Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
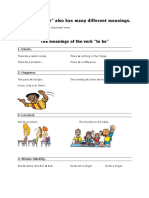
Phrases and Rules for Forming Indirect Questions
Загружено:
Syndell Avalos AparicioИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Phrases and Rules for Forming Indirect Questions
Загружено:
Syndell Avalos AparicioАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Phrases for Indirect Questions
Could you tell me
Do you know
I was wondering
Do you have any idea
Id like to know
Would it be possible
Is there any chance
Direct and Indirect Questions in English: Examples
Direct: Where is Market Street?
Indirect: Could you tell me where Market Street is?
In indirect questions with is/are, the verb (is) comes after the subject (Market Street).
Direct What time does the bank open?
Indirect: Do you know what time the bank opens?
In indirect questions, we dont use the auxiliary verbs do/does/did. Also, you can see
that the verb is open in the direct question, and opens in the indirect question.
Direct: Why did you move to Europe?
Indirect: I was wondering why you moved to Europe.
Again, there is no auxiliary verb did in the indirect question. In fact, this indirect
question isnt even a question its more of a statement that invites the other person to
give more information.
Direct: How has he managed to get in shape so quickly?
Indirect: Do you have any idea how hes managed to get in shape so quickly?
The auxiliary verbs have and has can be used in both the direct and indirect questions
but in the direct question, has comes before the subject (he), and in the indirect
question, has comes after the subject.
Direct: How much does this motorcycle cost?
Indirect: Id like to know how much this motorcycle costs.
To form the indirect question, remove does and change cost to costs.
Direct: Can you finish the project by tomorrow?
Indirect: Would it be possible for you to finish the project by tomorrow?
For direct questions with can, we can use the phrase would it be possible to make
it indirect.
Direct: Can we change the meeting to Thursday?
Indirect: Is there any chance we could change the meeting to Thursday?
Is there any chance is another option for forming indirect questions with can.
Yes/No Direct Questions > If in Indirect
Questions
If the direct question is a yes or no question (it has no question word such as what,
who, when, where, why, or how), then the indirect question will have if.
Direct: Does Tom like Italian food?
Indirect: Do you know if Tom likes Italian food?
Direct: Are your parents joining us for dinner?
Indirect: Could you tell me if your parents are joining us for dinner?
Direct: Do they speak English?
Indirect: I was wondering if they speak English.
Direct: Has Barbara ever studied abroad?
Indirect: Do you have any idea if Barbaras ever studied abroad?
Direct: Do you plan on traveling this summer?
Indirect: Id like to know if you plan on traveling this summer.
Indirect questions: grammar rules with examples
If we want to make questions in the English language, we can do it by changing the word order (Is
he your brother? Was she there? Have you been to Ireland?) or by using the auxiliary do (Do you
know them? Does he live with you? Did you enjoy it?)
The indirect questions are not normal questions. They have the same word order as statements
and we do not use the verb do to form a question. They usually come after introductory phrases
combined with interrogative pronouns and adjectives (who, whom, what, which, whose),
adverbs (when, where, how, why) or if, whether.
Compare the following direct and indirect questions:
Direct: What did she want? - Indirect: Do you know what she wanted?
Direct: Where was it? - Indirect: Do you remember where it was?
Direct: Will they come? - Indirect: I wonder if they will come.
We can use many other introductory phrases to start such questions, e. g. I ask, I wonder, I
want/would like to know, I can't remember, I have no idea, I am sure etc., or they can be introduced
by direct questions such as Can you tell me, Do you know, Do you remember, Have you any idea.
We use the indirect questions similarly in the reported speech, but we have to make some other
changes in the Reported questions.
Look at more examples to understand how we change the direct questions:
How much is it? - I'd like to know how much it is.
Is this seat free? - He is asking if this seat is free.
Where did she go? - Have you any idea where she went?
Does he want to buy it? - Do you know whether he wants to buy it?
These questions are more common in English than in some other languages. They are more polite
and more formal than the direct questions. Compare the following examples of the direct - indirect
questions.
Why did you do it? - Could you tell me why you did it?
Could I use your telephone? - Do you think I could use your telephone?
Are you married? - I wonder if you are married.
