Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Rotation Equations Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
Roberto MartinezАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Rotation Equations Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
Roberto MartinezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
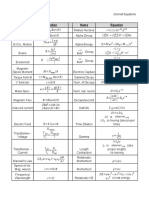
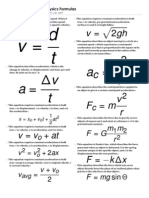
Linear (Translational) vs.
Angular (Rotational) Motion
concept linear conversion angular notes
rev.2011.08.05
C=2r
position x (in meters) x=r (in radians)
= theta
v=r v=r
velocity v (in m/s) (in rad/s) = omega
(no slipping)
a=r
acceleration a (in m/s2) (in rad/s2) = alpha
Physics A: Foundations of College Physics
a=v+r
net force = F = 0, net torque = = 0, = capital gamma
Newtons 1st
Physics A: Foundations of College Physics
v = constant = constant or = tau
I = mi ri2
inertia m (in kg) = ICM + mT r2 I = k m r2 (in kgm2) k depends on shape
(Parallel Axis Theorem)
= r F (as vector)
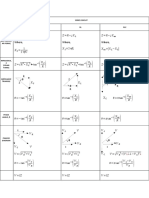
Linear vs. Angular Reference Table
Newtons 2nd F=ma =I
= F x= F r sin
Newtons 3rd action-reaction forces action-reaction torques
2
x = xo + vo t + a t = o + o t + t2
kinetic motion v = vo + a t = o + t
2 2
v = vo2 + 2 a (x xo) = o2 + 2 ( o)
Orig Material 2004-2011 S.T.Randall
kinetic energy KE = EKT = m v2 KE = EKR = I 2 x
W = F x (as vector)
work W =
W = EW = F x
power P = EW / t = F v P=
L=rp=rmv
L = I (rigid body)
momentum p=mv L = r p = r m v = m r 2
L = net t
(single point in rotation)
6022
Module 6
Вам также может понравиться
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64От EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64Оценок пока нет
- Moment of Inertia and TorqueДокумент12 страницMoment of Inertia and TorqueMary Rhose VidalloОценок пока нет
- Physics NotesДокумент12 страницPhysics NotesMary Rhose VidalloОценок пока нет
- Equations+Sheet DynamicsДокумент1 страницаEquations+Sheet DynamicsMamon HoroubОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion: T 2π r T holdsДокумент13 страницCircular Motion: T 2π r T holdsUti MichaelОценок пока нет
- Formula SheetДокумент6 страницFormula SheetpaulineannedimapilisОценок пока нет
- Midterm Review PDFДокумент16 страницMidterm Review PDFMt RushОценок пока нет
- Formula Lab Sheet - 1p22 PDFДокумент2 страницыFormula Lab Sheet - 1p22 PDFRoy VeseyОценок пока нет
- Formulae FOR Numericals: PhysicsДокумент5 страницFormulae FOR Numericals: PhysicsLuciferОценок пока нет
- 139514485-YCT Oscillations NEET JEE Questions PracticeДокумент219 страниц139514485-YCT Oscillations NEET JEE Questions PracticeRamesh R ReddyОценок пока нет
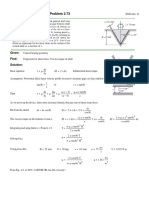
- Problem 2.73: Given: Find: SolutionДокумент1 страницаProblem 2.73: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoОценок пока нет
- AEP 3330 Final - Some EquationsДокумент1 страницаAEP 3330 Final - Some EquationsJesse ZhangОценок пока нет
- Graphs PracticeДокумент1 страницаGraphs Practicesoumyaranjansahoo7008Оценок пока нет
- Formula SheetДокумент14 страницFormula SheetQER TUGОценок пока нет
- CM Ext, Tot CM CM CM CM CM Ext, Tot Ext, Tot 0 I I CMДокумент4 страницыCM Ext, Tot CM CM CM CM CM Ext, Tot Ext, Tot 0 I I CMsudhildeyОценок пока нет
