Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
@acute Nephritic Syndrome
Загружено:
Mazlia FarzanaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
@acute Nephritic Syndrome
Загружено:
Mazlia FarzanaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
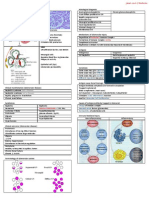
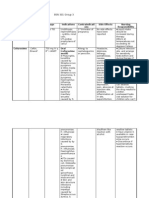
ACUTE NEPHRITIC NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
SYNDROME
Clinically, presented as: Clinically: Causes: Primary glomerular disease: Secondary systemic cause:
# Hematuria # Heavy proteinuria capillary permeability # some are directly According to morphology, -diabetes mellitus
# Proteinuria # Hypoproteinemia 2ry to loss of protein targeting the -minimal change disease -amyloidosis
# Oliguria & azotemia # Generalized edema plasma osmotic glomeruli(1ry glomerular -focal segmented -SLE
# Hypertension pressurecompensatory secretion of disease) glomerularsclerosis -infections(HBV, malaria,
# Mild edema aldosteronesalt and water retention # some are due to -membronaous schistosomiasis)
# Hyperlipidemia synthesis of lipoprotein systemic disease that glomerulonephritis -drugs, maignancies,
# Lipiduria GBM permeability to affect glomeruli & other -membranoproliferative hereditary
lipoprotein. tissue(2ry) glomerulonephritis
-Ig A nephropathy
POST STREPTOCOCCAL MINIMAL CHANGES FOCAL SEGMENTED MEMBRANOUS MEMBRANOPROLIFERATIVE IG A NEPHROPATHY
(ACUTE DIFFUSE GLOMERULOSCLEROSIS GLOMERULONEPHRITIS GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
PROLIFERATIVE GN)
INCIDENCE
Common disorder Main cause of NS NS in 15% of adults and Most frequent cause of 5-10% of cases of primary NS Most common glomerular
among children that among children children NS among adults in in children and adults disease worldwide
follow infection of skin < 15 years western countries Peak: children and young
or URT by nephritogenic adults
strain of B-haem.
streptococci.
CHARACTERISTICS HISTOLOGICAL FEATURES
Normal looking Focal & segmental Accumulation of immune Glomerular hypercellularity Deposition of immune
glomeruli with LM & obliteration of capillary complexes in with thickening of GBM. complex formed
diffuse loss of loop by deposition of subepithelial zone of predominantly of Ig A
epithelial foot collagen(sclerosis)+accu glomerular capillaries.
processes by EM. mulation of lipid &
proteinaceous material
PATHOGENESIS
-immune complex -might be 1ry -injury to epithelial cell Immune complex -Type I caused by circulating -genetic or aquired
deposited within the epithelial injury(no lead to focal mediated disease: immune complexes abnormality of immune
glomeruli initiate immune complex hyperpermeable foci -1ry: due to in situ -Type II: autoimmune disease. regulation leading to
inflammation by deposition) entrapment of plasma deposition of immune The patients serum has factor mucosal Ig A synthesis in
activation of -disorder in T- protein & lipid complexes against renal called C3 nephritic factor that response to resp of GIT
complement system lymphocytes leading -result in mesangial cell autoantigen activate alternate exposure to environmental
to elaboration of reaction with mesangial -2ry: due to circulating complement pathway with agents. Ig A and Ig A
cytokines that affect matrix immune complexes elaboration of biologically complex then get trapped
synthesis of against exogenous active complement pathway. within mesangium,
nephrin. antigen activate alternate
Consequently, there complement pathway &
is loss of podocyte. initiate glomerular injury.
CLINICAL PICTURES
1.nephritic syndrome In NS, there is 1.non selective NS, sometimes non- Both types present mainly by 1.gross hematuria that
2.low serum neither proteinuria nephrotic range non- NS, sometimes with non- occur within 1-2 days of
complement level hypertension nor 2.may progress to NS selective proteinuria nephrotic range proteinuria nonspecific URT/GIT
3.high titre of anti- hematuria 3.may develop infection. Hematuria lasts
streptolysin O(ASO) in hypertension & several days then subsides.
serum hematuria Its recurs every few
months & associated with
loin pain.
