Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2
Загружено:
Dayu Mirah0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров1 страницаThis document discusses the Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2, which examines the qualitative characteristics that make accounting information useful. It identifies relevance, reliability, and neutrality as the main qualitative characteristics. It also discusses other characteristics like comparability, consistency, materiality, and understandability. The statement separates user-specific qualities like understandability from qualities inherent in the information itself.
Исходное описание:
sa no 2
Оригинальное название
SA No 2
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses the Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2, which examines the qualitative characteristics that make accounting information useful. It identifies relevance, reliability, and neutrality as the main qualitative characteristics. It also discusses other characteristics like comparability, consistency, materiality, and understandability. The statement separates user-specific qualities like understandability from qualities inherent in the information itself.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров1 страницаStatement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2
Загружено:
Dayu MirahThis document discusses the Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2, which examines the qualitative characteristics that make accounting information useful. It identifies relevance, reliability, and neutrality as the main qualitative characteristics. It also discusses other characteristics like comparability, consistency, materiality, and understandability. The statement separates user-specific qualities like understandability from qualities inherent in the information itself.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
Ni Nyoman Tri Setya Prajayanti/1506305080
Ida Ayu Artha Widya Sari/1506305143
Made Cahyani Prastuti/1506305144
Accounting Theory EKA 441 C3*
Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2
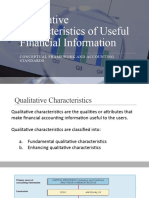
The qualitative characteristics of financial statements are useful in ensuring that
financial information is beneficial in economic decision making (FASB 1980). It requires
attribute or quality that financial information should have the main qualitative characteristics
that are relevant and reliable. Another characteristic are comparability, consistency and
materiality.
The purpose of this Statement is to examine the characteristics that make accounting
information useful. Bias Bias in measurement is the tendency of a measure to fall more often
on one side than the other of what is represents instead of being equally likely to fall on either
side. Comparability The quality of information that enables users to identify similarities in
and differences between two sets of economic phenomena. Completeness The inclusion in
reported information of everything material that is necessary for faithful representation of the
relevant phenomena. Conservatism A prudent reaction to uncertainty to try to ensure that
uncertainty and risks inherent in business situations are adequately considered. Consistency
Conformity from period to period with unchanging policies and procedures. Feedback Value
The quality of information that enables users to confirm or correct prior expectations.
Materiality The magnitude of an omission or misstatement of accounting information that, in
the light of surrounding circumstances Neutrality Absence in reported information of bias
intended to attain a predetermined result or to induce a particular mode of behavior.Predictive
Value The quality of information that helps users to increase the likelihood of correctly
forecasting the outcome of past or present events. Relevance The capacity of information to
make a difference in a decision by helping users to form predictions about the outcomes of
past, present, and future events or to confirm or correct prior expectations. Reliability The
quality of information that assures that information is reasonably free from error and bias and
faithfully represents what it purports to represent. Representational Faithfulness
Correspondence or agreement between a measure or description and the phenomenon that it
purporte to represent (sometimes called validity). Timeliness Having information available to
a decision maker before it loses its capacity to influence decisions. Understandability The
quality of information that enables users to perceive its significance. Verifiability The ability
through consensus among measurers to ensure that information represents what it purports to
represent or that the chosen method of measurement has been used without error or bias.
Accounting choices are made at two levels at least. At one level they are made by the
Board or other agencies that have the power to require business enterprises to report in some
particular way. The hierarchy separates user-specific qualities, for example, understandability,
from qualities inherent in information. Understandability of information is related to the
characteristics of the decision maker as well as the characteristics of the information itself and,
therefore, understandability cannot be evaluated in overall terms but must be judged in relation
to a specific class of decision makers.
