Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Economics: Summary of Assessing Performance of Different Market Structures
Загружено:
WeimingОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Economics: Summary of Assessing Performance of Different Market Structures
Загружено:
WeimingАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
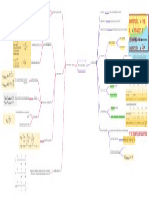
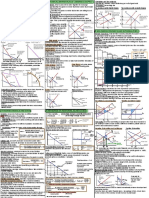
PC: price taker, DD
perfectly elastic:
P=AR=MR, at prot
maximising level where
MR=MC, P=MC
Society value last unit P>MC at prot
of good produced more maximising level where
than its opportunity Allocative inecient: MR=MC
cost, welfare loss to produces at lower
output and higher Imperfect competition:
society, DWL
price, underallocation downward sloping
Greater price setting
of scarce resources demand (AR) curve,
ability, less price elastic
Better off if additional price setter
demand curve, steeper
units produced AR curve, price greater
Allocative eciency than MC to a greater
Compete in terms of
price cutting and other extent
Incumbent domestic
non pricing strategies,
monopoly can face Globalisation and
advertising and
competition from big removal of protectionist Resources may be put
promotion, highly
foreign conglomerates barriers led to growth into more productive
differentiated products
that vie for a share of in international use
--> affect sales of
lucrative domestic competition
incumbent, need to
market
reduce X-ineciency to
However if provide
survive
better consumer
Productive eciency Advertising to
In spite of information, move
differentiate products
At prot max ineciencies, monopoly market closer to PC
and increase market
Consumers enjoy equilibrium MR=MC, can be desirable in model in terms of
share -- may be seen as
benets of lower prices higher output and industries where perfect information
a form of economic
with huge iEOS in a lower price compared to substantial iEOS can be waste
monopoly perfectly competitive reaped, LRAC falls over
Misallocation of
industry a large range of output,
Monopoly Economic eciency resources, competitive
lower AC, lower MC
oligopoly, resources can
be used to produce
Consumers suffer from more goods and
exploitive pricing services
Exacerbate inequity, supernormal prots Firm in imperfect
concentrated in the hands of a selected few Equity competition settle at LR
monopolies who can block potential entrants equilibrium level that is
iEOS not fully exploited,
Productive eciency not necessarily at the
productive inecient
minimum LRAC, operate
However consumer surplus needs not necessarily at downward sloping
be reduced when enjoy substantial iEOS portion of LRAC curve
Argued that in very LR, Monopolies and
no BTE due to change in Criteria for assessing oligopolies can afford to
level of technology performance/ X-eciency be X-inecient because
Possible LR supernormal prots, able to reinvest
desirability ability to retain LR
into R&D especially with threat of potential
supernormal prots
entrants Dynamic eciency
Strong incentive to
break through market
from entrants
Fairness in distribution
Dynamic eciency of wealth, income and
May not have incentive because dominant position is opportunities
secured, less need (unless theory of contestable markets)
Equity
Idea of equitable
May erode value of monopolist's existing products, distribution is
tend to favour status quo normative
Tend to spread opportunities and wealth widely Consumers able to
and more evenly, prots spread evenly among choose from a wide
many small rms because no BTE variety of products +
Consumer choice
purchase similar goods
from different
Consumer surplus max producers
