Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fu Rose Mide
Загружено:
cheesybacon210 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
455 просмотров1 страницаEdema associated with CHF, cirrhosis of liver, and kidney disease, including nephrotic syndrome. May be used for management of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документEdema associated with CHF, cirrhosis of liver, and kidney disease, including nephrotic syndrome. May be used for management of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
455 просмотров1 страницаFu Rose Mide
Загружено:
cheesybacon21Edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis of liver, and kidney disease, including nephrotic syndrome. May be used for management of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
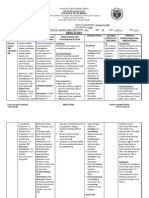
Drug Name Dosage & Route Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility
Rapid-acting potent CV: Postural hypotension,
FUROSEMIDE Edema Treatment of edema History of hypersensitivity to Assessment & Drug Effects
sulfonamide "loop" diuretic dizziness with excessive
(fur-oh'se-mide) Adult: PO 20–80 mg associated with CHF, furosemide or sulfonamides;
and antihypertensive with diuresis, acute hypotensive
in 1 or more divided cirrhosis of liver, and kidney increasing oliguria, anuria,
pharmacologic effects and episodes, circulatory collapse. • Observe patients receiving
doses up to 600 mg/d disease, including nephrotic fluid and electrolyte depletion
Fumide , Furomide , Lasix, uses almost identical to those Metabolic: Hypovolemia, parenteral drug carefully; closely
if needed IV/IM 20–40 syndrome. May be used for states; hepatic coma;
Luramide of ethacrynic acid. Exact dehydration, hyponatremia monitor BP and vital signs. Sudden
mg in 1 or more management of hypertension, pregnancy (category C),
mode of action not clearly hypokalemia, hypochloremia death from cardiac arrest has been
divided doses up to alone or in combination with lactation.
defined; decreases renal metabolic alkalosis, reported.
Classifications: 600 mg/d other antihypertensive agents,
vascular resistance and may hypomagnesemia,
ELECTROLYTIC AND Child: PO 2 mg/kg,
increase renal blood flow
and for treatment of
hypocalcemia (tetany), • Monitor BP during periods of
WATER BALANCE may be increased by hypercalcemia. Has been used diuresis and through period of dosage
hyperglycemia, glycosuria,
AGENT; LOOP DIURETIC 1–2 mg/kg q6–8h concomitantly with mannitol adjustment.
elevated BUN,
(max: 6 for treatment of severe
mg/kg/dose) IV/IM 1 cerebral edema, particularly
hyperuricemia. GI: Nausea, • Observe older adults closely
vomiting, oral and gastric during period of brisk diuresis.
mg/kg, may be in meningitis.
burning, anorexia, diarrhea, Sudden alteration in fluid and
increased by 1 mg/kg
constipation, abdominal electrolyte balance may precipitate
q2h if needed (max:
cramping, acute pancreatitis, significant adverse reactions. Report
mg/kg/dose)
jaundice. Urogenital: symptoms to physician.
Neonate: PO 1–4
Allergic interstitial nephritis, • Lab tests: Obtain frequent blood
mg/kg q12–24h IV/IM
irreversible renal failure, count, serum and urine electrolytes,
1–2 mg/kg q12–24h
urinary frequency. CO2, BUN, blood sugar, and uric
Hematologic: Anemia, acid values during first few months
Hypertension
leukopenia, of therapy and periodically thereafter.
Adult: PO 10–40 mg
thrombocytopenic purpura;
b.i.d. (max: 480 mg/d)
aplastic anemia, • Monitor for S&S of hypokalemia.
agranulocytosis (rare). • Monitor I&O ratio and pattern.
Special Senses: Tinnitus, Report decrease or unusual increase
vertigo, feeling of fullness in in output. Excessive diuresis can
ears, hearing loss (rarely result in dehydration and
permanent), blurred vision. hypovolemia, circulatory collapse,
Skin: Pruritus, urticaria, and hypotension. Weigh patient daily
exfoliative dermatitis, under standard conditions.
purpura, photosensitivity, • Monitor urine and blood glucose
porphyria cutanea tarde, & HbA1C closely in diabetics and
necrotizing angiitis patients with decompensated hepatic
(vasculitis). Body as a cirrhosis. Drug may cause
Whole: Increased hyperglycemia.
perspiration; paresthesias;
activation of SLE, muscle
spasms, weakness;
thrombophlebitis, pain at IM
injection site.
