Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ojg 2013102214440112
Загружено:
YovenAlis Diong LadjarОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ojg 2013102214440112
Загружено:
YovenAlis Diong LadjarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Open Journal of Geology, 2013, 3, 25-27
doi:10.4236/ojg.2013.32B006 Published Online April 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg)
Ground Penetrating Radar Survey of Dam Structures of
Kazakhstan on example of Aktobe and Karatomar
Water Storage Basins
Zhumabek Zhantayev, Baurzhan Kurmanov, Nikolai Breusov, Shigayev Dauren, Kirsanov Alexandr
Department of Geophysical and Geodynamic Monitoring, LLP Institute of Ionosphere, Almaty, Kazakhstan
Email: nckit@spaceres.kz, dashigaev@gmail.com
Received 2013
ABSTRACT
Ground penetrating radar surveys of technical condition of Karatomar and Aktobe water storage basins on the river
Tobol are shown. In this article we have shown that dams have problems with cavities and identified longitudinal di-
mensions of anomalous zones of decompression.
Keywords: Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR); Hydraulic Structures; Anomalous Zones; Dam; Decompression Zone;
Areas of High Humidity
1. Introduction received by the receiving antenna, amplified, digitized
and stored. [3]
Authors have examined about 30 reservoirs in Kazakh-
To get decompactification zones and zones of anoma-
stan. Below the reservoir are large dams, which highlight
lies in the soil of dam embankment on longitudinal pro-
the most significant anomalous zones. Investigation of
files on the crest and slopes of dams, along with tradi-
grounds lying at the base of hydraulic structures, includ-
tional methods (seismic and geoelectric survey) used
ing the dynamic changes of ground properties during
ground penetrating radar sounding which is a more mod-
long-term use, is a timely and very important task.
ern, high-tech and informative tool of non-destructive
Changing of the properties of grounds, that lies in the
measurements, allows to get results in real time [2].
base of the dam may lead to the settlement and destruc-
tion of hydraulic structure and if these changes are not 2. Goals and Objectives
taken into account in the design decisions during the
construction, the danger of over-voltage of anomalous The necessary of sensing caused by prolonged exploita-
zones springs up, which could lead to shift of the body tion of water storage basins, which are built of loam and
and the building elements of the dam. When the value of gravel-pebble material. Filtration flow and changes in
stresses and displacements exiting for the limit values of curve of depression of water saturation with time gives
specified security criteria, the state of hydraulic struc- rise to dangerous of overvoltage of anomalous zones,
tures in general may become an emergency. [1] Analysis which could lead to a shift of the body and the elements
of experience of using of various methods showed that of the dam building. [4]
the GPR method provides to receive a more detailed pic-
ture of the geological structure of the subject area on 3. Method
continuous sections compared to the traditional meth- In the process of GPR survey of Karatomar and Aktobe
ods.[2] water storage basins the following main stages of sensing
GPR is widespread and acute in construction and geo- carried out:
technical firms of most highly developed countries, such - Construction of GPR profiling on the axis of the dam,
as Russia, USA, Canada, Sweden, Korea, etc. The where shown a more general picture of structure of the
method is based on the difference of rock on dielectric dam;
capacitivity. Emit pulses propagating in the survey envi- - Construction of GPR profiles along the upper side of
ronment or object are reflected from the boundary, on the dam, where the most visible filtration flows and de-
which change the electrical properties-electrical conduc- compactification zones in the body of the dam. [5]
tivity and dielectric capacitivity. The reflected signal is Karatomar water storage basin was built in 1965. Pro-
Copyright 2013 SciRes. OJG
26 Z. ZHANTAYEV ET AL.
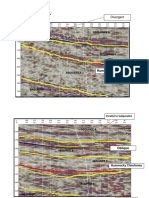
jected volume of the reservoir is 586.0 million m3. Conclusion Geosciences using ground penetrating ra-
Channel type of water storage basin. The dam by maxi- dar "OKO-2" AB-400 profile 0003 by Karatomarskomu
mum height of 18 m and width along the ridge up to 10 reservoir.
