Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Visual Inspection
Загружено:
Mani Rathinam RajamaniАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Visual Inspection
Загружено:
Mani Rathinam RajamaniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2000 West Grandview Boulevard
Erie, PA USA 16514-0038
USA
LORD Corporation Cage Code 76005
Technical Specification Number PRC-T-0010
Supersedes Technical Document Number
Original Issue Date 5/6/2009
Revision A Date 10/8/10
TITLE: Requirements for Visual Inspection of Aerospace Products
RESTRICTED DISCLOSURE NOTICE
The information contained herein is proprietary to LORD Corporation and shall not be reproduced or
disclosed in whole or in part or used for any design or manufacture except when such user possesses
direct written authorization from LORD Corporation.
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page ii
Revision Summary
Revision Date Prepared By Change Description
Original 05/06/2009 R.P. Biondi Initial release
A 10/8/10 J. Fullum Paragraph 7.1 Added the term "Tin Solder" method and
added the need to establish a "Master" part from the
manufacturing lot and compare remaining parts to the
master. This change is being made as a result of DMAIC
100266 Part Marking Project.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page iii
INDEX
Section Description Page
1.0 Scope ................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Purpose .......................................................................................... 1
1.2 Application ...................................................................................... 1
2.0 Applicable Documents ....................................................................... 1
2.1 LORD Corporation Documents ....................................................... 1
3.0 Definitions ........................................................................................... 1
4.0 Equipment Requirements................................................................... 2
4.1 Lighting ........................................................................................... 2
4.2 Supplemental Lighting ..................................................................... 2
4.3 Probe .............................................................................................. 2
4.4 Special Aids .................................................................................... 2
5.0 Personnel Requirements .................................................................... 3
5.1 Proficiency ...................................................................................... 3
5.2 Vision .............................................................................................. 3
6.0 General Requirements........................................................................ 4
7.0 Specific Inspection Requirements..................................................... 4
7.1 General Appearance ....................................................................... 4
7.2 Surface Condition ........................................................................... 4
7.2.1 Machined Parts ......................................................................... 5
7.2.2 Elastomeric Bonded and Molded Parts...................................... 5
7.3 Acceptance Criteria ......................................................................... 5
List of Figures
Figure 1 LORD Part Number FIS-56177-1 Inspection Probe .............................. 2
List of Tables
Table 1 Vision Requirements ............................................................................. 3
Table 2 General Acceptance Criteria for Surface Imperfections on
Machined Parts ..................................................................................... 6
Appendices
Appendix A Use of a Probe for Visual Inspection .................................................. A-1
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page 1 of 7
1.0 SCOPE
1.1 Purpose. This specification describes the general requirements for evaluating
surface imperfections on parts using visual techniques. It also defines the
acceptance limits for imperfections on parts.
1.2 Application. This specification applies to aerospace products and is applicable when
referenced on a LORD engineering drawing or LORD inspection procedure or in the
case of a supplier when invoked by contract (if not invoked by the LORD engineering
drawing). When there is a conflict between this specification and a visual inspection
requirement specified by the engineering drawing, the drawing requirement shall
take precedence.
2.0 APPLICABLE DOCUMENTS
The following documents form a part of this specification to the extent applied
herein. Unless otherwise specified, the latest issue of the documents shall apply. In
the event of conflicts between the requirements of this specification and the
references cited herein, the requirements of this specification shall take precedence.
2.1 LORD Corporation Documents
TS-002 Standard Elastomeric Component Quality Requirements
(LORD Corporation proprietary document)
3.0 DEFINITIONS
The listed below definitions apply to machined parts. Refer to TS-002 for definitions
that apply to elastomer products.
Imperfection: An interruption (non-uniformity) in the normal surface condition of a
part configuration which shall be evaluated for acceptance to the applicable
standard.
Lay: The direction of the predominant surface pattern.
Smooth: A surface that is continuously even, free of irregularities, presenting no
resistance to the sliding of a finger or probe.
Superficial Imperfection: An imperfection on a surface which although appears to
penetrate the surface finish texture, does not have a dark bottom, and would not
cause a probe to hesitate (catch) when passed over it.
Surface Roughness: Marks left on the surface of a part by the action of machined
tools.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page 2 of 7
4.0 EQUIPMENT REQUIREMENTS
4.1 Lighting. Fixed white lighting in the inspection area shall be a white light intensity of
100 foot-candles minimum when measured at the inspection surface for the parts.