at equilibrium price Equity
where P=MC
"Excess capacity
theorem": attempts at
PC markets do not rectify pre-existing Not productively productive
Argue if there is merit
inequity, retain old structure of ecient, producing at differentiation incurs
in product
inequitable wealth distribution the falling portion of costs, results in rms
Assessing performance differentiation
the LRAC curve producing at higher
across different market
average cost than
Normal prots, structures
necessary
restricted R&D which
requires high MPC
expenditure Incentive to innovate
Dynamic eciency but easy to copy tech +
LR normal prots
But in reality often
engage in innovation to
Homogeneous products Perfect competition
improve quality and Enhances consumer
makes innovation to Dynamic eciency
earn higher prots in SR choice
improve quality of
product an irrelevant
discussion
Competition key driver Anti-competitive
of innovation behaviour such as
collusion and practice
Equity of price discrimination
Perfect information: innovations quickly replicated by often serve to further
competitor/ new rms, discourage R&D, no benets reduce consumer
surplus
Does not offer
consumer choice in Supernormal prots,
terms of product capable
variety but choice of
many producers Consumer choice
Existing competition
amongst few dominant
There is consumer Reduce fear of rival's
rms induces
sovereignty reactions to their
investment in R&D to
pricing strategies
Oligopoly Dynamic eciency differentiate products
(non pricing strategy)
Pace can be slow in
collusive/ entrenched
oligopolies - lack of
Perfectly contestable competition deter R&D
market when entry into like monopoly
and exit from market by
potential rivals is
costless and can be Also limits consumer choice to existing dominant
done rapidly rms in the market because of advertising
Contestable markets
Consumer choice
Key conditions Tends to engage in multiple branding whereby rm
1. no sunk costs and exit costs, capital equipment is produces same products packaged under different
transferable brand names -- false illusion of consumer choice
2. perfect information and ability of all suppliers to use
the best available production tech in the market
3. low consumer loyalty
Theory of contestable markets: what is
crucial in determining price and output is
Hit and run competition presence of real threat of competition
Economists theorise that this is new way to encourage
rms to act like perfect competitors + shows that
inecient rms cannot survive + why rms act
competitively despite market structure as long as
market is contestable
Вам также может понравиться
- Specific Pricing Strategy: Marketing Mix - 4PsДокумент1 страницаSpecific Pricing Strategy: Marketing Mix - 4PsJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- ReviewДокумент17 страницReview10622006Оценок пока нет
- Electricity Pricing Model Input Data Range Names UsedДокумент3 страницыElectricity Pricing Model Input Data Range Names UsedJohn WIckОценок пока нет
- Cfa - R1Документ1 страницаCfa - R1Thanh TuyềnОценок пока нет
- Midterm 3 ReviewДокумент34 страницыMidterm 3 ReviewSameer JainОценок пока нет
- Break Even AnalysisДокумент20 страницBreak Even AnalysisSachi DhanandamОценок пока нет
- P-C SurplusesДокумент4 страницыP-C SurplusesWajiha RajaniОценок пока нет
- Yeni Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationДокумент33 страницыYeni Microsoft PowerPoint Presentationdob14Оценок пока нет
- NEC DND 3.5 UltimateCharacterSheet PDFДокумент3 страницыNEC DND 3.5 UltimateCharacterSheet PDFMatteo MorlacchiОценок пока нет
- Economic GrowthДокумент2 страницыEconomic Growthximenaliza6Оценок пока нет
