mission statement should be inspiring. The reader
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -7-
should want to become a part of the organization after reading the mission
statement. A mission statement should be enduring though not cast in stone. The
statement should project a sense of worth, intent, and shared expectations.
The following nine components should be included in writing a mission statement:
1. Customers (specify who is target market)
2. Products/Services (specify products and services provided to customers)
3. Geographic Markets (specify where firm seeks customers)
4. Technology (specify technological acumen)
5. Concern for Survival/Growth/Profits (specify concern for financial
soundness)
6. Philosophy (specify values, ethics, beliefs)
7. Public Image (specify contributions being made to community)
8. Employees (specify importance of personnel)
9. Distinctive Competence (specify what the firm does especially well)
Using the CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software, write a mission statement for
your firm. If you are part of a team using CheckMATE, then you will have the
opportunity to see and assess the mission statements proposed by the other
members of the team. In this manner, the team, led by an administrator, can then
decide upon the mission statement for the firm.
Back To Top
II. Step 2 - Perform External Audit
Step 2 in strategic planning and this software is to "Perform an External Audit." This
activity involves identifying and evaluating opportunities and threats facing the
organization in five key focus areas:
1. Economic Conditions and Facts
2. Social, Cultural, Demographic Trends and Facts
3. Political, Legal, Governmental Factors
4. Technological Changes
5. Competition
External opportunities and threats in these areas include such factors as economic
conditions, population shifts, advances in computers, competition from other medical
firms, government regulation of medical practices, or malpractice lawsuits. Any
factors beyond control of the organization itself, yet that significantly affect the
organization operations and delivery of services, should be considered in the external
audit.
An external audit is important in developing a Strategic Plan because changes in the
focus areas translate into changes in consumer demand for the firm's products and
services. This is important information since strategies must take advantage of
external opportunities and must avoid the impact of external threats. The nature of
opportunities and threats change rapidly because the world changes, customers
change, and competitors change. This all means that demand for the firm's products
and services can change, so the firm should continually monitor external trends and
events in order to pursue effective strategies. Performing an external audit is vital
for staying abreast of changing conditions that affect the organization.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -8-
In performing an external audit, review information in all focus areas, including facts,
trends, statistics, and projections that affect demand of the organization's products
and services. Sources of information could include the Internet, trade publications,
chambers of commerce, government documents, magazines, newspapers,
constituencies, etc.
The users of CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software should independently develop a
list of the most important external opportunities and threats facing the firm. Be
careful not to list strategies as opportunities. Also, be specific when stating factors;
include %, $, and #'s whenever possible.
Back To Top
III. Step 3 - Perform Internal Audit
Step 3 in strategic planning and this software is to "Perform an Internal Audit." The
internal audit is very similar to the external audit except the focus in on internal
factors, that is, areas the business can control such as its own budget, hiring, and
policies. The internal audit is not an accounting audit, but rather an assessment of
all internal activities. Performing an internal audit requires the organization to
determine its own strengths and weaknesses in terms of its operations, products,
facilities, staff, policies, marketing, equipment, and all other internal areas. An
assessment of strengths and weaknesses is needed before objectives or strategies
can be established.
An internal audit is important in strategic planning because strategies must capitalize
on strengths and must improve upon weaknesses. A firm's strengths and
weaknesses evolve and change. Relative deficiency or superiority is important
strategic information. Comparisons with competitors represent strengths and
weaknesses and can change rapidly.
The users of CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software should be candid throughout
the planning process but especially during the internal audit. In performing an
internal audit, the administrator should if possible gather and distribute to
CheckMATE users, ahead of time, relevant internal information including
benchmarks, performance data, financial statements, exit interview data,
comparisons over time, etc.
Users of CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software should independently develop a list
of the most important strengths and weaknesses facing the firm. Be as specific as
possible in stating each strength and weakness. Include facts, figures, ratios,
numbers, and percentages - anything that moves decision making from the realm of
mere opinion.
Back To Top
IV. Step 4 - Establish Objectives
Step 4 in strategic planning and this software is to "Establish Objectives." Objectives
are specific results an organization seeks to achieve in pursuing its basic mission.
Objectives are specific targets designed to achieve particular strategies. Objectives
are specific, quantifiable, and time-bound statements of a desired accomplishment or
result. They should be measurable and aggressive but attainable. Objectives need to
be challenging, understandable, clear, reasonable, and quantitative, specify a time
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems -9-
element, prioritized, and consistent across departments. Objectives should be easily
understood and should clearly state the specific results that the organization seeks to
accomplish. The real art of setting objectives is to create a challenging but
achievable target. The best objectives are those that stretch the capacities of people
and programs but are, nonetheless, possible. This not only results in genuine
improvement in products and services but also builds employee pride and
confidence. Impossible performance targets, on the other hand, discourage initiative
and stifle innovation.
It is hard to imagine an organization or individual being successful without having
clear objectives. Objectives can be compared to a compass by which a ship
navigates. A compass bearing is firm, but in actual navigation, a ship may veer off
its course for many miles. Without a compass, a ship would never find its port.
Objectives are important in strategic planning because they provide direction and
purpose. They establish priorities, allow coordination, reduce uncertainty, aid in
evaluation, stimulate exertion, minimize conflicts, are used to allocate resources, and
to design jobs. Objectives improve manager and employee motivation and
productivity and inform customers of how well the firm is meeting the needs of the
public. The development of objectives aids decision-making and accountability. For
example as an aid in evaluation, it is beneficial for managers to know up front what
the objective or expectation is for the year.
The users of CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software should identify and list specific
objectives that the firm should strive to achieve.
Back To Top
V. Step 5 - Establish Strategies
Step 5 in strategic planning and this software is to "Establish Strategies." Strategies
are not something to nail together in slap-dash fashion by sitting around a
conference table. Many organizations unfortunately rely too heavily on emotion,
politics, opinion, subjectivity, and intuition in formulating strategies, rather than
conducting some research, collecting some facts and information, and performing
some analyses. The penalty for pursuing the wrong strategies can be disastrous, so
research and analysis is needed to formulate strategies effectively. Use information
gathered in the external and internal assessment.