The lighting shall be designed and arranged so as to provide shadow free and glare
free illumination of the part surface to be inspected.
4.2 Supplemental Lighting. Hand held white lights shall be available to provide a
minimum of 200 foot-candles at a distance of 8 inches. High intensity light sources
shall have an intensity of 200 foot-candles at 1.5 inches.
4.3 Probe. A probe (stylus) with a spherical end (nose) radius ranging in size from
0.005 to 0.025 inch shall be available to assist in the detection of raised material or
an imperfection. See LORD Corporation part number FIS-56177-1 probe shown in
Figure 1. For inside surfaces that cannot be accessed by a straight probe, an angle
probe shall be available for use. Probes may be purchased from:
Gary Tool Company
26 Grant Street
Stratford, CT 06615-6136
Phone No. (203) 377-3077
Probes can be ordered in any end radius size. The following standard part number
probes are available from Gary Tool Company:
P/N STD 1360-453-005 straight probe
P/N STD 1360-453-006 angled probe
A Diameter R Radius
.130 0.025
Figure 1. LORD Part Number FIS-56177-1 Inspection Probe
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page 3 of 7
4.4 Special Aids. Mirrors, borescopes (rigid and non-rigid), video systems and other
optical devices.
5.0 PERSONNEL REQUIREMENTS
5.1 Proficiency. Personnel performing visual inspection shall be proficient in the
operation of all visual inspection equipment and techniques and be capable of
interpreting engineering drawings, standards and inspection instructions that pertain
to the parts being inspected.
5.2 Vision. Personnel performing visual inspection shall meet the near vision and color
perception requirements listed in Table 1 in at least one eye natural or corrected.
Near vision and color perception examinations shall be administered annually.
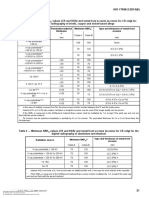
Table 1 - Vision Requirements
Vision Examination Requirement
Near Vision Snellen 14/18 (Snellen 20/25) or equivalent
Color Perception Distinguish and differentiate between colors applicable
to the product being inspected.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page 4 of 7
6.0 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
6.1 Visual inspection shall be performed without magnification. However, magnification
up to 10X may be used as an aid in the evaluation of an observed condition.
6.2 A probe (see 4.3) shall be used to assist in the detection and evaluation of surface
imperfections and conditions. See Appendix A for the instructions in using a probe.
6.3 All accessible surfaces shall be inspected. Parts shall be inspected from various
angles and directions to assure the detection of all imperfections. Holes shall be
inspected at both ends when possible.
6.3.1 In areas when visual access results in a line of sight viewing angle greater than 45
degrees from a line perpendicular to the surface being inspected, or where the
surface to be inspected extends beyond a depth to opening ratio greater than 1, or
where other limitations prevent a valid unaided (direct vision) inspection, probes and
special aids (see 4.4) shall be used. Inspection of holes less than 0.25 inches in
diameter shall be confined to the edges.
6.3.2 Enclosed surfaces shall be inspected prior to closing.
6.4 Visual imperfections which will be removed by subsequent machining or processing
operations specified in the work instructions/routing/planning may be disregarded.
7.0 SPECIFIC INSPECTION REQUIREMENTS
7.1 General Appearance. When visually inspecting a group of parts, use the "Tin Soldier
Method". Establish a "Master" part from the manufacturing lot and verify it meets the
drawing requirement for part marking. Line up the remaining parts from the
manufacturing lot on the examination surface such that they are all in the same
orientation. Visually inspect the remaining parts against the "Master" checking for
the following:
Proper geometry (i.e., no missing features such as holes, threads, chamfers,
radii, etc.)
For an assembly, presence and proper installation of all components (including
inserts, bushings, hardware, lock-wire, etc.)
Presence of required surface treatment (e.g., shot peen, plating, anodize, paint,
etc.)
Correct, legible and properly located marking
No damage
7.2 Surface Condition. Visually inspect surfaces of the parts to identify any surface
imperfections or flaws. Use a probe, magnification and other special aids as
required to assist in the detection of any imperfections. Comparison with similar
parts or photographs may be used to assess any observed conditions.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page 5 of 7
7.2.1 Machined Parts. Typical surface imperfections for machined parts are listed in Table
2. Table 2 also includes imperfections associated with surface treatments applied to
machined parts.
