Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
The Main Relative Pronouns Are
Загружено:
Lely0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров2 страницыAn adjective clause is used to describe a noun and is usually introduced by a relative pronoun like who, whom, which, that, or whose. There are two main types of adjective clauses: non-defining clauses, which provide extra but non-essential information about the noun and are separated by commas; and defining clauses, which provide essential information about the noun to identify which noun is being referred to and are not separated by commas. The main relative pronouns and their uses are who for humans as subjects, whom for humans as objects, which for things/animals as subjects or objects, that for humans/things/animals as subjects or objects, and whose to show possession.
Исходное описание:
Adjective Clause
Оригинальное название
Adjective Clause
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAn adjective clause is used to describe a noun and is usually introduced by a relative pronoun like who, whom, which, that, or whose. There are two main types of adjective clauses: non-defining clauses, which provide extra but non-essential information about the noun and are separated by commas; and defining clauses, which provide essential information about the noun to identify which noun is being referred to and are not separated by commas. The main relative pronouns and their uses are who for humans as subjects, whom for humans as objects, which for things/animals as subjects or objects, that for humans/things/animals as subjects or objects, and whose to show possession.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
11 просмотров2 страницыThe Main Relative Pronouns Are
Загружено:
LelyAn adjective clause is used to describe a noun and is usually introduced by a relative pronoun like who, whom, which, that, or whose. There are two main types of adjective clauses: non-defining clauses, which provide extra but non-essential information about the noun and are separated by commas; and defining clauses, which provide essential information about the noun to identify which noun is being referred to and are not separated by commas. The main relative pronouns and their uses are who for humans as subjects, whom for humans as objects, which for things/animals as subjects or objects, that for humans/things/animals as subjects or objects, and whose to show possession.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
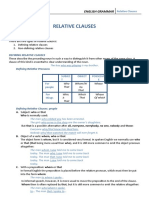
Here is a brief review of adjective clauses and relative pronouns.
An adjective clause is used to describe a noun:
The car, which was red, belonged to Young-Hee.
A relative pronoun is usually used to introduce an adjective clause:
Young-Hee, who is a Korean student, lives in Victoria.
The main relative pronouns are:
Pronoun Use Example
Hans, who is an architect, lives in
Who used for humans in the subject position
Berlin.
Marike, whom Hans knows well, is
Whom used for humans in the object position
an interior decorator.
used for things and animals in the subject or Marike has a dog which follows her
Which
object position everywhere.
used for humans, animals and things, in the Marike is decorating a house that
That
subject or object position (but see below) Hans designed.
used for humans, animals and things in the Marike, whose dog follows her
Whose
subject or object position to show possession everywhere, is an animal lover.
There are two main kinds of adjective clause:
1. Non-defining clauses
Non-defining clauses give extra information about the noun, but they are not essential:
The desk in the corner, which is covered in books, is mine.
Explanation: We don't need this information in order to understand the sentence. The desk in
the corner is mine is a good sentence on its own we still know which desk is referred to.
Note that non-defining clauses are usually separated by commas, and that is not usually used
in this kind of context.
2. Defining clauses
Defining clauses give essential information about the noun:
The package that arrived this morning is on the desk.
Explanation: We need this information in order to understand the sentence. Without the relative
clause, we don't know which package is being referred to. Note that that is often used in
defining relative clauses, and they are not separated by commas.
When you are sure that you understand the lesson, you can continue with the exercises.
Вам также может понравиться
- Examples of Adjective ClausesДокумент3 страницыExamples of Adjective ClausesSahara GerraldiОценок пока нет
- GuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarОт EverandGuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Adjective ClausesДокумент3 страницыAdjective ClausesArifОценок пока нет
- Adjective Clauses: The Main Relative Pronouns AreДокумент2 страницыAdjective Clauses: The Main Relative Pronouns AretanedraОценок пока нет
- Adjective Clauses ExplainedДокумент11 страницAdjective Clauses ExplainedArimu MusarofahОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses With or WithoutДокумент2 страницыRelative Clauses With or Withoutopatro100% (1)
- Adjectives ClausesДокумент15 страницAdjectives ClausesCristian MartinezОценок пока нет
- Study Zone - IntermediateДокумент88 страницStudy Zone - IntermediateAisy AstarinaОценок пока нет