meters, is composed of three parts: the precoat to integra- The processing and interpretation of GPR profile No
tion with the right bank by length 1420 m, bulk to inte- 0003 (Figure 3) had a decompression zone and areas of
gration with the left bank by length 240 meters and the high humidity in the dam body. On GPR profiles clearly
central rollway by length 134 meters and consists 7 evident geological layers and boundaries decompression
spans. in points from 160 to 215 meters at a depth of up to 6
Aktobe water storage basin is located to 8 km to south meters from the level of the crest of the dam. The prob-
from Aktobe, in the middle reaches of Ilek River. ing depth of 6 meters is achieved by increasing the ac-
Earthen dam is bulk of sandy-gravelly loam soil with cumulation of signals in the longitudinal profile. Fixed
loamy screen and diaphragm of the clay wall. Mark of boundary of the zone of distribution, which is redistrib-
the dam crest is 234.20 m, width of the crest is 10 meters. uted in the soil stress state, leads to the development of
Fastening of the top escarpment is made of reinforced cracks in the transverse directions of the gap relative to
concrete slabs. Reservoir fills since 1985. Reservoir area the longitudinal axis of the dam. The concept of de-
is 3570 ha, the total water volume is 245 million m3, the compression zone in this terminology means that the
effective water volume is 220 million m3. soil in this area is less denser than the surrounding layers.
In the process of GPR profiling on Karatomar water Cavities (voids) in the base are missing, because they
storage basin were conducted eight longitudinal profiles have a characteristic radiopicture - often repeating the
by lenght 200 - 250 meters along the crest and the upper signal due to multipath waves in the cavity, which is the
reach of the dam, by depth of sounding over 10 meters performance of work were found. It also showed very
(Figure 1). high humidity in the area of the dam body at around 115
When the GPR profiling Aktobe reservoir held 90 lon- - 155 meters depth penetration of up to 2 meters, which
gitudinal and cross sections along the ridge and the upper can also lead to anomalous zones in the dam body.
reach of the dam, the probing depth is of about 8 meters From these profiles were selected profile 0001,
(Figure 2). 0002, 0003 by Headwater Aktobe reservoirs, which are
most suitable for data analysis, identification of anoma-
4. Conclusions lous zones, areas of distribution (Figures 4, 5 and 6)
The main result and the more prominent of them was the
definition of anomalous zones profile No 0003 on Kara-
tomarskomu reservoir (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Longitudinal profile 0003 section of the reservoir
Karatomar.
Figure 1 Location of GPR profiles by Karatomarskomu
reservoir.
Figure 4. The longitudinal profile 0001 of the upstream
Figure 2. Location of GPR profiles of Aktobe reservoir. Aktobe reservoir.
Copyright 2013 SciRes. OJG
Z. ZHANTAYEV ET AL. 27
(Figure 6), and found decompression zone damp loca-
tions in the body of the dam. On GPR profiles clearly
evident in the intense colors degree anomaly. Anomalies
include voids under concrete slabs, which are filled with
water, which leads to decompaction of the dam structure.
Fixed boundary of the zone of distribution, at which the
ground state of stress redistribution, leading to the de-
velopment of cavities and fissures divide transversely to
the longitudinal axis of the dam. Also in the body of the
dam revealed a high content of moisture, which can lead
Figure 5. Longitudinal profile 0002 of the upstream reser- to the formation of abnormal areas in the body of the
voir Aktobe. dam.
These results support the hypothesis of filtration proc-
esses and leaching sandy loam soil with gravel screen
diaphragm mud wall in the location of the anomalous
zones and suffusion removal of soil from the base of the
dam as a result of the hydrodynamic effects of the cycli-
cal filling and emptying of the reservoir.
