Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Prophase I
Загружено:
Omar Khalif Amad PendatunОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Prophase I
Загружено:
Omar Khalif Amad PendatunАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
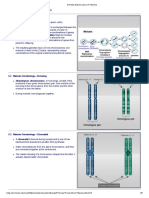
PROPHASE I PACHYTENE
Prophase I is the longest phase of meiosis. During The pachytene stage, also known as pachynema, from
prophase I, DNA is exchanged between homologous Greek words meaning "thick threads",. At this point a
chromosomes in a process called homologous tetrad of the chromosomes has formed known as a
recombination. This often results in chromosomal bivalent. This is the stage when chromosomal
crossover. This process is critical for pairing between crossover (crossing over) occurs. Nonsister chromatids of
homologous chromosomes and hence for accurate homologous chromosomes may exchange segments
segregation of the chromosomes at the first meiosis over regions of homology. Sex chromosomes however,
division. The new combinations of DNA created during are not wholly identical, and only exchange information
crossover are a significant source of genetic variation, over a small region of homology. At the sites where
and result in new combinations of alleles, which may be exchange happens, chiasmata form. The exchange of
beneficial. The paired and replicated chromosomes are information between the non-sister chromatids results in
called bivalents or tetrads, which have two chromosomes a recombination of information; each chromosome has
and four chromatids, with one chromosome coming the complete set of information it had before, and there
from each parent. The process of pairing the are no gaps formed as a result of the process. Because
homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. At this the chromosomes cannot be distinguished in the
stage, non-sister chromatids may cross-over at points synaptonemal complex, the actual act of crossing over is
called chiasmata (plural; singular chiasma). not perceivable through the microscope, and chiasmata
are not visible until the next stage.
LEPTOTENE
The first stage of prophase I is the leptotene stage, also DIPLOTENE
known as leptonema, from Greek words meaning "thin During the diplotene stage, also known as diplonema,
threads". In this stage of prophase I, individual from Greek words meaning "two
chromosomeseach consisting of two sister threads", the synaptonemal complex degrades and
chromatidscondense from the diffuse interphase homologous chromosomes separate from one another a
conformation into visible strands within the nucleus. little. The chromosomes themselves uncoil a bit, allowing
However the two sister chromatids are still so tightly some transcription of DNA. However, the homologous
bound that they are indistinguishable from one another. chromosomes of each bivalent remain tightly bound at
During leptotene, lateral elements of the synaptonemal chiasmata, the regions where crossing-over occurred.
complex assemble. Leptotene is of very short duration The chiasmata remain on the chromosomes until they
and progressive condensation and coiling of are severed at the transition to anaphase I.
chromosome fibers takes place. In mammalian and human fetal oogenesis all developing
oocytes develop to this stage and are arrested before
ZYGOTENE birth. This suspended state is referred to as
The zygotene stage, also known as zygonema, from the dictyotene stage or dictyate. It lasts until meiosis is
Greek words meaning "paired threads",occurs as the resumed to prepare the oocyte for ovulation, which
chromosomes approximately line up with each other into happens at puberty or even later.
homologous chromosome pairs. In some organisms, this
is called the bouquet stage because of the way the DIAKINESIS
telomeres cluster at one end of the nucleus. At this Chromosomes condense further during
stage, the synapsis (pairing/coming together) of the diakinesis stage, from Greek words meaning "moving
homologous chromosomes takes place, facilitated by through". This is the first point in meiosis where the four
assembly of central element of the synaptonemal parts of the tetrads are actually visible. Sites of crossing
complex. Pairing is brought about in a zipper-like fashion over entangle together, effectively overlapping, making
and may start at the centromere (procentric), at the chiasmata clearly visible. Other than this observation, the
chromosome ends (proterminal), or at any other portion rest of the stage closely resembles prometaphase of
(intermediate). Individuals of a pair are equal in length mitosis; the nucleoli disappear, the nuclear
and in position of the centromere. Thus pairing is highly membrane disintegrates into vesicles, and the meiotic
specific and exact. The paired chromosomes are called spindle begins to form.
bivalent or tetrad chromosomes.