Strategies are derived from an organization's underlying vision, mission, external
opportunities/threats, internal strengths/weaknesses, and objectives. The
organization should use its strengths to capitalize on opportunities and improve upon
weaknesses and avoid threats. There are four especially useful strategic planning
tools, which the CheckMATE software incorporates - SPACE Matrix, IE Matrix, GRAND
Matrix, and TOWS Matrix. These matrices use the important external and internal
factors that you listed earlier in the CheckMATE program.
The users of CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software should develop a SPACE Matrix,
IE Matrix, GRAND Matrix, and TOWS Matrix. Users should also use the "Refine
Strategies" section in the program to provide detail regarding the general strategies
recommended for your organization based on your input and use the "Select
Strategies" section of the program to select the best strategies for your firm.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 10 -
Back To Top
VI. Step 6 - Implement Strategies
Step 6 in strategic planning is to Implement Strategies. Implementing strategies is
much more difficult than formulating strategies because implementing involves
motivating everyone to execute and perform. Vince Lombardi, the legendary coach
of the Green Bay Packers, once said "The best game in the world never blocked or
tackled anyone." Of course he was saying you can formulate the best strategy
possible, but that does not mean it will result in success. It must be implemented
well. The greatest strategy is doomed if implemented badly.
When Dwight Eisenhower took office, former president Harry Truman said "Poor Ike;
when he was a general, he gave an order and it was carried out. Now, he's going to
sit in that office and give an order and not a damn thing is going to happen."
Truman of course was saying that unlike the military, managers and employees in
organizations today do not (may not) execute on demand. They are much more
likely to execute if they have participated in establishing the organization's mission,
objectives, and strategies. Managers need to be fully involved and informed about
the organization's mission, objectives, and strategies, and need to participate, to the
extent possible, in developing a clear Strategic Plan. A basic tenet of the CheckMATE
Strategic Planning Software is to "plan with people, not for people."
Back To Top
VII. Step 7 - Evaluate Strategies
Step 7 in strategic planning is to "Evaluate Strategies." Strategy evaluation is critical
for assuring that objectives are being achieved. Even the best formulated and
implemented strategies become obsolete as a firm's external and internal
environments change. Top management desperately needs to know when strategies
are not working well, yet no one likes to be evaluated too closely.
Evaluating strategies involves three activities:
1. Review underlying bases of strategy
2. Measure performance and make comparisons
3. Take corrective actions.
Strategy evaluation is essential for all organizations. Strategy evaluation activities
should be widely understood and supported, should trigger a review of
mission/objectives/strategies, should involve all managers, and should not be
overbearing. Strategy evaluation should be economical and meaningful, should
provide a true picture, should provide timely information, should foster mutual trust,
should be simple, and should consist of three activities.
Back To Top
Conclusion
Rudin's Law says "When a crisis forces choosing among alternatives, most people will
choose the worst possible one." A primary purpose of strategic planning is to avoid a
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 11 -
crisis. Discuss and establish strategies ahead of time thus being proactive. One of
the worst things a top manager can do is develop strategies himself or herself and
then present them to operating managers to execute. Ownership of strategies by
the people who have to execute them is a key to success. Ownership comes through
participation. Involve as many managers as possible in doing strategic planning.
Plan with people, not for people.
Remember the seven steps in strategic planning:
Step 1 - Develop Vision and Mission Statement
Step 2 - Perform External Audit
Step 3 - Perform Internal Audit
Step 4 - Establish Objectives
Step 5 - Establish Strategies
Step 6 - Implement Strategies
Step 7 - Evaluate Strategies
Strategic planning can yield great people and financial benefits for any business.
Businesses that plan ahead are much more likely to become what they want to
become than those who do not plan at all. A good manager "...plans and controls
the plans, while a bad manager never plans and then tries to control people."
The CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software can enable any organization to
effectively formulate a clear Strategic Plan. For technical support in using this
software you may email checkmate@frippdata.com. For conceptual and sales
information, you may email strategy29@aol.com. Be reminded that CheckMATE
Strategic Planning Software is fully copyrighted and owned by Strategic Planning
Systems which may be contacted at P.O Box 13065, Florence, South Carolina, 29504
or by phone at (843) 669-6960 or fax at (843) 629-1831.
Back To Top
Getting Started
Installation
Network Setup
Setup the CheckMATE Environment - To setup the CheckMATE Environment for a
network application, a couple of thing must be in place. The first thing you must
have is a network server or desktop computer that all users can access over the
network. This does not need to be a dedicated server, as CheckMATE does not use
much space or many resources. This can even be the machine of one of the users,
preferably the Administrator. Here are the steps to setup the network
server/desktop computer:
1. Create a folder on the hard drive just for CheckMATE. (Example:
C:\CheckMATE)
2. Share this folder out for the users to access. To do this:
a. Right-Click on the folder and choose "Sharing"
b. Go to the "Sharing" tab if it is not already active and choose "Shared
As:"
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 12 -
c. Type "CheckMATE$" in the "Share Name:" text box.
d. Click "Permissions." The default permissions for this folder should be
"Everyone Full Control." This is fine, but can be changed if your
network security requires it.
3. Install CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software into the new folder that you
created. To do this:
a. Place the CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software in your CD-ROM
drive.
b. Right-Click on "My Computer"
c. Find your CD-ROM drive (i.e. D:\) and double-click
d. Find "cm_setup.exe," double-click, and follow the on-screen
instructions.
NOTE: When you get to the step to choose the install directory, STOP.
Here is where you will specify the new folder you created. (Example:
C:\CheckMATE). Then, continue with the install.
4. VERY IMPORTANT! You must now Map the new folder to each user's
computers INCLUDING THE ONE YOU INSTALLED THE SOFTWARE ON. To do
this:
a. Right-Click on "My Computer" and choose "Explore"
b. Choose "Tools" on the menu bar and then choose "Map Network
Drive"
c. Choose a "Drive:" letter. NOTE: The drive letter MUST be the same
on all of the user's computers INCLUDING THE ONE YOU INSTALLED
THE SOFTWARE ON. Choose a drive letter that is not being used and
that is not likely to be use for any other network applications.
(Example: X:\)
d. Type the path to the folder that you shared out earlier. This path
should look like: \\[computer name]\folder. The computer name is
the name of the computer that you installed the software on and the
folder is the one that you shared out earlier. (Example:
\\ThisComputer\CheckMATE$)
e. Leave "Connect As" blank.
f. Check the "Reconnect at Logon" checkbox and click OK.