- Mindmap Returns Management XPOДокумент1 страницаMindmap Returns Management XPONgoc PhamОценок пока нет
- Econ201 ReviewДокумент4 страницыEcon201 ReviewChristopher Demmerle-McGregorОценок пока нет
- Micro Economics PDFДокумент54 страницыMicro Economics PDFNguyen Châu AnhОценок пока нет
- Foundation Formulas PDFДокумент12 страницFoundation Formulas PDFsayma saraОценок пока нет
- The White DwarfДокумент4 страницыThe White DwarfBezerkerRageОценок пока нет
- Writing Skill OneДокумент1 страницаWriting Skill OneSylvia CHENОценок пока нет
- Cleric: HP MovementДокумент13 страницCleric: HP MovementRiccardo ForlaniОценок пока нет
- 3 Forces, Work and Materials: Types of Force Turning Effects of ForcesДокумент1 страница3 Forces, Work and Materials: Types of Force Turning Effects of ForcesSyed Wajahat AliОценок пока нет
- 2013 07-20-223905 Jones Family Minicase Analysis ModelДокумент1 страница2013 07-20-223905 Jones Family Minicase Analysis ModelXuân DungОценок пока нет
- 6 - Portfolio TheoryДокумент5 страниц6 - Portfolio TheoryAmit GuptaОценок пока нет
- Alchemi T: HP MovementДокумент16 страницAlchemi T: HP MovementRiccardo ForlaniОценок пока нет
- Oxford IB Diploma Programme IB Economics Course Book (JOCELYN. DORTON BLINK (IAN.), Ian Dorton)Документ601 страницаOxford IB Diploma Programme IB Economics Course Book (JOCELYN. DORTON BLINK (IAN.), Ian Dorton)sophieperervinОценок пока нет
- Ghost in The Shell RPG d20 Sheet PDFДокумент2 страницыGhost in The Shell RPG d20 Sheet PDFice79Оценок пока нет
- Demand and SupplyДокумент25 страницDemand and SupplyArjit Verma 1035Оценок пока нет
- Ficha Personagem 5e Editavel InglesДокумент3 страницыFicha Personagem 5e Editavel Inglesgregorywallace1221Оценок пока нет
- 25 MaretДокумент8 страниц25 MaretIndri Br SitumorangОценок пока нет
- MI DnDCharSheet23Документ4 страницыMI DnDCharSheet23Sgt. MushroomОценок пока нет
- 4 PDFДокумент1 страница4 PDFSim Pei YingОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic Analysis I Topic 10: Keynesianism and Wage-Price Rigidity (Abel, Bernanke & Croushore: Chapter 11)Документ50 страницMacroeconomic Analysis I Topic 10: Keynesianism and Wage-Price Rigidity (Abel, Bernanke & Croushore: Chapter 11)Enigmatic ElstonОценок пока нет
- CH 17Документ11 страницCH 17jamalyyy111Оценок пока нет
- Take PhotoДокумент3 страницыTake PhotopunthadewaОценок пока нет
- Competitor Price Location Facility Strength Weakness StrategyДокумент2 страницыCompetitor Price Location Facility Strength Weakness StrategyRoeder IgnacioОценок пока нет
- KinematicsДокумент12 страницKinematicssaifaly shaheenОценок пока нет
- D&D 4e Character SheetДокумент3 страницыD&D 4e Character SheetcynaragriloОценок пока нет
- Quality at an affordable priceДокумент27 страницQuality at an affordable priceAbhishekh GuptaОценок пока нет
- PZO1110 CharacterSheetДокумент2 страницыPZO1110 CharacterSheetLuis MartínezОценок пока нет
- PZO1110 CharacterSheetДокумент2 страницыPZO1110 CharacterSheetTakumiОценок пока нет
- Character Sheet: STR DEX CON INT WIS CHA HP SpeedДокумент2 страницыCharacter Sheet: STR DEX CON INT WIS CHA HP SpeedFОценок пока нет
- Pathfinder 2e Kitsune SorcererДокумент4 страницыPathfinder 2e Kitsune SorcererLuiz GustavoОценок пока нет
- HGA Data Model DiagramsДокумент1 страницаHGA Data Model DiagramsIna-Lu MuresanОценок пока нет
- Semiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007Документ1 страницаSemiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007civixxОценок пока нет
- 5e Character Sheet (Out of The Abyss Format)Документ3 страницы5e Character Sheet (Out of The Abyss Format)Migz CasasОценок пока нет
