Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Arrythmia Part 2 - Dr. Payawal PDF
Загружено:
Medisina101Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Arrythmia Part 2 - Dr. Payawal PDF
Загружено:
Medisina101Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
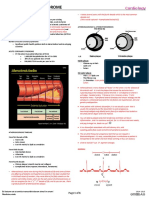
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
SLOW ARRYTHMIA SA Fails to fire
Inverted P wave has better prognosis,
<60 bpm
ESCAPE RHYTHMS
JUNCTIONAL RHYTHM
o Recall: when Px has sinus arrest or pauses thats prolonged, a Px
does not necessarily go into cardiac arrest because. that Px usually
has back-up pacemakers that take over from sinus node if there is
sinus arrest/pause.
-e.g. if there is a pacemaker in AV node which is in the AV
junction, this is how it would look like. [junctional rhythm]
CRITERIA:
o QRS is narrow
- <0.12 sec or < 3 small squares
QRS not widened (0.04 sec)
o P wave can appear in 3 different ways: P wave follows QRS
the wandering pacemaker Rate= around 50; 1500 divided by 28
- pacemaker of heart keeps on changing from within AV
junction IDIOVENTRICULAR RHYTHM
-sometimes can be from sinus??
Before QRS but Inverted this is usually what we see in a dying heart, wherein you can see
-pacemaker comes from upper portion of AV junction the rhythm on ecg or cardiac monitor but you cannot feel the pulse
Absent of the Px
-bec. It is buried in the QRS o because usually this is an evidence of substancial
-pacemaker from middle portion of AV junction myocardial damage;
Follow qrs o QRS is already damaged and ventricle is poorly functioning;
will definitely go into asystole and DIE
-pacemaker from lower portion of AV junction
-means that the atrium is depolarized after the ventricle -but not all flat line is asystole, electrodes might just have
o P-R interval is short been removed :P for the nth time, CORRELATE CLINICALLY
- < 0.12 sec :D #umay :P
most difficlut cardiac arrythmia
- Distinguishes it from PAC which also has narrowed QRS
o Rate is usually 40-60 per min
Compatible with life
thats the one facing the whole heart which faces both atrium
and ventricle instead of the sinus node when there is prolonged
sinus arrest/pause (ano daw? Haha!)
the one facing the whole heart comes from the ventricle (may be
from L or R)
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 1 of 8
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
looks like a PVC o sometimes they go into bradycardia, tachycardia, with no
-QRS is widened apparent reason
-rate is <40 o some may possess prolong sinus pauses
CRITERIA
o QRS is widened
o no P wave
-because it comes from ventricle
o rate is <40 (in junctional it is 40-60)
Massive heart damage
Ventricular pacemaker
Widened QRS
ALGORITHM FOR SLOW HEART RATES (BRADYCARDIA)
[please refer to the algorithm on the Arrythmia (part I) trans to better
MEMORIZE this kasi this will come out on the exam daw]
SINUS BRADYCARDIA
Slow (<60bpm)
Regular
There is P-wave before QRS
JUNCTIONAL RHYTHM
slow
regular
no P wave before QRS
QRS narrow
IDIOVENTRICULAR RHYTHM
slow
regular
no P wave before QRS
QRS wide
THIRD DEGREE/COMPLETE AV BLOCK
slow
regular
no P-QRS relation (P does not cause the QRS)
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
slow
irregular
no P wave
SECOND DEGREE HEART BLOCK
slow
irregular
with P wave
abnormal PR
group beating
SINUS SYNDROME
o in Px with sinus node disease?