7.2.2 Elastomeric Bonded or Molded Parts. Typical elastomer surface defects for
elastomeric bonded or molded parts are listed in TS-002.
7.3 Acceptance Limits. Visual surface imperfections for machined parts shall be
evaluated in accordance with Table 2. Visual surface imperfections or flaws for
elastomeric bonded and molded parts shall be evaluated in accordance with TS-002.
Superficial imperfections are acceptable unless other specified by the engineering
drawing.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page 6 of 7
Table 2 General Acceptance Criteria for Surface Imperfections of Machined Parts
Imperfection Type Definition Applicable Parts Disposition Comments
Blister A localized lifting of a coating, plating or paint All coated, plated or Not Acceptable
from the surface of the part base material. It painted parts
appears as a protuberance that may break
when probed.
Burnish Mark A local smoothing of a metal surface, often to All parts Acceptable Acceptable provided it cannot be
a high luster from rubbing. It may show (see comments) felt by a probe and that the
scratches of no apparent depth. Includes material thickness still meets the
buffing and polishing marks. drawing requirement.
Burr A rough ridge or edge left at the intersection of All parts Not Acceptable
two surfaces. A fragment of metal which
remains attached to the surface after a
machining operation.
Chatter Mark Recurring undulations or irregularities on the All parts Acceptable Acceptable provided it meets the
surface that result from vibration or jumping of (see comments) drawing surface roughness
a machining cutting tool. requirement.
Corrosion A deterioration of a metal surface resulting in All parts Not Acceptable
a change of color and leaving a rough surface
that may show pitting. Caused by chemical or
electrochemical interaction.
Crack A separation of metal on the surface visible to All parts Not Acceptable
the un-aided eye.
Crazing A network of fine cracks All parts Not Acceptable
Deformation Convex or Concave change in the profile a All parts Not Acceptable
part.
Dent A surface depression having rounded edges, All parts Not Acceptable
corners and bottom caused by impact with an
object.
Foreign material Material or substance not integral to the part. All parts Not Acceptable
The material or substance may or may not be
adherent to the part surface. Chips from
machining are considered foreign material.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Page 7 of 7
Table 2 General Acceptance Criteria for Surface Imperfections of Machined Parts
Imperfection Type Definition Applicable Parts Disposition Comments
Gouge A relatively wide trough-like depression All parts Not Acceptable
caused by tearing away of the surface by
another object.
Heat Discoloration Staining, ranging from straw color (low Heat treated parts Acceptable Acceptable provided it is light
temperature effects) to purple in color (high (see comments) straw to light blue in color.
temperature effect).
Nick A negative indication having raised sharp All parts Not Acceptable Acceptable provided it can not be
edges, corners or bottom. (see comments) felt by a probe or it is not deeper
then the machining lay.
Peeling A section of a coating, plating or paint lifting All coated, plated or Not Acceptable
away from the surface. painted parts
Pits Small irregular cavities in surfaces generally All parts Not Acceptable
rough or dark bottomed resulting from
corrosion.
Rolled Edges A plastic deformation of the edges resulting in Shot peened parts Not Acceptable
a lap of the adjacent surface and normally
appearing after shot peeing.
Scoring Multiple scratches caused by contact with a All parts Not Acceptable Acceptable provided the
mating part or tooling. (see comments) scratches cannot be felt by a
probe (see 4.3).
Scratch A linear depression with a sharp bottom. All parts Not Acceptable Acceptable provided it cannot be
(see comments) felt by a probe (see 4.3).
Stain Visual indication result from liquid drying on a All parts Acceptable Acceptable provided it does not
part surface. (see comments) detract from the overall
appearance of the part.
Step An abrupt change in the surface contour which All parts Not Acceptable
looks like a step in cross section.
Tool Marks A mark in the direction of the machining lay All machined parts Acceptable Acceptable provided they cannot
left by the machining tool or across the lay (See comments) be felt by a probe (see 4.3).
caused by improper tool withdrawal or metal
chips. Mark can be straight, circular or spiral.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Specification No. PRC-T-0010
Rev. A Date 10/8/10
Appendix A
Page A-1
USE OF A PROBE FOR VISUAL INSPECTION
A probe with a specified radius is used to detect raised material around a surface imperfection
or the minimum drop of the imperfection from the surrounding surface. The proper use of a
probe shall be as follows:
The probe shall be held lightly near the top, between the thumb and forefinger, inclined at a
60 degree angle to the part surface toward the imperfection, and be pushed forward over
the surface without applying pressure other than the weight of the probe itself, in a direction
approximately 90 degrees to the lay of the imperfection. If the movement is smooth with no
interruption and the radius point of the probe does not hesitate or pause in the imperfection,
the imperfection is acceptable.