2.less 10% with NS
PROGNOSIS AND FATE
Depend on pts age 7 Good prognosis Poor response to Proteinuria usually does Both types have poor Has remitting & relapsing
causative agents with excellent corticosteroids with not respond to prognosis, more than 50% of course. Rarely resolves but
-good prognosis with response to progression to renal corticosteroids. However them progress to chronic Gn many patients maintain
streptococcal infection & corticosteroid failures within 10 years in it has an indolent course after 10 years. normal renal functions for
among children. therapy in > 90% of about 50% of cases. & only about 40% of pts Type II has tendency to recur decades. 50% slowly
-children: usually recover affected children & Lesion tend to recur in progress to renal failure in renal allograft. progress to chronic renal
(90%) after sveral weeks less figures in adult. renal allograft. failure within 20 years.
- few cases developed
rapidly progressive Gn or
chronic renal disease.
-in adult: 15-50%
develop chronic Gn
within few years
MICROSCOPIC PICTURES
LIGHT MICROSCOPE
-Diffuse in mesangial Normal looking Some show segmental Diffuse thickening of Both types have similar LM. Not specific. The glomeruli
cells with infiltration by glomeruli obliteration of capillary GBM, normal glomerular Glomeruli are diffusely commonly show mesangial
neutrophils leading to loop with mesangial cellularity. enlarged, proliferation
compression of capillary matrix, collapsed GBM & hypercellular(mesangial
lumina (bloodless accumulation of lipid & proliferation) & leukocytes
glomeruli) proteinaceous material. with diffuse thickening of
-cresent GBM that displayed double
formation(proliferation contour(tram-track
of parietal cells) appearance) by silver stain.
FLUOROSCENCE MICROSCOPE
Granular deposits of Ig G No deposits Usually negative Typical granular deposits Type I: granular deposits of Ig Intense mesangial staining
and C3 along capillary of Ig & complement & complement along capillary for Ig A
wall along GBM wall & mesangium
Type II: granular deposits of
C3 allong capillary with
absence of Ig deposition.
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
Scattered subepithelial Diffuse loss of Focal segmental in Subepithelial deposits Type I: marked mesangial Electron dense deposits
deposits shaped like epithelial foot mesangial matrix with nestle against GBM & hypercellularity + mesangial within the mesangium.
humps processes prominent injury of separated from each interposition between
overlying podocyte other by small spike-like capillary wall splllitting
protrusion of GBM associat with subendothelial &
matrix mesangial electron dense
deposits
Type II: ribbon-like dense
deposits in the centre of
thickened GBM.
Вам также может понравиться
- Glomerular Diseases My NotesДокумент5 страницGlomerular Diseases My Notesmalar_km43Оценок пока нет
- Renal Pathology I. Clinical Manifestations of Renal DiseasesДокумент18 страницRenal Pathology I. Clinical Manifestations of Renal DiseasesKrisha Marie BadilloОценок пока нет
- Glomerulonephritis: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK Tim Ginjal Hipertensi Unhas 2019Документ68 страницGlomerulonephritis: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK Tim Ginjal Hipertensi Unhas 2019uzan100% (1)
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneДокумент5 страницDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPEОценок пока нет
- Differential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesДокумент2 страницыDifferential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesMaryam Fadah100% (1)
- Nephritic SyndromeДокумент15 страницNephritic Syndrome76q88b4yrxОценок пока нет
- Glomerulonephritis EngДокумент43 страницыGlomerulonephritis EngNosirova ManijaОценок пока нет
- Summary of Renal Disorders - 9.11.19Документ4 страницыSummary of Renal Disorders - 9.11.19Nicole Juliette CCОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ2 страницыChapter 7Mychelle MenesОценок пока нет
- SN 1Документ9 страницSN 1lilisОценок пока нет
- Renal DiseaseДокумент5 страницRenal DiseasefeajhanineladagaОценок пока нет
- Renal DiseasesДокумент7 страницRenal DiseasesXyleene Jency Bien IIОценок пока нет
- PATH - Nephritic SyndromeДокумент14 страницPATH - Nephritic SyndromeMuhamad Zul ImanОценок пока нет
- Bagian Patologi Anatomi Fk-Uisu 2011Документ22 страницыBagian Patologi Anatomi Fk-Uisu 2011rizapuspairyaniОценок пока нет