5. Create a shortcut on each of the user's computers INCLUDING THE ONE THAT
YOU INSTALLED THE SOFTWARE ON. NOTE: You must first delete the default
shortcut on the desktop of the computer you installed the software. To create
a new shortcut:
a. Right-Click on "My Computer" and choose "Explore"
b. Navigate to the shared folder via the MAPPED DRIVE. (Example: X:\)
c. Now find the file called "CheckMATE.EXE". It is in the root of the
mapped drive. (Example: X:\CheckMATE.EXE)
d. Right-Click on this file and choose "Send To" now choose "Desktop
(Create Shortcut)"
6. Start CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software by double-clicking the new icon
on your desktop called CheckMATE.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 13 -
Single-User Setup
The Single-User Version of CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software is much easier to
setup. There are only two steps and you are on your way.
1. Install CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software into the new folder that you
created. To do this:
a. Place the CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software in your CD-ROM
drive.
b. Right-Click on My Computer
c. Find your CD-ROM drive (i.e. D:\) and double-click
d. Find cm_setup.exe, double-click, and follow the on-screen
instructions.
NOTE: The default install directory is acceptable but you may change it if
you would like.
2. Start CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software by double-clicking the icon on
your desktop called CheckMATE.
Login Instructions
To Login to CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software:
1. Start CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software.
2. Enter your username and password.
3. Click OK or press Enter.
Add a New User
To Add a New User:
1. Start CheckMATE and choose Tools -> Security on the menu.
2. Click the Add User button on the Security Administrator interface.
3. Complete the form with the new user's information. NOTE: Fields marked
with * are required.
4. Choose Administrator or End User.
5. Click Save and then Close.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 14 -
Delete a User
To Delete a User:
1. Start CheckMATE and choose Tools -> Security on the menu.
2. Select user by clicking on the users name.
3. Click the Delete User button on the Security Administrator interface.
4. You will be prompted to confirm your choice to delete a user, press Yes to
delete or No to cancel.
NOTE: If you delete a user, all of that user's entries into the database will be also
deleted. Please be careful when deleting a user.
Edit User Properties
To Edit User Properties:
1. Start CheckMATE and choose Tools -> Security on the menu.
2. Select User to edit by either Double-Clicking on the name of the user or
highlighting the user's name and Clicking Properties.
Once in the User Properties form, you may:
Reset the user's password
Change the user's status
Select/Unselect "Notify for Rankings"
3. Click Save and Close
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 15 -
Reset User Password
To Edit User Properties:
1. Press the Reset Password button.
2. Enter a new password.
3. Confirm the new password.
4. Click Save.
5. Click Save and Close.
Back To Top
Choose User Status
To Choose User Status:
1. Select Administrator or End User.
2. Click Save and Close.
Back To Top
Set "Reports Enabled" Option
To Set "Reports Enabled" Option:
1. Click the "Reports Enabled" Check Box to toggle the status. If the box is
checked, the reports are enabled for the user. If the box is unchecked, the
reports are not enabled for the user.
2. Click Save and Close.
Back To Top
Set "Notify for Rankings" Option
To Set "Reports Enabled" Option:
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 16 -
1. Click the "Notify for Rankings" Check Box to toggle the status. If the box is
checked, the user will be able to rank the final entries. If the box is
unchecked, the user will not be able to rank the final entries.
2. Click Save and Close.
Back To Top
Start a New Strategic Plan
To Start a New Strategic Plan:
1. Start CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software.
2. Click File -> New or press CNTL + N.
NOTE: Starting a new Strategic Plan will clear all entries in the database for the
current user. Once you have started a Strategic Plan, be careful with starting a new
one.
Open a Strategic Plan
To Open a Strategic Plan:
1. Start CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software.
2. Click File -> Open or press CNTL + O.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 17 -
NOTE: Each user can only have one Strategic Plan in progress. When you open a
Strategic Plan, CheckMATE will only open the plan in progress for the user that is
logged in.
Compile A Strategic Plan
CheckMATE Navigation
The navigation in CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software is designed to allow the
user full control of all aspects of the Strategic Plan. It allows the user to navigate
between forms with ease. There is, however, an order to which the plan should be
completed so, at time, some of the menu may not be available. For example:
You must complete the Internal and External Audit before you can complete
the TOWS Matrix.
You must complete the IE Analysis, SPACE Matrix, and GRAND Matrix before
you can complete the Refine Strategies section.
You must complete the TOWS Matrix and the Refine Strategies section before
you can complete the Select Strategies section.
After you have entered data in all of the forms, you may go back at any time to edit
your entries. Use the navigation bar at the top of the application to switch between
forms. NOTE: As you switch between forms, the current form will be saved
automatically for you.
Vision Statement
A "vision statement" answers the question "What Do We Want To Become?"
Developing a vision statement is often considered the first step in strategic planning,
preceding even development of a mission statement. It is especially important for
managers and employees to agree upon the basic vision for which the organization
strives to achieve long term. A clear vision provides the foundation for development
of a comprehensive mission statement. The vision statement should be short,
preferably one sentence. All physicians and administrators should have input into
developing the statement.
To complete the Vision Statement of the Strategic Plan:
1. Choose Vision on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Type a Vision Statement in the text box on the form.
3. Click Save.
Remember, the Vision Statement is just that, a vision. It is a one-sentence
statement about what the company wants to become.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 18 -
Mission Statement
The "mission statement" should define the organization in a concise and clear
manner. A lay reader, after viewing the statement, should have a vivid picture of
what is unique about the organization and should be inspired to support the
organization. Further, every program and activity in the organization should tie to its
mission.
To complete the Mission Statement of the Strategic Plan:
1. Choose Mission on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Type one sentence in each of the tabs on the form. Each tab has a topic and
poses a question to be answered. (Fig. 1)
3. Click Compile Mission. In this section, you can combine your entries into a
comprehensive Mission Statement. Add or delete information for a complete
Mission Statement. (Fig. 2)
4. Click Save Mission and Close.
5. Click Save.
The mission is part of the organization's identity. It is the ultimate rationale for the
existence of the firm and its operations.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 19 -
Figure 1
Back to Top
Figure 2
Back to Top
Internal Audit
The internal audit is very similar to the external audit except the focus in on internal
factors, that is, areas the business can control such as its own budget, hiring, and
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 20 -
policies. The internal audit is not an accounting audit, but rather an assessment of
all internal activities. Performing an internal audit requires the organization to
determine its own strengths and weaknesses in terms of its marketing,
management, finance, packing, shipping, personal, facilities, equipment, resources,
and all other internal areas. An assessment of strengths and weaknesses is needed
before objectives or strategies can be established.