Вам также может понравиться
- FUROSEMIDEДокумент2 страницыFUROSEMIDEa_lavina02Оценок пока нет
- Pedia Drug StudyДокумент11 страницPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsДокумент5 страницGeneric Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsKat ZОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteДокумент26 страницGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)Документ2 страницыDrug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)mikErlh80% (5)
- Fusid®: TabletsДокумент8 страницFusid®: Tabletsddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Phenobarbi Tal Sodium: Adult: PO 100-300Документ1 страницаPhenobarbi Tal Sodium: Adult: PO 100-300Jeremiash Noblesala Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- AldactoneДокумент2 страницыAldactoneianecunarОценок пока нет
- A Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletДокумент7 страницA Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletRaijenne VersolaОценок пока нет
- Furosemide (LASIX)Документ1 страницаFurosemide (LASIX)Amanda CoadОценок пока нет
- Pharma Cards CHF DVTДокумент14 страницPharma Cards CHF DVTRiza Angela BarazanОценок пока нет
- Generic Name LasixДокумент4 страницыGeneric Name LasixSabita PaudelОценок пока нет
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityДокумент5 страницDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoana Marie GuanОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsДокумент4 страницыGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol Indication & DosageДокумент18 страницHaloperidol Indication & DosageRon Java FantillanОценок пока нет
- Furosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites EliminationДокумент4 страницыFurosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites Eliminationmole_fkОценок пока нет
- FluconazoleДокумент3 страницыFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosОценок пока нет
- Furosemide Mims EngДокумент17 страницFurosemide Mims EngNur Ilmi SofiahОценок пока нет
- FurosemideДокумент2 страницыFurosemideJm RomancapОценок пока нет
- FRUSEMIDEДокумент3 страницыFRUSEMIDEkrishna chandrakani100% (1)
- Furosemide: Online AudioДокумент4 страницыFurosemide: Online AudioDani PhilipОценок пока нет
- FurosemideДокумент2 страницыFurosemidezimmerstyle09Оценок пока нет
- Furosemide Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEДокумент12 страницDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioОценок пока нет
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oДокумент5 страницFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- Drug Study - FurosemideДокумент3 страницыDrug Study - FurosemideIzza DeloriaОценок пока нет
- AcetazolamideДокумент5 страницAcetazolamideIanDiel ParagosoОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics For Urinary Tract Infections: Nani MaharaniДокумент45 страницAntibiotics For Urinary Tract Infections: Nani MaharaniMelinda FiskaОценок пока нет
- w15 - Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoДокумент6 страницDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotОценок пока нет
- FurosemДокумент10 страницFurosemMir ElaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study (MS)Документ9 страницDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoОценок пока нет
- Drug CardsДокумент4 страницыDrug CardsBrittany Lynn MyersОценок пока нет
- Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilititesДокумент4 страницыDosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilititesEmm Estipona HaoОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент17 страницDrug StudyJoan RabeОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент15 страницDrug StudyLene Derlene Gerona100% (2)
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationДокумент5 страницHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdОценок пока нет
- Availability: Classifications: Central Nervous System Agent Nsaid (Cox-1) Analgesic Antipyretic Pregnancy Category: BДокумент4 страницыAvailability: Classifications: Central Nervous System Agent Nsaid (Cox-1) Analgesic Antipyretic Pregnancy Category: BCay SevillaОценок пока нет
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationДокумент5 страницSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinОценок пока нет
- LasixДокумент2 страницыLasixMary Tiara DinantiОценок пока нет
- IndapamideДокумент2 страницыIndapamideNovi Yuliana100% (1)
- High Risk DrugsДокумент12 страницHigh Risk Drugsarshiya.manasekiОценок пока нет
- DrugsДокумент20 страницDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- SOAP Pharm D HepaДокумент13 страницSOAP Pharm D HepaFatma HasanОценок пока нет
- FurosemideДокумент4 страницыFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Bumetanide (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыBumetanide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse68880% (1)
- DrugsДокумент5 страницDrugsJicel Camille EdeaОценок пока нет
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideДокумент14 страницMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsДокумент5 страницTherapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsAbby MontealegreОценок пока нет
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesОт EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Hypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Fast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonОт EverandFast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonОценок пока нет
- CLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSОт EverandCLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSОценок пока нет
- Acute Biologic CrisisДокумент2 страницыAcute Biologic CrisisIan Kenneth Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- Ginger Tea BenefitsДокумент1 страницаGinger Tea BenefitsIan Kenneth Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- Course Outline NCMДокумент4 страницыCourse Outline NCMIan Kenneth Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- Altered Sleeping PatternДокумент4 страницыAltered Sleeping PatternIan Kenneth Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- OR InstrumentsДокумент2 страницыOR InstrumentsIan Kenneth Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- NR DrugsДокумент2 страницыNR DrugsIan Kenneth Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- Operating Room DrugsДокумент3 страницыOperating Room DrugsIan Kenneth Da Silva67% (3)
- Inflamation of LungsДокумент23 страницыInflamation of LungsIan Kenneth Da SilvaОценок пока нет