Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Tle 62326 Low Side Switch
Загружено:
Diego CaceresАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tle 62326 Low Side Switch
Загружено:
Diego CaceresАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Smart Six Channel Low-Side Switch
Features Product Summary
Short Circuit Protection up to 24 V
Over-temperature Protection
Supply voltage VS 4.5 5.5 V
Over-voltage Protection
16 bit Serial Data Input and Diagnostic Drain source clamping voltage VDS(AZ)typ. 53 V
Output (2 bit/ch. acc. SPI protocol) On resistance RON1-4 0.25
Direct Parallel Control of all six Chan- RON 5,6 0.45
nels for PWM Applications Output current (Channel 1-4) ID(NOM) 2 A
General Fault Flag
(Channel 5,6) ID(NOM) 1 A
Low Quiescent Current
Compatible with 3V Micro Controllers
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
Parallel Inputs High or Low Active Programmable
Application
C Compatible Power Switch for 12 V and 24V Applications
Switch for Automotive and Industrial System
Solenoids, Relays and Resistive Loads
Robotic Controls P-DSO 36-12
Ordering Code:
General description Q67007A9397A702
Six Channel Low-Side Switch in Smart Power Technology (SPT) with a
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) and six open drain DMOS output stages. The TLE 6232 GP is pro-
tected by embedded protection functions and designed for automotive and industrial applications. The
output stages are controlled via an SPI Interface. Additionally all six channels can be controlled direct
in parallel for PWM applications. Therefore the TLE 6232 GP is particularly suitable for engine man-
agement and powertrain systems.
Block Diagram
PRG RESET VS FAULT
GND VS
VBB
IN1
Protection
as Ch. 1 Functions
as Ch. 1 LOGIC
as Ch. 1
OUT1
as Ch. 1
Output Stage
IN6 as Ch. 1
16 1 6
SCLK 6 6
Output Control
SI Serial Interface
Buffer OUT6
SPI
CS
SO
GND
V1.2 Page 1 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Detailed Block Diagram
RESET FAULT VS
Normal function
GND VS
PRG SCB/Overload/OT
Open load
IN1
IN2 as Ch.1 short to ground
IN3 as Ch.1
IN4 as Ch.1
IN5 as Ch.1
Output Stage
IN6 OUT1
as Ch.1
16
Channel 2 OUT2
SO
6 Output Channel 3 OUT3
Control
SI SPI Buffer Channel 4 OUT4
Interface
SCLK 16 bit Channel 5 OUT5
Channel 6 OUT6
CS
GND
V1.2 Page 2 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Pin Description Pin Configuration (Top view)
Pin Symbol Function
GND 1 36 GND
1 GND Ground
NC 2 35 NC
2 NC not connected
OUT5 3 34 NC
3 OUT5 Power Output Channel 5 NC 4 33 NC
4 NC not connected OUT1 5 32 OUT4
5 OUT1 Power Output Channel 1 IN5 6 31 NC
6 IN5 Input Channel 5 IN1 7 30 IN4
7 IN1 Input Channel 1 VS 8 29 SI
8 Vs Supply Voltage RESET 9 28 SCLK
9 RESET Reset CS 10 27 SO
10 CS Slave Select PRG 11 26 FAULT
IN2 12 25 IN3
11 PRG Program (inputs high or low-active)
IN6 13 24 NC
12 IN2 Input Channel 2
OUT2 14 23 OUT3
13 IN6 Input Channel 6 NC 15 22 NC
14 OUT2 Power Output Channel 2 OUT6 16 21 NC
15 NC not connected NC 17 20 NC
16 OUT6 Power Output Channel 6 GND 18 19 GND
17 NC not connected Power SO 36
18 GND Ground
19 GND Ground
20 NC not connected
21 NC not connected
22 NC not connected
23 OUT3 Power Output Channel 3
24 NC not connected
25 IN3 Input Channel 3
26 FAULT General Fault Flag
27 SO Serial Data Output
28 SCLK Serial Clock
29 SI Serial Data Input
30 IN4 Input Channel 4
31 NC not connected
32 OUT4 Power Output Channel 4
33 NC not connected
34 NC not connected
35 NC not connected
36 GND Ground
Heat Slug internally connected to ground pins
V1.2 Page 3 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Maximum Ratings for Tj = 40C to 150C
Parameter Symbol Values Unit
Supply Voltage VS -0.3 ... +7 V
Continuous Drain Source Voltage (OUT1...OUT8) VDS 45 V
Input Voltage, All Inputs and Data Lines VIN - 0.3 ... + 7 V
Operating Temperature Range Tj - 40 ... + 150 C
Storage Temperature Range Tstg - 55 ... + 150
Output Current per Channel (see el. characteristics) ID(lim) ID(lim) min A
Single pulse inductive Energy (internal clamping) E mJ
Tj=125C, Ch1-4: 3A linear decreasing 40
Ch5,6: 1,5A linear decreasing 20
Output Current per Channel @ TA = 25C ID 1-4 1.1 A
(All 6 Channels ON; Mounted on PCB ) 1) ID 5,6 0.55
Power Dissipation (mounted on PCB) @ TA = 25C Ptot 3.3 W
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage (Human Body Model) VESD 2000 V
according to MIL STD 883D, method 3015.7 and EOS/ESD
assn. standard S5.1 - 1993
DIN Humidity Category, DIN 40 040 E
IEC Climatic Category, DIN IEC 68-1 40/150/56
Thermal Resistance
junction case (die soldered on the frame) RthJC 2 K/W
junction - ambient @ min. footprint RthJA 50
junction - ambient @ 6 cm2 cooling area with heat pipes
38
PCB with heat pipes,
2
backside 6 cm cooling area
Minimum footprint
1)
Output current rating so long as maximum junction temperature is not exceeded. At TA = 125 C the output cur-
rent has to be calculated using RthJA according mounting conditions.