Вам также может понравиться
- Classifications of Heart MurmursДокумент2 страницыClassifications of Heart MurmursVS100% (2)
- MITOSIS vs MEIOSISДокумент5 страницMITOSIS vs MEIOSISJohanna GultianoОценок пока нет
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsДокумент101 страницаCell Structures and Their FunctionsKyla Shayne100% (1)
- Cell Division For Grade 8Документ8 страницCell Division For Grade 8Janella RedrinoОценок пока нет
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetДокумент3 страницыThe Cell Cycle WorksheetAngelic ZapantaОценок пока нет
- Mitosis - Worksheet KEYДокумент4 страницыMitosis - Worksheet KEYGeorgia0% (1)
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualДокумент12 страницHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Solutions ManualSamanthaStuartijgt100% (36)
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsОт EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Perpetuation of LifeДокумент40 страницThe Perpetuation of LifeMr Shn Mrcd100% (1)
- 6 - Biology PDFДокумент237 страниц6 - Biology PDFJyoti Ranjan Jrd100% (1)
- Cell Division EssentialsДокумент5 страницCell Division EssentialsDanyal HairalОценок пока нет
- PhilHealth Member Registration Form (PMRF)Документ2 страницыPhilHealth Member Registration Form (PMRF)Vinson Gabato78% (9)
- Cell DivisionДокумент52 страницыCell DivisionRamachandran Ram100% (1)
- Meiosis: Meiosis Is A Special Type of Cell Division Necessary For Sexual ReproductionДокумент5 страницMeiosis: Meiosis Is A Special Type of Cell Division Necessary For Sexual ReproductionNaveed NishatОценок пока нет
- LeptoteneДокумент3 страницыLeptoteneJan GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Meiosis and The Sexual Life Cycle Reviewer NotesДокумент23 страницыMeiosis and The Sexual Life Cycle Reviewer NotesJestoni BigaelОценок пока нет
- MeiosisДокумент22 страницыMeiosisKOMAL NAVARIYAОценок пока нет
- CELL DIVISION-MeiosisДокумент37 страницCELL DIVISION-MeiosisAVINASH VARMAОценок пока нет
- Stages of Prophase 1: LeptoteneДокумент3 страницыStages of Prophase 1: LeptotenepixiedustОценок пока нет
- The Cell CycleДокумент72 страницыThe Cell CycleJerry Jeroum RegudoОценок пока нет
- MeiosisДокумент6 страницMeiosisAbhijeet KumarОценок пока нет
- Cell CycleДокумент6 страницCell CycleSTEINER 97Оценок пока нет
- Mitosis & MeiosisДокумент36 страницMitosis & MeiosisxerhaianОценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionДокумент44 страницыCell Cycle and Cell DivisionKILLER FFОценок пока нет
- MEIOSISДокумент2 страницыMEIOSISKate Lynne CamonayanОценок пока нет
- Meiosis StagesДокумент8 страницMeiosis StagesAmelie BalibagonОценок пока нет
- Cellular Reproduction and GeneticsДокумент14 страницCellular Reproduction and GeneticsJillian Marie100% (1)
- WMSTU Bio2 Course Genetics Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisДокумент5 страницWMSTU Bio2 Course Genetics Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisCobe Christian LascunaОценок пока нет
- KERYOKINESISДокумент6 страницKERYOKINESISMahibahОценок пока нет
- Text Boxes Have Links To Different SlideДокумент21 страницаText Boxes Have Links To Different SlideJuana Montoya VenegasОценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle BrainstormingДокумент3 страницыCell Cycle BrainstormingKimberley MendozaОценок пока нет
- STM007 1ST Sem at RevДокумент9 страницSTM007 1ST Sem at Revlujilleb11Оценок пока нет
- MEIOSIS: TURNING DIPLOID CELLS TO HAPLOIDДокумент4 страницыMEIOSIS: TURNING DIPLOID CELLS TO HAPLOIDcheryl galletoОценок пока нет
- MeiosisДокумент19 страницMeiosisDrech LanadoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Cell CycleДокумент28 страницChapter 6 Cell CyclefatimaОценок пока нет
- Why Meiosis Is Called Reductional DivisionДокумент3 страницыWhy Meiosis Is Called Reductional DivisionDipesh SAPKOTAОценок пока нет
- Cell DivisionДокумент12 страницCell DivisionRaýeęś AhmêðОценок пока нет
- MeiosisДокумент26 страницMeiosisTerence BalaneОценок пока нет
- m2- Cell DivisionДокумент40 страницm2- Cell DivisionDaisy RamaОценок пока нет
- 3 ScanДокумент5 страниц3 ScanAsadОценок пока нет
- Cell Division and Meiosis ExplainedДокумент92 страницыCell Division and Meiosis ExplainedHarpreet KaurОценок пока нет
- Meiosis and Cell DivisionДокумент12 страницMeiosis and Cell DivisionAD-MQОценок пока нет
- Mitosis MeiosisДокумент8 страницMitosis MeiosisSyndy Mae Wasing DosogОценок пока нет
- (Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisДокумент6 страниц(Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisFuzieanna BakhtiarОценок пока нет
- Science Grade-VIIДокумент20 страницScience Grade-VIIGie Ann GongobОценок пока нет
- What Happens During Prophase IIДокумент9 страницWhat Happens During Prophase IILotusОценок пока нет
- MitosisДокумент2 страницыMitosisGwen GwynethОценок пока нет
- MeiosisДокумент33 страницыMeiosisShrawani DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Mitosis and MeiosisДокумент38 страницMitosis and MeiosisLiar NitishОценок пока нет
- Lecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Документ21 страницаLecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Mohammad zreadОценок пока нет
- Meiosis I: Homologous Chromosomes AlignДокумент2 страницыMeiosis I: Homologous Chromosomes AlignLouie BarrientosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1. Cell Division: MeiosisДокумент16 страницChapter 1. Cell Division: Meiosisankurbiology100% (1)
- Cell DivisionДокумент10 страницCell DivisionGale SatsatinОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisДокумент3 страницыDifference Between Mitosis and MeiosisMaria Louisa EfrenОценок пока нет
- Cell Division and Cycle ExplainedДокумент4 страницыCell Division and Cycle ExplainedKalpanaОценок пока нет
- Mitosis in AДокумент6 страницMitosis in AGlen MangaliОценок пока нет
- Cell CycleДокумент19 страницCell CycleMoffat KaprezzoОценок пока нет
- JudeДокумент2 страницыJudeJude FabellareОценок пока нет
- Meiosis: Prophase IДокумент4 страницыMeiosis: Prophase IEthan Del FierroОценок пока нет
- CHROMOSOMESДокумент15 страницCHROMOSOMESMC NonesОценок пока нет
- Aneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish BetweenДокумент2 страницыAneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish Betweeneclipse1130Оценок пока нет
- Cell DivisionsДокумент6 страницCell DivisionsEuniceОценок пока нет
- Lesson 7. Stages of Mitosis and MeiosisДокумент37 страницLesson 7. Stages of Mitosis and MeiosisRoselie DuldulaoОценок пока нет
- SHS Exercise 2-3Документ4 страницыSHS Exercise 2-3Kikieth RociosОценок пока нет
- The Stages of Mitosis: ProphaseДокумент2 страницыThe Stages of Mitosis: ProphaseFamela ReyesОценок пока нет
- Ch-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionДокумент4 страницыCh-1 Cell Cycle and DivisionHans RajОценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesДокумент4 страницыCell Cycle and Cell Division - Short NotesShafa SiddiqueОценок пока нет
- Cell Division & Plant Tissue: University of Perpetual Help System of Laguna Senior High School Department Activity No. 2Документ7 страницCell Division & Plant Tissue: University of Perpetual Help System of Laguna Senior High School Department Activity No. 2Graciela GonzalesОценок пока нет
- SBI3U Unit 4 Task 1 Meiosis AssignmentДокумент12 страницSBI3U Unit 4 Task 1 Meiosis AssignmentSara SОценок пока нет
- ATP III Guideline KolesterolДокумент6 страницATP III Guideline KolesterolRakasiwi GalihОценок пока нет
- Increased ICPДокумент2 страницыIncreased ICPOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Islamic PerspectivesДокумент2 страницыIslamic PerspectivesOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Whooping Cough Vaccination - What You Should Know - CDCДокумент12 страницDiphtheria, Tetanus, and Whooping Cough Vaccination - What You Should Know - CDCOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Sex, Gender, SexualityДокумент3 страницыSex, Gender, SexualityOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Approach To Cardiac MurmursДокумент11 страницApproach To Cardiac Murmurstouthang0074085Оценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Polyphenol Content and Antioxidant Activities of Some Selected Organic and Aqueous Extracts of Cornsilk Zea Mays HairsДокумент4 страницыEvaluation of Polyphenol Content and Antioxidant Activities of Some Selected Organic and Aqueous Extracts of Cornsilk Zea Mays HairsOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Capsule (Orange Peel Tea)Документ3 страницыCapsule (Orange Peel Tea)Omar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Eb Hiv March-Aidsreg2017Документ6 страницEb Hiv March-Aidsreg2017Omar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Handout Subject Verb AgreementДокумент1 страницаHandout Subject Verb AgreementOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- RX TemplateДокумент1 страницаRX TemplateOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Scanned DocumentsДокумент7 страницScanned DocumentsOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Project - English 10Документ3 страницыProject - English 10Omar Khalif Amad Pendatun100% (1)