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 2 of 8
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
FAST RHYTHMS SINUS TACHYCARDIA
o Narrow QRS
o Regular
o P wave followed by QRS
1. determine if QRS is:
o narrow SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
-rate: >100 o No P wave
o wide
-0.12 sec or more / 3 small squares or more VENTRICULAT TACHYCARDIA
o Wide QRS
ALGORITHM FOR FAST RHYTHM (TACHYCARDIA)
MAT
o Narrow QRS
[again, please refer to the previous trans for fast rhythm algorithm to o Irregular
memorize this easier] o Fast
o Diff. P wave morphologies
*just look at QRS and regularity
ATRIAL FLUTTER
TACHYCARDIA; REGULAR; NORMAL/UPRIGHT P WAVE; NARROW o Irregular
QRS: o No p wave
Sinus tachy o Flutter waves
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Atrial flutter ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
To differentiate: o Irreg
Do CAROTID SINUS MASSAGE o No p
-Px in tachy and you want to slow down HR or bring back o Rapid
rate to normal sinus
-only done in Px with narrow QRS tachycardia
-only on one side for 20 sec PAROXYSMAL SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
-increases vagal tone: stimulate carotid sinus (SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA)
-more common among young ladies (20-40)
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT/SVT) Arrhythmia that originates above the ventricles
o (supra): arrythmia comes above ventricle Regular rhythm
o 25% Pz will have normal sinus Very rapid HR with narrow QRS (normal in contour and duration)
Sinus tachy o 150-250 bpm
o may slow down upon carotid massage o 180-200 bpm in adults
Atrial flutter cannot exactly see P wave
o if you increase AV block o P waves might be buried in the QRS complex or in T wave
o saw-tooth appearance of P waves if you do carotid o may be seen just prior to or just after the end of causes
massage o alteration in the QRS complex that results in a pseudo-R
Sudden onset and termination
TACHYCARDIA; NARROW QRS; IRREGULAR Sometimes on P wave
Multifocal atrial tachycardia [MAT]
o there are more than 3 kinds of P wave you can see Supra ventricular = Class 4 only supra
(inverted, tall, small, flattened, etc.) Class 1a = causes torsades pointes
o in Px with severe pulmonary disease (chronic Class 1c = not recommended for PVC therefore supra
hypoxemia due to COPD) Class 1 b = ventricular only
Atrial fibrillation
o no P wave
o one of the most common cardiac arrythmias;
usuallyin adult >80 y.o
TACHYCARDIA; WIDE QRS
(90%) VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA until proven otherwise
o DDx: supraventriculat tachycardia with abberant
conduction?
MANAGEMENT OF SINUS TACHYCARDIA
[all of the above] haha sorry po di ko nasulat :>
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 3 of 8
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
QRS becomes small.. big.. then becomes
small again.. big.. small..
this was the cause of death of that lady
who had prolonged QTc after
thyroidectomy :(
VT and PVC are all deadly
o VT more dangerous
No P wave
o Blabla phenomenon causing V tach
Example case 1:
VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (VTACH) -Did not have previous heart attack, good LV func.
-developed multiform PVC which may progress to V tach
-sometimes they may just complain of palpitations and BP
may be a bit lower
give trial of antiarrythmic drug
Example case 2:
-Previous heart attack, has LV dysfunction
-developed sustained V tach (>30 sec)
-will go into arrest (no BP or pulse)
-V tach can kill instantaneously esp. in those with
previous asdfg ugh di ko marinig haha!
MULTIFOCAL ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA (MAT)
CRITERIA:
o Irregular
o Narrow QRS
o Has P waves but looks different from each other
-bec. it comes from different ectopic foci in atrium
WIDE QRS TACHYCARDIA Related to COPD: correct oxygenation
Three or more PVC in succession Impulse originate irregularly and rapidly at different parts of
<3o sec: non-sustained v tach (an emergency) the atrium
>30 sec: sustained
KINDS OF VTACH
Monomorphic
o looks the same (in same lead)
Polymorphic
o some wide, some narrow (not look the same)
Torsades de pointes (Torsa de pwa) :D
another kind of polymorphic VT
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 4 of 8
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
-first time Px discover he has AF: may be paroxysmal
AF (not always there)
-so Tx: anticoagulation
-warfarin
-NOACS (novel oral anticoagulants)
-new drugs
-Dabigatran
-Diparoxaban?
-Apixaban?