- Business Standard - 13 Jan 2011 - Should The Rural Job Guarantee Scheme Be Linked To Minimum WagesДокумент1 страницаBusiness Standard - 13 Jan 2011 - Should The Rural Job Guarantee Scheme Be Linked To Minimum WagesSuchna evum Rozgar ka adhikar AbhiyanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - Inflation and Philips CurveДокумент3 страницыChapter 9 - Inflation and Philips CurveGiang PhạmОценок пока нет
- Semiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007Документ1 страницаSemiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007civixxОценок пока нет
- Ae687 Assignment1Документ4 страницыAe687 Assignment1Shrutikirti SinghОценок пока нет
- Future Perfect Character SheetДокумент2 страницыFuture Perfect Character Sheet13thBlackAngelОценок пока нет
- Crack Width Short NoteДокумент1 страницаCrack Width Short NotePhanathon OunonОценок пока нет
- Semiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007Документ1 страницаSemiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007civixxОценок пока нет
- The Economics Way To Thinking About Business: Chapter 1: Dr. Rudi PurwonoДокумент25 страницThe Economics Way To Thinking About Business: Chapter 1: Dr. Rudi PurwonohanaОценок пока нет
- Character Sheet 14Документ2 страницыCharacter Sheet 14romain.delattre81Оценок пока нет
- Samsaran PathfinderДокумент2 страницыSamsaran PathfinderDa GeißerОценок пока нет
- Future Perfect Character SheetДокумент2 страницыFuture Perfect Character Sheet13thBlackAngelОценок пока нет
- CPT TK03 001Документ46 страницCPT TK03 001Şəhriyar ƏliyevОценок пока нет
- Résume MicroДокумент77 страницRésume MicroKerrian MathezОценок пока нет
- DnD5e en - Feuille de Personnage Interactive 13.1Документ4 страницыDnD5e en - Feuille de Personnage Interactive 13.1NicolasОценок пока нет
- Monopoly price ceilings effectДокумент4 страницыMonopoly price ceilings effectrandom122Оценок пока нет
- Acc 406Документ1 страницаAcc 406hanhvy04Оценок пока нет
- BSP1703 NotesДокумент33 страницыBSP1703 NotesChloe TewОценок пока нет
- Applying To Oxbridge 2019Документ10 страницApplying To Oxbridge 2019WeimingОценок пока нет
- KEY REVIEW Engineered Liver Platforms For Different Phases of Drug DevelopmentДокумент12 страницKEY REVIEW Engineered Liver Platforms For Different Phases of Drug DevelopmentWeimingОценок пока нет
- Superintelligence Book ReviewДокумент7 страницSuperintelligence Book ReviewMateo AcostaОценок пока нет
- Crypto-Assets UnencryptedДокумент49 страницCrypto-Assets UnencryptedWeimingОценок пока нет
- Magnetism Post Flip QuizДокумент3 страницыMagnetism Post Flip QuizWeimingОценок пока нет
- Social Studies GuideДокумент2 страницыSocial Studies GuideWeimingОценок пока нет
- Brightsparks Extract Report 2017Документ22 страницыBrightsparks Extract Report 2017WeimingОценок пока нет
- 2018 Year 6 Common Test 1 InfoДокумент2 страницы2018 Year 6 Common Test 1 InfoWeimingОценок пока нет
- Engineers Australia - 2010 Salary Survey - Answer To QONsДокумент73 страницыEngineers Australia - 2010 Salary Survey - Answer To QONsDaniel DinhОценок пока нет
- Personal Essay About The 21st CenturyДокумент2 страницыPersonal Essay About The 21st CenturyWeimingОценок пока нет
- Lian He Zao Bao NewspaperДокумент2 страницыLian He Zao Bao NewspaperWeimingОценок пока нет
- How To Win Every Argument PDFДокумент185 страницHow To Win Every Argument PDFWeiming100% (2)
- Habits: How They Form and How To Break ThemДокумент4 страницыHabits: How They Form and How To Break ThemWeimingОценок пока нет
- The Size of Countries: Does It Matter?Документ18 страницThe Size of Countries: Does It Matter?WeimingОценок пока нет
- Finnish Learning BookДокумент12 страницFinnish Learning BookMihai Voinea100% (7)