To complete the Internal Audit:
1. Choose Internal on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Enter at least 10 but no more than 15 internal strengths of your company.
3. Enter at least 10 but no more than 15 internal weaknesses of your company.
4. Click Save.
Remember, participants should independently develop a list of the most important
strengths and weaknesses facing the firm. Be as specific as you can in stating each
factor using #'s, %'s, $s and ratios where possible.
External Audit
The External Audit involves identifying and evaluating opportunities and threats
facing the organization in five key focus areas: 1) Economy 2) Competitors 3)
Technology 4) Social cultural, demographic trends, and 5) Political, legal,
governmental trends. External opportunities and threats in these areas include such
factors as economic conditions, population shifts, and advances in computers, and
competition from other firms, government regulations, or lawsuits. Any factors
beyond control the organization itself, yet that significantly affect the organization
operations and delivery of services, should be considered in the external audit.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 21 -
To complete the External Audit:
1. Choose Internal on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Enter at least 10 but no more than 15 external opportunities of your
company.
3. Enter at least 10 but no more than 15 external threats of your company.
4. Click Save.
Remember, participants should independently develop a list of the most important
external opportunities and threats facing the firm. Be as specific as you can in
stating each factor, using #'s %'s, $'s, and ratios where possible. Do not list
strategies as opportunities.
Objectives
Objectives are important in strategic planning because they provide direction and
purpose. They establish priorities, allow coordination, reduce uncertainty, aid in
evaluation, stimulate exertion, minimize conflicts, are used to allocate resources, and
to design jobs. Objectives improve manager and employee motivation and
productivity and inform customers of how well the firm is meeting the needs of the
public. The development of objectives aids decision-making and accountability. For
example as an aid in evaluation, it is beneficial for managers to know up front what
the objective or expectation is for the year.
To complete the Objectives section of the Strategic Plan:
1. Choose Objs on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Type up to 10 objectives that you feel your firm should strive to achieve.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 22 -
3. Click Save.
IE Analysis
The Internal - External Analysis reveals to managers the type of strategies most
appropriate: Hold and Maintain, Grow and Build, Harvest or Divest. In the IE
Analysis, you will score your firm's Internal and External position against the
competition. Later in the program, the CheckMATE software asks the participant to
elaborate and be more specific on the broad strategies indicated by the IE Matrix.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 23 -
Note: The IE Matrix was developed from the General Electric (GE) Business Screen Matrix. For a
description of the GE Matrix, see Michael Allen, "Diagramming GE's Planning for What's WATT" in
Corporate Planning: Techniques and Applications, eds, R. Allio and M. Pennington (New York: AMACOM,
1979).
Note: The IE Matrix was developed from the General Electric (GE) Business Screen Matrix. For a
description of the GE Matrix, see Michael Allen, "Diagramming GE's Planning for What's WATT" in
Corporate Planning: Techniques and Applications, eds, R. Allio and M. Pennington (New York: AMACOM,
1979).
To complete the IE Analysis:
1. Choose IE Analysis on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 24 -
2. Choose your firm's internal score.
3. Choose your firm's external score.
4. Click Save.
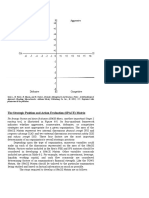
SPACE Matrix
The SPACE (Strategic Position and Action Evaluation) Matrix reveals to the firm the
type of strategies most appropriate to pursue: Aggressive, Conservative, Defensive,
or Conservative. Later in the program, the CheckMATE software asks the participant
to elaborate and be more specific on the broad strategies indicated by the SPACE
Matrix.
Source: H. Rowe, R. Mason, and K. Dickel, Strategic Management and Business Policy: A Methodological
Approach (Reading, Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley Publishing Co. Inc. (c) 1982):155. Reprint with
permission of publisher.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 25 -
Source: H. Rowe, R. Mason, and K. Dickel, Strategic Management and Business Policy: A Methodological
Approach (Reading, Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley Publishing Co. Inc. (c) 1982):155. Reprint with
permission of publisher.
To complete the SPACE Matrix:
1. Choose SPACE on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Rate your firm's Financial Strength.
3. Rate your firm's Competitive Advantage.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 26 -
4. Rate your firm's Industry Strength.
5. Rate your firm's Environmental Stability.
6. Rate your firm's Environmental Stability.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 27 -
GRAND Matrix
Another popular strategic planning tool utilized in the CheckMATE Strategic Planning
Software is the Grand Strategy Matrix. Strategies possibly suggested by the GRAND
include geographic expansion, market penetration, diversification, forward
integration, and others. Later in the program, the CheckMATE software asks the
participant to elaborate and be more specific on the broad strategies indicated by the
GRAND Matrix.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 28 -
Source: Adapted from Roland Christensen, Norman Berg, and Malcom Salter, Policy Formulation and
Administration (Homewood, Ill: Richard D. Irwin, 1976): 16-18.
To complete the GRAND Matrix:
1. Choose GRAND on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Rate your firm's Competitive Position in terms of market share, price, product
quality, service, and finances.
3. Rate your Industry's Growth Rate in annual revenues.
4. Click Save.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 29 -
TOWS Matrix
The TOWS (Threats-Opportunities-Weaknesses-Strengths) Matrix is used by the
CheckMATE software in formulating strategies. The TOWS generates specific
strategies that should be considered. The TOWS Matrix is the most widely used
strategic planning matrix among organizations. To develop a TOWS Matrix, consider
the firm's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that you earlier listed in
your internal and external audits. Then, list specific strategies that would benefit the
firm in light of those underlying factors. For example, SO Strategies should use the
firm's strengths (S) to capitalize on opportunities (O).
Source: Adapted from Heinz Weihrich, "The TOWS Matrix: A Tool for Situational Analysis," Long Range
Planning 15, no. 2 (April 1982): 61.
