Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Intro To Bio Reading Notes
Загружено:
Arianna Smith0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров2 страницыMacromolecules are giant molecules formed by polymerization. There are four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates which serve as an energy source; lipids which are used to store energy and form membranes; nucleic acids which store and transmit genetic information like DNA and RNA; and proteins which have a variety of functions like structure, movement and chemical reactions. These macromolecules are made up of monomers that join together through covalent bonds to form long chains called polymers.
Исходное описание:
reading notes yay
Оригинальное название
Intro to Bio Reading Notes - Google Docs
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документMacromolecules are giant molecules formed by polymerization. There are four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates which serve as an energy source; lipids which are used to store energy and form membranes; nucleic acids which store and transmit genetic information like DNA and RNA; and proteins which have a variety of functions like structure, movement and chemical reactions. These macromolecules are made up of monomers that join together through covalent bonds to form long chains called polymers.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров2 страницыIntro To Bio Reading Notes
Загружено:
Arianna SmithMacromolecules are giant molecules formed by polymerization. There are four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates which serve as an energy source; lipids which are used to store energy and form membranes; nucleic acids which store and transmit genetic information like DNA and RNA; and proteins which have a variety of functions like structure, movement and chemical reactions. These macromolecules are made up of monomers that join together through covalent bonds to form long chains called polymers.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
10
Reading Notes 9/27/17
INTRO TO SCIENCE AND BIOLOGY / PAGE 46-49
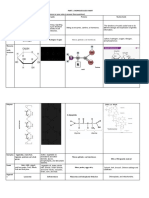
Macromolecules
+ Giant molecules
+ Made up of 1,000-1,000,000 molecules
+ Formed by polymerization
+ Monomers join to form polymers
+ Sort macromolecules into groups based on chemical composition
+ Carbohydrates
+ Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants, some
animals, and other organisms also use carbohydrates for structural uses
+ Glucose and other sugars supply immediate energy
+ Extra sugar stored in starch
+ Monosaccharides
+ Glucose, galactose, and fructose
+ Sucrose is a disaccharide
+ Complex Carbohydrates
+ Many animals store sugar in a polysaccharide called glycogen
+ When glucose levels are low, glycogen is broken down into glucose
+ Plants use starch to store excess sugar
+ Lipids
+ Common categories of lipids are fats, oils, and waxes
+ Made
+ Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of
biological membranes and waterproof coverings
+ Steroids, like hormones, are also lipids
+ Serve as chemical messengers
+ Formed when a glycerol molecule combines with fatty acids
+ If each carbon atom is joined to another carbon atom with a single bond, the
lipid is saturated
+ If there is at one carbon-carbon double bond, the lipid is unsaturated
+ If there is more than one carbon-carbon double bond, the lipid is
polyunsaturated
+ Nucleic Acids
+ Polymers assembled from nucleotides
+ Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) helps to capture and transfer chemical
energy
+ Nucleotides can be joined by covalent bonds to form nucleic acid
+ Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, information
+ Two types of nucleic acids:
11
+ Ribonucleic acid (RNA); contains ribose
+ Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA); contains deoxyribose
+ Proteins
+ Polymers of amino acids
+ Covalent bonds called peptide bonds link amino acids together to form
polypeptides
+ Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes.
Others form important cellular structures, while others transport
substances into or out of cells or help to ght diseases.