V1.2 Page 4 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter and Conditions Symbol Values Unit
VS = 4.5 to 5.5 V ; Tj = - 40 C to + 150 C ; Reset = H min typ max
(unless otherwise specified)
1. Power Supply, Reset
Supply Voltage2 VS 4.5 -- 5.5 V
Supply Current IS -- -- 10 mA
Supply Current in Standby Mode (RESET = L) IS(stdy) -- -- 10 A
Minimum Reset Duration tReset,min 1 -- -- s
2. Power Outputs
ON Resistance VS = 5 V; ID = 1 A TJ = 25C RDS(ON) -- 0.25 0.28
Channel 1-4 TJ = 150C -- -- 0.5
ON Resistance VS = 5 V; ID = 500 mA TJ = 25C RDS(ON) -- 0.45 0.55
Channel 5,6 TJ = 150C -- -- 1
Output Clamping Voltage Output OFF VDS(AZ) 45 53 60 V
Current Limit Channel 1-4 ID(lim) 1-4 3 4 6 A
Current Limit Channel 5,6 ID(lim) 5,6 1.5 2 3
Output Leakage Current VReset = L ID(lkg) -- -- 10 A
Turn-On Time Ch 1-4 ID = 2 A, resistive load tON -- 5 10 s
Ch 5,6 ID = 1 A, resistive load
Turn-Off Time Ch 1-4 ID = 2 A, resistive load tOFF -- 5 10 s
Ch 5,6 ID = 1 A, resistive load
Switch-On Slew Rate (resistive load) son 1 4 20 V/s
Switch-Off Slew Rate (resistive load) son 1 4 20 V/s
3. Digital Inputs
Input Low Voltage VINL - 0.3 -- 1.0 V
Input High Voltage VINH 2.0 -- -- V
Input Voltage Hysteresis VINHys 100 200 400 mV
Input Pull Down/Up Current (IN1 ... IN6) IIN(1..6) 10 20 50 A
Input Pull Up Current (Reset) IIN(Res) 10 20 50 A
Input Pull Down Current (PRG) IIN(PRG) 10 20 50 A
Input Pull Up Current ( CS , SI, SCLK) IIN(SI,SCLK) 10 20 50 A
4. Digital Outputs (SO, FAULT )
SO High State Output Voltage ISOH = -2 mA VSOH VS - 1 -- -- V
SO Low State Output Voltage ISOL = 2 mA VSOL -- -- 0.4 V
Output Tri-state Leakage Current CS = H, 0 VSO VS ISOlkg -10 0 10 A
FAULT Output Low Voltage IFAULT = 2 mA VFAULTL -- -- 0.4 V
2
For VS < 4.5V the power stages are switched according the input signals and data bits or are definitely switched
off. This under-voltage reset gets active at VS = 3V (typ. value) and is specified by design.
V1.2 Page 5 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Electrical Characteristics cont.
Parameter and Conditions Symbol Values Unit
VS = 4.5 to 5.5 V ; Tj = - 40 C to + 150 C ; Reset = H min typ max
(unless otherwise specified)
5. Diagnostic Functions
Open Load Detection Voltage VDS(OL) 0.52* 0.6* 0.68* V
Vs Vs Vs
Short to Ground Detection Voltage VDS(SHG) 0.32* 0.4* 0.48* V
Vs Vs Vs
Diagnostic Current (incl. Leakage) UOUTi,j = 14V IOUTi,j 325 580 980 A
UOUTi,j = 0V -IOUTi,j 50 130 250 A
Current Limitation; Overload Threshold Current ID(lim) 1-4 3 4 6 A
ID(lim) 5,6 1.5 2 3 A
Over-temperature Shutdown Threshold Tth(sd) 170 -- 200 C
Hysteresis Thys 5 10 20 K
Fault Delay Time td(fault) 60 120 240 s
6. SPI-Timing
Serial Clock Frequency (@ CSO 50pF) fSCK DC -- 5 MHz
Serial Clock Period (1/fclk) tp(SCK) 200 -- -- ns
Serial Clock High Time tSCKH 50 -- -- ns
Serial Clock Low Time tSCKL 100 -- -- ns
Enable Lead Time (falling edge of CS to rising edge of CLK) tlead 100 -- -- ns
Enable Lag Time (falling edge of CLK to rising edge of CS ) tlag 150 --- -- ns
Data Setup Time (required time SI to falling of CLK) tSU 20 -- -- ns
Data Hold Time (falling edge of CLK to SI) tH 20 -- -- ns
Disable Time tDIS -- -- 100 ns
3
Transfer Delay Time tdt 150 -- -- ns
( CS high time between two accesses)
Data Valid Time4 CL = 50 pF tvalid -- -- 100 ns
CL = 100 pF -- -- 120 ns
CL = 150 pF -- -- 150 ns
3
This time is necessary between two write accesses. To get the correct diagnostic information, the transfer delay
time has to be extended to the maximum fault delay time td(fault)max = 200s.
4
This parameter will not be tested but specified by design
V1.2 Page 6 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Description of the Power Stages
4 low side power switches for nominal currents up to 3A (power stages OUT1 to OUT4). Con-
trol is possible by input pins or via SPI. For TJ = 150C the on-resistance of the power
switches is below 500m.
2 low side power switches for nominal currents up to 1.5A (power stages OUT5 and OUT6).
Control is possible by input pins or via SPI. For TJ = 150C the on-resistance of the power
switches is below 1.
In order to increase the switching current or to reduce the power dissipation parallel connec-
tion of power stages is possible.
Each of the 6 output stages is equipped with its own zener clamp, which limits the output volt-
age to a maximum of 60V. The outputs are provided with a current limitation set to a minimum
of 1.5A resp. 3A. Each power stage is equipped with an own temperature sensor.