Control ventricular rate response
o count rate on an irregular rhythm (get 30 big squares and
count # of R waves x 6= estimated ventricular rate)
60-100: controlled/moderate ventricular response
<60: slow
asdfg: drug w/c slows down ventricular rate in AF (sorry di ko
talaga maintindihan hihi)
ATRIAL FLUTTER
(will be in the exam)
Flutter waves
Regular or Irregular Very rapid atrial rate
o depending on AV conduction RR may or may not be regular due to long refractory period
o may be irregularly irregular
QRS not widened o P-P interval (1500 div 4= >300)
Saw-tooth appearance of P waves -atrium is contracting more than 300x per minute
There are more P waves than QRS o The atrium which should be conducting this way is moving this
atrial rate= 250-350 per min way [refer to the heart image above]
o Ventricle rate is slower bec AV node has the longest
refractory period, which is good to Px
-so even if atrial rate of Px is >300, pulse rate will only be
70-80 bec. ventricle is the one that gives pulse
Thats why Tx for AF is DIGOXIN
-prolong refractory period of AV node
Difficult to treat. Hard to convert. Many go into atrial fibrillation
later on
May be compatible with life
Problem is when Px had previous heart attack or LV dysfunction
and develops AF. they usually decompensate (go to heart failure,
pulmonary edema, orthopnea, etc.) bec. atrial contraction
contributes 15-30% of cardiac output; decrease CO= heart failure
Put Px back to sinus rhythm: drug, cardioversion (kukuryentehin
puso)
More common complication of AF: high risk for Cardiac embolism
o when atrium just moves this way and it is not contracting,
blood inside atrium rarely moves and just swirls around
- relative stasis of blood in atrium= high risk to form clot
or thrombus inside
- 80% of time, clot from atrium goes to brain= massive
stroke
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 5 of 8
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
-After 10 min and you did nothing, V fib deteriorate to
ARREST RHYTHMS asystole. When asystole occurs, death!
-Early recognition is important
-We do not defibrillate asystole! (what we see on tv again).
-Will just make bad worse.
ASYSTOLE
*we only defibrillate pulseless VT and Vfib
Asystole (flat line) WILL be in the exam!
Aka Ventricular Standstill
(di nakunan ng pic, basta wavy line lang on ECG)
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION
there are so many ectopic fossa firing at the same time
ventricle just moving this way rather than the usual contraction
-will not produce any significant cardiac output
-no pulse, no BP, no perfusion to brain and will collapse
not see p wave, qrs, t wave (not contract much)
V TACH & VF
o most common sign of cardiac arrest
o in Px with heart attack/ACS, the kind of arrythmia that will
kill them will be either V tach or VF (VoyFriend) :P
o most common initial rhythm in cardiac arrest among
non-traumatic adults[18 and above]
see at ER lifeless, no pulse, no bp, no breathing
-ecg: fibrillatory waves
initial step: cardiodefibrillation (the one you see in tv :>)
-in Px who are practically dead already
-360 joules is the maximum
-if you are able to defibrillate this lifeless Px in less than 1 min
after onset of VF, chances of survival is >90% yeeey! :>
*For every minute delay, chances of survival goes down by
10%
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 6 of 8
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
BENIGN RHYTHMS MISCELLANEOUS
PREMATURE VENTRICULAR COMPLEX ARTIFICIAL PACEMAKER RHYTHM
(PVC)
[this was discussed na sa first part so yung mga references ng pictures
pa-refer nlng sa part 1 ng trans. Thank you ]
COUPLETS
o 2 PVCs in succession
BIGEMINY
o PVC occur every after normal beat
TRIGEMINY
o PVC comes after 2 normal beats
o Complex; we do not see contraction in ecg; uniform PVC
QUADRIGEMINY
o PVC comes after 3 normal beats
PVCs do not look similar (on SAME ECG LEAD)
o You should not compare PVCs of different leads because PVCs
really appear differently in different leads
o from several diff. foci within ventricle
Coupling intervals are not the same
o Coupling interval: interval bet. normal beat and PVC
In Px who suffer from complete heart block, or those in blabla
sinus syndrome, we put an artificial pacemaker usually in RV
MULTIFORM PVC (on same lead)
apex?
o increases risk of Px to have sudden cardiac death even if the Px is
you can set rate
young, physically active and w/o Sx
-If heart beats more than what you set, it would not fire.
o Distinguish. bec. not all PVCs are lethal/dangerous.