- PreAcaMath 18S0 Lecture1 - 0 PDFДокумент2 страницыPreAcaMath 18S0 Lecture1 - 0 PDFKaveesha DinamiduОценок пока нет
- Physics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Документ15 страницPhysics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Chetan SainiОценок пока нет
- AP1 Rotational Motion Presenter W Answers PDFДокумент34 страницыAP1 Rotational Motion Presenter W Answers PDFMisakiОценок пока нет
- Physics FormulasДокумент10 страницPhysics FormulasFaith Laurence SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Taken Time Total NT Displaceme Total T R R : Slop e AДокумент5 страницTaken Time Total NT Displaceme Total T R R : Slop e AsatyamОценок пока нет
- Physics Formula: Topic Phase-1Документ13 страницPhysics Formula: Topic Phase-1testerОценок пока нет
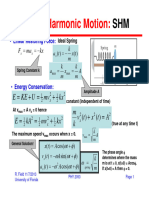
- CH2.2b Harmonic Motion AДокумент4 страницыCH2.2b Harmonic Motion AkhaledОценок пока нет
- Wave Motion Short Notes65dd7338188cf00018e54b2bДокумент2 страницыWave Motion Short Notes65dd7338188cf00018e54b2bDevansh BansalОценок пока нет
- Differentiation of Vectors: 4.1 Vector-Valued FunctionsДокумент17 страницDifferentiation of Vectors: 4.1 Vector-Valued FunctionsMirabella AstraОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheet Physics 220 PDFДокумент6 страницFormula Sheet Physics 220 PDFNimish RamtekeОценок пока нет
- Introduccion Teoria Perturbaciones Juan PabloДокумент29 страницIntroduccion Teoria Perturbaciones Juan PabloCarlos Alberto Meza MoralesОценок пока нет
- Vector Derivatives: Ds DX 1 ( Det G)Документ5 страницVector Derivatives: Ds DX 1 ( Det G)Peter He ZhengОценок пока нет
- Formulae You Should Know For TN2421 (2018) : Wave OpticsДокумент1 страницаFormulae You Should Know For TN2421 (2018) : Wave OpticsBenodОценок пока нет
- AFM - 10,12 NovДокумент12 страницAFM - 10,12 Novswetapriya97Оценок пока нет
- Ec1 FormulaДокумент10 страницEc1 Formulaborja familyОценок пока нет
- Simple Harmonic Motion:: KX MV U KE E A T X T V K MДокумент8 страницSimple Harmonic Motion:: KX MV U KE E A T X T V K Msoonh jatoiОценок пока нет
- Lecture - 7 StudentДокумент12 страницLecture - 7 Studenturdustories610Оценок пока нет
- Formula SheetДокумент1 страницаFormula SheetMama PigОценок пока нет
- SERIESДокумент2 страницыSERIESkhaito K5Оценок пока нет
- TUT - 06 WorksheetДокумент10 страницTUT - 06 WorksheetSamiul Alam KhanОценок пока нет
- Bahan Kukiah Matematika Ekonomi Lanjutan Prof. Nachrowi Djalal Nachrowi, PHDДокумент3 страницыBahan Kukiah Matematika Ekonomi Lanjutan Prof. Nachrowi Djalal Nachrowi, PHDKusnadi SPdОценок пока нет
- Time Independent Schrodinger's Equation: Stationary StatesДокумент1 страницаTime Independent Schrodinger's Equation: Stationary StatesAbhishek SharmaОценок пока нет
- Basics: TransformsДокумент3 страницыBasics: TransformsYoussef HaouchatОценок пока нет
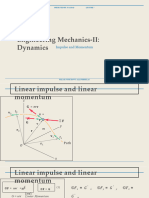
- Dynamics Coursera1Документ16 страницDynamics Coursera1Subhro RoyОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Formu PDFДокумент2 страницыFinal Exam Formu PDFJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowОценок пока нет
- Formulae SheetДокумент4 страницыFormulae SheetOMARОценок пока нет
- 2 ND Half Equation SheetДокумент3 страницы2 ND Half Equation SheetMatt CaponeОценок пока нет