5)
Each output is protected by embedded protection functions . In case of overload or short-
circuit to UBatt the current is internally limited and the corresponding bit combination is set
(early warning). If this operation leads to an over-temperature condition, a second protection
level (about 170C) will change the output into a low duty cycle PWM (selective thermal shut-
down with restart) to prevent critical chip temperatures.
The following faults can be detected (individually for each output):
- short to UBatt: (SCB/overload) can be detected when switches are On state
- short to ground: (SCG) can be detected when switches are Off state
- open load: (OL) can be detected when switches are Off state
- over-temperature: (OT) will only be detected when switches are On state
The fault conditions SCB, SCG and OL will not be stored until an integrated filtering time is
expired (please note for PWM application). If, at one output, several errors occur in a se-
quence, always the last detected error will be stored (with filtering time). All fault conditions are
encoded in two bits per switch and are stored in the corresponding SPI registers. Additionally
there are two central diagnostic bits: one especially for over-temperature (latched result of an
OR-operation out of the 6 signals of the temperature sensor) and one for fault occurrence at
any output. A fault that has been detected and stored in the fault register must not be replaced
by o.k.-state (11) unless it is read out by the RD_DIAG command sent by the microcontroller
or an internal or external reset has been applied. I.e. the fault register will be cleared only by
the RD_DIAG command.
PRG - Program pin. PRG = High (VS): Parallel inputs Channel 1 to 6 are high active
PRG = Low (GND): Parallel inputs Channel 1 to 6 are low active.
If the parallel input pins are not connected (independent of high or low activity), channels 1 to
6 are switched OFF.
PRG pin itself is internally pulled down when it is not connected.
5)
The integrated protection functions prevent device destruction under fault conditions and may not be used in
normal operation or permanently.
V1.2 Page 7 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
The effect of the integrated under-voltage detection is similar to the effect of an external reset
at pin Reset (except low current consumption):
- locks all power switches regardless of their input signals
- clears the fault registers
- resets SPI control register
Parallel Connection of Power Stages
The power stages which are connected in parallel have to be switched on and off simultane-
ously.
In case of overload the ground current and the power dissipation are increasing. The applica-
tion has to take into account that all maximum ratings are observed (e.g. operating tempera-
ture TJ and total ground current IGND, see Maximal Ratings).
The maximum current limitation value (or overload detection threshold) of the parallel con-
nected power stages is the summation of the corresponding maximum values of the power
stages (IOUT(lim)x + IOUT(lim)y + ....).
Max. Nominal Current Max. Clamping Energy On Resistance
2 power stages of the
same type (Imax,OUTx+Imax,OUTy) x 0.9 0.8 x (Ex + Ey) 0.5 xRON ,OUTx , y
(see note 1)
3 power stages of the
same type (Imax,OUTx+Imax,OUTy+ 0.7 x (Ex + Ey + Ez) 0.34 xRON ,OUTx , y , z
(see note 1,2) Imax,OUTz) x 0.8
2 power stages with the RON ,OUTx xRON ,OUTy
same clamping voltage, (Imax,OUTx+Imax,OUTy) x 0.8 Min (Eclpx , Eclpy)
RON ,OUTx + RON ,OUTy
but different nominal
current (see note 3)
Note 1: Power stages of the same type have the same nominal current
Note 2: Only for 3A power stages
Note 3: Parallel connection of power stage type 3A/53V with type 1.5A/53V
SPI Interface
The serial SPI interface makes possible communication between TLE6232 and the microcon-
troller.
TLE 6232 GP always works in slave mode whereas the microcontroller provides the master
function. The maximum baud rate is 5MBaud.
Applying a chip select signal at CS and setting bit 7 and bit 6 of the instruction byte to 1 and
0 TLE 6232 GP is selected by the SPI master. SI is the data input (Signal In), SO the data
output
(Signal Out). Via SCLK (Serial Clock Input) the SPI clock is given by the master.
V1.2 Page 8 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
SPI Signal Description
CS - Chip Select. The system microcontroller selects the TLE 6232 GP by means of the CS
pin. Whenever the pin is in a logic low state, data can be transferred from the C and vice
versa.
CS High to Low transition: - diagnostic status information is transferred from the
power
outputs into the shift register.
- serial input data can be clocked in from then on
- SO changes from high impedance state to logic high or low
state corresponding to the SO bits
CS Low to High transition: - transfer of SI bits from shift register into output buffers
- reset of diagnosis register
To avoid any false clocking the serial clock input pin SCLK should be logic low state during
high to low transition of CS . When CS is in a logic high state, any signals at the SCLK and
SI pins are ignored and SO is forced into a high impedance state.
SCLK - Serial Clock. The system clock pin clocks the internal shift register of the TLE
6232 GP. The serial input (SI) accepts data into the input shift register on the falling edge of
SCLK while the serial output (SO) shifts diagnostic information out of the shift register on the
rising edge of serial clock. It is essential that the SCLK pin is in a logic low state whenever
chip select CS makes any transition. The number of clock pulses will be counted during a
chip select cycle. The received data will only be accepted, if exactly 16 clock pulses were
counted during CS is active.
SI - Serial Input. Serial data bits are shifted in at this pin, the most significant bit first. SI infor-
mation is read in on the falling edge of SCLK. Input data is latched in the shift register and
then transferred to the control buffer of the output stages.
The input data consists of two bytes - a "control byte followed by a "data byte". The control
byte contains the information as to whether the data byte will be accepted or ignored (see di-
agnostics section). The data byte contains the input information for the six channels. A logic
high level at this pin (within the data byte) will switch on the power switch, provided that the
corresponding parallel input is also switched on (AND-operation for channel 1 to 6).
SO - Serial Output. Diagnostic data bits are shifted out serially at this pin, the most significant
bit first. SO is in a high impedance state until the CS pin goes to a logic low state. New diag-
nostic data will appear at the SO pin following the rising edge of SCLK.