-If lower, it will firE
-It can be caused by that moment when exams are coming and
o Rate here: around 80
students have increased sympathetic tone and under stress
(inc. noradrenaline level)
-can infuse cardiac arrythmia (multiform PVC)
R or T PHENOMENON
*Recall: boundary bet. Absolute refractory period and relative
refractory period in ventricle [Phase 0,1,2..]
At the peak of T wave or at the middle of Phase 3 of ventricle
-most dangerous time to stimulate heart bec it is the when
some part of ventricle is in absolute refractory period and
some are still in the relative refractory period (there is
electrical heterogeneity in ventricle at this time)
-most vulnerable period of heart
so if you have PVC that occurred at peak of T wave, thats
the most dangerous PVC= can trigger malignant arrythmia
which can kill instantaneously
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 7 of 8
ARRYTHMIA (Part II) 2014 -2015
Dr. Payawal
CLASS 1B
o most popular: Lidocane (also use for local anesthesia)
o for ventricular arrythmias
o only available here: lidocane. tocalnide
o do not use lidocaine routinely for it can cause bradycardia
-> asystole
CLASS 1C
o only available here:flocainide, propafenone
o oral form
o only recommended for supraventricular arrythmias
CLASS 2 (Beta blockers)
o one of the most utilized cardiac drugs
Accurate ecg interpretation o potent antiarrythmic (sympatolytic)
Determine cause of arrythmia o also used for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, htn
o not all arrythmias are due to cardiac pathology o for both supra and vent
o order for Ca, Na, K, Mg
-corerct electrolyte then arrythmia disappears CLASS 3
o pulmo disease( hypoxemia) o Amiodarone is widely utilized
-get O2 sat or ABG esp if you see MAT o for both supra and vent
Nature of underlying disease
-get cardiac function CLASS 4 (Ca blockers)
Consequences of arrythmia *but not all ca blockers have anti-arrythmic properties
o Asymptomatic PAC is benign: Go on with you life and take -Mifedipine: widely used but does not have anti-arrythmia;
your exams :D actually induces tachycardia
-Only give medication if has bothering Sx o Only Verapamil and Diltiazem have anti-arr but useful only
o even Tx is clinically correlated for supra
ADENOSINE
o For supra
DIGITALIS
o AF!!
Know what type of arrythmia first before giving drugs. Because
sometimes its the drug that kills.
[TAKE NOTE OF INDICATIONS. IF FOR SUPRA ONLY, FOR BOTH SUPRA
AND VENT, ETC.]
Sorry madami pages hiniwalay ko kasi per classification para madali
aralin :>
TO GOD BE ALL THE GLORY!