- Formulas FinalДокумент2 страницыFormulas FinalTam AdıОценок пока нет
- MainДокумент2 страницыMainIngoОценок пока нет
- HKPHO Booklet2 en PDFДокумент48 страницHKPHO Booklet2 en PDFMan SanОценок пока нет
- Lecture13 PDFДокумент10 страницLecture13 PDFDeril_RistianiОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of A Particle Live Class-4 Teacher Notes PDFДокумент45 страницKinematics of A Particle Live Class-4 Teacher Notes PDFANSHUMAN GHUGHUTIYALОценок пока нет
- BSC, HS23 - CheatSheet LinAlg.Документ6 страницBSC, HS23 - CheatSheet LinAlg.sakoy30708Оценок пока нет
- Equation SheetДокумент2 страницыEquation SheethiyoОценок пока нет
- Materi Kuliah 7Документ20 страницMateri Kuliah 7Ikhsan PrasetyoОценок пока нет
- Vacuum PolarizationДокумент95 страницVacuum PolarizationQUAH KAH CHUN UPSIОценок пока нет
- Pdf. AP Physics C Mechanics Comprehensive Equations GuideДокумент7 страницPdf. AP Physics C Mechanics Comprehensive Equations GuideJohn McEnroeОценок пока нет
- Metc SesiuneДокумент10 страницMetc SesiuneRazvan 888Оценок пока нет
- Rotation QuantitiesДокумент2 страницыRotation QuantitiesChris DackowОценок пока нет
- Exam3 FormulasДокумент1 страницаExam3 FormulasJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowОценок пока нет
- Lecture 14+16marchДокумент35 страницLecture 14+16marchAd EverythingОценок пока нет
- Physics FormulasДокумент3 страницыPhysics FormulasJames Patrick TorresОценок пока нет
- Binder 1Документ153 страницыBinder 1selaroth168Оценок пока нет
- Summary of Velocity, Acceleration, and CurvatureДокумент1 страницаSummary of Velocity, Acceleration, and CurvatureJohn NelsonОценок пока нет
- Definition of The Trig Functions: Right Triangle Definition Unit Circle DefinitionДокумент4 страницыDefinition of The Trig Functions: Right Triangle Definition Unit Circle DefinitionjonahОценок пока нет
- Apuntes Circuitos ElectricosДокумент1 страницаApuntes Circuitos ElectricosRoberto MartinezОценок пока нет
- DC Motor ChopperДокумент7 страницDC Motor ChopperRoberto MartinezОценок пока нет
- Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis 8th Ed SolutionsДокумент1 254 страницыBasic Engineering Circuit Analysis 8th Ed SolutionsAndrew David Bushner87% (188)
- Cadence OrCAD 17 - 2 Installation Guide PDFДокумент8 страницCadence OrCAD 17 - 2 Installation Guide PDFRoberto MartinezОценок пока нет
- Materials Technology - Failure of Al 6061 PipesДокумент4 страницыMaterials Technology - Failure of Al 6061 PipesRoberto MartinezОценок пока нет
- Probabilidad y Estadistica - Formulario 2ndo ParcialДокумент2 страницыProbabilidad y Estadistica - Formulario 2ndo ParcialRoberto Martinez100% (1)
- Materials Technology - Team Problem #3: All That Glitters Is Not GoldДокумент5 страницMaterials Technology - Team Problem #3: All That Glitters Is Not GoldRoberto MartinezОценок пока нет
- 00-Introduccion-Conceptos Actividad 1 Rev00 PDFДокумент1 страница00-Introduccion-Conceptos Actividad 1 Rev00 PDFRoberto MartinezОценок пока нет
- Mathematica ManualДокумент157 страницMathematica Manualjf2oo6100% (1)
- Ultimate Russian Beginner-Intermediate PDFДокумент524 страницыUltimate Russian Beginner-Intermediate PDFCamarada Kolobanov100% (1)
- Short Questions-11Документ44 страницыShort Questions-11Talha MaqsoodОценок пока нет