+ Structure and Function
+ 20+ different amino acids are found in nature
+ Any amino acid can be joined to another amino acid
+ Amino acids differ from each other because of their R-groups
+ Some are acidic and some are basic
+ Some are polar, some are nonpolar
+ Levels of Organization
+ Assembled into polypeptide groups according to DNA
+ Proteins have 4 levels of structure
+ Sequence of amino acids
+ Folding/coiling of the polypeptide chain
+ Complete 3-D arrangement of a polypeptide chain
+ If more than 1 chain: How the different polypeptides are
arranged around each other
Vocabulary and Important Concepts:
Polymerization- Large compounds are built by joining smaller ones together
Monomers- single part; the smaller units making up polymers
Polymers- Many monomers bonded together
Carbohydrates- Compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
Monosaccharide- A single sugar molecule
Disaccharide- A compound made by joining two simple sugars together
Polysaccharides- The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides
Lipids- Biological molecules that are not soluble in water
Nucleic Acids- Macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and
phosphorus
Nucleotides- Consist of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group ( P O4 ), and a nitrogenous
base
Proteins- Macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. A
functional molecule built from one or more polypeptides
Amino Acids- Compounds with an amino group ( N H 2 ) on one side and a carboxyl group
(-COOH) on the other side
Вам также может понравиться
- PHARMACOLOGY Students WorkbookДокумент87 страницPHARMACOLOGY Students WorkbookPABLO, JACKSON P.Оценок пока нет
- 4 1 - 16 10 Lws Preventers Installation and OperationДокумент28 страниц4 1 - 16 10 Lws Preventers Installation and Operationcrni roko100% (1)
- For The Steam and Condensate Loop - 01Документ4 страницыFor The Steam and Condensate Loop - 01zoraze32Оценок пока нет
- Competitive Solutions For Joining TechnologyДокумент19 страницCompetitive Solutions For Joining Technologyjy12bhuОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules: Your Body's Building BlocksДокумент39 страницBiomolecules: Your Body's Building BlocksJoanna Ruth SeproОценок пока нет
- SBI4U Biochemistry NotesДокумент13 страницSBI4U Biochemistry NotesAli MalikОценок пока нет
- Solar Energy - The Ultimate Renewable ResourceДокумент21 страницаSolar Energy - The Ultimate Renewable ResourceArpit AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Biological Molecules - Chapter 4Документ9 страницBiological Molecules - Chapter 4Bimbo, Arabela June G.Оценок пока нет
- Pattern Matching Online Version ShortenendДокумент9 страницPattern Matching Online Version Shortenendapi-5217817230% (1)
- Organic Compounds Basis of LifeДокумент7 страницOrganic Compounds Basis of LifeJune Emerson ManalangОценок пока нет
- Test - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ TestДокумент15 страницTest - Molecular Spectroscopy - 30 Questions MCQ Testsatish100% (1)
- Bio MoleculesДокумент32 страницыBio MoleculesCarrie Lhee BoadoОценок пока нет
- Biological Macromolecules PDFДокумент31 страницаBiological Macromolecules PDFAngeline CortezОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules Chart and ReviewДокумент6 страницBiomolecules Chart and ReviewJOHN CARLO ASTILLAОценок пока нет
- LeaP Science 10 Q4 W3 4Документ5 страницLeaP Science 10 Q4 W3 4D Garcia100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsОт EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsОценок пока нет
- Softwood and Hardwood in Dissolving PulpДокумент126 страницSoftwood and Hardwood in Dissolving PulpAlan KurniawanОценок пока нет
- DNA and ProteinsДокумент4 страницыDNA and ProteinsjazzОценок пока нет
- Gen Bio Reviewer Final 1Документ5 страницGen Bio Reviewer Final 1Emmanuelle CalleОценок пока нет