Traditional way of classifying anti-arrythmic drugs
CLASS 1A
o prolong QT interval
o already banned in first world countries
o monitor Px QTc. If prolonged: stop or dec. dose
o for supra and ventricular arrythmias
Magno Opere Somnia Dura Page 8 of 8
Вам также может понравиться
- Congestive Heart Failure - Dra. DeduyoДокумент10 страницCongestive Heart Failure - Dra. DeduyoMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Acute Coronary Syndrome - Dra. Deduyo PDFДокумент6 страницAcute Coronary Syndrome - Dra. Deduyo PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Infective Endocarditis - Dr. Payawal PDFДокумент6 страницInfective Endocarditis - Dr. Payawal PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Diseases of the Aorta: Causes and Types of Aortic AneurysmsДокумент11 страницDiseases of the Aorta: Causes and Types of Aortic AneurysmsMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Valvular Heart Diseases Part 1 - Dr. BartolomeДокумент18 страницValvular Heart Diseases Part 1 - Dr. BartolomeMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Coronary Artery Disease - Dra. Deduyo PDFДокумент7 страницCoronary Artery Disease - Dra. Deduyo PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Detecting Abnormal Cardiac RhythmsДокумент10 страницDetecting Abnormal Cardiac RhythmsMedisina101100% (1)
- Deep Vein Thrombosis - Dr. Deduyo PDFДокумент17 страницDeep Vein Thrombosis - Dr. Deduyo PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- ECG Part 1 - Dr. Payawal PDFДокумент10 страницECG Part 1 - Dr. Payawal PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- ECG Part 2 - Dr. Payawal PDFДокумент4 страницыECG Part 2 - Dr. Payawal PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Aortic Stenosis Symptoms and Physical Exam FindingsДокумент9 страницAortic Stenosis Symptoms and Physical Exam FindingsMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Peripheral Vascular Medicine - Dr. Deduyo PDFДокумент14 страницPeripheral Vascular Medicine - Dr. Deduyo PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Acquired Heart DiseaseДокумент44 страницыAcquired Heart DiseaseMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Cardiac Tumors Slides - Dr. BartolomeДокумент81 страницаCardiac Tumors Slides - Dr. BartolomeMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart Diseases - Dr. BartolomeДокумент12 страницCongenital Heart Diseases - Dr. BartolomeMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- SURGERY Lecture 2 - Liver & Gallbladder (Dr. Wenceslao)Документ19 страницSURGERY Lecture 2 - Liver & Gallbladder (Dr. Wenceslao)Medisina101100% (1)
- Diagnosing Chest Pain CausesДокумент8 страницDiagnosing Chest Pain CausesMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- Cardiac Tumors - Dr. BartolomeДокумент12 страницCardiac Tumors - Dr. BartolomeMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- SURGERY Lecture 4 - Breast (Dra. Fernandez)Документ15 страницSURGERY Lecture 4 - Breast (Dra. Fernandez)Medisina101100% (1)
- Pedia Pulmo I 10.4.16Документ129 страницPedia Pulmo I 10.4.16Medisina101Оценок пока нет
- Pedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Документ73 страницыPedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Medisina101Оценок пока нет
- Pedia Pulmo 3 11.03.16Документ49 страницPedia Pulmo 3 11.03.16Medisina101Оценок пока нет
- PEDIA - Cardio (Esguerra) PDFДокумент9 страницPEDIA - Cardio (Esguerra) PDFMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- External Abdominal Hernias GuideДокумент12 страницExternal Abdominal Hernias GuideMedisina101100% (1)
- Pediatric Cardiology II Lecture SummaryДокумент5 страницPediatric Cardiology II Lecture SummaryMedisina101Оценок пока нет
- SURGERY Lecture 1 - Small Intestine (Dr. Mendoza)Документ16 страницSURGERY Lecture 1 - Small Intestine (Dr. Mendoza)Medisina101100% (1)
- SURGERY Lecture 5 - Abdominal Wall, Omentum, Mesentery, Retroperitoneum (Dr. Wenceslao)Документ13 страницSURGERY Lecture 5 - Abdominal Wall, Omentum, Mesentery, Retroperitoneum (Dr. Wenceslao)Medisina101Оценок пока нет
