Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Switching and Queuing Delay Models 248
Загружено:
rohitАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Switching and Queuing Delay Models 248
Загружено:
rohitАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ivan Marsic Rutgers University 238
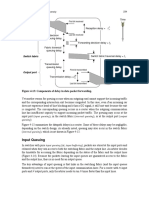
Arrival times sequence Departure times sequence
C3
C2 C1 C2 C3
C1 Server
:17
:41
:00
:05
10 9
:00
:00
:29
:00
:13
:0
10
10
10
10
10
11
10
10
11
Time Time
Figure 4-18: Illustration of how queues are formed. The server can serve 5 customers per
hour and only 3 customers arrive during an hour period. Although the server capacity is
greater than the arrival rate, some customers may still need to wait before being served,
because their arrivals are too closely spaced.
sequence arrived at a server that can service only four customers per hour, again there would be
queuing delays. Thus, having a server with service rate greater than the arrival rate is no
guarantee that there will be no queuing delays. In summary, queuing results because packet
arrivals cannot be preplanned and provisioned forit is too costly or physically impossible to
support peak arrival rates.
Note also that in the steady state, the average departure rate equals the average arrival rate. Server
utilization = (arrival rate / max. service rate)
Communication Channel
Queuing delay is the time it takes to transmit the packets that arrived earlier at the network
interface. Packets service time is its transmission time, which is equal to L/C, where L is the
packet length and C is the server capacity. In case of packet transmission, server capacity is the
outgoing channel capacity. The average queuing time is typically a few transmission times,
depending on the load of the network.
()_____) delay capacity 1
Another parameter that affects delay is error rateerrors result in retransmissions, which
significantly influence the delay. Reliable vs. unreliable (if error correction is employed +
Gaussian channel)
We study what are the sources of delay and try to estimate its amount. In a communication
system, main delay contributors are (see Section 1.3):
Processing (e.g., conversion of a stream of bytes to packets or packetization,
compression/fidelity reduction, encryption, switching at routers, etc.)
Queuing, due to irregular packet arrivals, sometimes too many, sometimes just few
Transmission, converting the digital information into analog signals that travel the
medium
Propagation, signals can travel at most at the speed of light, which is finite
Errors or loss in transmission or various other causes (e.g., insufficient buffer space in
routers, recall Figure 2-11 for TCP), resulting in retransmission
Вам также может понравиться
- Switching and Queuing Delay Models 251Документ1 страницаSwitching and Queuing Delay Models 251rohitОценок пока нет
- Switching and Queuing Delay Models 247Документ1 страницаSwitching and Queuing Delay Models 247rohitОценок пока нет
- Switching and Queuing Delay Models 244Документ1 страницаSwitching and Queuing Delay Models 244rohitОценок пока нет
- Identifying The Firmware of A Qlogic or Emulex FC HBAДокумент2 страницыIdentifying The Firmware of A Qlogic or Emulex FC HBArohitОценок пока нет
- Switching and Queuing Delay Models 234Документ1 страницаSwitching and Queuing Delay Models 234rohitОценок пока нет
- Asset Management GuidelinesДокумент9 страницAsset Management GuidelinesrohitОценок пока нет
- Packet FragmentationДокумент15 страницPacket FragmentationrohitОценок пока нет
- Opmanager Best Practices, Tips, TricksДокумент40 страницOpmanager Best Practices, Tips, TricksrohitОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Rain Fading - Kizer - Rev BДокумент39 страницRain Fading - Kizer - Rev Btavakoli_communicationОценок пока нет
- SidekickQuickGuide enДокумент2 страницыSidekickQuickGuide enalogeno_Оценок пока нет
- Digital Booklet - Human AgainДокумент6 страницDigital Booklet - Human AgainStephanie Linsdell100% (1)
- Small Steps 2m DДокумент4 страницыSmall Steps 2m DJose Edmond RoldanОценок пока нет
- Nancy Drew 19 - The Haunting of Castle Malloy WalkthroughДокумент33 страницыNancy Drew 19 - The Haunting of Castle Malloy WalkthroughayukОценок пока нет
- GHJNBBДокумент38 страницGHJNBBAngelica M. ManagaОценок пока нет
- C'est Si BonДокумент1 страницаC'est Si BonBill Swing0% (1)
- The Wireless Revolution: © 2006 by Prentice HallДокумент36 страницThe Wireless Revolution: © 2006 by Prentice HallMicku SinghОценок пока нет
- Lora / Lorawan Tutorial 1: Iot, Lpwan, Semtech, LoraДокумент13 страницLora / Lorawan Tutorial 1: Iot, Lpwan, Semtech, LoragamdounОценок пока нет
- Guide To Comcast Remote ModsДокумент2 страницыGuide To Comcast Remote ModsinnerlogikОценок пока нет
- Schneider Conext XW 5548 Inverter Installation Manual 2118445606.2430023 1Документ170 страницSchneider Conext XW 5548 Inverter Installation Manual 2118445606.2430023 1torrencial07Оценок пока нет
- Appendix A - Basic Feature of English PronunciationДокумент7 страницAppendix A - Basic Feature of English PronunciationAndrewGlanvilleОценок пока нет
- RealismДокумент23 страницыRealismIrish ReyesОценок пока нет
- Gatecounsellor: Ec: Electronics & Communication EngineeringДокумент17 страницGatecounsellor: Ec: Electronics & Communication EngineeringRoshan JayswalОценок пока нет
- FATE - Blake's 7Документ11 страницFATE - Blake's 7TОценок пока нет
- McIntosh MAC-4200 Owners ManualДокумент28 страницMcIntosh MAC-4200 Owners ManualSaleem AhmadОценок пока нет
- Optical Transport NetworksДокумент18 страницOptical Transport Networksshahramkarimi76Оценок пока нет
- IMSLP23776 PMLP54151 Forsyth Viola ConcertoДокумент9 страницIMSLP23776 PMLP54151 Forsyth Viola ConcertoVazal Van Tacet100% (1)
- Pro Audio SecretsДокумент61 страницаPro Audio Secretsrahul jangidОценок пока нет
- Modern Music InstrumentДокумент21 страницаModern Music InstrumentMuhammad Salehuddin TalibОценок пока нет
- Muck Globe MagazineДокумент14 страницMuck Globe MagazineAlexandru Pătrașcu100% (1)
- AOC+Service+Manual+HP W17e,+HP A13+Monitor+LcdДокумент120 страницAOC+Service+Manual+HP W17e,+HP A13+Monitor+LcdVicente Malvica50% (2)
- Hard Times Short SummaryДокумент3 страницыHard Times Short SummarySanja GorgievaОценок пока нет
- Huawei 2g HandoverДокумент101 страницаHuawei 2g HandoverÖmer Albat100% (3)
- Jackie Chan (成龙): By: Austin HwaДокумент26 страницJackie Chan (成龙): By: Austin HwaAustin HwaОценок пока нет
- DeLong Phrasing SampleДокумент13 страницDeLong Phrasing SampleCardician7100% (2)
- Jobs and OccupationsДокумент2 страницыJobs and OccupationsmemoinrealifeОценок пока нет
- SWIC Catalog2009Документ388 страницSWIC Catalog2009Josh StutsmanОценок пока нет
- Pico Cell Planning Design and InstallationДокумент32 страницыPico Cell Planning Design and InstallationWong_Hong_WeiОценок пока нет
- Cinemas and FilmsДокумент1 страницаCinemas and FilmsmirabikaОценок пока нет