Analysis of GPR profiles confirmed the possibility of
using non-destructive methods for subsurface sounding
dams with sufficient reliability of the data and their
quantitative and qualitative interpretation. On the dy-
Figure 6. The longitudinal profile 0003 of the upstream namics of the process of deformation of rock mass area
reservoir Aktobe.
of interest, was evidenced by the monitor for a few years.
[6]
The processing and interpretation of GPR profile 0001
(Figure 4) were found decompression zone and areas of
high humidity in the dam body. On GPR profiles clearly REFERENCES
evident in the intense colors degree anomaly. These [1] M. A. Kolosov, K. P. Morgunov and G. V. Kogan, Is-
anomalies include voids under concrete slabs, which are polzovanie GPR soil testing methods vosnovany lock
filled with water, which leads to a gradual decompaction chamber, the Journal of the University of Water Com-
structure of the dam. Fixed boundary of the zone of dis- munications, No. 4, 2009, pp. 29-33.
tribution, at which the ground state of stress redistribu- [2] A. Salamov and F. G. Gabibov, The Study of Landslide
tion, leading to the development of cavities and fissures Processes Bail Slope in Baku by Vertical Electrical
divide transversely to the longitudinal axis of the dam. Sounding, Engineering Survey, No. 11, 2010, pp. 36-41.
Also in the body of the dam showed many moisture, [3] M. A. Bandurin, Survey of Irrigation Channels Through
which can lead to anomalous zones in the dam body. Azov Irrigation System of Non-Destructive Methods,
The processing and interpretation of GPR profile 0002 Scientific journal KubSAU, Vol. 24, No. 8, 2006. pp.
67-73.
(Figure 5) were found decompression zone and areas of
high humidity in the dam body. On GPR profiles clearly [4] R. M. Narayanan and J. W. Jakub, Railroad Track
evident in the intense colors degree anomaly. Anomalies Modulus Estimation Using Ground Penetrating Radar
(GPR), Railway Engineering, Proceedings of 5th Inter-
include voids under concrete slabs, which are filled with national Conference, London, 4-6 July 2002, Engineering
water, which leads to decompaction of the dam structure. Technics Press, UK, CD-Rom.
Also showed the boundary of the zone of distribution, at [5] T. R. Sussmann, Application of Ground Penetrating
which the ground is a redistribution of the stress state, Radar to Railway Track Substructure Maintenance Man-
leading to the development of cavities and cracks gap in agement, Doctoral Dissertation, University of Massa-
the transverse direction relative to the longitudinal axis chusetts Amherst, 1999.
of the dam. In the body of the dam is fixed high moisture [6] G. Gallagher, Q. Leiper, M. Clark and M. Forde, Ballast
content, which can lead to the formation of anomalous Evaluation Using Ground Penetrating Radar, Railway
zones in the dam body. Gazette International, Feb, 2000, pp. 101-102.
The processing and interpretation of GPR profile 0003
Copyright 2013 SciRes. OJG
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Tesla Market AnalysisДокумент25 страницTesla Market Analysisapi-339850807100% (2)
- HSC Business Studies Revision Guide PDFДокумент96 страницHSC Business Studies Revision Guide PDFckОценок пока нет
- Synergy Deck Cadet Exam Question PaperДокумент32 страницыSynergy Deck Cadet Exam Question PaperAryan Bhatnagar100% (3)
- 4G11T, TP, 4G11TG1,4G11TPG2 Operation and Maintenance Manual-16.03.09Документ68 страниц4G11T, TP, 4G11TG1,4G11TPG2 Operation and Maintenance Manual-16.03.09KiranKumarReddy67% (3)