Вам также может понравиться
- Narrative Tenses PracticeДокумент3 страницыNarrative Tenses PracticeAlina SemeniukОценок пока нет
- Jon Meets Amy: Episode 1Документ6 страницJon Meets Amy: Episode 1Joseanne SantosОценок пока нет
- Unit 24 - Subject and Object Pronouns - Direct and Indirect ObjectsДокумент14 страницUnit 24 - Subject and Object Pronouns - Direct and Indirect ObjectsVictor PastranaОценок пока нет
- Simple Future TenseДокумент1 страницаSimple Future Tensetz14Оценок пока нет
- 2-Past Simple and Past ProgressiveДокумент8 страниц2-Past Simple and Past ProgressiveMagy RomeroОценок пока нет
- Direct and Indirect QuestionsДокумент8 страницDirect and Indirect QuestionsIuli JulieОценок пока нет
- Learn phrasal verbs with this guide to particles, meanings and usageДокумент18 страницLearn phrasal verbs with this guide to particles, meanings and usageGuitargirlMimiОценок пока нет
- FOG Indirect SpeechДокумент14 страницFOG Indirect Speechsolrac4371Оценок пока нет
- Passive ActiveДокумент14 страницPassive ActiveMaycol Antonio RojasОценок пока нет
- Where Do You LiveДокумент3 страницыWhere Do You LiveOmar Ruben Garcia AragonОценок пока нет
- Articles - Grammar DrillsДокумент2 страницыArticles - Grammar DrillsJay Be-ElОценок пока нет
- Bda Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыBda Lesson Planapi-490993052Оценок пока нет
- Another Vs Other Vs The Other Vs Others.Документ2 страницыAnother Vs Other Vs The Other Vs Others.Pilar RodríguezОценок пока нет
- Confusing Words Part 1 84193Документ6 страницConfusing Words Part 1 84193Success MentorОценок пока нет
- Grammar 1A - Question formationДокумент4 страницыGrammar 1A - Question formationTijana CurcicОценок пока нет
- Making Suggestions EffectivelyДокумент9 страницMaking Suggestions EffectivelyTasneem AbbadiОценок пока нет
- Zero/ First Conditional Putting The Verbs in The Correct FormДокумент2 страницыZero/ First Conditional Putting The Verbs in The Correct FormYousraОценок пока нет
- Modals and Modal PerfectsДокумент3 страницыModals and Modal PerfectsAnonymous d5q96ww4vnОценок пока нет
- Learning modal verbs and grammarДокумент7 страницLearning modal verbs and grammarRosanna BellaubiОценок пока нет
- Developing Self-Awareness for Financial ManagersДокумент15 страницDeveloping Self-Awareness for Financial ManagersDego100% (1)
- Simple Present Tense and Past TenseДокумент23 страницыSimple Present Tense and Past TenseLisa Aulia100% (1)
- Question TagsДокумент4 страницыQuestion TagsGlessy HuamanОценок пока нет
- Direct and Indirect QuestionsДокумент10 страницDirect and Indirect QuestionsManuel DraicchioОценок пока нет
- The Perfect TensesДокумент6 страницThe Perfect TensesledracОценок пока нет
- Compound AdjectivesДокумент2 страницыCompound AdjectivesAlexandra RistovicОценок пока нет
- Past Perfect 2 American English Intermediate b1 b2 Group American English StudentДокумент3 страницыPast Perfect 2 American English Intermediate b1 b2 Group American English StudentmarycarolitchaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыThermodynamics Lesson PlanDiajeng Ramadhan100% (2)
- 88 Yes-No-Questions US StudentДокумент12 страниц88 Yes-No-Questions US StudentJulie MulvanyОценок пока нет
- Inversions: Worksheet 8 - C1 LevelДокумент24 страницыInversions: Worksheet 8 - C1 LevelViviana PaolaОценок пока нет
- Direct and Indirect Questions in EnglishДокумент5 страницDirect and Indirect Questions in EnglishErick ValdovinosОценок пока нет
- Collocations Delexical Verbs Make, Do, Have and TakeДокумент1 страницаCollocations Delexical Verbs Make, Do, Have and Takesam kadadoОценок пока нет