Вам также может понравиться
- Module 1Документ3 страницыModule 1Rochelle Mae DiestroОценок пока нет
- 2 Qualitative Characteristics of Financial InformationДокумент2 страницы2 Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Informationapi-299265916Оценок пока нет
- Qualitative Characteristics of Financial InformationДокумент2 страницыQualitative Characteristics of Financial InformationHamza AlBulushiОценок пока нет
- W2 Module 4 Conceptual Framework Andtheoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 2Документ3 страницыW2 Module 4 Conceptual Framework Andtheoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 2leare ruazaОценок пока нет
- Framework For FRДокумент11 страницFramework For FRDeep JoshiОценок пока нет
- Dembe Dangale 08ha1900848 Accounting Principles (Hacp130-1) Summative Assessment 2Документ4 страницыDembe Dangale 08ha1900848 Accounting Principles (Hacp130-1) Summative Assessment 2dangale418Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual FrameworkДокумент45 страницConceptual FrameworkKendall JennerОценок пока нет
- (English (Auto-Generated) ) Auditing and Assurance Services - Auditing (DownSub - Com)Документ20 страниц(English (Auto-Generated) ) Auditing and Assurance Services - Auditing (DownSub - Com)trangdoan.31221023445Оценок пока нет
- Conceptual FrameworkДокумент8 страницConceptual Frameworkcessyyyy12Оценок пока нет
- Glosario en InglesДокумент10 страницGlosario en InglesGinna Fernanda CUBILLOS GONZALEZОценок пока нет
- Conceptual FrameworkДокумент8 страницConceptual FrameworkHashi OrloОценок пока нет
- SFAC No 8Документ1 страницаSFAC No 8Dessy Tri BhuwanaОценок пока нет
- bài tập kiểm toánДокумент2 страницыbài tập kiểm toántrangdoan.31221023445Оценок пока нет
- 8th Week Qualitative CharacteristicsДокумент13 страниц8th Week Qualitative CharacteristicsMikaela CatimbangОценок пока нет
- 02 Qualititive Characteristics of Financial InformationДокумент19 страниц02 Qualititive Characteristics of Financial InformationBelle VillaroelОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Conceptual FrameworkДокумент49 страницModule 2 Conceptual FrameworkNicole ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK - Qualitative CharacteristicsДокумент7 страницCONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK - Qualitative CharacteristicsAllaine ElfaОценок пока нет
- Quality of Financial ReportingДокумент7 страницQuality of Financial ReportingRafiullah MangalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Conceptual Framework Qualitative CharacteristicsДокумент4 страницыChapter 3 Conceptual Framework Qualitative CharacteristicsEllen MaskariñoОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Good Accounting InformationДокумент1 страницаCharacteristics of Good Accounting Informationramakrishna Bandi120Оценок пока нет
- Qualitative CharactetisticsДокумент9 страницQualitative CharactetisticsKristina Angelina ReyesОценок пока нет
- The FASB Identi-WPS OfficeДокумент2 страницыThe FASB Identi-WPS OfficeJes SelОценок пока нет
- Conceptual Framework Module 2Документ6 страницConceptual Framework Module 2Jaime LaronaОценок пока нет
- BlahtДокумент14 страницBlahtjessa mae zerdaОценок пока нет
- CFASДокумент61 страницаCFASPrinces Jamela G. AgraОценок пока нет
- Summary Enhancing Qualitative CharacteristicsДокумент3 страницыSummary Enhancing Qualitative CharacteristicsCahyani PrastutiОценок пока нет
- Data Collection and EducationДокумент13 страницData Collection and EducationNabiha ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Conceptual FrameworkДокумент33 страницыConceptual FrameworkzillxsОценок пока нет
- Financial Performance Reflected by Past Cash Flows: Pengguna UtamaДокумент3 страницыFinancial Performance Reflected by Past Cash Flows: Pengguna UtamaberrysОценок пока нет
- Cfas and Pas 1 AnswersДокумент10 страницCfas and Pas 1 AnswersFrancene Shalanda SapilanОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - Definitions J Concepts and Qualitative CharacteristicsДокумент11 страницLesson 1 - Definitions J Concepts and Qualitative Characteristicschembejosephine40Оценок пока нет
- CFAS Chapter 3 Q&AДокумент3 страницыCFAS Chapter 3 Q&ACINDY BALANONОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Characteristic Financial StatementsДокумент3 страницыQualitative Characteristic Financial StatementskathkathОценок пока нет