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeДокумент3 страницы@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Renal DiseaseДокумент7 страницChapter 8 - Renal DiseaseCha GuingabОценок пока нет
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisДокумент4 страницыPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- UTI Dan Glomerular DiseaseДокумент58 страницUTI Dan Glomerular DiseaseLiana Ika SuwandyОценок пока нет
- 05 - GinjalДокумент119 страниц05 - GinjalAna ambiyaОценок пока нет
- Disease PDFДокумент6 страницDisease PDFJohn Christopher LucesОценок пока нет
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: PathogenesisДокумент5 страницSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: PathogenesisMiguel Cuevas DolotОценок пока нет
- Imunosupresan For Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome DR Harnavi HarunДокумент27 страницImunosupresan For Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome DR Harnavi HarunM Ivan Pratama ZebuaОценок пока нет
- Patologi GinjalДокумент94 страницыPatologi GinjalDenoОценок пока нет
- Glomerular Diseases: Pathogenesis of Glomerular Diseases Progression of Glomerular DiseasesДокумент6 страницGlomerular Diseases: Pathogenesis of Glomerular Diseases Progression of Glomerular DiseasesSeff CausapinОценок пока нет
- Renal Diseases - BSMLS OLFUДокумент15 страницRenal Diseases - BSMLS OLFUMitch IbayОценок пока нет
- AUBF Lec - Renal DiseasesДокумент6 страницAUBF Lec - Renal Diseasescdsteenkamp18Оценок пока нет
- Dr. Dhian Endarwati, Spa Maret 2017Документ60 страницDr. Dhian Endarwati, Spa Maret 2017Diany LarasatiОценок пока нет
- NEPHROTIC SYNDROME - HamidДокумент20 страницNEPHROTIC SYNDROME - HamidAbdul Hamid OmarОценок пока нет
- LEC AUBF Renal-Diseases MIDTERMS 02Документ3 страницыLEC AUBF Renal-Diseases MIDTERMS 02Jashmine May TadinaОценок пока нет
- AUBF Lecture-I FINДокумент8 страницAUBF Lecture-I FINChrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyОценок пока нет
- Renal DiseaseДокумент4 страницыRenal DiseaseApril Lady Faith P. PaundogОценок пока нет
- Glomerulonephritis 2019Документ31 страницаGlomerulonephritis 2019EsoklailОценок пока нет
- PATH - Nephrotic SyndromeДокумент11 страницPATH - Nephrotic SyndromeTeshale TekleОценок пока нет
- Nephritic SyndromeДокумент2 страницыNephritic Syndromevalari8069Оценок пока нет
- Glomerular Diseases: Membrano Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (MPGN) - in This LectureДокумент12 страницGlomerular Diseases: Membrano Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (MPGN) - in This LectureWalaa abo foolОценок пока нет
- 1 Glomerular DiseasesДокумент127 страниц1 Glomerular DiseasesCoy NuñezОценок пока нет
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeДокумент9 страницAcute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeAjeng DwiОценок пока нет
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeДокумент8 страницAcute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeMichael HusainОценок пока нет
- General Pathology EdgeДокумент2 страницыGeneral Pathology EdgeskОценок пока нет
- Glomerular Disease - Dr. LuДокумент8 страницGlomerular Disease - Dr. LuMACATANGAY, GAELLE LISETTEОценок пока нет
- Glomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2Документ67 страницGlomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2ibnbasheer100% (12)
- Nephritic SyndromeДокумент24 страницыNephritic SyndromeMuhamed Al Rohani100% (1)
- Activity On Renal DiseasesДокумент6 страницActivity On Renal DiseasesRicca Christyl SumalpongОценок пока нет
- Medical KidneyДокумент13 страницMedical KidneyJose SirittОценок пока нет
- Dr. Fairuz Quzwain, Sppa, M.Kes: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter Universitas JambiДокумент119 страницDr. Fairuz Quzwain, Sppa, M.Kes: Bagian Patologi Anatomi Program Studi Pendidikan Dokter Universitas JambiAlfian DaudОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics Solved WBUHS Question Papers PDFДокумент162 страницыPediatrics Solved WBUHS Question Papers PDFγιαννης παπαςОценок пока нет
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeДокумент8 страницAcute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeWenny A. YuliantiОценок пока нет
- Diseases For The BoardsДокумент2 страницыDiseases For The BoardsBrendan MillinerОценок пока нет
- Pathology of Urinary SystemДокумент384 страницыPathology of Urinary SystemNzau MuangeОценок пока нет