To complete the TOWS Matrix:
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 30 -
1. Choose TOWS on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Develop and list some SO Strategies.
3. Develop and list some WO Strategies.
4. Develop and list some ST Strategies.
5. Develop and list some WT Strategies.
6. Click Save.
Refine Strategies
In the "Refine Strategies" section of CheckMATE you will see a list of suggested types
of strategies base on your input on the matrices. This list is just suggested and does
not mean that these are the only strategies that your firm may want to pursue and
your firm may want to pursue strategies that are not on this list.
To complete the Refine Strategies section of the Strategic Plan:
1. Choose Refine on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Choose suggested strategy to refine. (Fig. 1)
3. Double-Click any/each of the listed strategies to enter text.
4. Enter one or two sentences of detail for each strategy that you feel may be
implemented. (Fig. 2)
5. Click Save and Close.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 31 -
Figure 1
Back to Top
Figure 2
Back to Top
Select Strategies
To complete the Select Strategies section of the strategic plan:
1. Choose Select on the CheckMATE Navigation bar.
2. Double-Click or select and click "Select" the strategies you feel are the most
important and feasible to your firm. Only choose those that you feel can be
implemented and most beneficial to your firm.
3. To select all strategies, click "Select All".
4. To remove any of the strategies from the selected list, Double-Click or select
and click "Select" the strategy you wish to remove.
5. To remove all strategies, click "Remove All".
6. Click Save.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 32 -
The strategies that you select in this section will be compiled with other strategies
selected by all users. The administrator will then evaluate these and your firm will
use this information to determine which, if any, of the strategies will be pursued.
Administrative Tools
Security Interface
The full version of Security Interface will only be available for use with a Network
License. With an individual license, you may only change the administrator
username or password.
This Security Interface utility is designed for the administrator to add, delete, edit,
and maintain the users of CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software. With this utility
you can:
1. Add a new user to the CheckMATE database.
2. Delete a user from the CheckMATE database.
3. Edit users information, permissions, and password.
To open the Security Administrator:
1. Start CheckMATE and log in.
2. Choose Tools -> Security from the menu. (Fig. 1)
3. Select user by highlighting the name. (Fig. 2)
4. Select task to complete.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 33 -
Figure 1
Back to Top
Figure 2
Back to Top
Administrator Interface
The Administrator Interface utility is designed for the administrator to manipulate the
data entered by the users into CheckMATE Strategic Planning Software. With this
utility you can:
1. Review data entered by users into the CheckMATE database.
2. Delete duplicate entries from the CheckMATE database.
3. Send data back to user's to rank.
4. Invoke the CheckMATE Editor to compile administrator recommendations.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 34 -
To open the Administrator Interface:
1. Start CheckMATE and log in.
2. Choose Tools -> Administrator from the menu. (Fig. 1)
3. Select task to complete using the buttons on the tool bar. (Fig. 2)
Review User Entered Data
To Review User Entered Data:
1. Press the Drop-Down arrow to the right of the button.
2. Select the section that you want to review. (Fig. 3)
3. Choose the user that you wish to view. You may also choose "All Items..."
where available. (Fig. 4)
4. The information that you have selected to view will be shown in the box (es)
to the right of the user list.
5. You may also use the and buttons to switch between users. By
pressing the button, you will get the previous user's information and by
pressing the button you will get the next user's information.
Delete Duplicate Entries
To Delete Duplicate Entries:
1. Press the Drop-Down arrow to the right of the button.
2. Select the section that you want to review. (Fig. 3)
3. Choose the user that you wish to view. You may also choose "All Items..."
where available. (Fig. 4)
4. The information that you have selected to view will be shown in the box (es)
to the right of the user list.
5. Highlight the data that you want to delete by clicking on the entry.
6. Click the button the delete the entry. Your deletion will take place
immediately.
NOTE: Not all sections are enabled for deletion because some are read only. If you
cannot highlight an item, it is there for review only. This is because some of the
information is numeric averages and have been calculated previously.
Send data back to users
This option is used to enable the user's to "complete" the Strategic Plan. With this
option on, the users gain access to the "Complete Planning" menu item. In this
section, the users will be able to rank all of the data from each of the users in order
of importance to the firm.
To Send Data Back to users:
1. Click the "Finished - Send to Users" Check Box. If this box is checked, the
users will have access to the "Complete Planning" section of CheckMATE. If
this box is unchecked, the users will not have access to the "Complete
Planning" section of CheckMATE. (Fig. 5)
2. Click the button to save the settings.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 35 -
3. Notify the users that they now have access to the "Complete Planning"
section of CheckMATE.
Figure 1
Back to Top
Figure 2
Back to Top
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 36 -
Figure 3
Back to Top
Figure 4
Back to Top
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 37 -
Figure 5
Back to Top
Complete Strategic Plan Interface
The Complete Strategic Plan utility is designed to let the users rank all of the entries
in each section. With this utility, the users will see all of the entries and will rank
and save them in order of importance to the firm. With this utility the users will:
1. View all of the data entered, ordered by section.
2. Rank the data based on importance to the firm.
You must remember the Complete Strategic Plan interface will not be available until
all of the users have completed the entry of data and the administrator has cleaned
and approved the data.
To open the Complete Strategic Plan Interface:
1. Start CheckMATE and log in.
2. Choose File -> Complete Planning from the menu. (Fig. 1)
3. Select the section to rank. (Fig. 2)
Review User Entered Data
To View All Entered Data:
1. Choose the section that you want to review by clicking on the corresponding
button. NOTE: If a selection is too long to fit into the grid, Double-Click the
selection to read the entire statement. (Fig. 3)
Rank the Data
To Rank the Data:
1. Choose the section that you want to rank by clicking on the corresponding
button. NOTE: If a selection is too long to fit into the grid, Double-Click the
selection to read the entire statement. (Fig. 3)
2. Choose the rank for each item in the box to the left of the selection. You may
either type in the number or you may choose the number from the drop down
list. Remember, you must rank your top 10 selections in each section or an
error message will appear. (Fig. 4)
NOTE: Please remember to save before switching to between sections so your
rankings will not be lost.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 38 -
You may also see tips on this interface at any time by pressing the tips button. (Fig.
5) After all of the users have ranked the data, the "Tentative Strategic Plan" report
will become available for viewing.