RESET - Reset pin. If the reset pin is in a logic low state, it clears the SPI shift register and
switches all outputs OFF. An internal pull-up structure is provided on chip.
In case of inactive chip select signal (High) or bit 7 and bit 6 of the instruction byte differing
from1 and 0 the data output SO remains into tri-state.
V1.2 Page 9 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
SPI Interface
Power Stages 1...6 Power Stages 1...6
SCON_REG MUX_REG
CS
SCLK
CS
SPI Control:
SCK
State Machine
Clock Counter
Control Bits
SI Parity Generator
Shift Register
SO
DIA_REG
Power Stages 1...6
SPI Communication
A SPI communication starts with a SPI instruction (SI control word) sent from the controller to
TLE 6232 GP. Simultaneously the device sends the first SO byte back to the C.
During a writing cycle the controller sends the data after the SPI instruction, beginning with the
MSB. During a reading cycle, after having received the SPI instruction, TLE 6232 GP sends
the corresponding data to the controller, also starting with the MSB.
The SPI Interface consists of three register:
- MUX_REG: 8-bit (1 byte) length for parallel operation mode (IN1 ... IN6 enabled or not)
- SCON_REG: 8-bit (1 byte) length for serial control of the outputs (serial data bits)
V1.2 Page 10 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
- DIAG_REG: 16-bit (2 byte) length. Contains the diagnostic information (2 bits per chan-
nel), a common over-temperature bit and a common fault bit.
Registers MUX_REG and SCON_REG are writeable as well as readable from the microcon-
troller. The DIAG_REG can only be read from the C.
This leads to five different control bytes which are recognized by the IC. The following table
shows the different modes.
MSB LSB MSB LSB
WR_SCON SI: H L L H H L X X D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 X X Write to SCON Register.
SO: Z Z F OT DIA6 DIA5 DIA4 DIA3 DIA2 DIA1
RD_SCON SI: H L L H L H X X X X X X X X X X Read SCON Register
SO: Z Z F OT DIA6 DIA5 SCON6 .. . SCON1 H H
WR_MUX SI: H L H L H L X X M6 M5 M4 M3 M2 M1 X X Write to MUX Register.
SO: Z Z F OT DIA6 DIA5 DIA4 DIA3 DIA2 DIA1
RD_MUX SI: H L H L L H X X X X X X X X X X Read MUX Register
SO: Z Z F OT DIA6 DIA5 MUX6 . . MUX1 H H
RD_DIAG SI: H L L L L L X X X X X X X X X X Read DIAG Register
SO Z Z F OT DIA6 DIA5 DIA4 DIA3 DIA2 DIA1
SI Control Byte SI Data Byte
Note:
X means dont care, because data will be ignored
Dx represents the serial data bits, either being H (= OFF) or L (= ON)
Mx enables parallel control of channel x H (=parallel) or L (=serial)
Z means tri-state
F is the common fault flag
OT is the common over-temperature flag
DIAx is the 2 bit diagnosis information per channel
All other possible control bytes will lead to an ignorance of the data bits, but the full diagnosis
information (like RD_DIAG command) is provided at the SO line. A reset of all fault registers
(and OT bit) the will only be done if the RD_DIAG command was clocked in.
Characteristics of the SPI Interface
If the slave select signal at CS is High or bit 7 and bit 6 of the instruction byte differ from 1
and 0, the state machine is set on default condition, i.e. the state machine expects an in-
struction.
If the 5V-reset (RESET) is active, the SPI output SO is switched into tri-state.
In order to increase the possible number of SPI participants on one and the same CS signal,
bits 7 and 6 of the instruction byte are fixed as shown above. While receiving the first two bits
of the instruction byte the data output SO has to be in tri-state. After having received the first
two bits TLE6232 has to decide if it is addressed (bit 7 = high, bit 6 = low). In this case the re-
maining 6 bits of the instruction byte and the data byte are accepted and the diagnostic feed-
back respectively the data byte content (MUX, SCON) is sent to the microcontroller. Otherwise
instruction and data bits are rejected and SO remains in tri-state.
On a reading access the bit pattern of the data byte at the SPI input SI will be ignored. The
first SO byte sent out simultaneously by the TLE 6232 GP always contains the common fault
bit, the over-temperature bit and the diagnostic information of channels 6 and 5 (2 bits each).
Depending on the SI control byte, the second SO byte contains the requested information.
V1.2 Page 11 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
- Read back of SCON_REG (SCON bits 6 to 1 and two high bits)
- Read back of MUX_REG (MUX information for channel 6 to 1 and two high bits)
- Diagnostic information of channel 4 to 1 (2 bits per channel)
On a writing access always the full diagnostic information of the 6 channels (2 bit per channel)
and the over-temperature and common fault bit is performed.
Invalid instruction/access:
An instruction is invalid, if the following condition is fulfilled:
- an unused instruction code is detected (see tables with SPI instructions).
If an invalid instruction is detected, a writing access on a register of TLE6232 GP is not allow-
wed. In addition an access is invalid if the number of SPI clock pulses counted during active
CS differs from exactly 16 clock pulses (falling edges are counted).
- On a writing access the received data is only taken over into the internal registers and
- the fault register is only cleared by the RD_DIAG command,
if exactly 16 SPI clock pulses were counted while CS active.
Writing access / 8 bit + 8 bit resp.
SS
SPI Instruction Data/8 Bit
SI 1 0 - - - - - -
MSB MSB
SO Z Z F OT DIA6 DIA5 DIA4 DIA3 DIA2 DIA1
MSB
Reading access / 8 bit + 8 bit
SS
SPI Instruction
SI 1 0 - - - - - - XXXX XXXX
MSB
SO Z Z F OT DIA6 DIA5 Data/8 Bit
MSB MSB
V1.2 Page 12 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Serial/Parallel Control of the Power Stages 1...6
(SPI-Instructions: WR_MUX, RD_MUX, WR_SCON, RD_SCON)
The following table shows the truth table for the control of the power stages 1...6. The register
MUX_REG prescribes parallel or serial control of the power stages. The register SCON_REG
prescribes the state of the power stage in case of serial control.