- Comment On The True and Fair View'. As Being An Auditor Can You Guarantee That The Financial Statements Are True and Fair?Документ2 страницыComment On The True and Fair View'. As Being An Auditor Can You Guarantee That The Financial Statements Are True and Fair?Hashir AslamОценок пока нет
- ASPL2 Activity 1n2 DoneДокумент4 страницыASPL2 Activity 1n2 DoneConcepcion FamilyОценок пока нет
- PART 2 - Financial Accounting and Reporting OverviewДокумент4 страницыPART 2 - Financial Accounting and Reporting OverviewHeidee BitancorОценок пока нет
- Qualitatative CharacteristicsДокумент15 страницQualitatative CharacteristicsMunchq NoriegaОценок пока нет
- Module 4 FarДокумент9 страницModule 4 FarCallie EllieОценок пока нет
- Conceptual Framework Qualitative CharacteristicДокумент99 страницConceptual Framework Qualitative CharacteristicXander Clock0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - ConframeДокумент6 страницChapter 2 - ConframeNow OnwooОценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet - Module 2Документ4 страницыActivity Sheet - Module 2Elisabeth HenangerОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Characteristics of Useful Financial InformationДокумент12 страницQualitative Characteristics of Useful Financial InformationLayla MainОценок пока нет
- Conceptual Framwork - Qualitative CharacteristicsДокумент11 страницConceptual Framwork - Qualitative Characteristicsmhel cabigonОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Financial ReportingДокумент7 страницQualitative Financial ReportingarshadОценок пока нет
- Karakteristik InformasiДокумент2 страницыKarakteristik InformasiAnis Dwi LestariОценок пока нет
- ACCY 305 Assignment (Complete)Документ16 страницACCY 305 Assignment (Complete)Bella SeahОценок пока нет
- Who Are The Users of Accounting Information and How Do They Benefit From This Information?Документ4 страницыWho Are The Users of Accounting Information and How Do They Benefit From This Information?Marco PaulОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 SummaryДокумент3 страницыChapter 3 SummaryXiaoyu KensameОценок пока нет
- Financial Reporting StandardsДокумент2 страницыFinancial Reporting StandardsAngeline BautistaОценок пока нет
- Tugas AKM 2Документ7 страницTugas AKM 2muhammad alif dzakiОценок пока нет
- The Objective of General Purpose Financial ReportingДокумент86 страницThe Objective of General Purpose Financial ReportingAlex liaoОценок пока нет
- Copy - 2 - of Principles of Accounting Note Year 1Документ213 страницCopy - 2 - of Principles of Accounting Note Year 1Rexford Atta-boakye JnrОценок пока нет
- Task 1:: Fundamental Accounting ConceptsДокумент24 страницыTask 1:: Fundamental Accounting Conceptsisha_fagar008Оценок пока нет
- Auditing and Assurance Services Learning ObjectivesДокумент15 страницAuditing and Assurance Services Learning Objectiveshuma1208Оценок пока нет
- Informatics and Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators: Name Institution Date CourseДокумент5 страницInformatics and Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators: Name Institution Date CourseKevin SangОценок пока нет
- 01 JournalДокумент5 страниц01 Journalits me keiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Qualitative CharacteristicsДокумент15 страницChapter 3 Qualitative CharacteristicsMicsjadeCastilloОценок пока нет
- Pengaruh Financial Distress, Komite Audit Dan Spesialisasi Industri Auditor Terhadap Integritas Laporan KeuanganДокумент12 страницPengaruh Financial Distress, Komite Audit Dan Spesialisasi Industri Auditor Terhadap Integritas Laporan Keuangandeny asgarОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingДокумент9 страницModule 2 Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingVivo V27Оценок пока нет
- Financial Intelligence: Mastering the Numbers for Business SuccessОт EverandFinancial Intelligence: Mastering the Numbers for Business SuccessОценок пока нет
- Laporan Penjualan Dwijaya Desember 2019Документ70 страницLaporan Penjualan Dwijaya Desember 2019Dayu MirahОценок пока нет
- Uji HeteroskedastisitasДокумент5 страницUji HeteroskedastisitasDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- Sap ViraДокумент3 страницыSap ViraDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- UnknownДокумент20 страницUnknownDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- How SAK ETAP To Be Implemented in LPDДокумент5 страницHow SAK ETAP To Be Implemented in LPDDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- Jawaban MetodДокумент2 страницыJawaban MetodDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ21 страницаChapter 5Dayu MirahОценок пока нет