- Sımple and Complex Indırect QuestıonsДокумент13 страницSımple and Complex Indırect Questıonsgamze100% (1)
- Present Perfect ContinuousДокумент3 страницыPresent Perfect ContinuousKuok HuaОценок пока нет
- Conditionals Grammar ExercisesДокумент4 страницыConditionals Grammar ExercisesDaniel OksОценок пока нет
- 88 Wh-Questions USДокумент19 страниц88 Wh-Questions USİrem PiyaleОценок пока нет
- Format and Question - ESEM5553 ASSIG 2 UNITARДокумент3 страницыFormat and Question - ESEM5553 ASSIG 2 UNITARMiz TatyОценок пока нет
- Past of Be, Regular and Irregular Verbs in PastДокумент2 страницыPast of Be, Regular and Irregular Verbs in PastianОценок пока нет
- Phrases For Indirect QuestionsДокумент4 страницыPhrases For Indirect QuestionsMiguel Eduardo P GОценок пока нет
- Direct and Indirect Questions in EnglishДокумент3 страницыDirect and Indirect Questions in EnglishCecilia PerreraОценок пока нет
- Indirect QuestionsДокумент3 страницыIndirect QuestionsOlivera PetrovicОценок пока нет
- How to form indirect questions in EnglishДокумент11 страницHow to form indirect questions in EnglishclanmortОценок пока нет
- Already Yet Still Anymore ChartДокумент2 страницыAlready Yet Still Anymore ChartOrlando SilvaОценок пока нет
- Other AnotherДокумент5 страницOther Anotherdursitarosales9353Оценок пока нет
- Understanding common verb-noun collocationsДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding common verb-noun collocationsLena IlievaОценок пока нет
- Continuous Infinitive With Modal VerbsДокумент2 страницыContinuous Infinitive With Modal VerbsIvana Lalic100% (1)
- Grammar and Written ExpressionДокумент31 страницаGrammar and Written ExpressionloreG22Оценок пока нет
- Adverb Clauses Explained: Types and FunctionsДокумент3 страницыAdverb Clauses Explained: Types and FunctionsHelenОценок пока нет
- Pronouns Exercise (Beginner Level)Документ4 страницыPronouns Exercise (Beginner Level)Shweta PrajapatОценок пока нет
- Modal Verbs of ObligationДокумент2 страницыModal Verbs of ObligationJayanth Samavedam100% (2)
- Past Perfect SimpleДокумент2 страницыPast Perfect SimpleNita TanaОценок пока нет
- Word Order Rules and Exercises PDFДокумент10 страницWord Order Rules and Exercises PDFgabriella56Оценок пока нет
- REDUNDANCYДокумент2 страницыREDUNDANCYrimsha mehboobОценок пока нет
- Te3 Int Entcheck 01Документ2 страницыTe3 Int Entcheck 01Dasha MoskalenkoОценок пока нет
- Word-Order-In-English - Vi2 PDFДокумент6 страницWord-Order-In-English - Vi2 PDFwahyu chandra wijayaОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect Continuous TenseДокумент5 страницPresent Perfect Continuous Tenseapi-3718916100% (4)
- Learn the Difference Between Adjectives and AdverbsДокумент17 страницLearn the Difference Between Adjectives and AdverbsLaura CamilaОценок пока нет
- The Verb To Be ExplanationsДокумент5 страницThe Verb To Be ExplanationsLuz Maria Batista MendozaОценок пока нет
- B2 - C1 - Passive VoiceДокумент19 страницB2 - C1 - Passive VoiceAlina IugaОценок пока нет
- Indirect QuestionsДокумент15 страницIndirect QuestionsJosué Negrete FloresОценок пока нет
- Useful Expressions To Express Your OpinionДокумент2 страницыUseful Expressions To Express Your OpinionSimayОценок пока нет
- Indirect Questions - Espresso EnglishДокумент2 страницыIndirect Questions - Espresso EnglishRonan RyanОценок пока нет
- Direct and Indirect QuestionsДокумент2 страницыDirect and Indirect QuestionslucezziitaОценок пока нет
- What Are Indirect QuestionsДокумент3 страницыWhat Are Indirect QuestionsAldo Jei IronyОценок пока нет