- Falklands V2.0 Order of BattleДокумент25 страницFalklands V2.0 Order of BattleArthur Barie100% (1)
- Jurnal Kukar Februari 2016 PDFДокумент14 страницJurnal Kukar Februari 2016 PDFRadhitya Adzan HidayahОценок пока нет
- 03 3 Lambot1Документ7 страниц03 3 Lambot1YovenAlis Diong LadjarОценок пока нет
- 03 3 Lambot1Документ7 страниц03 3 Lambot1YovenAlis Diong LadjarОценок пока нет
- Sequence 3 Chaotic: DivergentДокумент3 страницыSequence 3 Chaotic: DivergentYovenAlis Diong LadjarОценок пока нет
- Temporary Printing WindowДокумент49 страницTemporary Printing WindowYovenAlis Diong LadjarОценок пока нет
- 10 Seismic StratigraphyДокумент48 страниц10 Seismic Stratigraphyzemabder100% (2)
- Ineffective But Reasonable - Why Do European Airlines Operate Short-Haul Flights?Документ9 страницIneffective But Reasonable - Why Do European Airlines Operate Short-Haul Flights?tanvir ehsanОценок пока нет
- US vs. DasalДокумент6 страницUS vs. DasalDeric MacalinaoОценок пока нет
- PPP ModelДокумент40 страницPPP ModelMainak BhattacharjeeОценок пока нет
- Affirmations For Defensive DrivingДокумент2 страницыAffirmations For Defensive DrivingManju KrushnaОценок пока нет
- Beneficial Interactions - Charity QueencyДокумент3 страницыBeneficial Interactions - Charity QueencyCharity QueencyОценок пока нет
- Evidence: Planning My TripДокумент14 страницEvidence: Planning My TripRosaAnggeliicaNieto63% (24)
- 05 - Autonomous VehiclesДокумент6 страниц05 - Autonomous VehiclesBill PetrieОценок пока нет
- CashlessGarage Motor MultiBrandДокумент46 страницCashlessGarage Motor MultiBrandMunish KumarОценок пока нет
- Kerem David ENGДокумент46 страницKerem David ENGאר מסОценок пока нет
- Final Design Report: Package-III (Malekhu - Mugling) Ch. 43+542 To Ch. 82+403Документ55 страницFinal Design Report: Package-III (Malekhu - Mugling) Ch. 43+542 To Ch. 82+403Santosh AryalОценок пока нет
- A Study On Passenger S Satisfaction Towards Railway Services in Erode JunctionДокумент6 страницA Study On Passenger S Satisfaction Towards Railway Services in Erode JunctionEBIN JOHNОценок пока нет
- Long-Term Pavement Performance Program Manual For FWD PDFДокумент82 страницыLong-Term Pavement Performance Program Manual For FWD PDFzakwanramliОценок пока нет
- 14 Driver Fatigue Management Guide 4804Документ20 страниц14 Driver Fatigue Management Guide 4804info kzОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 12th EditionДокумент34 страницыTest Bank For Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 12th Editionoscines.filicide.qzie100% (41)
- 2022 Utility and Street Rehabilitation ProjectДокумент26 страниц2022 Utility and Street Rehabilitation ProjectinforumdocsОценок пока нет
- Frenos WabcoДокумент61 страницаFrenos WabcoFastcross HondaОценок пока нет
- ExxonMobil CCM WhitepaperДокумент8 страницExxonMobil CCM WhitepaperMahanteshОценок пока нет
- Well FoundationДокумент28 страницWell FoundationGaurav Maharana100% (1)
- Rigging-Manual Dart16Документ10 страницRigging-Manual Dart16Adi ATMОценок пока нет
- Quotation Bina Megah Indowood 30 HPДокумент1 страницаQuotation Bina Megah Indowood 30 HPKurniawan FebryОценок пока нет
- Brochure Elp319 PDFДокумент2 страницыBrochure Elp319 PDFFirman GustiОценок пока нет
- Final ThesisДокумент57 страницFinal ThesisAndhika Supriat PutraОценок пока нет
- Menghitung Minimum Bollard PullДокумент2 страницыMenghitung Minimum Bollard PullWilly SastraleksanaОценок пока нет
- 747 FB 13-02Документ2 страницы747 FB 13-02JOEL VITOR PEREIRA DOS SANTOSОценок пока нет
- Tanker Management Self Assessment LP BriefingДокумент11 страницTanker Management Self Assessment LP BriefingSlimОценок пока нет