If the 60 degree probe position is impractical due to the part configuration, the probe can be
held at any angle between 60 and 90 degrees.
Use or disclosure of data on this page is subject to the restriction on the title page
UNCONTROLLED COPY, IF PRINTED
Вам также может понравиться
- Weld Log PDFДокумент1 страницаWeld Log PDFDeniz AydinОценок пока нет
- Ac7114 1 Rev F Audit Criteria For Nondestructive Testing Facility Penetrant SurveyДокумент27 страницAc7114 1 Rev F Audit Criteria For Nondestructive Testing Facility Penetrant Surveyimrakesh8014Оценок пока нет
- q1 Interpretations FaqДокумент8 страницq1 Interpretations Faqjaymuscat100% (1)
- Vernier Calibration ProcedureДокумент12 страницVernier Calibration ProcedureAaron QuinnОценок пока нет
- WPS AWS TemplateДокумент3 страницыWPS AWS TemplateMohd SaffririzalОценок пока нет
- AC7114 Rev M NADCAP AUDIT CRITERIAДокумент37 страницAC7114 Rev M NADCAP AUDIT CRITERIARaja Hone100% (2)
- Ancillary Specification (Generic) : Subject: Full Length Drift/End Drift Inspection ProcedureДокумент4 страницыAncillary Specification (Generic) : Subject: Full Length Drift/End Drift Inspection ProcedureDefi Jodi PermanaОценок пока нет
- API Spec Q1 9th Edition - Mandatory Documented Procedures: No. Clause No. DescriptionДокумент1 страницаAPI Spec Q1 9th Edition - Mandatory Documented Procedures: No. Clause No. Descriptionzae nuddinОценок пока нет
- Mil STD 867cДокумент16 страницMil STD 867cDimitris GrimanelisОценок пока нет
- Calibration ValidationДокумент12 страницCalibration ValidationAlberto LobonesОценок пока нет
- D.Muthu Swamy: QMS Lead AuditorДокумент4 страницыD.Muthu Swamy: QMS Lead Auditormuthuswamy77Оценок пока нет
- API Audit Planning GuidanceДокумент3 страницыAPI Audit Planning GuidanceTasha RamisettiОценок пока нет
- Ruane PTДокумент27 страницRuane PT9703422499Оценок пока нет
- PMI Testing - Limitations With XRFДокумент3 страницыPMI Testing - Limitations With XRFArun Kumar Kar100% (2)
- Asme Sec V A-2-2004 PDFДокумент39 страницAsme Sec V A-2-2004 PDFjaire esparzaОценок пока нет
- Procedure Progress ISO 3834 2 PDFДокумент3 страницыProcedure Progress ISO 3834 2 PDFKumar DОценок пока нет
- Auditing Qms p1Документ53 страницыAuditing Qms p1Ahmad Imran100% (1)
- Sae Geia-Std-0006a-2016Документ18 страницSae Geia-Std-0006a-2016wodonit136Оценок пока нет
- Q1 9th Conformity Matrix - Rev 2Документ32 страницыQ1 9th Conformity Matrix - Rev 2Raheel MalikОценок пока нет
- Pmi Testing ProcedureДокумент4 страницыPmi Testing ProcedureDhanushОценок пока нет
- Quality Manual: Tianjin Dehua Petroleum Equipment Manufacturing Co., LTDДокумент46 страницQuality Manual: Tianjin Dehua Petroleum Equipment Manufacturing Co., LTDIjabi100% (1)
- Validation of Special ProcessesДокумент3 страницыValidation of Special ProcessesJeyakumarОценок пока нет
- The Nadcap Approval in NDTДокумент3 страницыThe Nadcap Approval in NDTmahmood750Оценок пока нет
- Calibration Interval 1Документ7 страницCalibration Interval 1fajar_92Оценок пока нет
- AC7122-R Rev CДокумент33 страницыAC7122-R Rev CNamelezz ShadowwОценок пока нет
- Pt. Alfa Valves Indonesia: Production General Process Flow Chart of ValvesДокумент0 страницPt. Alfa Valves Indonesia: Production General Process Flow Chart of ValvesZoebairОценок пока нет
- AL Problem Solving Process Manual - Updated 10 - May 2016Документ74 страницыAL Problem Solving Process Manual - Updated 10 - May 2016Akshi Karthikeyan100% (1)
- Heat Treatment ProcedureДокумент3 страницыHeat Treatment ProcedureKunal AjgaonkarОценок пока нет
- Used Thread Inspection / Repair Procedures: Dimensional Inspection Method / QP200-007 / Rev. UДокумент45 страницUsed Thread Inspection / Repair Procedures: Dimensional Inspection Method / QP200-007 / Rev. UIvan MauricioОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Praticle Inspection ProcedureДокумент9 страницMagnetic Praticle Inspection ProcedureTouil HoussemОценок пока нет