- Indirect QuestionsДокумент4 страницыIndirect QuestionsAndres Portillo0% (1)
- Process CL Assification FR Ame Work: The Framework For Process ImprovementДокумент20 страницProcess CL Assification FR Ame Work: The Framework For Process ImprovementSyndell Avalos AparicioОценок пока нет
- Listado Verbos InglésДокумент5 страницListado Verbos InglésLeticia Palma GonzálezОценок пока нет
- Listado Verbos InglésДокумент5 страницListado Verbos InglésLeticia Palma GonzálezОценок пока нет
- 20140522190531Документ1 страница20140522190531Alex Ivan Díaz TafurОценок пока нет
- Thieseen Kitty ExcellДокумент9 страницThieseen Kitty ExcellSyndell Avalos AparicioОценок пока нет
- Pikolo Pota Ka 2Документ2 страницыPikolo Pota Ka 2Marvin TalahibanОценок пока нет
- POLS 4210 Course Teaches Crucial Peace ConceptsДокумент5 страницPOLS 4210 Course Teaches Crucial Peace ConceptsFernanda AzevedoОценок пока нет
- Relaxed Pronunciation ReferenceДокумент8 страницRelaxed Pronunciation Referencevimal276Оценок пока нет
- Lam Van Dang: ObjectiveДокумент2 страницыLam Van Dang: ObjectiveDũng NguyênОценок пока нет
- Chapter IIIДокумент4 страницыChapter IIIjek vinОценок пока нет
- Teaching Science Through InquiryДокумент57 страницTeaching Science Through InquiryAnivic ManileОценок пока нет
- Counselling Process and Counselling RelationshipsДокумент9 страницCounselling Process and Counselling RelationshipsYash JhaОценок пока нет
- Updated Ubd-Lesson-Plan Twana AmbroseДокумент6 страницUpdated Ubd-Lesson-Plan Twana Ambroseapi-326631801Оценок пока нет
- Unit PlanДокумент40 страницUnit Planapi-257586514100% (1)
- Spiral CurriculumДокумент17 страницSpiral Curriculumharlyn21Оценок пока нет
- ResearchДокумент8 страницResearchQuen QuenОценок пока нет
- Weeek1 Listening StrategiesДокумент21 страницаWeeek1 Listening StrategiesDave AronОценок пока нет
- The Role of Technology in Delivering The CurriculumДокумент11 страницThe Role of Technology in Delivering The CurriculumRicca Piadozo VelasquezОценок пока нет
- Decision-Making Competence in Everyday Life.Документ6 страницDecision-Making Competence in Everyday Life.Chelsea AcostaОценок пока нет
- SP Iii-14Документ7 страницSP Iii-14Edwin DagunotОценок пока нет
- Kla Maths Investigation PatternДокумент6 страницKla Maths Investigation PatternOliver Gabaon GalimbaОценок пока нет
- UnixДокумент40 страницUnixPj GuptaОценок пока нет
- Intrapersonal Barriers To CommunicationДокумент10 страницIntrapersonal Barriers To CommunicationJhanvi VaghelaОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan in Diss Defining Social ScieДокумент4 страницыLesson Plan in Diss Defining Social ScieCerelina MestiolaОценок пока нет
- Presentation Rubric 9-12Документ2 страницыPresentation Rubric 9-12api-291179388Оценок пока нет
- Bridging Discourses in The ESL Classroom PDFДокумент329 страницBridging Discourses in The ESL Classroom PDFChristopher SmithОценок пока нет
- PSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngДокумент17 страницPSU TOU 442 - Đề CươngThanh Thảng Phan ThịОценок пока нет
- Chapter IIДокумент26 страницChapter IIRizki Amelia IsmailОценок пока нет
- ''Constructional Morphology - The Georgian Version'' (Olga Gurevich, 2006)Документ257 страниц''Constructional Morphology - The Georgian Version'' (Olga Gurevich, 2006)ThriwОценок пока нет
- STD 8th Perfect English Balbharati Notes English Medium MH Board PDFДокумент11 страницSTD 8th Perfect English Balbharati Notes English Medium MH Board PDFNIVEDITA PATIL67% (42)
- Advanced Algorithms Logic and Proving TechniquesДокумент25 страницAdvanced Algorithms Logic and Proving TechniquesTayyaba TanoliОценок пока нет