- Organic Carbon Hydrogen Inorganic: Introduction: All Compounds Can Be Classified in 2 Broad CategoriesДокумент4 страницыOrganic Carbon Hydrogen Inorganic: Introduction: All Compounds Can Be Classified in 2 Broad CategorieslelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 MicroДокумент40 страницChapter 2 MicroEmma LillyОценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент48 страницBiomoleculesOliric FabiolasОценок пока нет
- Building Macromolecules - Teacher Notes and Review Questions Answer Key - Updated 2020Документ3 страницыBuilding Macromolecules - Teacher Notes and Review Questions Answer Key - Updated 2020Jean Filet ScipioniОценок пока нет
- Intro Macromolecule LectureДокумент34 страницыIntro Macromolecule Lectureapi-300252239Оценок пока нет
- Biological Molecules - For K-12 TrainingДокумент187 страницBiological Molecules - For K-12 TrainingAlicia CatalanОценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент54 страницыBiomoleculeslevi0417Оценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент6 страницBiomoleculesgeecyjane YguintoОценок пока нет
- Biological Importance of Organic Compound: Represented By: Moawiz Gondal Reg: Bsen02203018 Course: BiologyДокумент13 страницBiological Importance of Organic Compound: Represented By: Moawiz Gondal Reg: Bsen02203018 Course: BiologyMoawiz GondalОценок пока нет
- Bio MoleculeДокумент14 страницBio MoleculeMohit KaushikОценок пока нет
- Organic Compounds 2010Документ52 страницыOrganic Compounds 2010Judy MelegritoОценок пока нет
- Activity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaДокумент3 страницыActivity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaPreiy Julian De GuiaОценок пока нет
- Biomolecule - WikipediaДокумент11 страницBiomolecule - WikipediaSumeet MahapatraОценок пока нет
- Bio MoleculesДокумент39 страницBio MoleculesMilani ReyesОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 NotesДокумент38 страницUnit 2 NotesElen Mae PadugaОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Key BiomoleculesДокумент15 страницIntroduction to Key BiomoleculesManish GuptaОценок пока нет
- Topic2 Biomolecule PPДокумент28 страницTopic2 Biomolecule PPismail aeryОценок пока нет
- Biological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingДокумент185 страницBiological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingVj RanchesОценок пока нет
- CHEMISTRYДокумент10 страницCHEMISTRYShyam SundarОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER-6-micropara (Outline)Документ9 страницCHAPTER-6-micropara (Outline)Jezrylle BalaongОценок пока нет
- Molecules of LifeДокумент5 страницMolecules of LifeEmmaОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes CHPTR 4Документ3 страницыBiology Notes CHPTR 4Wan HasliraОценок пока нет
- Bab 11 Kidas 2019Документ16 страницBab 11 Kidas 2019marianaОценок пока нет
- Introduction to BiomoleculesДокумент25 страницIntroduction to Biomoleculesvivitri.dewiОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes SLДокумент69 страницBiology Notes SLIker GОценок пока нет
- Carbon Molecules Key to Life StructuresДокумент29 страницCarbon Molecules Key to Life StructuresDestiny DunkleyОценок пока нет
- Organic MoleculesДокумент7 страницOrganic MoleculesJames CadizОценок пока нет
- MoleculesДокумент33 страницыMoleculesValentina Figueroa HerreraОценок пока нет
- Biological MoleculesДокумент20 страницBiological MoleculesUbaid Ur rahmanОценок пока нет
- 4 Biological MoleculesДокумент2 страницы4 Biological MoleculesmeerzasarahОценок пока нет
- MACROMOLECULESДокумент17 страницMACROMOLECULESPhoebe Kate YaunОценок пока нет
- Webcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Документ2 страницыWebcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Abhishek Kumar VermaОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes 1Документ2 страницыBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroОценок пока нет
- 2.3 BiologyДокумент4 страницы2.3 Biologyminda.eslteacherОценок пока нет
- Biological MoleculesДокумент49 страницBiological Moleculesneeti100% (1)
- Organic-compoundsДокумент16 страницOrganic-compoundsjezzaniexyane28Оценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент75 страницBiomoleculesHumms B Lyka Jenny Alterado BangugОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Molecules To MetabolismДокумент39 страниц2.1 Molecules To MetabolismssjqryОценок пока нет