- Exemples - Relative Pronouns - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryДокумент10 страницExemples - Relative Pronouns - English Grammar Today - Cambridge Dictionaryclotildeta100% (1)
- 2 Série EMMV - Relative Pronouns - Theory - 2ºTRI 2022teacher Robson FernandesДокумент4 страницы2 Série EMMV - Relative Pronouns - Theory - 2ºTRI 2022teacher Robson FernandesGabriel SantosОценок пока нет
- 1 Alberto Relative Clauses TheoryДокумент2 страницы1 Alberto Relative Clauses Theoryyvonne carlileОценок пока нет
- Adjective Clauses and Relative Pronouns ExplainedДокумент3 страницыAdjective Clauses and Relative Pronouns ExplainedOsvaldo SolisОценок пока нет
- Relative Pronouns: WhoДокумент10 страницRelative Pronouns: WhoLenni KurniaОценок пока нет
- Relative ClausesДокумент4 страницыRelative ClausesRoxana BalcescuОценок пока нет
- Relative PronounsДокумент8 страницRelative PronounsRutОценок пока нет
- Relative PronounsДокумент5 страницRelative PronounsClaudio100% (1)
- Unit 2. Relative Clause. Theory and ExercisesДокумент10 страницUnit 2. Relative Clause. Theory and Exercisesizasbj100% (1)
- Grammar - Relative PronounsДокумент24 страницыGrammar - Relative PronounsDivanildo De Oliveira Ramos JuniorОценок пока нет
- Relative ClausesДокумент11 страницRelative Clausessaeed100% (1)
- Members List and Relative Clause BasicsДокумент12 страницMembers List and Relative Clause Basicsjohann worbisОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses: English GrammarДокумент10 страницRelative Clauses: English GrammarDr MontyОценок пока нет
- Pronouns and AdjectivesДокумент11 страницPronouns and AdjectivesMiguel Reis CarvalhoОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses ExplainedДокумент21 страницаRelative Clauses ExplainedPhúc ThịnhОценок пока нет
- Relative PronounДокумент7 страницRelative Pronounnato.kharshiladze.1Оценок пока нет
- The Passive Voice SummaryДокумент5 страницThe Passive Voice SummaryJavier LeonОценок пока нет
- Ud5 Comunicacion Prof InglesДокумент25 страницUd5 Comunicacion Prof InglesJose Miguel Ortega AndresОценок пока нет
- Relative ClausesДокумент12 страницRelative ClausesTấn DũngОценок пока нет
- Functional words: By: Minh Hưng And Quốc HuyДокумент22 страницыFunctional words: By: Minh Hưng And Quốc HuyHaaKroraОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses ExplainedДокумент15 страницRelative Clauses Explainedander oviedoОценок пока нет
- Adjective Clauses HandoutДокумент5 страницAdjective Clauses HandoutMedo BasaОценок пока нет
- (Key) Relative ClausesДокумент16 страниц(Key) Relative ClausesThu UyenОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses - 10 AnoДокумент10 страницRelative Clauses - 10 AnoAna Sofia SantosОценок пока нет
- Relative Adjective ClauseДокумент6 страницRelative Adjective ClauseMaria QuinteroОценок пока нет
- Tugas B.Inggris: Adjective ClausesДокумент37 страницTugas B.Inggris: Adjective ClausesJefriAzwarAnasОценок пока нет
- Relative Pronouns GuideДокумент3 страницыRelative Pronouns GuideAnonymous yyzxrD3Оценок пока нет
- Relative-Clauses Theory 2º BACHДокумент5 страницRelative-Clauses Theory 2º BACHmaria sanchezОценок пока нет
- Relative PronounsДокумент17 страницRelative PronounsPaulo MorsОценок пока нет
- PronounsДокумент14 страницPronounsDefender proОценок пока нет
- ADJECTIVE CLAUSES: A CONCISE GUIDE TO RELATIVE PRONOUNS AND CLAUSESДокумент8 страницADJECTIVE CLAUSES: A CONCISE GUIDE TO RELATIVE PRONOUNS AND CLAUSESsummer wheelerОценок пока нет
- Deixis 1Документ34 страницыDeixis 1sofiaaltaweelОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses - HOДокумент2 страницыRelative Clauses - HOSignorina SchwarzОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses: 1 Examples: (Defining: People)Документ7 страницRelative Clauses: 1 Examples: (Defining: People)CameliaMateianaОценок пока нет
- What is an Adjective ClauseДокумент20 страницWhat is an Adjective ClauseYesi LismawatiОценок пока нет
- English Language: Semester 2Документ63 страницыEnglish Language: Semester 2lelanieОценок пока нет
- Relative ClausesДокумент17 страницRelative Clauseslucia santroОценок пока нет
- Relative Clause 2Документ31 страницаRelative Clause 2Mirai KuriyamaОценок пока нет
- TOEFL Skill 9 & 10Документ13 страницTOEFL Skill 9 & 10Elsa ChristiОценок пока нет
- The Use of Articles in EnglishДокумент16 страницThe Use of Articles in EnglishМария АрнаутОценок пока нет
- Makalah Adjective ClauseДокумент12 страницMakalah Adjective Clausesaimi duaОценок пока нет
- Definite ArticleДокумент3 страницыDefinite ArticleurielОценок пока нет
- Definite Article The/ Zero ArticleДокумент3 страницыDefinite Article The/ Zero ArticleurielОценок пока нет
- How to Use Adjective Clauses and PhrasesДокумент36 страницHow to Use Adjective Clauses and PhrasesGilang MaulanaОценок пока нет
- Adjective ClausesДокумент36 страницAdjective ClausesAnang FatkhuroziОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses (Adjective Clauses)Документ10 страницRelative Clauses (Adjective Clauses)M MОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses ExplainedДокумент2 страницыRelative Clauses ExplainedBruce GrayОценок пока нет
- Defining Relative ClausesДокумент3 страницыDefining Relative Clausescostica_irimescuОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Документ16 страницRelative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Roberta OrlandoОценок пока нет