- Sem 4Документ8 страницSem 4Bea EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Nephrotic Syndrome PDF 2Документ2 страницыNephrotic Syndrome PDF 2MОценок пока нет
- GLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Документ8 страницGLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Anjitha K. JОценок пока нет
- Summary Nephritic, Nephrotic SyndromesДокумент22 страницыSummary Nephritic, Nephrotic SyndromesmariapaulaguerrerocОценок пока нет
- Systemic Effects of Inflammation The Acute Phase ResponseДокумент3 страницыSystemic Effects of Inflammation The Acute Phase ResponseJenward Hostallero100% (1)
- Disorder Etiology: Acute GlomerulonephritisДокумент1 страницаDisorder Etiology: Acute GlomerulonephritisChynna Izzabelle Alcantara AbellanaОценок пока нет
- Renal PathДокумент71 страницаRenal PathSuha AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Nephrotic SyndДокумент21 страницаNephrotic Synd238439904Оценок пока нет
- Glomerular Disease and DiureticsДокумент26 страницGlomerular Disease and DiureticsDapot SianiparОценок пока нет
- PATHO Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial DiseaseДокумент43 страницыPATHO Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial DiseaseHananya ManroeОценок пока нет
- Emergency Medicines List (EML) : First EditionДокумент42 страницыEmergency Medicines List (EML) : First EditionMalik TufailОценок пока нет
- MCQ Anaesthesia QuestionsДокумент8 страницMCQ Anaesthesia QuestionsOanamikaela VaidaОценок пока нет
- Methanol Information 2 PDFДокумент5 страницMethanol Information 2 PDFPark RangerОценок пока нет
- Urinary TractДокумент3 страницыUrinary TractRifki MuhamadОценок пока нет
- EHOPE GuidelinesДокумент5 страницEHOPE GuidelinesranОценок пока нет
- 2 Hand HygieneДокумент44 страницы2 Hand HygieneAdelina SilimonОценок пока нет
- NCP MastectomyДокумент2 страницыNCP MastectomyDoc Duday100% (2)
- How Health Should Be DefinedДокумент3 страницыHow Health Should Be DefinedFernando Casado CampolongoОценок пока нет
- Uterine CancerДокумент10 страницUterine CancerKristen Leigh MarianoОценок пока нет
- Universal ECG Sample ReportsДокумент6 страницUniversal ECG Sample ReportsHemant Soni100% (1)
- BLS Healthcare Provider AlgorithmДокумент7 страницBLS Healthcare Provider AlgorithmyuniОценок пока нет
- Befungin PreparationДокумент3 страницыBefungin PreparationmobsivacОценок пока нет
- Euros Core OrgДокумент6 страницEuros Core OrgClaudio Walter VidelaОценок пока нет
- Rebt Vs CT Vs Med in DepressionДокумент19 страницRebt Vs CT Vs Med in DepressionPaula StroianОценок пока нет
- Juliette Blanchard PosterДокумент1 страницаJuliette Blanchard Posterapi-340980701Оценок пока нет
- Assessment of The Nervous System - FinalДокумент76 страницAssessment of The Nervous System - FinalRona Lucido100% (1)
- Dental Practice ManagementДокумент5 страницDental Practice ManagementTavi HeroiuОценок пока нет
- Psychological Report FormatДокумент3 страницыPsychological Report FormatAn Jannette AlmodielОценок пока нет
- Thalassemia BrochureДокумент4 страницыThalassemia Brochurevein94Оценок пока нет
- Anil Degaonkar, Nikhil Bhamare, Mandar Tilak Arterio-Enteric Fistula A Case ReportДокумент6 страницAnil Degaonkar, Nikhil Bhamare, Mandar Tilak Arterio-Enteric Fistula A Case ReportDr. Krishna N. SharmaОценок пока нет
- Arellano University Graduate School of NursingДокумент2 страницыArellano University Graduate School of NursingBest of pinoyОценок пока нет
- Swan Ganz CathetersДокумент27 страницSwan Ganz CatheterschadchimaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDat boiОценок пока нет
- Acteon Surgery Clinical BookletДокумент56 страницActeon Surgery Clinical BookletJTDentalGroupОценок пока нет
- Drug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexДокумент5 страницDrug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexLorina Lynne ApelacioОценок пока нет
- Unilateral Greater Occipital Nerve Compression Causing Scalp NumbnessДокумент2 страницыUnilateral Greater Occipital Nerve Compression Causing Scalp NumbnessIzzati N. SariОценок пока нет
- Bipolar Disorder or ManicДокумент16 страницBipolar Disorder or Manicbbkanil100% (1)
- WNSSP Estimulacion SensorialДокумент3 страницыWNSSP Estimulacion Sensoriallgomezb11100% (1)
- Neurological Physiotherapy AssessmentДокумент7 страницNeurological Physiotherapy Assessmentramesh babuОценок пока нет
- NURS2002 Assignment 4 Case-Study Instructions 2019 PDFДокумент2 страницыNURS2002 Assignment 4 Case-Study Instructions 2019 PDFjohnmccauleyОценок пока нет