- AC7114 Rev F - Nadcap NonDestructive Testing (NDT) Suppliers Accreditation Program Audit Criteria (To Be Used On or AFTER 1-JUL-12)Документ23 страницыAC7114 Rev F - Nadcap NonDestructive Testing (NDT) Suppliers Accreditation Program Audit Criteria (To Be Used On or AFTER 1-JUL-12)skluxОценок пока нет
- Control Procedures For The Calibration and Measurement of The Welding Power Supplies For PDFДокумент11 страницControl Procedures For The Calibration and Measurement of The Welding Power Supplies For PDFNenad NedeljkovicОценок пока нет
- NO. PNB/DC-QAD-04/ ISSUE:2.0 / Revision: 00/ DATE:-01.04.16 Page 1 of 2Документ2 страницыNO. PNB/DC-QAD-04/ ISSUE:2.0 / Revision: 00/ DATE:-01.04.16 Page 1 of 2sonnu151Оценок пока нет
- 12l14 Bright Mild SteelДокумент2 страницы12l14 Bright Mild SteelStefany Carolina Chavez DavidОценок пока нет
- TS 0071Документ1 страницаTS 0071Seleccion Tecnico IndustrialОценок пока нет
- ISO 17636-2 - 2013 Part 2 X - and Gamma-Ray Technical - Table3 & 4Документ1 страницаISO 17636-2 - 2013 Part 2 X - and Gamma-Ray Technical - Table3 & 4Sơn Nguyễn TháiОценок пока нет
- Advanced Quality ManualДокумент17 страницAdvanced Quality ManualalexrferreiraОценок пока нет
- Q1 PDFДокумент8 страницQ1 PDFSandra SandersОценок пока нет
- VGS 8.1.2 Rev.20 - UTДокумент29 страницVGS 8.1.2 Rev.20 - UTPaul-Petrus MogosОценок пока нет
- Astm E479-91 R00 PDFДокумент5 страницAstm E479-91 R00 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTAОценок пока нет
- API Q1 Supplier Audit Check List - MRДокумент8 страницAPI Q1 Supplier Audit Check List - MRSandra SandersОценок пока нет
- Visual Inspection ProcedureДокумент8 страницVisual Inspection ProcedureTouil Houssem100% (3)
- ASTM E 1444 11 MT Magnetic Particle TestingДокумент21 страницаASTM E 1444 11 MT Magnetic Particle TestingeliuОценок пока нет
- Astm E1476.2014Документ12 страницAstm E1476.2014Mukesh kumar100% (4)
- PMI TestingДокумент3 страницыPMI TestinghungОценок пока нет
- Radiation Safety ProcedureДокумент57 страницRadiation Safety ProcedureibrahimОценок пока нет
- Guidelines Overall NDT Quality System Issue 1 080618Документ73 страницыGuidelines Overall NDT Quality System Issue 1 080618HassanSoboh100% (2)
- Coatings Audit Handbook Nov 2011Документ19 страницCoatings Audit Handbook Nov 2011Neil PiersonОценок пока нет
- MT Form Asme PDFДокумент1 страницаMT Form Asme PDFTrung Tinh HoОценок пока нет
- Is Is Not TemplateДокумент1 страницаIs Is Not TemplateAnonymous hkWIKjoXFVОценок пока нет
- WPQR Sample FormДокумент1 страницаWPQR Sample FormshwayeОценок пока нет
- Schoeller-Bleckmann Darron CatalogueДокумент35 страницSchoeller-Bleckmann Darron CatalogueDon Braithwaite100% (2)
- NDT Audit Check ListДокумент7 страницNDT Audit Check ListShrikant Utekar50% (6)
- P 11 CNDT JP41 Ut-Aws D1.1 Rev 07Документ22 страницыP 11 CNDT JP41 Ut-Aws D1.1 Rev 07Vimal MenonОценок пока нет
- QSP-577-03 Magnetic Particle Inspection ProcedureДокумент10 страницQSP-577-03 Magnetic Particle Inspection ProcedureCandy KendeeОценок пока нет
- Proceso Cold RollingДокумент7 страницProceso Cold RollingFernando FiallosОценок пока нет
- UT Procedure PDFДокумент14 страницUT Procedure PDFAbhayОценок пока нет
- Smart Inspection Systems: Techniques and Applications of Intelligent VisionОт EverandSmart Inspection Systems: Techniques and Applications of Intelligent VisionОценок пока нет
- D. All of The AboveДокумент3 страницыD. All of The AboveramarajanenggОценок пока нет
- Catalog For Bearing DesignДокумент70 страницCatalog For Bearing DesignHameer ReddyОценок пока нет