RST PRG INx MUXx SCONx Output OUTx of Power Stage x, x = 1..6
0 X X X X OUTx off
1 X X 0 0 Serial Control: OUTx on
1 X X 0 1 Serial Control: OUTx off
1 0 0 1 X Parallel Control: OUTx on
1 0 1 1 X Parallel Control: OUTx off
1 1 0 1 X Parallel Control: OUTx off
1 1 1 1 X Parallel Control: OUTx on
Note: Serial Data bits are low active. Parallel Inputs are high or low active depending on the PRG pin.
Description of the SPI Registers
Register: MUX_REG
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
MUX6 MUX5 MUX4 MUX3 MUX2 MUX1 1 1
State of FFH
Reset:
Access by Read/Write
Controller:
Bit Name Description
7 MUX6 Serial or parallel control of power stage 6
6 MUX5 Serial or parallel control of power stage 5
5 MUX4 Serial or parallel control of power stage 4
4 MUX3 Serial or parallel control of power stage 3
3 MUX2 Serial or parallel control of power stage 2
2 MUX1 Serial or parallel control of power stage 1
1-0 No function: HIGH on reading
Register: SCON_REG
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SCON6 SCON5 SCON4 SCON3 SCON2 SCON1 1 1
State of FFH
Reset:
Access by Read/Write
Controller:
Bit Name Description
7 SCON6 State of serial control of power stage 6
6 SCON5 State of serial control of power stage 5
5 SCON4 State of serial control of power stage 4
4 SCON3 State of serial control of power stage 3
3 SCON2 State of serial control of power stage 2
2 SCON1 State of serial control of power stage 1
1-0 No function: HIGH on reading
Diagnostics/Encoding of Failures
V1.2 Page 13 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Description of the SPI Registers
(SPI Instructions: RD_DIAG)
Register: DIAG_REG1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
ST7 ST6 ST5 ST4 ST3 ST2 ST1 ST0
State of FFH
Reset:
Access by Read only
Controller:
Bit Name Description
7-6 DIA4 Diagnostic Bits of power stage 4
5-4 DIA3 Diagnostic Bits of power stage 3
3-2 DIA2 Diagnostic Bits of power stage 2
1-0 DIA1 Diagnostic Bits of power stage 1
Note: This byte is always clocked out (second SO-byte), except the SI control words says:
RD_SCON or RD_MUX. But: The content of the fault register will only be deleted if the control command
RD_DIAG was clocked in and 16 clock pulses were counted.
Register: DIA_REG2
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Z Z F OT ST11 ST10 ST9 ST8
State of FFH
Reset:
Access by Read only
Controller:
Bit Name Description
7-6 Z Bit 7 and 6 are always tri-state
5 F Common error flag
4 OT Common over-temperature flag
3-2 DIA6 Diagnostic Bits of power stage 6
1-0 DIA5 Diagnostic Bits of power stage 5
Encoding of the Diagnostic (Status) Bits of the Power Stages
ST(2*x-1) ST(2*x-2) State of power stage x x = 1..6
1 1 Power stage o.k.
1 0 Overload, short circuit to battery (SCB) or over-temperature (OT)
0 1 Open load (OL)
0 0 Short circuit to ground (SCG)
Note:DIA_REG2 is always clocked out as first byte
F, OT Bit = 1: No Fault
F, OT Bit = 0: Fault, Over-temperature
The over-temperature bit is the latched result of an OR-operation out of the 6 signals of the
temperature sensor)
The general fault bit shows the fault occurrence at any of the outputs.
Reset of the Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic information will only be reset after the RD_DIAG command on the rising edge
of slave select or a reset signal is applied (RESET = low).
V1.2 Page 14 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Timing Diagrams
CS
SCLK
SI C O N T R O L Byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
MSB LSB
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SO
Figure 2: Serial Interface
Figure 3: Input Timing Diagram
CS
0.7VS
0.2 VS tdt
trSI tlag
tSCKH
tlead 0.7VS
SCLK 0.2VS
tSCKL tfSI
tSU
tH
0.7VS
SI
0.2VS
Figure 4:
0.7 VS CS
SCLK 0.2 VS
tvalid
tDis
SO 0.7 VS SO
0.2 VS
SO
0.7 VS
0.2 VS
SO Valid Time Waveforms Enable and Disable Time Waveforms
V1.2 Page 15 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
VIN
tON tOFF
VDS
80%
20%
t
Figure 5: Power Outputs
Timing is valid for resistive load with parallel and serial control.
Rising edge of chip select initiates the switching
Application Circuits
VBB
VS = 5V C
10k
VS
PRG
OUT1
FAULT OUT2
RESET
IN1
C
e.g. C167 TLE
IN6
6232 GP
MTSR SI
MRST SO OUT6
CLK CLK
P xy CS
GND
V1.2 Page 16 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Parallel SPI Configuration
Engine Management Application
TLE 6232 GP in combination with TLE 6240 GP (16-fold switch) for relays and general pur-
pose loads and TLE 6220 GP (quad switch) to drive the injector valves. This arrangement
covers the numerous loads to be driven in a modern Engine Management/Powertrain system.
From 26 channels in sum 18 can be controlled direct in parallel for PWM applications.