Figure 1
Back to Top
Figure 2
Back to Top
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 39 -
Figure 3
Back to Top
Figure 4
Back to Top
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 40 -
Figure 5
Back to Top
CheckMATE Editor
The CheckMATE Editor is designed for the administrator to create a final report based
on their recommendations and feeling for the firm. The CheckMATE Editor is a text
editor that creates reports in Rich Text Format (*.rtf). These reports can also be
viewed using Microsoft Word. With the CheckMATE Editor, you may:
1. Create reports in Rich Text Format.
2. Open/Edit any document that is RTF.
3. Print Reports and Documents that are created.
The CheckMATE Editor is not available to all users the user must be listed as an
administrator to have access to this utility. The CheckMATE Editor has all of the
functionality of a basic text editor. You may explore the formatting options by
pressing the buttons on the toolbar.
To open the CheckMATE Editor:
1. Start CheckMATE and log in.
2. Choose Tools -> Administrator from the menu. (Fig. 1)
3. Press the button to invoke the CheckMATE Editor. (Fig. 2)
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 41 -
Once open, you may complete any of the following tasks:
1. Create a New Report
2. Open an Existing Report
3. Save a Report
4. Print a Report
Create a New Report
To Create a New Report:
Click File -> New Report (Ctrl + N) or press the button.
After you create a new report, you will see the file in the editor main window. The
new file is named "NewFile.rtf" but you may save it with any name when you save
the first time. (Fig. 3)
Open an Existing Report
To Open an Existing Report:
Click File -> Open Report (Ctrl + O) or press the button.
After you open an existing report, you will see the file in the editor main window.
(Fig. 4)
Save A Report
To Save A Report:
Click File -> Save (Ctrl + S) or press the button.
You may also do a "Save As..." by clicking File -> Save As...
Print A Report
To Open an Existing Report:
Click File -> Print... (Ctrl + P) or press the button.
You will see a print dialog box appear, choose any options that you may need and
press ok. (Fig. 5)
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 42 -
Figure 1
Back to Top
Figure 2
Back to Top
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 43 -
Figure 3
Back to Top
Figure 4
Back to Top
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 44 -
Figure 5
Back to Top
CheckMATE Editor Toolbar
This tool bar includes the following buttons:
= Create New Report
= Open Existing Report
= Save Report
= Print Report
= Cut Selected Text (Ctrl + X)
= Copy Selected Text (Ctrl + C)
= Paste Selected Text (Ctrl + V)
= Bold
= Italic
= Underline
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 45 -
= Font Selections
= Align Left
= Align Center
= Align Right
CheckMATE Reports
The CheckMATE Reports are a set of static reports compiled from the data entered
by the users. These reports show the data based on which report is chosen.
VISION
The Vision Report shows all of the proposed Vision Statements as entered by each
user.
MISSION
The Mission Report shows all of the proposed Mission Statements as entered by each
user.
STRENGTHS
The Strengths Report shows all of the firm's strengths as entered by each user.
WEAKNESSES
The Weaknesses Report shows all of the firm's weaknesses as entered by each user.
OPPORTUNITIES
The Opportunities Report shows all of the firm's opportunities as entered by each
user.
THREATS
The Threats Report shows all of the firm's threats as entered by each user.
OBJECTIVES
The Objectives Report shows all of the firm's objectives as entered by each user.
TOWS
The Tows Report shows all of the firm's Strength\Opportunity Strategies,
Weakness\Opportunity Strategies, Strength\Threat Strategies, and Weakness\Threat
Strategies as entered by each user.
SELECTED STRATEGIES
The Selected Strategies Report shows all of the strategies that the users have
selected for consideration.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 46 -
TENTATIVE STRATEGIC PLAN
The Tentative Strategic Plan Report shows all of the data entered by the users in
ranked order. This report is separated by section.
NOTE: The "Tentative Strategic Plan" report is only available to network users. This
report shows the compiled data from the users rankings in the "Complete Strategic
Plan" section.
Copyright 2001 2002 Strategic Planning Systems - 47 -
Вам также может понравиться
- Managing Catastrophic Loss of Sensitive Data: A Guide for IT and Security ProfessionalsОт EverandManaging Catastrophic Loss of Sensitive Data: A Guide for IT and Security ProfessionalsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- SAP B1 on Cloud GuideДокумент38 страницSAP B1 on Cloud GuideMarcos Jose AveОценок пока нет
- Pricing and Costing Final Examination Key To CorrectionДокумент8 страницPricing and Costing Final Examination Key To CorrectionSherwin Francis MendozaОценок пока нет
- Master in Managerial Advisory Services: Easy QuestionsДокумент13 страницMaster in Managerial Advisory Services: Easy QuestionsKervin Rey JacksonОценок пока нет
- 02 MavisДокумент41 страница02 MavisSantosh TalariОценок пока нет
- Chapter I Iii Revision 115Документ49 страницChapter I Iii Revision 115Jamie Rose AragonesОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 17-scmДокумент15 страницCHAPTER 17-scmZsisum Meroo1Оценок пока нет
- Long QuizДокумент4 страницыLong QuizJoshua Rey Sapuras0% (1)
- Auditing Business ProcessesДокумент2 страницыAuditing Business ProcessesChristlyn Joy BaralОценок пока нет
- Module 1.a The Accountancy ProfessionДокумент6 страницModule 1.a The Accountancy ProfessionJonathanTipay0% (1)
- Assignment 1Документ2 страницыAssignment 1Betheemae R. MatarloОценок пока нет
- Chap 8 Responsibility AccountingДокумент51 страницаChap 8 Responsibility AccountingXel Joe BahianОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Responsibility Accounting Problems AnswersДокумент5 страниц1.3 Responsibility Accounting Problems AnswersAsnarizah PakinsonОценок пока нет
- Standard Costs and Variance Analysis Mcqs by Hilario TanДокумент18 страницStandard Costs and Variance Analysis Mcqs by Hilario TanAhmadnur JulОценок пока нет