- Surgery II - Pancreas 2014Документ20 страницSurgery II - Pancreas 2014Medisina101Оценок пока нет
- Head and Neck SurgeryДокумент15 страницHead and Neck SurgeryMedisina101100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Cardioembolic StrokeДокумент13 страницCardioembolic StrokeAzarel JimmyОценок пока нет
- CardiologyДокумент88 страницCardiologyAlshare NisreenОценок пока нет
- Symptoms, Types and Risk Factors of StrokesДокумент12 страницSymptoms, Types and Risk Factors of StrokesReymund Timog TalarocОценок пока нет
- Pediatric ECG Survival Guide - 2nd - May 2019Документ27 страницPediatric ECG Survival Guide - 2nd - May 2019Marcos Chusin MontesdeocaОценок пока нет
- Phlebitis and ThrombophlebitisДокумент27 страницPhlebitis and ThrombophlebitisSushant SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Polyclinic AllДокумент92 страницыPolyclinic AllFatima ShahОценок пока нет
- Mitral Stenosis Etiology and TreatmentДокумент19 страницMitral Stenosis Etiology and TreatmentAdi TrisnoОценок пока нет
- AdenosineДокумент2 страницыAdenosinejdmedicОценок пока нет
- PMR Poster TBI Takotsubo AAP 2010 PosterДокумент1 страницаPMR Poster TBI Takotsubo AAP 2010 PosterjuanvelasquezОценок пока нет
- By Dr.B.S.Koushika.,B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu) Dept of Panchakarma, SJSACH, ChennaiДокумент55 страницBy Dr.B.S.Koushika.,B.A.M.S, M.D (Ayu) Dept of Panchakarma, SJSACH, ChennaiAyurvriksha100% (4)
- Morgan 2012Документ5 страницMorgan 2012aixacamila3Оценок пока нет
- Cartlidge Timothy Role of Percutaneous CoronaryДокумент7 страницCartlidge Timothy Role of Percutaneous Coronarybruno baileyОценок пока нет
- Aortic RegurgitationДокумент18 страницAortic RegurgitationAbdur RaqibОценок пока нет
- Vesalio Initiates Clinical Study Evaluating Innovative Thrombectomy Technique For Patients With STEMIДокумент3 страницыVesalio Initiates Clinical Study Evaluating Innovative Thrombectomy Technique For Patients With STEMIPR.comОценок пока нет
- Doppler-Atlas Stroke ManagementДокумент7 страницDoppler-Atlas Stroke ManagementdanielОценок пока нет
- 12 Lead EKG 101Документ84 страницы12 Lead EKG 101Clarke KrugmanОценок пока нет
- CM3 - Cu12 Assessment of Heart & Neck VesselsДокумент15 страницCM3 - Cu12 Assessment of Heart & Neck Vesselseli pascualОценок пока нет
- ACS DR Rini PramestiДокумент52 страницыACS DR Rini PramestiJackSaripantungОценок пока нет
- The Six Step Method of Interpreting EcgsДокумент3 страницыThe Six Step Method of Interpreting EcgsSivakumar Gounden100% (1)
- Hubungan Neutrophyl To Lymphocyte Ratio Dengan Derajat Disfungsi Diastolik Pada Pasien HipertensiДокумент7 страницHubungan Neutrophyl To Lymphocyte Ratio Dengan Derajat Disfungsi Diastolik Pada Pasien HipertensiLutfhi ArshaldoОценок пока нет
- The Muscle Blood Flow and Coronary CirculationДокумент16 страницThe Muscle Blood Flow and Coronary CirculationMaxamed Faarax XaashiОценок пока нет
- Walking For A Healthy Heart: How To Prevent Heart Failure? What Is Heart Failure?Документ1 страницаWalking For A Healthy Heart: How To Prevent Heart Failure? What Is Heart Failure?Karla SombilloОценок пока нет
- Sas 13Документ5 страницSas 13Sistine Rose LabajoОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseДокумент6 страницIschemic Heart DiseaseApril Joy Villacorta PonceОценок пока нет
- Neurology. 58 (5) : 688-97 Review and Meta-Analysis". Stroke. 47 (5) : 1253-7Документ2 страницыNeurology. 58 (5) : 688-97 Review and Meta-Analysis". Stroke. 47 (5) : 1253-7Marius FlaminzianuОценок пока нет
- Infectious Disease of The HeartДокумент3 страницыInfectious Disease of The HeartClaire GidoОценок пока нет
- Arterias FacialesДокумент23 страницыArterias FacialesDaniela GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Management of Perioperative ArrhythmiasДокумент51 страницаManagement of Perioperative ArrhythmiasAbhishek LonikarОценок пока нет
- 9501-001-50 REV H1 Physicians GuideДокумент54 страницы9501-001-50 REV H1 Physicians GuidejimurgaОценок пока нет
- Aortic Dissection ExplainedДокумент2 страницыAortic Dissection ExplainedIka MelaniaОценок пока нет