Injector 1
4
P x.1-4 4 PWM
Channels Injector 2
MTSR SI Injector 3
MRST SO TLE
CLK 6220 GP
CLK Injector 4
P x.y CS Quad
CS
4
P x.1-6 6 PWM
Channels
C
SI
SO TLE
C167 CLK
6232 GP
P x.y Hex
CS
8
P x.1-8 8 PWM
Channels
SI
SO TLE
CLK 6240 GP
P x.y 16-fold
CS
V1.2 Page 17 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Package and Ordering Code
(All dimensions in mm)
P-DSO 36-12 Ordering Code
TLE 6232 GP Q67007A9397A702
V1.2 Page 18 08.Oct. 2003
Data Sheet TLE 6232 GP
Published by
Infineon Technologies AG,
Bereichs Kommunikation
St.-Martin-Strasse 76,
D-81541 Mnchen
Infineon Technologies AG 1999
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
The information herein is given to describe certain components and shall not be considered as warranted characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to technical change reserved.
We hereby disclaim any and all warranties, including but not limited to warranties of non-infringement, regarding circuits,
descriptions and charts stated herein.
Infineon Technologies is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Information
For further information on technology, delivery terms and conditions and prices please contact your nearest Infineon Tech-
nologies Office in Germany or our Infineon Technologies Representatives worldwide (see address list).
Warnings
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types in question
please contact your nearest Infineon Technologies Office.
Infineon Technologies Components may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the express written approval of
Infineon Technologies, if a failure of such components can reasonably be expected to cause the failure of that life-support
device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device or system. Life support devices or systems are in-
tended to be implanted in the human body, or to support and/or maintain and sustain and/or protect human life. If they fail, it
is reasonable to assume that the health of the user or other persons may be endangered.
V1.2 Page 19 08.Oct. 2003
Вам также может понравиться
- Am29f400bb 90si Amd Datasheet 72825Документ5 страницAm29f400bb 90si Amd Datasheet 72825Joel AgbekponouОценок пока нет
- SSM71985 - Smart Key Health Check Quick Reference Guide v2bДокумент4 страницыSSM71985 - Smart Key Health Check Quick Reference Guide v2bKent WaiОценок пока нет
- Lista Scripts Potencia-3Документ10 страницLista Scripts Potencia-3Garage82 Engenharia de Software100% (1)
- SD313 5 MFI Control System (G4HE/G4HG: EPSILON 1.0L/1.1L M/T)Документ1 страницаSD313 5 MFI Control System (G4HE/G4HG: EPSILON 1.0L/1.1L M/T)Huy Trần Quốc100% (1)
- Sat Filter Left 110HzДокумент2 страницыSat Filter Left 110HzxxОценок пока нет
- Kefico Cpegd2.20.x Irom Tc1782 Tprot Kia HyundaiДокумент4 страницыKefico Cpegd2.20.x Irom Tc1782 Tprot Kia HyundaiMohamed FoxОценок пока нет
- Trouble Diagnosis Circuit Diagram: (QG (With Euro-Obd) )Документ18 страницTrouble Diagnosis Circuit Diagram: (QG (With Euro-Obd) )Electronicdeivi DeiviОценок пока нет
- Service Manual DVD Sony MEX-V30Документ10 страницService Manual DVD Sony MEX-V30tcggoulartОценок пока нет
- SD313 1 MFI Control System (G4HE/G4HG: EPSILON 1.0L/1.1L M/T) (1) ECM Terminal InformationДокумент1 страницаSD313 1 MFI Control System (G4HE/G4HG: EPSILON 1.0L/1.1L M/T) (1) ECM Terminal InformationHuy Trần QuốcОценок пока нет
- DTC B1182/19 Short in D Squib (2Nd Step) Circuit (To Ground)Документ4 страницыDTC B1182/19 Short in D Squib (2Nd Step) Circuit (To Ground)Phang KumwingОценок пока нет
- 3505021-Bmw Ews2 Ews3 2 Emulator User ManualДокумент4 страницы3505021-Bmw Ews2 Ews3 2 Emulator User ManualSutiknoОценок пока нет
- 30296 Details PDF - Find 30296 Price, Stock, DatasheetДокумент1 страница30296 Details PDF - Find 30296 Price, Stock, DatasheetMaikel Borges IglesiasОценок пока нет
- Pioneer Avh-P5950dvd Crt3916Документ193 страницыPioneer Avh-P5950dvd Crt3916boroda24100% (1)
- Opel Vectra BX 25 XeДокумент1 страницаOpel Vectra BX 25 XeNikola Lordan0% (1)
- Circuito Conversor A-D Cy100 BoschДокумент5 страницCircuito Conversor A-D Cy100 BoschAlberto MiglinoОценок пока нет
- BOSCH - ME7.9.9 - FAL - OPEL: Imensione Port S.R.L - 15020 Gabiano (AL) - ITALY - Tel. +39 0142 955 201 - WEBДокумент2 страницыBOSCH - ME7.9.9 - FAL - OPEL: Imensione Port S.R.L - 15020 Gabiano (AL) - ITALY - Tel. +39 0142 955 201 - WEBMarcio MartinsОценок пока нет
- MFE Module DTC ChartДокумент28 страницMFE Module DTC ChartMarcelo LealОценок пока нет
- MH3292F16Документ1 страницаMH3292F16Perla LeticiaОценок пока нет
- Bemodeadp1 Schematic V1: External Power Supply I/O Terminal DB-9 ConnectorДокумент1 страницаBemodeadp1 Schematic V1: External Power Supply I/O Terminal DB-9 Connectorsoportenacional nacional100% (1)
- Microsquirt IObox 1Документ21 страницаMicrosquirt IObox 1jesus roblesОценок пока нет