- Relative ClausesДокумент28 страницRelative ClausesMeyke Jayanti KinasihОценок пока нет
- Jaw Crusher Gyratory Cone CrusherДокумент1 страницаJaw Crusher Gyratory Cone CrusherLelyОценок пока нет
- 4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersДокумент16 страниц4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersAdnan ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- 30 Examples Adjective Phrases English SentencesДокумент1 страница30 Examples Adjective Phrases English SentencesLelyОценок пока нет
- Low Voltage Anode Materials For Lithium-Ion BatteriesДокумент24 страницыLow Voltage Anode Materials For Lithium-Ion BatteriesLelyОценок пока нет
- Morphology of Intermetallic Phases in Al-SiДокумент4 страницыMorphology of Intermetallic Phases in Al-SiLelyОценок пока нет
- Metals 07 00013Документ11 страницMetals 07 00013LelyОценок пока нет
- Microstructure, Textureandpreci P Itatesofgrain OrientedsiliconsteelpДокумент6 страницMicrostructure, Textureandpreci P Itatesofgrain OrientedsiliconsteelpLelyОценок пока нет
- A Summary of Classical Lamination TheoryДокумент4 страницыA Summary of Classical Lamination TheoryFrank DetchokulОценок пока нет
- Solidification PathДокумент1 страницаSolidification PathLelyОценок пока нет
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds: S.J. Liu, G.Y. Yang, S.F. Luo, W.Q. JieДокумент8 страницJournal of Alloys and Compounds: S.J. Liu, G.Y. Yang, S.F. Luo, W.Q. JieLelyОценок пока нет
- Modelling Solidification Kinetics: Scheil vs Lever RuleДокумент18 страницModelling Solidification Kinetics: Scheil vs Lever RuleLelyОценок пока нет
- V2i3 Ijertv2is3166Документ6 страницV2i3 Ijertv2is3166LelyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 34Документ19 страницLecture 34LelyОценок пока нет
- D790-02 (Flexural Properties of Composites)Документ9 страницD790-02 (Flexural Properties of Composites)M.Ubaid Ullah KhalidОценок пока нет
- Sciencedirect: +,B B, B + 7 BДокумент11 страницSciencedirect: +,B B, B + 7 BLelyОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S004060901630548X MainДокумент6 страниц1 s2.0 S004060901630548X MainLelyОценок пока нет
- Failure Analysis of Pipes in Hydrodesulfuration SystemДокумент16 страницFailure Analysis of Pipes in Hydrodesulfuration SystemLelyОценок пока нет
- Martempering and AustemperingДокумент6 страницMartempering and AustemperingRecep Vatansever100% (2)
- Basics of Corrosion MeasurementsДокумент25 страницBasics of Corrosion MeasurementsmoizmuetОценок пока нет
- TC JIS-G3101 VatLieu PDFДокумент11 страницTC JIS-G3101 VatLieu PDFhbookОценок пока нет
- Assignment 7Документ2 страницыAssignment 7LelyОценок пока нет
- THK Paint Defects GB PDFДокумент24 страницыTHK Paint Defects GB PDFmaddyОценок пока нет
- Assignment 7Документ2 страницыAssignment 7LelyОценок пока нет
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsОт EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsОценок пока нет
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisОт EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (80)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Learn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandLearn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (47)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonОт EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundОт Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (13)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (136)
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllОт EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (83)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageОт EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (916)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachОт EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (15)
- Empires of the Word: A Language History of the WorldОт EverandEmpires of the Word: A Language History of the WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (236)
- On Speaking Well: How to Give a Speech with Style, Substance, and ClarityОт EverandOn Speaking Well: How to Give a Speech with Style, Substance, and ClarityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (15)
- How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingОт EverandHow to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (26)
- How to Tell a Story: An Ancient Guide to the Art of Storytelling for Writers and ReadersОт EverandHow to Tell a Story: An Ancient Guide to the Art of Storytelling for Writers and ReadersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Writing That Works, 3rd Edition: How to Communicate Effectively in BusinessОт EverandWriting That Works, 3rd Edition: How to Communicate Effectively in BusinessРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (29)
- The Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsОт EverandThe Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (205)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageОт EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (425)
- How to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneОт EverandHow to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (115)
- How To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessОт EverandHow To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (308)