- Bio MoleculesДокумент26 страницBio MoleculesSHERRYL PANTAОценок пока нет
- BIOCHEMISTRY - The Study of The Chemistry of Living: LinkagesДокумент2 страницыBIOCHEMISTRY - The Study of The Chemistry of Living: LinkagesOdessa KwonОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules: Lynnette A. EjemДокумент103 страницыBiomolecules: Lynnette A. EjemAirene Mae SupilarОценок пока нет
- BioChem LESSON 1 and 2Документ8 страницBioChem LESSON 1 and 2Elvira MirajulОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 MacromoleculesДокумент48 страницChapter 5 MacromoleculesChaehyoung LimОценок пока нет
- Biology NotesДокумент5 страницBiology NotesFaith SNОценок пока нет
- AP Review Organic CompoundsДокумент72 страницыAP Review Organic Compounds둡챙브로Оценок пока нет
- Bio MoleculesДокумент11 страницBio Moleculesdemonzslayer809Оценок пока нет
- Biological-Macromolecules (1)Документ39 страницBiological-Macromolecules (1)MA. FRITZIE DE ASISОценок пока нет
- VNM-IPGN-PPL-SPC-EDG-0000-00019-00-G03 FBE SpecДокумент29 страницVNM-IPGN-PPL-SPC-EDG-0000-00019-00-G03 FBE SpecĐiệnBiênNhâm100% (1)
- Cracks in ConcreteДокумент45 страницCracks in ConcreteRanjeet SinghОценок пока нет
- OTC 15275 Design Challenges of A 48-Inch Pipeline Subsea ManifoldДокумент7 страницOTC 15275 Design Challenges of A 48-Inch Pipeline Subsea Manifoldgvsha88Оценок пока нет
- Solar System GK Notes in PDFДокумент7 страницSolar System GK Notes in PDFPintu KumarОценок пока нет
- SCBA protects users from gases and vaporsДокумент1 страницаSCBA protects users from gases and vaporsdulichsinhthaiОценок пока нет
- An800 6Документ3 страницыAn800 6jcОценок пока нет
- Technical Bulletin: Ammonium Sulfate Solution, 4.1 MДокумент4 страницыTechnical Bulletin: Ammonium Sulfate Solution, 4.1 MToe PaingОценок пока нет
- FE Thermodynamics 7th Appendices: Water Property TablesДокумент71 страницаFE Thermodynamics 7th Appendices: Water Property TableshollegansОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент188 страницChemistrySamveg ClassesОценок пока нет
- Kligler Iron AgarДокумент3 страницыKligler Iron AgarOsama BakheetОценок пока нет
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAMДокумент4 страницыKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAMhweta173Оценок пока нет
- Agribusiness Project Cargill Adhesive ApplicationДокумент23 страницыAgribusiness Project Cargill Adhesive ApplicationFananh11Оценок пока нет
- Hosmane2017 Point Group BookДокумент12 страницHosmane2017 Point Group BookRenato EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Soldering and Desoldering Techniques.Документ6 страницIntroduction To Soldering and Desoldering Techniques.Arsalan Ahmed100% (1)
- ASTM D7777 - Densimetro Digital PortatilДокумент7 страницASTM D7777 - Densimetro Digital PortatilAlvaro Correa100% (2)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Absorption Chillers ToДокумент4 страницыAdvantages and Disadvantages of Using Absorption Chillers Toأحمد صلاحОценок пока нет
- 5052 Aluminum Sheet SuppliersДокумент13 страниц5052 Aluminum Sheet Supplierssanghvi overseas incОценок пока нет
- Total Solutions For Electrocatalysis Research: Discover The ECAT-packagesДокумент2 страницыTotal Solutions For Electrocatalysis Research: Discover The ECAT-packagescipta irawanОценок пока нет
- Physical Science Lesson on Intermolecular ForcesДокумент12 страницPhysical Science Lesson on Intermolecular ForcesBilly Jasper DomingoОценок пока нет
- Selectividad Ingles 2011-2012Документ2 страницыSelectividad Ingles 2011-2012sergiosanroОценок пока нет
- Fiber Optic-Supreme PDFДокумент17 страницFiber Optic-Supreme PDFdHanE anasОценок пока нет
- Explorer XRF: X-Ray Fluorescence SpectrometerДокумент11 страницExplorer XRF: X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometerhossam hamdyОценок пока нет
- Deeper Neet DCT - ChemistryДокумент8 страницDeeper Neet DCT - Chemistryhbhaiya643Оценок пока нет