- ProgramДокумент1 страницаProgramMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- TL 9000 Quality Management System Measurements Handbook NPR ExamplesДокумент7 страницTL 9000 Quality Management System Measurements Handbook NPR ExamplesMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Computer Aided Process Planning Techniques: Mani Rathinam Rajamani PHD RoadmapДокумент6 страницComputer Aided Process Planning Techniques: Mani Rathinam Rajamani PHD RoadmapMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Payment Acknowledgment - 180604092233Документ1 страницаPayment Acknowledgment - 180604092233Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- M.SC Result 2017Документ1 страницаM.SC Result 2017Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Learning Plan Dec 2017-Apr 2018Документ5 страницLearning Plan Dec 2017-Apr 2018Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- VSM TemplateДокумент7 страницVSM TemplateMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Join The Big Family. Sign Up Is Open For The Time Being... Join Us!!!!Документ1 страницаJoin The Big Family. Sign Up Is Open For The Time Being... Join Us!!!!Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- List of Certifications DiscontinuedДокумент30 страницList of Certifications DiscontinuedMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- LSS Mani Rathinam RajamaniДокумент2 страницыLSS Mani Rathinam RajamaniMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Product, Process, and Problem Analysis Quality SystemДокумент25 страницProduct, Process, and Problem Analysis Quality SystemMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Leave PlanДокумент2 страницыLeave PlanMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- AS9100 Certification StatusДокумент192 страницыAS9100 Certification StatusMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- 3x5 Why Worksheet For SuppliersДокумент1 страница3x5 Why Worksheet For SuppliersMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Flight 1 Mon, Mar 4: Cathay PacificДокумент6 страницFlight 1 Mon, Mar 4: Cathay PacificMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Letter of ParticipationДокумент1 страницаLetter of ParticipationMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Month Wise NC TrendДокумент2 страницыMonth Wise NC TrendMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Standards Made Available Free of Cost To Combat COVID-19Документ4 страницыStandards Made Available Free of Cost To Combat COVID-19Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Fod Compliance & Findings - Bay 1Документ2 страницыFod Compliance & Findings - Bay 1Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Minitab Print Window PDFДокумент1 страницаMinitab Print Window PDFMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Matecconf Imanee2018 08013Документ6 страницMatecconf Imanee2018 08013Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- BCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFДокумент8 страницBCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Mani Rathinam Rajamani: Certificate of CompletionДокумент1 страницаMani Rathinam Rajamani: Certificate of CompletionMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- BCB 501 (O&G) - Competence Requirements For Inspection Bodies For Accreditation Against PNGRB Regulations PDFДокумент10 страницBCB 501 (O&G) - Competence Requirements For Inspection Bodies For Accreditation Against PNGRB Regulations PDFMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Mani Rathinam Rajamani: Certificate of CompletionДокумент1 страницаMani Rathinam Rajamani: Certificate of CompletionMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- BCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFДокумент8 страницBCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- BCB 201 (IB) - Mar 2019 PDFДокумент38 страницBCB 201 (IB) - Mar 2019 PDFMani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- 09 - Chapter 3Документ11 страниц09 - Chapter 3Mani Rathinam RajamaniОценок пока нет