- Setting Standard Costs-Ideal and Practical StandardsДокумент2 страницыSetting Standard Costs-Ideal and Practical StandardsAmmar Ul ArfeenОценок пока нет
- Topic 5. The Basics of Capital BudgetingДокумент10 страницTopic 5. The Basics of Capital BudgetingCerf VintОценок пока нет
- STRATEGIC COST MANAGEMENT: RELEVANT COSTING DECISIONSДокумент6 страницSTRATEGIC COST MANAGEMENT: RELEVANT COSTING DECISIONSMon Ram0% (1)
- The Purchasing/ Accounts Payable/ Cash Disbursement (P/AP/CD) ProcessДокумент17 страницThe Purchasing/ Accounts Payable/ Cash Disbursement (P/AP/CD) ProcessJonah Mark Tabuldan DebomaОценок пока нет
- Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: © 2019 Cengage. All Rights ReservedДокумент45 страницCost-Volume-Profit Analysis: © 2019 Cengage. All Rights ReservedKriz TanОценок пока нет
- Hansen Aise Im Ch16Документ55 страницHansen Aise Im Ch16Daniel NababanОценок пока нет
- Risk Management Strategies for Del Monte PhilippinesДокумент9 страницRisk Management Strategies for Del Monte PhilippinesPricia AbellaОценок пока нет
- The Role of Accounting Information System On Business PerformanceДокумент9 страницThe Role of Accounting Information System On Business Performanceindex PubОценок пока нет
- Chapter Review Guide QuestionsДокумент1 страницаChapter Review Guide QuestionsRick RanteОценок пока нет
- Chapter 27 - Answer PDFДокумент22 страницыChapter 27 - Answer PDFRafael Renz DayaoОценок пока нет
- CMA2011 CatalogДокумент5 страницCMA2011 CatalogDaryl DizonОценок пока нет
- Test Bank Management 8th Edition BatemanДокумент40 страницTest Bank Management 8th Edition BatemanIris DescentОценок пока нет
- Fin Man - Module 3Документ38 страницFin Man - Module 3Francine PrietoОценок пока нет
- Management Advisory ServicesДокумент11 страницManagement Advisory ServicesAnonymous 7m9SLrОценок пока нет
- FM Second AssignmentДокумент3 страницыFM Second AssignmentpushmbaОценок пока нет
- Capital Budgeting Techniques and Project Risk AnalysisДокумент3 страницыCapital Budgeting Techniques and Project Risk AnalysisbalachmalikОценок пока нет
- ABC and Standard CostingДокумент16 страницABC and Standard CostingCarlo QuinlogОценок пока нет
- AE120 - Final Activity 1Документ1 страницаAE120 - Final Activity 1Krystal shaneОценок пока нет
- Auditing in CIS Environment - Auditing Operating Systems and Networks (Final)Документ44 страницыAuditing in CIS Environment - Auditing Operating Systems and Networks (Final)Luisito100% (2)
- Case Study Analysis On CWO GROUP 8Документ10 страницCase Study Analysis On CWO GROUP 8Jonarissa BeltranОценок пока нет
- Strategic Business AnalysisДокумент39 страницStrategic Business AnalysisArman DalisayОценок пока нет
- Responsibility Accounting and Reporting: Multiple ChoiceДокумент23 страницыResponsibility Accounting and Reporting: Multiple ChoiceARISОценок пока нет
- Measures of Central Tendency ProblemsДокумент6 страницMeasures of Central Tendency Problemsgazer beamОценок пока нет
- Finman Midterms Part 1Документ7 страницFinman Midterms Part 1JerichoОценок пока нет
- AC16-602P-REGUNAYAN-COMPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF THE GOVERNMENT, COOPERATIVES, & OTHER NPOsДокумент5 страницAC16-602P-REGUNAYAN-COMPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF THE GOVERNMENT, COOPERATIVES, & OTHER NPOsMarco RegunayanОценок пока нет
- Ia3 IsДокумент3 страницыIa3 IsMary Joy CabilОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 FullДокумент73 страницыChapter 1 FullAnjali Angel ThakurОценок пока нет
- MODULE 6 ExerciseДокумент2 страницыMODULE 6 ExerciseomsfadhlОценок пока нет
- Midterms - 2 - Capital - Budgeting - Techniques - PDF Filename UTF-8''Midterms 2 CapiДокумент17 страницMidterms - 2 - Capital - Budgeting - Techniques - PDF Filename UTF-8''Midterms 2 CapiAirille CarlosОценок пока нет
- Taxation Law Reviewer Highlights Key ConceptsДокумент19 страницTaxation Law Reviewer Highlights Key ConceptsPatricia Blanca SDVRОценок пока нет
- 2.6 Activity Based Costing Abc Activity Based Management AbcДокумент22 страницы2.6 Activity Based Costing Abc Activity Based Management AbcだみОценок пока нет
- Activity Based Costing, Management, and Budgeting - ABC in A Government SettingДокумент9 страницActivity Based Costing, Management, and Budgeting - ABC in A Government Settingelvarg09Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 Expenditure Cycle PDFДокумент19 страницLesson 4 Expenditure Cycle PDFJoshua JunsayОценок пока нет
- Ppsas 27 in Comparison With Ias 41Документ2 страницыPpsas 27 in Comparison With Ias 41Lia SyОценок пока нет
- Part 2 Competencies - Ipcrf 2018-2019Документ11 страницPart 2 Competencies - Ipcrf 2018-2019Faith Clavaton MoralesОценок пока нет
- Receivables ManagementДокумент5 страницReceivables ManagementInocencio TiburcioОценок пока нет
- Solved ProblemsДокумент8 страницSolved Problemsantony1993Оценок пока нет
- Justa Corporation US market analysisДокумент11 страницJusta Corporation US market analysisMohsin Rehman0% (1)
- The IFRS Conceptual Framework Was First Published in 1989 With The Aim of Setting A Theoretical Framework Upon Which The IFRS Standards Are Based OnДокумент4 страницыThe IFRS Conceptual Framework Was First Published in 1989 With The Aim of Setting A Theoretical Framework Upon Which The IFRS Standards Are Based OnFarhan Farook AbdullaОценок пока нет
- Comp 3Документ28 страницComp 3CristineJoyceMalubayIIОценок пока нет
- Guide To Successful Data Loss Prevention Risk Reduction: Part 1Документ16 страницGuide To Successful Data Loss Prevention Risk Reduction: Part 1arunchockanОценок пока нет
- Power Platform Admin and Governance WhitepaperДокумент120 страницPower Platform Admin and Governance WhitepaperGiancarlo Herrera100% (1)
- Peoplesoft Enterprise CRM 8.4 To 9.0 Cumulative Feature OverviewДокумент59 страницPeoplesoft Enterprise CRM 8.4 To 9.0 Cumulative Feature OverviewAnonymous P3sQECwОценок пока нет
- Pentaho Report Designer User GuideДокумент248 страницPentaho Report Designer User GuidewawanknОценок пока нет
- E13634 PDFДокумент770 страницE13634 PDFMuSiCit LiFeОценок пока нет