- Flight Date Depart Arrive PriceДокумент1 страницаFlight Date Depart Arrive PriceDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- Etika Bisnis Chapter 8Документ20 страницEtika Bisnis Chapter 8Dayu MirahОценок пока нет
- The Case StudyДокумент7 страницThe Case StudyDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- International Trade and Indonesia'S Balance of PaymentsДокумент34 страницыInternational Trade and Indonesia'S Balance of PaymentsDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- 2.1 The Objective of General Purpose Financial ReportingДокумент10 страниц2.1 The Objective of General Purpose Financial ReportingDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- Model Development Models Are Representations of Real Objects or Situations and Can Be Presented in Various Forms. ForДокумент2 страницыModel Development Models Are Representations of Real Objects or Situations and Can Be Presented in Various Forms. ForDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- New Doc 2017-09-19Документ4 страницыNew Doc 2017-09-19Dayu MirahОценок пока нет
- BPHTB CaseДокумент2 страницыBPHTB CaseDayu MirahОценок пока нет
- IPTV PresentationДокумент21 страницаIPTV PresentationHiren ChawdaОценок пока нет
- Catalog VaneДокумент16 страницCatalog VanehbcbmwtuningОценок пока нет
- CL 263 CertДокумент3 страницыCL 263 CertS SHALUОценок пока нет
- Computer Hardware & NetworkingДокумент6 страницComputer Hardware & Networkingmansha99Оценок пока нет
- J4500 (2012 Technical Specifications)Документ2 страницыJ4500 (2012 Technical Specifications)Philippine Bus Enthusiasts SocietyОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент5 страницAssignmentnaya inboxОценок пока нет
- Automatic Distillation UnitДокумент8 страницAutomatic Distillation UnitAlexander Amado QuinteroОценок пока нет
- Positive Displacement Dosing Pump: The Right Dosing ChoiceДокумент12 страницPositive Displacement Dosing Pump: The Right Dosing ChoiceTrungGVОценок пока нет
- Network Topology NoteДокумент12 страницNetwork Topology NoteHaftamu HailuОценок пока нет
- Script (Powerpoint)Документ7 страницScript (Powerpoint)Laurence Niña X. OrtizОценок пока нет
- School FEE Management: Class:-XII-A Roll NoДокумент29 страницSchool FEE Management: Class:-XII-A Roll Nochirag jainОценок пока нет
- User Manual For CommunicationДокумент28 страницUser Manual For CommunicationAdi kurniantoОценок пока нет
- Of The Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (KTA)Документ41 страницаOf The Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (KTA)Ehab MohamedОценок пока нет
- 2 Ic695acc400Документ4 страницы2 Ic695acc400MUHAMMAD TAUFIQОценок пока нет
- JavaДокумент1 331 страницаJavaKarthik NarayanaОценок пока нет
- ISO14120 2015 - Guards - Troax - Theguide - Direktiv - en - 0Документ11 страницISO14120 2015 - Guards - Troax - Theguide - Direktiv - en - 0Carlos Moreno100% (1)
- Beckhoff EtherCATДокумент30 страницBeckhoff EtherCATjoshi_ragsОценок пока нет
- S62 EngineДокумент26 страницS62 EngineALJASMI78Оценок пока нет
- PEC (Phil Elec. Code) (By JVM) - Part-1Документ56 страницPEC (Phil Elec. Code) (By JVM) - Part-1aluism50% (2)
- Uganda Management Institute Vacancies Announcement: ND ND THДокумент4 страницыUganda Management Institute Vacancies Announcement: ND ND THtaabuОценок пока нет
- Using External Data Integration Services R10Документ47 страницUsing External Data Integration Services R10gule29Оценок пока нет
- Data Kamag 2400Документ4 страницыData Kamag 2400titieОценок пока нет
- Dealing With Construction Permits in TurkeyДокумент5 страницDealing With Construction Permits in Turkeysmimtiaz8958Оценок пока нет
- Datasheet URM37Документ8 страницDatasheet URM37Thơm PhùngОценок пока нет
- High Performance FTTA Site SolutionsДокумент20 страницHigh Performance FTTA Site SolutionsAbdeladhim StichОценок пока нет
- GSM KPI Flow Chart ProcessДокумент12 страницGSM KPI Flow Chart ProcessTawfiq Al-QershiОценок пока нет
- Cellular 0.5W RF Repeater User Manual 1 - 0Документ57 страницCellular 0.5W RF Repeater User Manual 1 - 0Mithun GhoshОценок пока нет
- NETW310 WEEK 2 IlabДокумент2 страницыNETW310 WEEK 2 Ilabkicker1time100% (1)
- VAL - 170401 - BMAA VAL Activity 3 URS - Template PDFДокумент10 страницVAL - 170401 - BMAA VAL Activity 3 URS - Template PDFDineshОценок пока нет
- DD Env 1991 1 1996Документ67 страницDD Env 1991 1 1996Vishwakarma VishwakarmaОценок пока нет