- Marriage Practices Among The Gidda Oromo, Northern Wollega, EthiopiaДокумент2 страницыMarriage Practices Among The Gidda Oromo, Northern Wollega, Ethiopiajoseph mathewОценок пока нет
- Midterm Decision Analysis ExercisesДокумент5 страницMidterm Decision Analysis ExercisesAYLEN INJAYAОценок пока нет
- Mathematicaleconomics PDFДокумент84 страницыMathematicaleconomics PDFSayyid JifriОценок пока нет
- REVISION For END COURSE TEST - Criticial ThinkingДокумент14 страницREVISION For END COURSE TEST - Criticial Thinkingmai đặngОценок пока нет
- 06 Cruz v. Dalisay, 152 SCRA 482Документ2 страницы06 Cruz v. Dalisay, 152 SCRA 482avatarboychrisОценок пока нет
- 1929 Davos DisputationДокумент20 страниц1929 Davos DisputationEstevao Cruz100% (1)
- Rectification or Correction of Sale DeedДокумент4 страницыRectification or Correction of Sale Deedsumanth_0678Оценок пока нет
- Radiography Safety ProcedureДокумент9 страницRadiography Safety ProcedureأحمدآلزهوОценок пока нет
- Ubi Jus Ibi RemediumДокумент9 страницUbi Jus Ibi RemediumUtkarsh JaniОценок пока нет
- Angel Number 1208 Meaning Increased FaithДокумент1 страницаAngel Number 1208 Meaning Increased FaithKhally KatieОценок пока нет
- Impact of Micro FinanceДокумент61 страницаImpact of Micro FinancePerry Arcilla SerapioОценок пока нет
- What Are RussiaДокумент3 страницыWhat Are RussiaMuhammad SufyanОценок пока нет
- Million-Day Gregorian-Julian Calendar - NotesДокумент10 страницMillion-Day Gregorian-Julian Calendar - Notesraywood100% (1)
- Gothic Revival ArchitectureДокумент19 страницGothic Revival ArchitectureAlexandra Maria NeaguОценок пока нет
- Number SystemsДокумент165 страницNumber SystemsapamanОценок пока нет
- Argumentative Essay Project DescriptionДокумент5 страницArgumentative Essay Project DescriptionKaren Jh MoncayoОценок пока нет
- IUGRДокумент4 страницыIUGRMichael Spica RampangileiОценок пока нет
- Plastique: Art and EducationДокумент7 страницPlastique: Art and EducationJackStevensonОценок пока нет
- The Bible Does Not Condemn Premarital SexДокумент16 страницThe Bible Does Not Condemn Premarital SexKeith502100% (3)
- Vocabulary Task Harry PotterДокумент3 страницыVocabulary Task Harry PotterBest FriendsОценок пока нет
- Unsung Ancient African Indigenous Heroines and HerosДокумент27 страницUnsung Ancient African Indigenous Heroines and Herosmsipaa30Оценок пока нет
- DUN Bukit Lanjan CNY Sponsorship Form2Документ1 страницаDUN Bukit Lanjan CNY Sponsorship Form2alamsekitarselangorОценок пока нет
- Sickle Cell AnemiaДокумент13 страницSickle Cell Anemiamayra100% (1)
- Task Basis JurisprudenceДокумент10 страницTask Basis JurisprudenceKerwin LeonidaОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three: Research MethodologyДокумент3 страницыChapter Three: Research MethodologyEng Abdulkadir MahamedОценок пока нет
- Design of Experiments: I. Overview of Design of Experiments: R. A. BaileyДокумент18 страницDesign of Experiments: I. Overview of Design of Experiments: R. A. BaileySergio Andrés Cabrera MirandaОценок пока нет
- Reaction PaperДокумент3 страницыReaction PaperCecille Robles San JoseОценок пока нет
- Professional Education Pre-Licensure Examination For TeachersДокумент12 страницProfessional Education Pre-Licensure Examination For TeachersJudy Mae ManaloОценок пока нет
- Institute of Actuaries of India: Subject CT3-Probability and Mathematical Statistics May 2008 ExaminationДокумент10 страницInstitute of Actuaries of India: Subject CT3-Probability and Mathematical Statistics May 2008 ExaminationeuticusОценок пока нет
- Vrushalirhatwal (14 0)Документ5 страницVrushalirhatwal (14 0)GuruRakshithОценок пока нет