- My Card 1Документ2 страницыMy Card 1Omar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Citrus Flavonoids and Lipid MetabolismДокумент8 страницCitrus Flavonoids and Lipid MetabolismOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Emonc Protocol (Philhealth-DOH)Документ38 страницEmonc Protocol (Philhealth-DOH)Sandra BaileyОценок пока нет
- November 2017: SUN MON TUE WED THU FRI SATДокумент1 страницаNovember 2017: SUN MON TUE WED THU FRI SATOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Authorization LetterДокумент1 страницаAuthorization LetterOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Partograph: (Use This Form For Monitoring Active Labour)Документ1 страницаPartograph: (Use This Form For Monitoring Active Labour)Omar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Pituitary Gland and Its HormonesДокумент3 страницыPituitary Gland and Its HormonesOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- October, November, December 2014 CalendarДокумент3 страницыOctober, November, December 2014 Calendarbill1018Оценок пока нет
- PKU Phenylketonuria: Polly Bainbridge Samantha Miller Madison MitchellДокумент6 страницPKU Phenylketonuria: Polly Bainbridge Samantha Miller Madison MitchellOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- September 2010 Calendar TomKat StudioДокумент1 страницаSeptember 2010 Calendar TomKat StudioThe TomKat Studio100% (1)
- Reproductive Development 1Документ4 страницыReproductive Development 1Omar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Birth Facts (Information Sheet) : ST ND RDДокумент1 страницаBirth Facts (Information Sheet) : ST ND RDOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- I Got A BoyДокумент3 страницыI Got A BoyOmar Khalif Amad PendatunОценок пока нет
- Perbaikan DnaДокумент33 страницыPerbaikan DnavictoryОценок пока нет
- Role of Autophagy and Apoptosis in AcuteДокумент8 страницRole of Autophagy and Apoptosis in AcuteJesus_Arraiz_14Оценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet For Cell Division Week 4 MELC 8Документ19 страницActivity Sheet For Cell Division Week 4 MELC 8Lyka Mae BenitoОценок пока нет
- MONOPOLY OF MAIZEДокумент5 страницMONOPOLY OF MAIZELászló SágiОценок пока нет
- Science Module 4Документ16 страницScience Module 4Prince Mhar SurioОценок пока нет
- The Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualДокумент6 страницThe Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualJan Edward Abarientos MandaniОценок пока нет
- Botany Module#1Документ4 страницыBotany Module#1Allana Jane AbanteОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - MutationДокумент7 страницChapter 7 - MutationblaОценок пока нет
- Early DevelopmentДокумент5 страницEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaОценок пока нет
- Protein Synthesis Simulation ActivityДокумент4 страницыProtein Synthesis Simulation ActivitySHARIFAH BINTI HASSAN MoeОценок пока нет
- 7th Lecture The Third Week of DevelopmentДокумент17 страниц7th Lecture The Third Week of DevelopmentHussein Al SaediОценок пока нет
- BIO 1 - Module 2Документ17 страницBIO 1 - Module 2kiaraОценок пока нет
- Embryology Lecture Notes - 2 Cleavage and Types: The Planes of CleavageДокумент6 страницEmbryology Lecture Notes - 2 Cleavage and Types: The Planes of CleavageQurat Ul EynОценок пока нет
- Cell Division GuideДокумент30 страницCell Division Guidelandy leeОценок пока нет
- RTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 21 2008Документ9 страницRTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 21 2008iwan93Оценок пока нет
- Nesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 8th Edition Anderson Test BankДокумент32 страницыNesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 8th Edition Anderson Test Bankcaribchaudronpatp100% (28)
- MilliwaysДокумент12 страницMilliwaysTurtle ArtОценок пока нет
- Initiation 3 Defined Step of Transcription Initiation 1st StepДокумент1 страницаInitiation 3 Defined Step of Transcription Initiation 1st StepSivatharsini ArumugamОценок пока нет
- Plant BreedingДокумент36 страницPlant BreedingRhene BarcelonОценок пока нет
- A World That Stay Normally Hidden From Our Eyes But Matter A Lot To UsДокумент11 страницA World That Stay Normally Hidden From Our Eyes But Matter A Lot To UsVîñàý PãtêlОценок пока нет
- REMEMBER: Interphase Is NOT A Stage ofДокумент4 страницыREMEMBER: Interphase Is NOT A Stage ofWONG LI KING MoeОценок пока нет
- "Mitosis" (KEY) : Review Questions - Chapter 9Документ7 страниц"Mitosis" (KEY) : Review Questions - Chapter 9kylevОценок пока нет
- Symmetry-Breaking of Animal CytokinesisДокумент10 страницSymmetry-Breaking of Animal CytokinesisLizbeth EspinosaОценок пока нет