- Math SymbolsДокумент1 страницаMath SymbolsWeimingОценок пока нет
- Physician Labor Market ExplainedДокумент29 страницPhysician Labor Market ExplainedZineb LabiadОценок пока нет
- ICT 2022 Mentorship - Free DownloadableДокумент297 страницICT 2022 Mentorship - Free DownloadableSlw habbosОценок пока нет
- Examiners' commentary on Industrial economics examДокумент23 страницыExaminers' commentary on Industrial economics examShawn MorganОценок пока нет
- Amartya Sen CVДокумент28 страницAmartya Sen CVPrasad SawantОценок пока нет
- Cost Problem SetДокумент2 страницыCost Problem SetRayОценок пока нет
- Consumers, Producers, & Market EfficiencyДокумент40 страницConsumers, Producers, & Market EfficiencymanikОценок пока нет
- Econ Ch01 Chapter Test AДокумент3 страницыEcon Ch01 Chapter Test ATony DeCotisОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of TrainingДокумент2 страницыEvaluation of TrainingKav99Оценок пока нет
- Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition Nicholson Test BankДокумент7 страницIntermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition Nicholson Test Bankchiliasmevenhandtzjz8j100% (31)
- This Paper Is Not To Be Removed From The Examination HallsДокумент55 страницThis Paper Is Not To Be Removed From The Examination Halls陈红玉Оценок пока нет
- Measuring Economic Growth with GDP & GNPДокумент10 страницMeasuring Economic Growth with GDP & GNPLeigh CabritoОценок пока нет
- The Basic Tenets of Marxism Power PointДокумент29 страницThe Basic Tenets of Marxism Power PointShiela Fherl S. Budiongan100% (2)
- Cabanyss Et Al. (2014) - Preliminary Market Analysis and Plant CapacityДокумент5 страницCabanyss Et Al. (2014) - Preliminary Market Analysis and Plant Capacityvazzoleralex6884Оценок пока нет
- The Democratic SocietyДокумент11 страницThe Democratic SocietyBernardo Cielo IIОценок пока нет
- Ecs ShoesДокумент24 страницыEcs ShoesBilal Yasir100% (3)
- Michael Ceasar B. Abarca: BS Business Economics IIДокумент14 страницMichael Ceasar B. Abarca: BS Business Economics IIapi-26604549Оценок пока нет
- Basic Microeconomics (Reviewer)Документ3 страницыBasic Microeconomics (Reviewer)Patricia QuiloОценок пока нет
- Annual Review of Social Development in PakistanДокумент197 страницAnnual Review of Social Development in PakistanAsif IqbalОценок пока нет
- General Mills Marketing Research for New Yogurt ProductДокумент3 страницыGeneral Mills Marketing Research for New Yogurt ProductVivek Kumar BhagboleОценок пока нет
- Eco 2009 Het Final Exam QuestionsДокумент4 страницыEco 2009 Het Final Exam QuestionsAslı Yaren K.Оценок пока нет
- Market Structure ConfluenceДокумент7 страницMarket Structure ConfluenceSagar BhandariОценок пока нет
- Econ 4413 Poverty and Income DistributionДокумент509 страницEcon 4413 Poverty and Income DistributionAli Haider YaseenОценок пока нет
- Elasticity of Demand AДокумент4 страницыElasticity of Demand AAzlan Psp50% (2)
- Zara Project Report Part 01Документ15 страницZara Project Report Part 01adeel0523261Оценок пока нет
- Improving Sugarcane Farming in Rural PhilippinesДокумент2 страницыImproving Sugarcane Farming in Rural PhilippinesKim BalotОценок пока нет
- LibroДокумент212 страницLibromiguelchp02Оценок пока нет
- Commanding Heights Episode 1 Movie WorksheetДокумент3 страницыCommanding Heights Episode 1 Movie WorksheetBanana QОценок пока нет
- Managerial EconomicsДокумент15 страницManagerial Economicslovey50% (2)
- Executive Summary SCIENCEДокумент68 страницExecutive Summary SCIENCEJyotishmoi BoraОценок пока нет
- D0683ECO BQP QR (2021) .pdf-1-21Документ21 страницаD0683ECO BQP QR (2021) .pdf-1-21Tanya SinghОценок пока нет