- Chery Fault CodesДокумент16 страницChery Fault CodesMiguel RamirezОценок пока нет
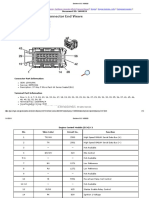
- Engine Control Module Connector End ViewsДокумент12 страницEngine Control Module Connector End ViewsAndrew RivasОценок пока нет
- Ford Fiesta ('96) 1.3 Engine Component Locations and SpecificationsДокумент9 страницFord Fiesta ('96) 1.3 Engine Component Locations and SpecificationsReinaldo ArrivillagaОценок пока нет
- 16 Su Brazil-Kd WMДокумент88 страниц16 Su Brazil-Kd WMGustavo Sostenes Rodrigues Nunes100% (1)
- Tabela - de Componentes PDFДокумент2 страницыTabela - de Componentes PDFRobinson PaulinoОценок пока нет
- Home Dercomaster Public HTML Online Media Image CL GREATTEC Apoyo Modelos GWM Wingle5 Manual Electrico Wingle5!22!200203 BajaДокумент300 страницHome Dercomaster Public HTML Online Media Image CL GREATTEC Apoyo Modelos GWM Wingle5 Manual Electrico Wingle5!22!200203 BajaAUTO MAQОценок пока нет
- Tabela de Componentes SMDДокумент2 страницыTabela de Componentes SMDVillaça Villa50% (2)
- Sharp Lc-32d44e S Ru-Bk Gy - EtДокумент136 страницSharp Lc-32d44e S Ru-Bk Gy - Etlucas22010Оценок пока нет
- Defecte DirectieДокумент58 страницDefecte DirectieGoranka Bulatovic IlicОценок пока нет
- BCM Captiva 1 ConectorДокумент4 страницыBCM Captiva 1 Conectorjulio montenegroОценок пока нет
- Pinout PCM 3Документ4 страницыPinout PCM 3Gạt Tàn Đầy100% (1)
- Installation Manual for MP48 Dual Fuel SystemДокумент26 страницInstallation Manual for MP48 Dual Fuel SystemEduRoi100% (1)
- L9929 STMicroelectronicsДокумент23 страницыL9929 STMicroelectronicsJhonny ManzanoОценок пока нет
- Scripts de Formularios 01Документ4 страницыScripts de Formularios 01Kevin StrongОценок пока нет
- 08-CHERY - Tips Inmobilizador.Документ24 страницы08-CHERY - Tips Inmobilizador.Santiago Henao VillegasОценок пока нет
- Captiva 2010 - Direção Elétrica - Diagrama ElétricoДокумент1 страницаCaptiva 2010 - Direção Elétrica - Diagrama ElétricoWiterMarcosОценок пока нет
- Fiat SST 2Документ4 страницыFiat SST 2Sajin Raj100% (1)
- Lista Circuito Integrado 2010Документ116 страницLista Circuito Integrado 2010Ivanilto Martins da Cruz0% (1)
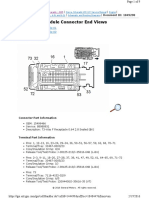
- Engine Control Module Connector End ViewsДокумент9 страницEngine Control Module Connector End ViewsELMERОценок пока нет
- 315 ManualДокумент119 страниц315 ManualLizardo Astudillo CruzОценок пока нет
- Airbag Renault Bosch Upa-Usb ConnectionsДокумент1 страницаAirbag Renault Bosch Upa-Usb ConnectionsOliver GarcíaОценок пока нет
- Manual Emulador Immo - VAG EmulДокумент4 страницыManual Emulador Immo - VAG Emulmmaaccoo100% (1)
- Features: When Fitted On A 2600 PCB This Chip Will Work But Needs Some Modification of Hardware For Full FonctionsДокумент114 страницFeatures: When Fitted On A 2600 PCB This Chip Will Work But Needs Some Modification of Hardware For Full Fonctions肖磊Оценок пока нет
- Crank No RunДокумент4 страницыCrank No RunAndres Colina CaricoОценок пока нет
- MC2100 Rev Engrd PDFДокумент1 страницаMC2100 Rev Engrd PDFMaria VochinОценок пока нет
- 4271 2GДокумент24 страницы4271 2GAlexandre Dantas HenriqueОценок пока нет
- Asus x555ld (Repair Guide)Документ7 страницAsus x555ld (Repair Guide)David VelazquezОценок пока нет
- Tire Pressure Indicator Sensor Learn Special Tools EL-46079 Tire Pressure Monitor Diagnostic ToolДокумент2 страницыTire Pressure Indicator Sensor Learn Special Tools EL-46079 Tire Pressure Monitor Diagnostic ToolRafael Cessa SolisОценок пока нет
- Volvo S40 2.0d 2008 Problem - Volvo Owners Club ForumДокумент4 страницыVolvo S40 2.0d 2008 Problem - Volvo Owners Club Forumalrahij8Оценок пока нет
- Sak c167cs LMДокумент80 страницSak c167cs LMChristiam OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Writenow! Isp Programmer Device List: Updated October 2018Документ59 страницWritenow! Isp Programmer Device List: Updated October 2018Djams HamsОценок пока нет
- 2013 G 1.6 DOHC MFI Control System Schematic DiagramsДокумент1 страница2013 G 1.6 DOHC MFI Control System Schematic DiagramsManuel GuevaraОценок пока нет
- 2014 Forntier IpdmДокумент3 страницы2014 Forntier IpdmMiguel Angel de la Cruz100% (1)
- ST10F273Документ4 страницыST10F273Poongodi RangasamyОценок пока нет
- Regulador 4949ed PDFДокумент11 страницRegulador 4949ed PDFluizОценок пока нет
- Diagrama Electronico Toyota RunerДокумент10 страницDiagrama Electronico Toyota RunerOmar Jara FelixОценок пока нет
- Smart Octal Low-Side Switch: LogicДокумент17 страницSmart Octal Low-Side Switch: Logicjuan echeverryОценок пока нет
- Smart Octal Low-Side Switch: Features Product SummaryДокумент16 страницSmart Octal Low-Side Switch: Features Product SummaryAriel MercochaОценок пока нет