- DC Motor QuestionsДокумент8 страницDC Motor Questionsankitj747Оценок пока нет
- Part#: 30B5TT, 30B1TT: Please Note Adapter Is Needed For The #30B5TT & #30B1TTДокумент3 страницыPart#: 30B5TT, 30B1TT: Please Note Adapter Is Needed For The #30B5TT & #30B1TTWimper SpeedОценок пока нет
- CH 9Документ85 страницCH 9Ferdinand Yohannes Van LankhorstОценок пока нет
- BIT Mesra SyllabusДокумент100 страницBIT Mesra SyllabusNikhil NigamОценок пока нет
- Chinmoy Taraphdar - The Classical Mechanics (2007)Документ241 страницаChinmoy Taraphdar - The Classical Mechanics (2007)Fernando Silva Pena100% (1)
- PLTW AR IntroToMechanismsPowerPointДокумент39 страницPLTW AR IntroToMechanismsPowerPointAbdulsalam OmotoshoОценок пока нет
- HMMMMДокумент2 страницыHMMMMNino MontaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Equivalent Systems of Forces PDFДокумент12 страницChapter 3 - Equivalent Systems of Forces PDFGabriel mongeОценок пока нет
- Osteokinematics and KineticsДокумент29 страницOsteokinematics and KineticskotraeОценок пока нет
- Week 1. Analysis of ForcesДокумент56 страницWeek 1. Analysis of Forcespauline aerielОценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Machinery Question Bank PDFДокумент10 страницDynamics of Machinery Question Bank PDFSree MurthyОценок пока нет
- Coulomb's Law ExperimentДокумент12 страницCoulomb's Law Experimentchafraed67% (3)
- MCAT Physics FormulasДокумент6 страницMCAT Physics Formulasjetone472100% (2)
- NVC in Motor Vehicle MechanicsДокумент165 страницNVC in Motor Vehicle Mechanicsoni Solomon oriireОценок пока нет
- Study of Interactive Bike Simulator in Application PDFДокумент9 страницStudy of Interactive Bike Simulator in Application PDFDIEGO ALEJANDRO PARRA GARRIDOОценок пока нет
- Torcao InelasticaДокумент10 страницTorcao InelasticaNicolli Zuchetti IacobucciОценок пока нет
- Permanent MagnetДокумент31 страницаPermanent MagnetKendra KaiserОценок пока нет
- Theory of Machines 00 An Guu of TДокумент360 страницTheory of Machines 00 An Guu of TRenso Arango100% (1)
- Engineering Science: Polytechnic Lab ManualДокумент21 страницаEngineering Science: Polytechnic Lab ManualEnth LahОценок пока нет
- Year I and Year II Applied Science Modules - Auto & Diesel (New)Документ20 страницYear I and Year II Applied Science Modules - Auto & Diesel (New)iiamakyraОценок пока нет
- Physics 40a Final Exam ReviewДокумент4 страницыPhysics 40a Final Exam ReviewRexRu100% (1)
- Right Angle Drives 1 To 1 Ratio InchДокумент11 страницRight Angle Drives 1 To 1 Ratio InchFRANCISCO JAVIER NIEVES GONZALEZОценок пока нет
- With Applications: Introduction To Stateflow®Документ522 страницыWith Applications: Introduction To Stateflow®Ksenia KuznetsovaОценок пока нет
- Capitulo 6 - Torsion en Ejes Prismaticos PDFДокумент42 страницыCapitulo 6 - Torsion en Ejes Prismaticos PDFCristian David BravoОценок пока нет
- ElectrostaticsДокумент26 страницElectrostaticsGopeshwar ShahuОценок пока нет
- Iveco Daily Repair ManualДокумент1 412 страницIveco Daily Repair ManualSzabolcs Juhasz100% (4)
- Mechanics of DB PDF 3Документ6 страницMechanics of DB PDF 3eysОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Energy and WorkДокумент15 страницKinetic Energy and WorkMahesh KumarОценок пока нет