- Oracle SCM Cloud Using Planning CentralДокумент114 страницOracle SCM Cloud Using Planning CentralMiguel FelicioОценок пока нет
- Launch Checklist PDFДокумент3 страницыLaunch Checklist PDFbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Strategic Management PDFДокумент21 страницаStrategic Management PDFbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Panduan 3 In1Документ7 страницPanduan 3 In1brahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Strategic Marketing DecisionДокумент28 страницStrategic Marketing Decisionbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- 5 Forces AssassmentДокумент2 страницы5 Forces Assassmentbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Strategic Marketing DecisionДокумент28 страницStrategic Marketing Decisionbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Keputusan Stratejik PemasaranДокумент28 страницKeputusan Stratejik Pemasaranbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- SM 2.4 (Matching & Decision Tools)Документ13 страницSM 2.4 (Matching & Decision Tools)brahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Space MatrixДокумент3 страницыSpace MatrixAdam DinОценок пока нет
- Strategi Manajemen PDFДокумент21 страницаStrategi Manajemen PDFbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- 5 Forces AssassmentДокумент2 страницы5 Forces Assassmentbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- The 10 Minute ChalllengeДокумент3 страницыThe 10 Minute Challlengebrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Business Model Canvas PosterДокумент1 страницаBusiness Model Canvas PostersunnyОценок пока нет
- FAO Year Book 2014 PDFДокумент195 страницFAO Year Book 2014 PDFbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Coconut Oil MiracleДокумент10 страницCoconut Oil Miraclebrahm2009100% (1)
- Business Model Canvas PosterДокумент1 страницаBusiness Model Canvas PostersunnyОценок пока нет
- Thinking Outside The BoxДокумент2 страницыThinking Outside The Boxbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Icebreaker: Team Trinkets: UrposeДокумент1 страницаIcebreaker: Team Trinkets: Urposebrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- 5 Forces AssassmentДокумент2 страницы5 Forces Assassmentbrahm2009Оценок пока нет
- Going Global Global Strategies Vs National Strategies: James LeontiadesДокумент9 страницGoing Global Global Strategies Vs National Strategies: James LeontiadeskainatОценок пока нет
- PGMPДокумент4 страницыPGMPadjerourouОценок пока нет
- Quality Assurance Management I To 12Документ435 страницQuality Assurance Management I To 12yesrhОценок пока нет
- NGO Management Workshop Narrative Report-Accra, Ghana (December, 2007)Документ24 страницыNGO Management Workshop Narrative Report-Accra, Ghana (December, 2007)wacsiОценок пока нет
- Deondra Avery MJB Internal Resume Current - No CL 1Документ3 страницыDeondra Avery MJB Internal Resume Current - No CL 1api-555568280Оценок пока нет
- CHED Strategic Plan 2011 2016Документ18 страницCHED Strategic Plan 2011 2016Joseff Anthony FernandezОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Strategic CommunicationДокумент9 страницAn Introduction To Strategic Communicationscrane@100% (1)
- Test Bank For Supervision Concepts and Practices of Management 11th Edition Edwin C Leonard DownloadДокумент11 страницTest Bank For Supervision Concepts and Practices of Management 11th Edition Edwin C Leonard DownloadKarenGlassmtwix100% (16)
- MNG3702 Study Guide 2023Документ128 страницMNG3702 Study Guide 2023Neferu MadzTwalОценок пока нет
- Emerging TrendsДокумент9 страницEmerging TrendscroputaОценок пока нет
- Raporti Ujerave 2010-AnglДокумент120 страницRaporti Ujerave 2010-AnglGani GashiОценок пока нет
- SMRP Guide To The Maintenance and Reliability Body of KnowledgeДокумент20 страницSMRP Guide To The Maintenance and Reliability Body of KnowledgeMiguel Carlin JimenezОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management Term PaperДокумент23 страницыStrategic Management Term PaperImOn NoMi100% (2)
- Apresentação Zee Nova en PDFДокумент16 страницApresentação Zee Nova en PDFise eggfОценок пока нет
- Clint Jan Salvaña, Lss GB: Project ManagerДокумент2 страницыClint Jan Salvaña, Lss GB: Project ManagerClint Jan SalvañaОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Strategic Management A Competitive Advantage Approach Concepts and Cases 17th Edition Fred R David 2Документ15 страницSolution Manual For Strategic Management A Competitive Advantage Approach Concepts and Cases 17th Edition Fred R David 2paijamamulmulxrrvy100% (48)
- Article - Benchmarking IntroДокумент5 страницArticle - Benchmarking Introkary290790Оценок пока нет
- Business 4050: Tim Horton's Case Analysis Group 8Документ15 страницBusiness 4050: Tim Horton's Case Analysis Group 8Prince FahadОценок пока нет
- Strategic Distribution Manufacturing President in Detroit MI Resume Kenneth McHenryДокумент4 страницыStrategic Distribution Manufacturing President in Detroit MI Resume Kenneth McHenryKennethMcHenryОценок пока нет
- Six Point Agenda TimelineДокумент21 страницаSix Point Agenda Timelineclifford alejoОценок пока нет
- SM Lecture 1 SMДокумент27 страницSM Lecture 1 SMAKSHITA SOODОценок пока нет
- Module 12 Strategic Planning and LeadershipДокумент41 страницаModule 12 Strategic Planning and LeadershipBackupОценок пока нет
- GD221 - Integrating A Human Rights-Based and Gender Equality Approach Into National Strategic Plans On HIVДокумент47 страницGD221 - Integrating A Human Rights-Based and Gender Equality Approach Into National Strategic Plans On HIVNeringa Ieva LenciauskaiteОценок пока нет
- Management Module 1Документ6 страницManagement Module 1Richard OcampoОценок пока нет
- ICT Strategic FrameworkДокумент26 страницICT Strategic FrameworkbelayОценок пока нет
- SCDL Strategic Management QuestionsДокумент6 страницSCDL Strategic Management QuestionsVinita PoddarОценок пока нет
- Communicating UChicago Financial StrategiesДокумент32 страницыCommunicating UChicago Financial StrategiesBen NgОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 TQMДокумент36 страницChapter 4 TQMHassan Bile BarreОценок пока нет
- CEOДокумент6 страницCEORao GoharОценок пока нет