- DatasheetДокумент16 страницDatasheetAndres GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Infineon Tle7230r Ds v03 04 enДокумент15 страницInfineon Tle7230r Ds v03 04 enياسين الطنفوريОценок пока нет
- Dokumen - Tips - Aladin Diagnostic Software For The Diwa 5 Transmission Turbo Aladin Diagnostic PDFДокумент4 страницыDokumen - Tips - Aladin Diagnostic Software For The Diwa 5 Transmission Turbo Aladin Diagnostic PDFDiego CaceresОценок пока нет
- Data SheetДокумент19 страницData SheetDiego CaceresОценок пока нет
- MK @MSITStore C Intelect INSITE FIS FIS4017893.Chm RtgraphicДокумент1 страницаMK @MSITStore C Intelect INSITE FIS FIS4017893.Chm RtgraphicDiego CaceresОценок пока нет
- 75332S. Trans PDFДокумент10 страниц75332S. Trans PDFDiego CaceresОценок пока нет
- Operating Instructions For Tachograph PDFДокумент28 страницOperating Instructions For Tachograph PDFCesar Bayes RamosОценок пока нет
- 815010029Документ60 страниц815010029احمد ابو عبدالله100% (1)
- 25n06 MosfetДокумент9 страниц25n06 MosfetDiego CaceresОценок пока нет
- Regulador 4271-2g PLD MercedesДокумент23 страницыRegulador 4271-2g PLD MercedesDiego CaceresОценок пока нет
- DPA Pinouts Dec2012Документ18 страницDPA Pinouts Dec2012Carolyn ThomasОценок пока нет
- Abs PDFДокумент98 страницAbs PDFMarcioMartinhoFerreira100% (3)
- Crouzet Syrline Datasheet TMR48DДокумент16 страницCrouzet Syrline Datasheet TMR48Djose uriel olvera chavezОценок пока нет
- Residential Code Update Part 1 of 2 HrsДокумент103 страницыResidential Code Update Part 1 of 2 HrsTakumi FujiwaraОценок пока нет
- Industrial Automation Engineer Interview QuestionsДокумент5 страницIndustrial Automation Engineer Interview QuestionsJêmš NavikОценок пока нет
- INA821 35 - V Offset, 7-nV/ HZ Noise, Low-Power, Precision Instrumentation AmplifierДокумент48 страницINA821 35 - V Offset, 7-nV/ HZ Noise, Low-Power, Precision Instrumentation AmplifierMichael Isael Altamirano CuevaОценок пока нет
- SFRA Testing On Two Winding TransformerДокумент4 страницыSFRA Testing On Two Winding TransformerNithya GowdaОценок пока нет
- Low-water cutoff module specificationsДокумент3 страницыLow-water cutoff module specificationsCarlos WayОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Energy ConversionДокумент77 страницChapter 1 Introduction To Energy ConversionBewnet GetachewОценок пока нет
- Est Can BusДокумент32 страницыEst Can BusRuben EstradaОценок пока нет
- Installn SS9-2 (1.12) en GB INTДокумент56 страницInstalln SS9-2 (1.12) en GB INTAurelien ValadeОценок пока нет
- Generation of Electrical Energy - B. R. GuptaДокумент171 страницаGeneration of Electrical Energy - B. R. GuptaIbrahim Ahmed43% (23)
- Tomasi Full Reviewer PDFДокумент159 страницTomasi Full Reviewer PDFAdriane Patrick QuirosОценок пока нет
- Big Blue 400 Eco Pro PDFДокумент76 страницBig Blue 400 Eco Pro PDFlookb64100% (1)
- Basics of Electrical SwitchesДокумент3 страницыBasics of Electrical SwitchesHsein WangОценок пока нет
- 6218 PDFДокумент111 страниц6218 PDFFrugal Labs - Digital LearnОценок пока нет
- HTSTP - List of Electrical Materials For ApprovalДокумент6 страницHTSTP - List of Electrical Materials For ApprovaljaymarОценок пока нет
- Soft-switching active snubbers reduce losses in DC-DC convertersДокумент13 страницSoft-switching active snubbers reduce losses in DC-DC convertersashish_rewaОценок пока нет
- Bor CelleДокумент11 страницBor CelleAdi KhardeОценок пока нет
- TU Physics Syllabus 2016Документ26 страницTU Physics Syllabus 2016S.M. Ashikur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Certification Results20141224Документ835 страницCertification Results20141224dskОценок пока нет
- M18 Chiwf34 402C1 PDFДокумент1 страницаM18 Chiwf34 402C1 PDFxakerОценок пока нет
- Methods of Writing Differential EquationДокумент9 страницMethods of Writing Differential EquationDillah UtamaОценок пока нет
- 027 LHD Brochure PatolДокумент12 страниц027 LHD Brochure PatolSandy J AronggearОценок пока нет
- Samsung SM-A105F - M - G Service Manual (Phonelumi - Com) PDFДокумент126 страницSamsung SM-A105F - M - G Service Manual (Phonelumi - Com) PDFJhonОценок пока нет
- Accessories and specifications for Trio MC302X motion controllerДокумент30 страницAccessories and specifications for Trio MC302X motion controllerthehanhctmОценок пока нет
- Device List for Prayagraj STPP TG Unit 1Документ12 страницDevice List for Prayagraj STPP TG Unit 1apsОценок пока нет
- D 3032 - 98 - RdmwmzitotgДокумент42 страницыD 3032 - 98 - RdmwmzitotgPrakash MakadiaОценок пока нет
- Fire ProtectionДокумент120 страницFire ProtectionTarik BenzinebОценок пока нет
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of PatentДокумент14 страницUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of PatentAlecsandrОценок пока нет
- Brochure 10 FINALДокумент2 страницыBrochure 10 FINALRodel PelimianoОценок пока нет
- PES Lab Report 1Документ22 страницыPES Lab Report 1UJJAL CHATTERJEEОценок пока нет